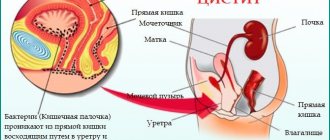
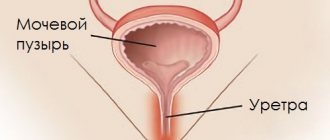
Urethritis, a pathological condition caused by the presence of inflammatory foci in the urethra, is treated with medications, and only in rare and advanced cases is surgical intervention required. The course of the disease and the recovery process in men is complicated due to the anatomical features of the body: a man’s urinary canal is on average 5 times longer than a woman’s, and, therefore, inflammation on the walls of this organ is more difficult to stop, painful symptoms manifest themselves more intensely, and it takes more time to recover the affected ones fabrics.
Urethritis in men: symptoms, treatment, medications
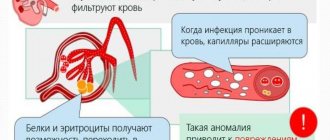
The disease is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the urinary canal, which is provoked by a number of strains. Urethritis is considered the most common problem in men who are sexually active without a condom and have more than one woman. As a rule, it occurs in other inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
When urethritis occurs, a man is tormented by the following unpleasant symptoms:
- Discharge of purulent exudate from the urethra.
- Increased body temperature.
- Frequent urge to empty the bladder.
- Itching.
- Pain when urinating.
- Burning.
Therefore, when such symptoms of urethritis appear in men, only a doctor selects treatment and medications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of urethritis typically become severe approximately 3 to 7 days after infection occurs. But it happens that acute urethritis appears after a two to three week incubation period. Symptoms in women and men manifest themselves primarily as a strong burning sensation or a feeling of pain during urination. A sick person feels a particularly sharp sting or burning sensation when urination begins. Another symptom that occurs in both adults and children is urethral discharge. As a rule, they are detected in the morning. If a person develops nonspecific bacterial urethritis, then such discharge can be profuse, it has a mucopurulent character and an unpleasant odor. Sometimes urethritis develops without discharge. There is only pain and burning.
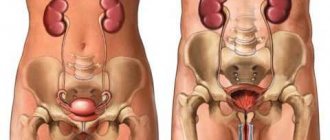
As a rule, symptoms in men with urethritis are more pronounced, as this is facilitated by the anatomy of the stronger sex. In men, the urethra is long and narrower, so they usually feel the signs of the disease more acutely. At the same time, in women the disease can be completely asymptomatic, or its symptoms are not pronounced. But this in no way means that treatment of the disease is not required. Without adequate therapy, acute urethritis becomes chronic.
Urethritis in men can also manifest itself with other signs. In the morning, patients may notice that the lips of the external opening of the urethra stick together and turn red. At the same time, despite the specific reasons that provoked the development of the disease, general inflammatory signs (weakness, fever) do not appear.
In some cases, the acute form of the disease gradually becomes chronic. As a rule, this happens if the patient has suffered from gonorrheal urethritis , which was not treated correctly. Gonorrheal processes can affect the urethra and prostate gland . In addition, chronic urethritis develops if the patient has a weakened immune system. This happens if a person has had other illnesses, took certain medications, etc.
If a person who has urethritis does not think about how to cure this disease and does not pay attention to the symptoms, then over time all the signs disappear by themselves, as the inflammatory process is suppressed. However, the pathogens of the disease remain in the human body.
In men, such pathogens are stored in the seminal vesicles and prostate gland. In women, they can remain for some time in the small glands of the vestibule, as well as in the Bartholin glands. As soon as hypothermia , a person consumes a large amount of alcohol, or another stressful situation occurs for the body, the inflammatory process in the urethra develops again. But with the repeated development of inflammation, the patient no longer develops not only urethritis, but also vesiculitis , chronic prostatitis , as well as other diseases that over time can even lead to infertility .
Medicines for urethritis
The order of use of the drug, which is intended to inhibit the activity of a bacterial infection, depends on the dosage, as well as the components included in its structure.
As a rule, if an antibacterial agent for eliminating urethritis was prescribed for use in tablet form, then on average it is enough to take 1-2 capsules three times a day daily. The duration of therapy varies from 10 to 12 days. Intramuscular injections can be administered to the patient twice a day for 5-7 days.
Much depends on the severity of the ongoing inflammatory process inside the urinary canal, so there is no generalized summary for all antibiotics, because each drug has its own special chemical or biochemical formula. What medications can you take for urethritis?
