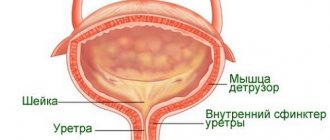
There are different opinions about the normal frequency of urination in a person with a healthy excretory system. However, all experts agree on one thing: if the urge occurs more often than ten times a day, and they are uncontrollable, disturbing day and night, most likely we are talking about the occurrence of some kind of pathology.
Due to the different physical structure of men and women, the reasons for the appearance of this symptom are clearly different. Frequent urge to urinate in women with the release of a small amount of urine can occur not only as a result of the development of pathology of the excretory system, but also as a result of gynecological and even endocrine problems.
Due to a malfunction, the body signals its needs much more often. That is why frequent urination in a woman is a serious reason to consult a doctor for medical help.
High probability confirmed by diagnostics
To correctly determine the disease that has caused such unpleasant symptoms as an increased urge to urinate in combination with an increase in body temperature, the specialist will have to carry out a series of diagnostic manipulations with the patient. Among them:
- survey (how severe are the symptoms, are they accompanied by pain, are there nighttime and false urges, how long does the fever last);
- examination (assessment of the condition of the skin, percussion of the abdomen);
- digital examination (palpation) of the prostate gland rectally;
- Ultrasound of the prostate, kidneys, bladder;
- general blood analysis;
- several types of urine tests.
Based on the research results and the symptom complex in the form of frequent urination and temperature, one of the four most probable diseases is determined:
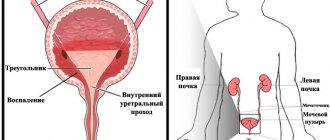
- inflammation of the bladder (cystitis);
- inflammation of the urethra (urethritis);
- inflammation of the renal pelvis (pyelonephritis);
- inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis).
Cystitis is an inflammatory process in the bladder cavity, in which the usual symptoms are fever, false strong and unbearable (imperative) urges, as well as frequent urination in men. This condition is also characterized by a pain syndrome, the peculiarity of which is that it manifests itself at a late stage of the development of the disease, when the affected walls of the bladder begin to collapse.
Urethritis is an inflammatory process involving the urethra that becomes noticeable when pain occurs when urinating.
Urethritis is an inflammatory process affecting the urethra, which mainly becomes noticeable when pain occurs when urinating in men, usually at the beginning or in the middle of the process. In addition to pain, a slight increase in body temperature and a frequent urge to empty the bladder, patients note a change in the color and amount of urine excreted at one time.
Pyelonephritis, a disease that is an inflammatory lesion of the renal pelvis, is characterized by approximately the same symptoms as the other diseases on the list: high fever, discomfort when urinating, unhealthy color and an abnormally small amount of urine excreted once.
Prostatitis, inflammation of the prostate tissue, is the most common cause of damage to the male genitourinary system, and, consequently, problems with urination. Frequent, strong, often painful urge to go to the toilet, difficulty “pushing” the stream through the urethra up to acute retention of urine outflow, pain syndrome involving the pelvic organs, lower back, rectum and genitals - all these are clear signs of prostatitis. They also include pain and difficulty with defecation, discharge from the urethra and increased body temperature as additional evidence of the inflammatory process.
The cause of frequent urination together with fever may be these or other reasons, but only a urologist can determine them and then prescribe proper treatment.
How to recognize food intoxication?
What are the signs of food poisoning?
Poisoning appears suddenly, and the state of health sharply deteriorates from normal to requiring medical intervention. The first signs may appear half an hour after a harmful toxin enters the body. The average time for food poisoning to manifest is 2-5 hours. Some toxins can be stored in the body for up to a week, but this is a rare exception.
Group 1 symptoms of food poisoning
The body tries to get rid of the harmful substance. During this period, the gastrointestinal tract, affected by toxins, tries to get rid of spoiled food on its own. During the first period of disease development, the symptoms of food poisoning are as follows:
- Vomit. First, the stomach gets rid of all the food in it. The urge continues even when the stomach is already empty, vomiting of gastric juice or painful urges begins. Taking any liquid, food or medicine provokes vomiting. During this period, rapid gastric lavage can stop the disease.
- Diarrhea. The intestines, like the stomach, are rapidly emptied. First, the entire contents of the intestines are released, followed by loose, greenish stools with a pungent odor.
