Indications for use
1. Monitoring kidney function.
2. Endocrine diseases. 3. Assessing the impact of heavy physical activity. Using the creatinine clearance index, pathological conditions associated with impaired renal function are diagnosed by identifying deviations of indicators in the normal formula, up or down.
The study is prescribed:
- To determine renal failure.
- During pregnancy to assess the functional load on the urinary system.
- For congenital anomalies of the urinary system.
- Before and after hemodialysis in order to determine the need for the procedure and its effectiveness.
- For endocrine pathologies to identify metabolic and energy failures.
- For athletes to determine the functional state of the urinary and cardiovascular systems, as well as identify signs of doping.
- For chronic inflammatory kidney diseases.
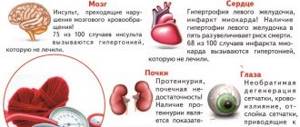
- With high blood pressure.
- For experimental and scientific purposes to determine the boundaries of the norm and derive effective measurement formulas.
In medicine, several methods are used to calculate creatinine clearance; the Cockcroft-Gault formula is considered the most convenient and reliable.
conclusions
Calculation of creatinine clearance and glomerular filtration rate is mandatory for pregnant women and people with severe forms of immunodeficiency, as well as congenital anomalies. If you accidentally notice changes in the tests (preventive examination), it is recommended to consult a therapist who will refer you to the necessary specialist with a more specialized profile (nephrologist, urologist, endocrinologist).
Normalization of indicators is possible when the causative disease is eliminated. Chronic damage often requires lifelong treatment and lifestyle modifications, so it is necessary to try to prevent progression by seeking qualified medical help in a timely manner.
source
general characteristics
Purification of the blood from metabolic products is ensured mainly by the kidneys (glomerular filtration, tubular secretion and reabsorption). Endogenous creatinine clearance is a hemorenal test that evaluates the cleansing capacity of the kidneys. The method is based on calculating glomerular filtration based on the rate of plasma purification from creatinine, which normally enters the urine only by filtration and, after passing through the glomeruli, is not reabsorbed in the tubules. Therefore, a decrease in creatinine excretion in the urine and an increase in its concentration in the blood indicate a decrease in filtration in the kidneys. After 40 years, glomerular filtration decreases by 1% annually. Glomerular filtration is determined by the formula: V(pl) = U(cr) x V(m) / C(cr)xT, where V(pl) is the volume of plasma filtered through the renal filter per minute; V(m) - volume of urine for a given time; C(cr)—creatinine concentration in plasma (serum); U(cr) - creatinine concentration in urine; T is the urine collection time in minutes. Since the minute volume of filtration in the kidneys depends on the height and weight of a person, to normalize the indicator in people who deviate significantly in size from the average values, creatinine clearance is recalculated to the conditional value of the standard average body surface (1.7 m2), taking into account the person’s height and weight.
Rehberg test (endogenous creatinine clearance)
[02-011] Rehberg test (endogenous creatinine clearance) 415 rub.
Determination of endogenous creatinine clearance is a test used to assess the level of glomerular filtration.
Synonyms Russian
Glomerular filtration rate, GFR.
English synonyms
Test of renal function, creatinine clearance test, Rehberg test.
Research method
Kinetic method (Jaffe method).
Units
µmol/l (micromoles per liter), mmol/day. (millimoles per day), ml (milliliter), ml/min. (milliliters per minute), % (percent).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood, daily urine.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Eliminate alcohol from your diet 24 hours before the test.
- Do not eat for 12 hours before the test.
- Do not take diuretics within 48 hours before collecting urine (as agreed with your doctor).
- Avoid physical and emotional stress 24 hours before the test.
- Do not smoke for 30 minutes before the test.
General information about the study
All human blood passes through the kidneys hundreds of times a day. They pass the liquid part of the blood through tiny filters (nephrons), then most of the liquid is reabsorbed back into the blood. Liquid waste that is not reabsorbed by the kidneys is eliminated from the body in urine.
Creatinine (from the Greek kreas - “flesh”) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate in muscle tissue. The amount of it in the body is quite constant and depends on the person’s muscle mass. According to its chemical structure, it is a cyclic derivative of creatine.
Creatinine is filtered from the blood by the kidneys, and a small amount is actively excreted in the urine. Tubular reabsorption of creatinine is minimal. If the filtering capacity of the kidneys is insufficient, the level of creatinine in the blood increases.
Knowing the levels of creatinine in urine and blood, it is possible to calculate creatinine clearance, which reflects the level of glomerular filtration. Creatinine clearance (from the English clearance - “purification”, i.e. cleansing of creatinine, its removal) is the amount of blood that the kidneys can clear of creatinine in one minute.
In a healthy young person, it is about 125 ml per minute, which means that his kidneys clear 125 ml of creatinine from the blood every minute.
Glomerular filtration level is the sum of filtration levels in all functioning nephrons. This indicator allows you to determine the number of these nephrons in the kidneys. It has important clinical significance because it is a fundamental measure of renal function.
In cases of severe renal impairment, creatinine clearance increases, since active secretion of creatinine releases a larger fraction.