Prices of medicines for urethritis
The estimated cost of the main antibiotics and uroantiseptics used for urethritis is given below.
| Azithromycin | 3 tablets of 500 mg – 4.90 $ |
| Metronidazole | 20 tablets of 250 mg – 0.42 $ |
| Cefixime | 10 tablets of 400 mg – 7.36 $ |
| Doxycycline | 10 capsules of 100 mg – 0.25 $ |
| Erythromycin | 20 tablets of 250 mg – 2.18 $ |
| Ofloxacin | 200 mg tablets, 10 pcs. – 0.77 $ |
| Canephron | 60 dragees – 8.55 $ |
| Urolesan | 40 capsules – 6.71 $ |
| Nitroxoline (5-NOK) | 50 tablets of 50 mg – 3.35 $ |
The price of ointments ranges from $1.5-8. The cost of vaginal and rectal suppositories is $1-11 per package.
Any types of medications prescribed for urethritis are available for purchase both in regular and online pharmacies.
Pills
Most antimicrobial agents for the effective treatment of urethritis, which occurs in acute or chronic form, are produced in tablet form.
In practice, the following best medications for urethritis in men and women have shown increased effectiveness in the fight against infections that cause inflammation:
- Azithromycin.
- "Amoxiclav".
- "Amoxicillin."
- "Biseptol".
- "Wilprafen".
- "Doxycycline."
- "Canephron."
- "Levomycetin".
- "Metronidazole".
- "Monural".
- "Nitroxyline".
- "Nolitsin."
- "Ofloxacin."
- "Palin."
- "Sumamed."
- "Furagin."
- "Furadonin".
- "Furamag."
- "Ceftriaxone".
- "Tsiprolet".
- "Erythromycin".
How to treat urethritis in men, what medications are prescribed?
How to treat urethritis?
At home, treatment of urethritis in men should be comprehensive. All procedures are carried out on an outpatient basis, medications are selected by a specialist. The patient must scrupulously follow all instructions and follow certain recommendations during the treatment period. These include:
- temporary refusal of sexual intercourse;
- strict adherence to hygiene standards;
- compliance with all medical recommendations regarding the duration of treatment and medication;
- giving up bad habits (alcohol, smoking);
It is necessary to adjust the diet, aimed at eliminating fatty, fried, spicy foods, smoked meats, marinades, pickles, carbonated drinks, in short, all products that can increase the severity of the inflammatory process. The patient is advised to drink more fluids, follow a daily routine, avoid hypothermia, stress and the influence of other negative factors.
On average, treatment for almost any form of urethritis takes several weeks. Treatment should under no circumstances be abandoned when signs of improvement and subsidence of the clinical picture of the disease appear. At the end of treatment, a control smear is taken from the urethral canal to confirm recovery.
"Tsiprolet"
The tablets belong to the group of fluoroquinolones. "Tsiprolet" is prescribed to prevent various infectious bacterial diseases, which are aimed at eliminating pathogens.
The medicine “Tsiprolet” eliminates the symptoms of urethritis in men very effectively. The tablets are intended for oral use. They should not be chewed; for better passage of the drug through the esophagus, it can be washed down with water. Dosage depends on the pathological process and location in the body.
If the organs of the urogenital tract and reproductive system are affected, 250 milligrams are prescribed three times a day for 3 days in case of uncomplicated acute inflammation of the bladder; in other situations, it is necessary to consume from 500 to 750 mg of Tsiprolet twice a day.
Diagnostic methods
As with other diseases of the genitourinary system, a man needs to see a urologist or venereologist - these are the doctors who treat urethritis. Diagnostics will begin immediately at the appointment. The doctor will ask the patient about his lifestyle, the nature of his complaints, and the time of the first symptoms.
The specialist will also examine the penis and then send it for tests:
- a smear from the urethra for bacteriological culture - will determine the type of pathogen;
- urine and blood for general and other types of studies;
- PCR diagnostics.
If necessary, instrumental methods can also be used. An ultrasound can give a good result, especially if you need to exclude pathologies of the prostate or bladder. Also, for chronic urethritis, urethrography is done, during which an X-ray image of the pathological processes occurring in the urethra can be obtained.
Symptoms of urethritis are often similar to those of chronic prostatitis, with the exception of discharge from the penis. This point also needs to be taken into account and differential diagnosis must be carried out.
"Ofloxacin"
The drug is produced in tablet form. "Ofloxacin" belongs to the therapeutic group of fluoroquinolones antimicrobial agents. They are used for the etiotropic treatment of infectious diseases caused by microorganisms sensitive to the active substance.