Any intake of food, liquid or medication causes lightning-fast bowel movements. Adsorbents and medications taken at this stage are difficult to retain in the body. The gastrointestinal tract is inflamed, which is manifested by a number of typical symptoms:
- painful abdominal cramps and excruciating colic - it is difficult to stay upright;
- nausea - any food and drink, except water, causes acute disgust;
- increased salivation.
Group 2 symptoms of food poisoning
Intoxication of the body. During this period, pathogenic toxins enter the blood from the gastrointestinal tract, and a general deterioration of the condition begins. Intoxication occurs almost immediately after the manifestation of damage to the stomach and intestines and manifests itself as follows:
- weakness, lethargy - in case of food poisoning, bed rest is immediately required, since the patient is not able to stand;
- temperature increase - depends on the toxic agent, the temperature rises to 37-39 C.
- chills - the patient will need warm clothes and a blanket, since he is cold all the time;
- pain – due to blood intoxication, a painful toxin spreads throughout the body, and widespread severe pain occurs. Headache, muscles, joints hurt.
During this period, the body's defense mechanisms are activated. When the above signs of food poisoning appear, it is necessary to begin intensive treatment under the supervision of a doctor. Intoxication with botulinum or shigella derivatives can be fatal.
Poisoning is especially dangerous for older people; children - they have a weak body’s defense reaction to toxins; pregnant women - poisoning in some cases leads to the production of oxytocin, a sharp contraction of the uterus, and miscarriage is possible.
Frequent urination in men: how to deal with it
Regardless of what disease provoked the symptoms of increased body temperature and increased urge to urinate, to combat these manifestations you will first have to undergo treatment for the underlying disease. Identifying which one specifically is the task of a specialist who will prescribe optimal therapy.
In cases of cystitis and urethritis, for example, the attending physician will first of all prescribe a course of antibiotics (most often broad-spectrum drugs, but if the causative agent of inflammation is known, then a medicine directed specifically against it), due to which the main symptoms of the disease will be removed. Also, the course of treatment for these diseases includes the following drugs:
In cases of cystitis and urethritis, the attending physician will first prescribe a course of antibiotics
- analgesics;
- antispasmodics;
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs);
- antipyretics;
- immunomodulators.
With cystitis and urethritis, it is most often enough to restore the normal rhythm of urination and relieve inflammation, as the body temperature will also return to normal. If the prescribed drugs do not produce the desired effect (or you have to wait too long), the doctor may prescribe additional lavage of the bladder/urethra using an antiseptic solution, which helps to quickly destroy and remove pathogens from the bladder.
As additional help that a sick man can provide to himself, it is recommended to drink large quantities of liquid (at least 3 liters daily), exclude spicy, salty, sour foods from the diet, and take a complex of vitamins. You can drink diuretic decoctions based on medicinal plants, which will also help speed up the process of removing pathogenic factors from the body.
Since both cystitis and urethritis in most cases develop against the background of either diseases transmitted through sexual contact, or in the presence of inflammatory foci in other parts of the body, a separate part of therapy is the fight against these problems.
In case of acute pyelonephritis (it is in this condition that frequent urination with an increase in temperature is manifested), treatment is carried out with the use of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs that help eliminate inflammation in the kidneys, preventing it from turning into a full-fledged obstructive (purulent) and destructive lesion. Additionally, medications are prescribed that increase the body’s immune reactivity, and in the most severe cases, when the process has already progressed into a chronic form, procedures are used to eliminate the causes of the obstruction of urine outflow (including surgical ones). As in the first two cases, relieving inflammation and restoring the urination process will successfully reduce body temperature.
Methods and drugs for treating frequent loose stools
Frequent loose stools can become a real problem and a disruptor to many plans in a person’s modern life.
Treatment for frequent loose stools should begin when the urge to defecate is detected more than 3 times per day. Against the background of such a symptom, dangerous pathologies often occur, especially if an admixture of blood is detected in the stool. Before starting quality treatment, examinations and tests are prescribed that help identify the causes of frequent loose stools. Afterwards a diagnosis is made. Regular diarrhea with unpleasant impurities accompanies certain diseases:
- Irritable bowel syndrome. It is considered a chronic disease and haunts a person literally until the end of his life. Little to no blood is present, but unexplained weight loss may be present. Due to constant diarrhea, a feeling of fatigue occurs, and the urge to defecate is also observed at night.