According to reviews from men, the medicine for urethritis helps to effectively cope with the disease. The tablets are taken whole before or after meals. They are not chewed and washed down with water. The dosage and duration of therapy with Ofloxacin depends on the source of the disease and is therefore determined by a medical specialist.
The average concentration of the drug is 200-800 milligrams per day in 2 doses, the average duration of therapy varies from 7 to 10 days. For patients with a concomitant decrease in the functioning of the kidneys and liver, as well as those on hardware blood purification, dosage adjustments are necessary.
"Azithromycin"
When prescribing a drug for inflammation of the walls of the urethra, it is important to know that it is effective against diseases of chlamydial and mycoplasma etiology, and also effectively eliminates ureaplasmosis, an infectious vector-borne disease. Enterococci are considered resistant to the effects of this medicine.
The mechanism of action of the drug during inflammation is based on blocking the process of protein synthesis. Its small amount in the body inhibits the growth of bacteria and eliminates the reproduction process. If the concentration of the drug is increased, this will help completely prevent the addition of a secondary infection.
In this connection, “Azithromycin” belongs to the first-line antimicrobial agents for inflammation of the urethra, which are prescribed at the first signs of the disease.
For inflammation of the urethra in both men and women, the dosage, frequency of administration and duration of treatment are calculated by the doctor individually. However, in most situations the treatment regimen looks like this:
- One tablet with a concentration of 0.5 grams is prescribed for use once a day.
- The duration of therapy in this situation is two or three days.
- The drug must be taken with water.
Causes
Most often, urethritis pathogens enter from the external environment, during unprotected sexual intercourse or violation of hygiene rules. The causative agents can be chlamydia, trichomonas, herpes, gonococci, mycoplasma, candida and other fungal pathogens. As a rule, such infections affect the entire genitourinary system: diagnosis and treatment for sexually transmitted diseases and fungal infections are carried out comprehensively.
Other factors in the occurrence of the inflammatory process in the urethra and the genitourinary system as a whole may be hypothermia, decreased immunity as a result of stress and overwork.
With a general weakening of the body, the development of non-specific urethritis is possible, in which the tissues of the organ are affected by pathogens of their own microflora, or the microflora of the oral cavity, rectum, due to a metabolic failure. The causative agents of inflammation on the canal walls can be staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli and other fungi. That is, in this case, inflammation is caused by agents that the body cannot cope with due to low immunity or endocrine disorders.
The inflammatory process can be a consequence of mechanical damage - ruptures and abrasions caused, for example, during medical procedures such as catheter installation and bladder endoscopy . Traumatic urethritis can be caused by the process of removal of solid formations through the urethra due to urolithiasis of the kidneys and bladder.
Inflammation can also occur due to poor circulation in the pelvic area, caused by interrupted and prolonged sexual intercourse, hemorrhoids, severe constipation and other factors that cause stagnation of blood in the male urethra. This pathology of venous circulation is referred to as congestive urethritis.
The causes of inflammation of the urethra can also be the abuse of spicy, salty and sour foods, the intake of toxic substances (alcohol, smoking, drugs) and chemical poisoning. There are also cases of allergic reactions to hygiene products or other factors. An allergic reaction can also occur in the case of allergens resulting from the formation of urine when taking medications or poisoning the body. Inflammation and subsequent infection can also be caused by toxic components of hygiene products - soaps, creams, lubricants.
The inflammatory process in the urethra can be a secondary infection from a source of inflammation localized in the bladder or prostate gland.
"Amoxicillin"
The medication exhibits increased effectiveness in treating urethritis due to its antimicrobial properties, which means it can destroy different types of bacteria that provoke this lesion and other infections.
“Amoxicillin” for inflammation of the urethra turns out to be ineffective when pathogenic cells produce an enzyme that has the ability to break down beta-lactam antibiotics, which destroys the active component of the drug.
Depending on the concentration of the active substance, the medication is produced in several dosage forms: suspensions, tablets and capsules. Typically, the type of drug depends on the age and body weight of the patient, as this is important for the best fight against infection. The main advantage of Amoxicillin is resistance to an acidic environment, such as gastric juice.
As soon as the active component of the drug enters the blood, it immediately disrupts the protein compounds of bacterial cells. As a result, the proliferation of bacteria stops almost immediately, and the elimination of existing ones occurs somewhat later.
Due to the increased efficiency, the patient's health may deteriorate. Due to the rapid death of cells, the amount of toxins in the blood increases and the person begins to feel unwell, but within a day after the first use of Amoxicillin, the patient’s condition returns to normal. What medications and treatment do doctors prescribe for urethritis in women?