- Colon cancer. The cells in the lining of the colon change during the course of the disease. As a result, diarrhea may be accompanied by blood. The patient is sometimes not bothered by any other symptoms, only regular constipation alternating with diarrhea.
- Nonspecific colitis. It is characterized by a chronic course of the inflammatory process in the rectum or colon. Diarrhea mixed with blood can become a characteristic symptom of the pathology.
- Crohn's disease. Accompanied by severe diarrhea and destruction of the intestinal lining. Additionally, weight loss and the development of ulcers and fistulas in the stomach may occur.
- Celiac disease. Inflammatory pathology localized in the small intestine. It develops due to gluten intolerance and is accompanied by frequent diarrhea in adults. A characteristic symptom is strong-smelling stool with a pale color. A lot of liquid stool comes out.
- Hyperthyroidism. Occurs due to excess production of thyroid hormones. As a result, flatulence accelerates, urination becomes more frequent and diarrhea occurs frequently. There is a decrease in body weight.
- Typhoid fever. A specific pathology that can cause frequent bowel movements. Typhoid fever is characterized by stomach pain, dry cough, and fever during the first week. Loose stools occur by the 3rd week of illness.
- Dysbacteriosis. The microbial component in the intestines is disrupted, resulting in many unpleasant symptoms, including diarrhea. It may contain blood impurities.
- Diarrhea due to another disease affecting the intestines. Most often observed against the background of tuberculosis, HIV and other dangerous diseases. Occurs against the background of rapid bacterial growth.
- Parasitic infestations. Loose stools are accompanied by weight loss, flatulence, cramping pain and loss of appetite. There may be parasites in the stool, as well as blood impurities.
- Intestinal ischemia. Occurs due to poor condition of the vessels feeding the intestines. Bloating and diarrhea are worse immediately after eating.
Frequent diarrhea can be caused by taking certain medications: anti-diabetes, antibiotics and other drugs. Sugar substitutes can lead to pathology.
Principles of treatment of diarrhea
Once diagnosed, diarrhea can be treated, otherwise no therapy will provide permanent results. To treat pathology, you need to consult not only a therapist and a gastroenterologist, but also specialists such as an infectious disease specialist, a cardiologist, and even an endocrinologist and an oncologist.
About drugs! After making a diagnosis and the reasons for regular loose stools, antibacterial drugs and other agents are prescribed that reduce the amount of harmful flora in the intestines. To reduce the urge to constantly defecate, blocking drugs such as activated carbon are used.
It is important not to self-prescribe treatment using antidiarrheal drugs. In some diseases they can lead to toxic damage to the intestines.
After determining the causes of diarrhea, the first step is to protect yourself from dehydration and restore electrolyte balance. To do this, use a solution of Regidron, which is sold in powder form in a pharmacy. The electrolyte mixture replenishes the balance of the necessary components. The following medications are used:
- Activated carbon is a natural component based on animal or vegetable charcoal that removes harmful substances and stops diarrhea. When using it, it should be taken into account that it should not be used by people with ulcerative lesions;
- Acipol, Linex or any other probiotic - used to restore intestinal microflora, help produce B vitamins;
- Smecta is a drug for removing harmful substances, as well as for patients who develop diarrhea due to chronic allergies;
- Hilak Forte - a remedy for restoring the amount of beneficial flora in the intestines, helps fight bacteria and infections;
- Enterol is an antimicrobial drug that normalizes local immunity in the intestines.
To eliminate the causes and symptoms of frequent loose stools in an adult, a special diet is indicated.
Rational nutrition for chronic diarrhea
The diet during the treatment of frequent loose stools should consist of dry white bread and rice porridge with the addition of a decoction instead of a drink. You can also drink blueberry jelly and black tea. Cow's milk whey can be used if lactose intolerance is normal. Additionally, the diet includes lean fish and boiled or baked meat products.
Useful information: Causes of loose stools after each meal
You can eat potatoes and carrots, but you need to avoid the laxative beets. You should drink clean water more often, which restores the stomach and all cells. Fermented milk products are allowed in small quantities. You can eat low-fat cottage cheese, boiled eggs, and drink green tea. It is allowed to eat pasta in small quantities.