Complications
With male urethritis, the following types of complications are possible:
- In cases where there is no treatment for urethritis or if it is not treated correctly, the disease can go from acute to chronic.
- The occurrence of prostatitis.
- Vesiculitis is inflammation of the seminal vesicles.
- Orchitis is inflammation of the testicle.
- Balanitis is an inflammation of the skin on the head of the penis.
- Balanoposthitis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the foreskin.
- Narrowing of the urethra that occurs as a result of lack of proper treatment for urethritis, or during the chronic course of this disease. Advanced cases of narrowing require surgical intervention.
Such a number of existing complications in male urethritis is due to the fact that inflammation of the urethra can reach other organs and begin to develop there: the organs of the scrotum, bladder and prostate gland can become victims of urethritis. To avoid complications, special prevention of urethritis is required.
"Sumamed"
The tablets represent the pharmacological group of drugs macrolides. They are used for the etiotropic treatment of various infectious pathological processes, which are aimed at eliminating pathogens sensitive to this medication.
The main active component of Sumamed, azithromycin, is considered a chemical derivative of azalide macrolides. It has a bactericidal effect and leads to the elimination of sensitive bacteria.
The drug is used with extreme caution for muscle pain, as well as disturbances in the functional activity of the liver, various heart rhythm disturbances, or the presence of factors that lead to their occurrence. Before taking the drug "Sumamed", a medical specialist must make sure that there are no contraindications.
"Hexicon"
The drug is an antiseptic for local use. Hexicon suppositories are used in gynecology for elimination and prophylactic purposes to prevent infectious and inflammatory diseases of the vagina and cervix.
The main component of suppositories, chlorhexidine bigluconate, acts as an antiseptic. It belongs to the group of chlorine-containing biguanides and destroys bacterial cells.
After intravaginal administration of the Hexicon suppository, the active substance in the form of a thin film envelops the mucous cavity, has a local pharmacological effect and is practically not absorbed into the general bloodstream.
"McMirror"
The drug has a pronounced antimicrobial effect from the nitrofuran group. The active component has antiprotozoal, as well as antifungal and antibacterial effects. "Makmiror" is highly effective and low-toxic, it is used in many areas of medicine.
The drug has increased pharmacological activity against Helicobacter pylori, as well as against sources of the infectious process. In addition, "Makmiror" shows increased effectiveness in eliminating vaginal Trichomonas.
Medicine in the form of tablets during pregnancy can be prescribed to representatives of the fair sex only for health reasons in a situation where the likely benefit for the expectant mother will exceed the risk to the fetus.
List of effective liniments:
"Cycloferon"
Liniment is effective as immunotherapy in eliminating chlamydia, as well as fungal and bacterial infectious processes of the genitourinary system and bacterial infections.
Cycloferon ointment can be used topically, intravaginally and intraurethrally. Intravaginal use of the drug is carried out using an applicator, which is attached to a tube of ointment.
For candidiasis and nonspecific urethritis, Cycloferon ointment is used by injection in a volume of 5-10 milliliters. Lesions in men of the upper urethra involve filling the external opening of the urethra with medication through a syringe without a needle.
Immediately after applying the Cycloferon liniment, it must be pressed for several minutes. After half an hour, the patient should urinate. Duration of therapy is two weeks. Thus, only after a day, lesions of the posterior urethra are eliminated.
For urethritis of a specific origin, the ointment must be combined with antimicrobial agents. The duration of treatment varies from 10 to 14 days; if necessary, the course can be repeated after two weeks.
Reviews
Men and women who have experienced this disease note the greatest effectiveness from the use of antimicrobial drugs. This is explained by the fact that this form is most convenient to take while in any environment.
Regardless of whether the patient is at home or busy performing duties at work, antibiotics in tablet form are in great demand. Suppositories have also found approval among all patients who suffer from urethritis.
But still, men speak negatively about the treatment of urinary canal lesions by rectal administration of anti-inflammatory suppositories for inflammation of the urethra.
The Polygynax suppositories have proven themselves to be the best. Positive responses come from women who used this medicine for 10 to 12 days and carried out the accompanying therapeutic procedures prescribed by the gynecologist.
According to patient reviews, homeopathy and medicines based on it do not bring any benefit in eliminating inflammation of the urinary canal. Therefore, patients who have survived this disease are not advised to use such drugs.
Summarizing the reviews of all patients, we can confidently say that only an integrated approach and the use of all antimicrobial drugs at once help to quickly eliminate urethritis and the risk of a possible recurrence of the disease in the near future.