Traditional recipes for diarrhea
During the treatment of frequent loose stools, the use of decoctions and other folk recipes is allowed. They are able to combat the causes, but are most often necessary to completely eliminate the symptoms of diarrhea:
- dried blackberries mixed with honey, take 1 tsp. 3 times a day;
- chamomile, brewed according to the recipe, is taken 3 times a day;
- for blood impurities you need to take 1 tsp. dry rosehip branches and steam them with a glass of boiling water, boil for 30 minutes in a water bath, take a third of a glass;
- oak bark infusion – 1 tsp. for 2 glasses of water - infuse for 5 hours, take 0.125 l 4 times a day;
- Brewed dried blueberries will help get rid of diarrhea, drink the drink half a glass 4 times a day;
- Helps against diarrhea: common lingonberry - dry leaves in the amount of 4 tsp. brew 0.5 liters of boiling water for 20 minutes, cool and take 50 ml 4 times;
- You can brew 15 g of leaves in 0.3 ml of boiling water and boil in a water bath, and take a fresh portion every 8 hours.
A decoction of dried pomegranate peels, prepared during the fresh fruit selling season, is a good way to stop diarrhea. Brew from a glass of boiling water and 1 tsp. crushed crusts drink. In some situations, potato starch becomes the best cure for diarrhea. It is diluted at the rate of 1 tsp. product per 1 glass of warm water. Take a fresh portion each time.
If the condition does not worsen, frequent loose stools can be treated at home. But if this cannot be done within 3-4 weeks, contacting a doctor should no longer be delayed.
Source: https://diarey.net/simptomy-i-lechenie/lechenie-chastogo-zhidkogo-stula.html
Causes of frequent urination in men
All the reasons that force men to visit the toilet more often can be divided into two categories - physiological and pathological.
Physiological causes include changes in diet and increased fluid intake. Foods such as raw fruits and non-starchy vegetables can increase your average daily urine output. Coffee and alcohol have strong diuretic properties. The most obvious culprit for frequent urination is beer, a drink that many men consume heavily and frequently.
If the increase in diuresis is associated with nutrition, then within 24 hours after correcting the diet, normal urination is restored in the usual volumes. Moreover, errors in diet and single abuse of alcoholic beverages do not cause any pathological sensations associated with going to the toilet, for example, pain and cramps, unlike some diseases, the main symptom of which is frequent urination.
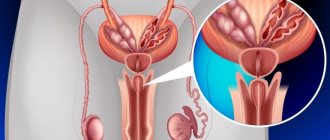
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is a disease of the prostate gland of inflammatory nature. It most often occurs due to a bacterial infection and can develop even at a relatively young age. In the absence of timely treatment, it can become chronic and torment a man for a long time. Chronicization of the process is also facilitated by an incomplete course of therapy. Men often disappear after receiving a list of prescriptions from the doctor and do not come for control, which may reveal the need to adjust the treatment regimen.
In addition to frequent urination with prostatitis, a man may complain of scanty urine output - that is, the urge will be frequent, but unproductive. It is possible that the patient will experience pain or other discomfort during the process.
Prostate adenoma
An adenoma is a benign prostate tumor that, growing in size, compresses the urethra.
At the same time, the man experiences frequent urge to go to the toilet, however, he cannot completely empty the bladder. Despite the fact that the patient is pushing hard, the stream appears sluggish and intermittent. Along with this, such patients may suffer from urinary incontinence, especially at night. Prostate adenoma most often occurs in old age. Young men are practically unfamiliar with this disease.
Often, frequent urination in men can be explained by diseases of the urinary system itself - pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis and urolithiasis. In such cases, the act of urination not only becomes frequent, but can also be very painful.
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is a kidney disease of inflammatory nature, in which the functions of urine formation and separation may be impaired. In the absence of adequate therapy, it can lead to such serious consequences as impaired renal function - renal failure. With pyelonephritis, a man will experience swelling, as well as painful and frequent urination. The main diagnostic sign in this case will be changes in laboratory parameters of a biochemical blood test and general clinical blood and urine tests.
Cystitis
Cystitis - inflammation of the bladder - is a rare phenomenon in men, however, it can also cause frequent urination. It can develop due to hypothermia or a urogenital infection. In this case, frequent urge to go to the toilet may be associated with various types of discharge from the urethra, as well as a slight fever, symptoms of general malaise and a rash in the groin area.
Physiological reasons
As mentioned above, there are physiological reasons that explain this condition. If frequent urination is caused by one of them, there is nothing to worry about, since it is of a normal physiological nature.
Let's name the main ones:
- Drinking large amounts of water or other liquids. It's quite simple: the more you drink, the more often you will need to remove this liquid.
- Use of diuretics. Diuretics are substances that have a distinct diuretic effect. In addition to specific pharmaceutical drugs, we can highlight products that also contribute to the removal of water from the human body and can cause frequent urination: alcohol, coffee, soda and other liquids, as well as many vegetables.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman’s body, especially her hormonal system, is rebuilt to perform maternal functions. Such changes can cause incontinence and many other symptoms.
- Menopause. As women age, they also experience hormonal changes, which can also make them want to relieve themselves more frequently.
- Physiological characteristics of the body. There are cases when a person often goes to the toilet without any obvious reason.
At the same time, medical diagnostics also do not find any pathologies. If such a condition does not cause discomfort, then in such cases they talk about the physiological characteristics of the body, including muscle weakness.
Symptoms that may accompany frequent urination in men
If the cause of frequent trips to the toilet is physiological factors, such as an increase in the amount of fluid consumed or a special diet, then frequent urination is usually not accompanied by any further symptoms. If the patient has one of the diseases described above, then it is quite possible that he will complain of:
- Pain or cutting during urination;
- Feeling of an intermittent stream, which resumes after a change in body position or shaking;
- The so-called false urge, when a man feels the urge to urinate, but cannot do so due to obstruction of the duct;
- Discharge from the urethra, the nature of which depends on the infection that caused it.
- Temperature, chills, fever and symptoms of general malaise;
- Pain in the lumbar region, which can be quite significant in sensation.
If frequent visits to the toilet are accompanied by the conditions described above, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. If the patient complains of acute pain in the back area just above the lower back, it is recommended to call an ambulance, since the passage of stones is very painful and requires immediate medical attention.
What are the standards?
Each woman has her own urination rate. Factors that influence how often you empty your bladder can vary, from physical activity to the amount of water you drink. If urination with discomfort appears due to a disease, then patients note frequent side symptoms:
- burning or pain, itching sensations in the urethral canal during deurination;
- small amount of urine excreted;
- if pollakiuria occurs at atypical times - at night or at work.
When visiting the toilet 10 times a day or more, especially several times at night, this should be the reason for an additional examination of the genitourinary system under the supervision of a specialist.
More on the topic: Methods of treating tuberculosis of the genitourinary system
Diagnosis of frequent urination in men
Diagnostic procedures in this case begin only after collecting anamnesis and external examination of the patient. The doctor will definitely ask about your lifestyle, diet, water regime and medications taken. It is likely that the specialist will be interested in some aspects of a man’s intimate life, especially if frequent urination is associated with pain and strange discharge from the urethra. Most often, the diagnosis is made based on the results of the following studies:
- A clinical blood test with determination of the formula allows us to assume the presence of an inflammatory process in the body, as well as draw conclusions regarding its nature (whether it is infectious in nature). Often, the data obtained can determine dehydration or the presence of internal bleeding.
- Biochemical blood test - the main interest in cases of frequent urination are markers of kidney condition such as creatinine, urea and uric acid.
- Clinical urine analysis is most indicative of diseases of the urinary system. It allows you to determine the presence of salts in the test material, as well as protein, blood and mucus. All these inclusions are pathological and signal that frequent urination in a man is caused by one or another disease.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder very clearly demonstrates the presence of stones in these organs, as well as the presence of an inflammatory process or other pathological changes. Before performing an ultrasound examination, you must drink at least a liter of clean still water for an hour for better visualization.
- A smear from the urethra followed by bacterial culture allows you to detect and identify urogenital infections or STD pathogens. Similarly, it is possible to identify pathogens from the TORCH group, which can also provoke frequent urination in some cases.
- Computed tomography is used in cases where ultrasound does not accurately determine the size and composition of stones. Typically, this procedure is performed at advanced stages of diagnosis, especially if non-contact lithotripsy or surgery is planned.