Urethritis is a bacterial, fungal or viral inflammation of the urethra (urethra). More often affects men. Accompanied by painful urination and discharge from the urethra. Treatment of urethritis in men with antiviral and antimicrobial drugs quickly destroys the pathogenic flora. To make you feel better, symptomatic medications are prescribed - decongestants, painkillers, antihistamines.
Diagnostics
To confirm the disease, you need to contact a urologist who will conduct the necessary studies. In this case, we are talking about seeding discharge from the urethra. If the patient does not have any discharge, the first portion of urine from a three-glass sample is used for analysis. Carrying out such studies makes it possible not only to determine which pathogen provoked the development of the disease, but also to identify the sensitivity of the causative agent of urethritis to antibiotics of different groups.
It is especially important to promptly identify urethritis in women, since signs of the disease may be completely absent. However, both acute and chronic urethritis can be easily detected by laboratory tests. Diagnostics also involves additional research, which makes it possible not only to determine the causes of the disease, but also to determine whether the inflammatory process has spread to other organs. Most often, the seminal vesicles and prostate gland are affected in men, and the bladder in women. Based on the results obtained, the doctor makes a decision on how to cure the disease.
Drugs that eliminate infection
The basis of conservative treatment of urethritis is etiotropic drugs - medications that destroy pathogenic flora. Depending on the cause of inflammation of the urethra, men are prescribed the following groups of medications:
- antiviral;
- antimycotics (antifungal agents);
- antitrichomonas;
- antibiotics.
The choice of medications depends on the sensitivity of pathogens to antimicrobial drugs. In 72% of cases, the disease is caused by bacteria, so it is treated with antibiotics.
Antibiotics
Before treating urethritis in a man, the type of infectious agent is determined. For bacterial inflammation of the urethra, the treatment regimen includes antibiotics from the group of macrolides, cephalosporins, and tetracyclines. The most effective tablet drugs include:
- fluoroquinolones – Moxifloxacin, Moximac, Tevalox, Ciprofloxacin;
- macrolides – Clarithromycin, Clamed, Azithromycin, Claricit;
- cephalosporins - Cefix, Loprax, Vinex, Suprax, Cedex;
- tetracyclines - Doxycycline, Vibramycin D, Unidox, Solutab.
For gonorrheal and chlamydial urethritis, fluoroquinolones and cephalosporins are most effective. Therefore, the treatment regimen includes:
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Aksetin;
- Cefuroxime;
- Bactilem;
- Zinnat.
Antibacterial drugs for the treatment of urethritis in men are used for at least 5-7 days. For mixed infections, drugs from different groups are taken simultaneously.
The best remedy for urethritis
The best treatment for urethritis is antibiotic therapy. The following groups of drugs are traditionally used for therapeutic purposes:
- Fluoroquinolones.
- Cephalosporins.
- Uroantiseptics.
The most popular in the treatment of urethritis are second-generation fluoroquinolones - ofloxacin, norfloxacin, enoxacin, ciprofloxacin, lomefloxacin. Among the cephalosprorins, ceftriaxone, cefixime and ceftibuten are considered the most effective. Among macrolides, clarithromycin, azithromycin, and erythromycin are in demand.
Uroantiseptics are a type of medicine that has a pronounced antimicrobial effect and minimal systemic effect on the body. Among these drugs there are products of synthetic and natural origin. Treatment of urethritis is carried out using:
- urolesana;
- canephron;
- furazidine;
- triseptol;
- nitroxoline (5-NOK);
- trimethoprim;
- nitrofurantoin.
The effectiveness of the medications used largely depends on the patient’s compliance with the basic recommendations of the attending physician.
Adjuvant therapy
Inflammation of the urethra in men is accompanied by pain and intoxication. Patients complain about:
- burning when urinating;
- pain in the suprapubic area;
- loss of appetite;
- fatigue;
- feverish condition;
- elevated temperature.
To eliminate local and general signs of the disease, symptomatic drugs are used.
To speed up recovery, the treatment regimen is supplemented with immunomodulatory agents. They stimulate the body to fight infection and reduce the likelihood of exacerbations of inflammation.
Immunostimulants
In case of recurrent urethritis, treatment is carried out with immunostimulating agents. They increase resistance to infections, which shortens the recovery period. In case of infection of the urethra, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Solkourovak;
- Interlock;
- Viferon;
- Genferon;
- Lycopid;
- Ribomunil;
- Immunal;
- Pyrogenal;
- Gepon;
- Interferon.
Immunostimulating medications for urethritis in men are used only on the recommendation of a urologist. People with immunodeficiency conditions are recommended to undergo immunostimulating therapy twice a year.
If relief does not occur within 2-3 days after starting drug therapy, consult a doctor. Inadequate treatment is dangerous due to complications - balanoposthitis, prostatitis, cystitis.
Anti-inflammatory
To combat symptoms, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the form of tablets and rectal suppositories. They have a complex effect:
- antipyretic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers.
When treating bacterial and viral forms of urethritis, the following drugs are prescribed:
The tablets are used in the treatment of acute inflammation, which is accompanied by fever and fever. Ketalgin, Indomethacin, Ketanov, Emodol have pronounced analgesic properties.
If urethritis occurs against the background of urological diseases (prostatitis, cystitis), rectal suppositories with an anti-inflammatory effect are used:
Suppositories are used 1-2 times a day after bowel movements. They are treated this way until the pain disappears.
Vitamins
In half of the cases, urethritis is caused by opportunistic bacteria. Their activation is associated with immunodeficiencies and vitamin and mineral deficiency. Therefore, for urethritis in men, fortified preparations are used. They make up for the lack of nutrients, which leads to strengthening of immune defense.
When treating urogenital infections, products with vitamins B, E, C are usually prescribed:
- Activated;
- Duovit;
- Complivit;
- Vitrum.
The tablets should be taken in accordance with the dosage indicated in the instructions. Abuse of vitamins is fraught with hypervitaminosis and allergic skin rashes.
Probiotics
Antimicrobial drugs destroy not only pathogenic, but also beneficial bacteria in the intestines. To prevent dysbiosis and vitamin deficiency, probiotics are included in the treatment regimen. They contain non-toxic living microorganisms that restore the bioactivity of the intestinal microflora:
- Acipol;
- Enterol;
- Probifor;
- Lactobacterin;
- Enterozermina;
- Bifiform;
- Florin forte;
- Linux.
The course of treatment depends on the duration of antibiotic use, and therefore varies from 5 to 20 days.
Antiallergic
Antihistamines are first-line drugs in the treatment of allergic urethritis. Their action is aimed at combating:
- burning in the urethra;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- itching in the genitals;
- skin rashes;
- redness of the head of the penis.
Third generation antihistamines are used to relieve symptoms:
Unlike 1st and 2nd generation antiallergy tablets, 3rd generation drugs do not have a harmful effect on the heart. Therefore, they are recommended for the treatment of urethritis in men with cardiovascular pathologies.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic medicine for urethritis is not recognized by official medicine, as it does not have proven therapeutic activity. But drugs of this group are often used in the treatment of chronic urethritis. Most of them do not have a direct antiviral or antimicrobial effect, but have a stimulating effect on the immune system.
Homeopathic remedies for urethritis:
- Sulfur;
- Cantharis;
- Medorrhinum;
- Pareier;
- Argentum nitricum;
- Kopaiva;
- Petrozelinum;
- Borax;
- Causticum;
- Equisetum.
Urethritis is an inflammatory lesion of the urethra of infectious or allergic origin. Delayed treatment is dangerous due to the penetration of pathogenic flora into other parts of the urinary system - the bladder, ureters, kidneys. The basis of therapy is etiotropic drugs that destroy the infection. The course of treatment depends on the nature of the inflammation and takes from 5 to 20 days.
Types of treatment for bacterial urethritis
Medicine today has effective methods of combating microbial diseases. The method of treatment is selected by the attending physician, taking into account the type of pathogen, the severity of the symptoms of the disease, and the development of complications. If, along with urethritis, there are also inflammatory processes, everything needs to be treated as a whole.
Main therapeutic areas
For nonspecific urethritis with a chronic status, antibiotics are combined with the administration of the drugs Collargol and Silver Nitrate. The patient is prescribed immunostimulants. A successful outcome in secondary urethritis is associated with the effectiveness of therapy for the primary infection on the basis of which it developed.
For patients with bacterial urethritis, the following is recommended:
- At the peak of the disease, bed rest is prescribed. The speed of recovery will depend on how diligently you follow this recommendation.
- You need to drink a lot of fluid, you should drink at least 2.5-3 liters per day. This can be not only water, but also compotes, fruit drinks, and medicinal decoctions. When there is a lack of fluid in the body, a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria is created.
- In nutrition, you must adhere to the rules: do without spices, herbs, fatty, smoked foods and consume a minimum of salt.
- During treatment, it is advisable to abstain from sex. Or condoms should be used if necessary.
Conservative treatment methods are based on taking antibiotics and antimicrobial medications. Features of the therapeutic course depend on the clinical picture of the disease.
It is important to know! If the cause of the pathology is representatives of a specific flora, then treatment is prescribed for both sexual partners.