Treatment
It is possible to achieve effective treatment at home. The only thing that must be strictly followed is the recommendations of the attending physician. It is necessary to drink plenty of fluids, because a lack of water can worsen the patient’s general condition. It is worth remembering that with this disease, vomiting and quite frequent diarrhea occur, due to which the body needs a fairly large amount of fluid.
You need to drink water regularly. Also, in case of severe dehydration, it is recommended to use oral rehydration medications. You can buy them at any pharmacy. These medications restore the loss of nutrients in the body and restore normal water balance.
Before you start taking these medications, they must be dissolved in water according to the instructions. Treatment of the intestines consists of a number of mandatory procedures that must be performed at the first symptoms of poisoning.
Treatment consists of the following:
- Keep your hands clean and pay attention to additional rules related to personal hygiene. It is worth remembering that this disease is quite contagious. The patient must have a separate towel, personal utensils, soap, etc. All these things should be stored separately.
- It is necessary to rinse the stomach as quickly as possible. Add a little salt or soda to the cooled boiled water, drink at least 700 ml of liquid in one gulp, and then artificially induce vomiting. It is advisable to repeat this procedure several times in a row.
- After the stomach is washed, you need to drink some liquid to restore normal water balance in the body. You can drink often, in small sips. If vomiting prevents you from drinking, you can take one of the antiemetic drugs that are available at the pharmacy.
- When diarrhea begins, it is recommended to take enterosorbents, which will help remove harmful toxins from the intestines.
- If the condition worsens, further treatment is carried out only by an experienced doctor. He can prescribe effective antibacterial drugs that will ensure a quick recovery of the patient.
After the patient begins to recover, he begins to develop an appetite, and here it is important not to eat heavy and fatty foods, but to stick to a diet for at least a couple of weeks. Eating fatty and fried foods is strictly not recommended. This also applies to raw vegetables and fruits, rough foods, and raw milk.
Various cereals, dried bread, lean broths, and steamed cutlets are recommended. They allow you to saturate the body with useful minerals and vitamins, but at the same time do not overload the stomach. It is very important to follow the above recommendations after recovery, this will help avoid complications and relapses.
Frequent urination in men: treatment
As already mentioned, therapy is effective only if increased frequency of urination is reliably a symptom of the disease. Otherwise, it is recommended to make changes in diet and give up alcoholic beverages or diuretics, if any.
To treat pathologies whose symptom is frequent urination, the following groups of medications are used:
- Diuretics - most often based on plant materials, which gently increase diuresis, thereby promoting the passage of stones or bacterial toxins.
- Drugs that change the pH of urine in a certain direction are necessary to destroy stones and crystals so that they can leave the body naturally.
Uroantiseptics are drugs that have a bactericidal effect on pathological microorganisms living in the urinary system.- Antibiotics – used to treat urogenital infections and STDs.
- Antiprotozoal - used to treat certain diseases caused by protozoa, such as chlamydia or ureaplasma.
- Antiviral drugs are effective if frequent urination is caused by an exacerbation of a viral infection, for example, genital herpes virus or human papillomavirus.
- Selective alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers - used to treat prostatitis and prostate adenoma. Most often as part of complex therapy.
What causes this condition?
Inflammatory diseases
If a child experiences frequent urination, then most often doctors do not consider this a deviation, since the normal amount of urination is directly related to age.
However, when in adults and young patients a temperature of 37 degrees appears, and against its background there is a frequent urge to urinate, we are talking about the development of diseases of a urological nature. Most often this problem is provoked by the following pathologies:
- Cystitis. Inflammation of the bladder, during which there is increased urine output, the presence of blood in the urine, pain when emptying, and vomiting.
- Urethritis. Inflammatory processes that are localized in the urethra. The symptoms of this disease are similar to cystitis.
- Pyelonephritis. An inflammatory disease that affects the pelvis, calyces and parenchyma of the kidneys. Patients complain of frequent and difficult urination, increased body temperature, and chills.
Other ailments
The following pathologies can provoke disruption of the urination process and an increase in body temperature:
- Neoplasms of a malignant or benign nature, which are localized in the bladder or kidneys. At the initial stages they have no symptoms, but as they grow, they cause pain in the lower back and interfere with the normal outflow of biological fluid.