Symptomatic therapy is aimed at reducing the manifestations of the disease and improving the patient’s well-being. Patients are recommended to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy), but only in the absence of pain symptoms.
Folk recipes
Traditional recipes are not an alternative to conservative therapy. They are only a complementary component to antibiotic agents and give good dynamics. Herbs are usually inexpensive and can be purchased at any pharmacy. It is important to choose the right herbal mixture to eliminate inflammation due to bacterial urethritis.
There are plants, decoctions and infusions of which have analgesic and diuretic effects, cope well with spasms and are antiseptics. For example, cranberry juice with lingonberries helps remove pathogenic flora from the urinary system. It contains a huge amount of vitamins, the drink has a pleasant taste. Bearberry leaves, a decoction of yarrow herb, parsley, an infusion of elderflower flowers, calendula flowers, knotweed, berries and rosehip roots have proven themselves well. Medicinal products are drunk before meals, one-third of a glass.
Patients are also recommended to make local warm chamomile baths at home with the addition of a string. They reduce inflammation and soothe.
Symptoms and causes
Most often, all the symptoms of the disease actively manifest themselves 2 days after infection. But there are rare cases when the incubation period lasted up to 30 days. It depends on the type of inflammatory agent.
- Painful urination, accompanied by pain and burning in the urethra.
- Itching and burning of the head of the penis and foreskin.
- The discharge is purulent in nature and has a yellow-green tint. Sometimes there is an unpleasant odor of discharge and urine.
- Blood and thread-like sediment in the urine.
The causes of urethritis are most often sexually transmitted infections. Irresponsible attitude towards your body and health.
It is not always that a man gets urethritis after sexual intercourse; there are several other equally common methods of infection:
- Non-traditional sexual relations.
- Anal sex.
- Unprotected sex with an infected partner.
- Failure to comply with water procedures.
- Using other people's washcloths and towels.
- Abuse of alcohol, coffee and carbonated drinks.
- Low physical activity and poor nutrition.
- Urethral injury.
- Weak immunity.
All possible pathogens are already present in our bodies in very small quantities. But the immune system successfully controls their activity and numbers. Therefore, they do not bring us any discomfort.
But if the body’s defenses have decreased for some reason, pathogens can be activated and begin to irritate the mucous membrane. Our body is especially sensitive to pathogens transferred from another person.
List of sources
- Ilyin I.I. Nongonococcal urethritis in men. - M.: Medicine, 1991;
- Kulakov, V.I. Gynecology: national. management / V.I. Kulakov, I.B. Manukhin, G.M. Savelyeva. -M., 2007;
- Savicheva A.M., Bashmakova M.A. Urogenital chlamydia in women and its consequences // Ed. E.K. Aylamazyan - N. Novgorod: Publishing House of NGMA, 1998;
- Urology: national guide / ed. ON THE. Lopatkina. - M.:GEOTAR-Media, 2009;
- Molochkov V.A. Sexually transmitted infections. Clinic, diagnosis, treatment / V.A. Molochkov, O.L. Ivanov, V.V. Chebotarev. M.: Medicine, 2006.
Types of urethritis and consequences
Urethritis can be infectious or non-infectious; the infectious type is divided into specific and non-specific:
- Specific urethritis is a disease caused by sexually transmitted infections (tyrchomonas, gonorrhea, ureaplasma, etc.).
- Nonspecific urethritis is caused by opportunistic bacteria that are found in the rectum and anus. These include: Escherichia coli, staphylococci, streptococci, etc.
- The non-infectious nature of the disease is caused by external factors. Insertion of a catheter can lead to urethritis. Or any other mechanical effects on the urinary canal. Allergic reactions and irritability to poor-quality underwear. Most often, serious treatment for non-infectious urethritis is not required. With the exception of carrying out preventive measures and anti-inflammatory procedures through installations in the canal.
The consequences of urethritis occur only in those who missed the acute and subacute stages of the disease. After two weeks, symptoms and discharge almost disappear, and the disease turns into a chronic disease. At any opportunity, a relapse will occur, which is almost impossible to avoid.
An advanced disease leads to infertility and irreversible changes in the mucous membranes and tissues of the genitourinary system. Benign and non-benign formations on the pelvic organs. Surgery may be required.
- Inflammation of the prostate and the formation of chronic infectious prostatitis.
- Inflammatory processes of the seminal vesicles.
- Testicular damage.
- Damage to the urinary and vas deferens.
- Infertility.
- Cancer.
- Lifelong carriage of the disease.
Features and classification
can most often become infected with bacterial urethritis .
As a result, inflammatory processes in the urethra occur due to the presence of pathogenic flora.
Microorganisms, penetrating the mucous membrane, begin to multiply, causing inflammatory processes.
Bacterial urethritis can manifest itself not only when infected through a partner, but also during various manipulations:
- during endoscopic examination of the canal;
- during catharization and other manipulations.
Urethritis due to bacteria is one of two options:
- Primary. This type of disease can occur in an acute form or become chronic. Signs of infection are not pronounced, as a result of which the man is a carrier of the disease.
There may be slight pain with the release of urine or pus, which should alert the patient.Swelling of the mucous membrane and tissues also occurs. To make a correct diagnosis of this type of disease, it is necessary to conduct laboratory tests that will confirm the presence of pathogenic flora.
This is especially true in the chronic form, since in this case the symptoms are practically invisible or the disease does not manifest itself for a long time.
The only discomfort may be burning and itching. With chronic inflammation, high drug resistance occurs.
- Secondary .
Microorganisms enter the urethral mucosa as a result of inflammatory processes of the bladder, prostate, other pelvic organs, as well as with sore throat and pneumonia. The secondary form of bacterial urethritis is characterized by a long course . The patient experiences a burning sensation, pain, and slight discharge in the form of mucus or pus when passing urine. Hyperemia and sponge gluing also appear.
On our website you can learn about the following types of urethritis:
- nonspecific;
- non-infectious;
- acute and chronic;
- gonorrheal and non-gonorrheal;
- trichomonas;
- chlamydial;
- candida;
- allergic.
The main differences between urethritis and cystitis are described here.
Treatment
Many men who started proper treatment in time completely got rid of the disease.
During treatment, the doctor bases his opinion on the results of an analysis to identify the causative agent of the disease. Several groups of medications are prescribed. It is recommended to give up junk food and completely avoid alcohol and sexual contact during treatment.
The basis of therapy is:
- Antibiotics. The most effective tablets for urethritis caused by gonorrhea and chlamydia are Erythromycin, Tetracycline, Gentamicin and Azithromycin. Mycoplasma and ureaplasma are treated with Doxycycline or Tetracycline. Against Trichomonas infection, the drug Azithromycin, Metronidazole. Norfloxacin, Lomadey and Enoxacin tablets are used against opportunistic bacteria. They have an effect against E. coli, staphylococci, Escherechia coli, etc. all antibiotics are taken under the strict supervision of the attending physician, as they can cause serious side effects and have a list of contraindications. Some of them can cause vomiting and dizziness. This is due to poor tolerability of the drug.
- Antimicrobial drugs using the example of Cefixime and its analogues (Ceforal, Fixim, Loprax), Furamag, Canephron and Biseptol.
- Immunostimulating drugs. The most prescribed are Cycloferon and Phlogenzyme.
- Antiviral drugs against the viral nature of the disease (Acyclovir, Gerpevir). Antibiotics for this etiology will only aggravate the situation and will not help.
- Antihistamine tablets. Prescribed for allergic causes of allergies or intolerance to antibiotics (Suprastin, Cetirizine).
To all of the above, you need to add rinsing the urethra with an antiseptic, mainly Miramistin, and prescribing sitz baths from herbal infusions.
The use of diuretic fruit drinks and infusions is recommended; the most common is lingonberry or cranberry juice.
To maintain immunity, you need to take a course of multivitamins and follow a diet. Stick to a healthy diet.
Most often, the doctor prescribes an antibiotic that has a wide spectrum of action in order to cover as many pathogens as possible and not use additional drugs.
If you seek help on time and do not refuse to take pills on time, then urethritis will be easily cured.
The approximate amount of time spent on treating the disease ranges from 2 weeks to 1 month. After a course of medications, you will need to be tested again to rule out recurrence of the disease.
Prevention measures
Prevention is often resorted to by men who have already experienced urethritis, who either do not want to become infected with it again, or who already have a chronic process and avoid relapse.
- Use condoms during sexual intercourse.
- Observe timely adoption of water procedures.
- Monitor your diet and fluid intake. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of plain water per day. Tea and other drinks do not count.
- Do not indulge in numerous sexual relationships.
- Minimize alcohol and coffee consumption. The best option would be to completely eliminate these drinks from your life.
- Stick to traditional sex and avoid anal sex without a condom.
In the chronic stage of urethritis, during relapses, mild antibiotics and antiseptics are prescribed.
In order to minimize the likelihood of recurrence of the disease, it is necessary to treat the sexual partner. Even if your significant other does not show symptoms, the disease cannot be ruled out.