- Kidney stone disease. In addition to the fact that an increased temperature appears and urination is difficult, pain may develop when emptying, and the color of the urine may change. Sometimes blood impurities are observed, which is caused by the movement of stones through the urethra, during which the stones injure its walls and cause bleeding.
- Diabetes. Body temperature also increases, urine becomes darker, has an unpleasant smell of acetone, and general fatigue appears.
- Overactive bladder. Most often, there is no elevated temperature, but there is discomfort during bowel movements, frequent urges, a strong desire to go to the restroom, and possible urinary incontinence.
- Urethral stricture. It is a pathological narrowing of the internal lumen of the urethra. In patients, the process of emptying is disrupted, there is a feeling that urine is not completely eliminated, discharge from the urethral canal is observed, and there may be pain and cramping when urinating.
Return to contents
Prevention
The most effective preventive measures against poisoning will be following the rules of personal hygiene, proper preparation and storage of food. You can protect your body from intoxication by adhering to the following recommendations:
- Wash your hands especially thoroughly before eating food and after visiting public places.
- Ensure proper heat treatment of meat products.
- Consume fully cooked food.
- It is also not recommended to store cooked dishes for a long time, even in refrigeration units, for example, more than three months.
- There is no need to purchase ready-made food in public places such as train stations, parks, bus stops, and so on. Practice shows that in most cases such food is prepared with significant violations of acceptable norms and rules.
By following the above rules, you can protect yourself from acute intestinal poisoning. Considering the fact that absolutely every person is susceptible to intestinal poisoning, you need to take additional safety measures that will protect you from the disease. By following the above recommendations, each person can not only quickly recover in case of poisoning, but also provide themselves with reliable protection against this disease. Follow basic hygiene rules and eat only quality foods.
, MD, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Most people urinate about 4–6 times a day, mostly during the daytime. Typically, adults produce between 700 ml and 3 liters of urine per day. Excessive urination may refer to:
increased volume of urine (polyuria);
normal volume of urine with a frequent urge to urinate (frequent urination);
Frequent urination may be accompanied by a feeling of urgent need to urinate (urinary urgency). Many people are particularly aware of polyuria due to the need to get up at night to urinate (nocturia). Nocturia can also occur with excess fluid intake immediately before bed, even if the total amount of fluid consumed during the day does not exceed the usual amount.
Additional symptoms
If a patient experiences frequent urination with pain and a high fever, other unwanted reactions are sometimes present, such as:
- breathing problems;
- rapid heartbeat;
- increase in blood pressure;
- general weakness and severe fatigue;
- pain when urinating;
- hematuria;
- itching and burning of intimate organs;
- discharge from the vagina or urethra.
Return to contents
Diagnostic measures
When a person has a fever and has trouble urinating, it is important not to delay a visit to the hospital. You will need to make an appointment with a urologist, who will initially interview the patient and find out how long the unwanted symptoms have been appearing, whether there is pain during bowel movements, whether the desire to go to the toilet has increased at night, and how long the elevated body temperature lasts. Then they begin the inspection. The doctor assesses the condition of the skin and taps the abdominal cavity. The final stage of the examination is a digital examination of the rectum. If the patient experiences pain, this method is not used. Next, the doctor sends the patient for the following examinations:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- urine testing according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys and organs located in the pelvis.
Return to contents
How to get rid of increased urination at fever?
When elevated temperature and frequent urination are caused by inflammatory processes that are localized in the kidneys, bladder or urethra, patients are prescribed antibacterial agents. The choice of medication is directly related to the type of disease and the severity of its course. Sometimes it is necessary to use uroseptics designed to improve kidney function. If the patient experiences pain, the use of painkillers and antispasmodics is required to help relieve spasms. Papaverine is mainly used for these purposes.
When treating the underlying disease of the genitourinary system, fever and frequent diuresis will go away.
One cannot do without antipyretic medications, the most accessible and well-known of which is Paracetamol. Immunostimulants can also be used to help regulate the functioning of the immune system. If an increase in temperature and disruption of the emptying process is associated with urolithiasis, then medications are prescribed that help break up the stones and subsequently remove them from the body. When conservative therapy does not provide the desired result in the fight against stones, they resort to surgical intervention, the type of which is determined by the treating doctor.