Ketone acids, cimetidine and trimethoprim limit tubular secretion of creatinine and reduce the accuracy of determination of glomerular filtration, especially in severe renal failure.
Creatinine clearance can be determined in two ways: by measuring the amount of creatinine in a person’s blood and 24-hour urine. In practice, a blood test is more often used, since this study is more convenient for the patient.
If the patient has a low glomerular filtration rate, the attending physician will develop an additional examination program to determine the cause of this pathological condition. The main causes of chronic kidney disease are arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus. If they are not identified, then further examination is necessary to determine the cause of the kidney disease.
Systematic determination of creatinine clearance allows the doctor to monitor changes in the patient’s kidney function over time and adjust drug therapy depending on the data obtained.
What is the research used for?
- To assess kidney function;
- to assess the dynamics of renal diseases;
- to assess renal function in patients taking nephrotoxic drugs;
- to detect severe dehydration.
When is the study scheduled?
- If a patient has pain in the kidney area, swelling around the eyes and ankles, hypertension, low urine output or problems with urination, dark urine, blood in the urine, Alport syndrome, amyloidosis, chronic renal failure, Cushing's syndrome, dermatomyositis, diabetes diabetes, intoxication with cardiac glycosides, generalized attacks of tonic-clonic seizures, Goodpasture's syndrome, hemolytic uremic syndrome, hepatorenal syndrome, interstitial nephritis, lupus nephritis, malignant arterial hypertension, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, thrombocytopenic purpura, Wilms' tumor (all of the above are factors that influence kidney function).
What do the results mean?
Reference values
Rehberg's test
| Floor | Age | Reference values |
| Male | Less than 1 month | 21 – 75 µmol/l |
| 1 month - 1 year | 15 – 37 µmol/l | |
| 1-3 years | 21 – 36 µmol/l | |
| 3-5 years | 27 – 42 µmol/l | |
| 5-7 years | 28 – 52 µmol/l | |
| 7-9 years | 35 – 53 µmol/l | |
| 9-11 years | 34 – 65 µmol/l | |
| 11-13 years old | 46 – 70 µmol/l | |
| 13-15 years old | 50 – 77 µmol/l | |
| More than 15 years | 62 – 106 µmol/l | |
| Female | Less than 1 month | 21 – 75 µmol/l |
| 1 month - 1 year | 15 – 37 µmol/l | |
| 1-3 years | 21 – 36 µmol/l | |
| 3-5 years | 27 – 42 µmol/l | |
| 5-7 years | 28 – 52 µmol/l | |
| 7-9 years | 35 – 53 µmol/l | |
| 9-11 years | 34 – 65 µmol/l | |
| 11-13 years old | 46 – 70 µmol/l | |
| 13-15 years old | 50 – 77 µmol/l | |
| More than 15 years | 44 – 80 µmol/l |
- Creatinine in daily urine
| Floor | Reference values |
| Female | 5.3 – 15.9 mmol/day. |
| Male | 7.1 – 17.7 mmol/day. |
| Floor | Reference values |
| Female | 75 – 115 ml/min. |
| Male | 95 – 145 ml/min. |
- Tubular reabsorption: 95 – 99%.
- Glomerular filtration rate according to EPI: > 60 ml/min./1.73 m2.
- Glomerular filtration rate according to MDRD: > 60 ml/min./1.73 m2.
- Glomerular filtration rate (Kokkfroft-Galt): > 60 ml/min./1.73 m2.
- Glomerular filtration rate (SCHWARTZ): > 60 ml/min./1.73 m2.
Reasons for decreased creatinine clearance:
- acute renal failure,
- block of urine outflow at the level of the bladder outlet,
- congestive heart failure,
- dehydration,
- chronic renal failure,
- glomerulonephritis,
- shock,
- kidney block.
Reasons for increased creatinine clearance:
- pregnancy,
- diabetes mellitus, before the development of diabetic nephropathy;
- a large amount of protein in the diet.
What can influence the result?
- Creatinine clearance may increase with intense physical activity preceding the study.
- Some drugs reduce creatinine clearance (cimetidine, trimetaprim, procainamide, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides and quinidine).
Important Notes
- Creatinine clearance decreases with age (by 6.5 ml/min every 10 years in people over 40 years of age).
- Ketone acids, cimetidine and trimethoprim limit tubular secretion of creatinine and reduce the accuracy of determination of glomerular filtration, especially in severe renal failure.
- Complete urine collection is very important for correct test results.
Also recommended
Who orders the study?
General practitioner, therapist, nephrologist, urologist.
Literature
- Post TW, Rose BD: Assessment of renal function: plasma creatinine; BUN; and G.F.R. In UpTo Date 9.1. Edited by BD Rose. 2001
- Kasiske BL, Keane WF: Laboratory assessment of renal disease: clearance, urinalysis, and renal biopsy. In The Kidney. Sixth edition. Edited by BM Brenner. Philadelphia, WB Saunders Company, 2000, pp 1129-1170
- Landry DW, Bazari H. Approach to the patient with renal disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Cecil Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier; 2011:chap 116.
- Pagana KD, Pagana TJ (2010). Mosby's Manual of Diagnostic and Laboratory Tests, 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier.
Source: https://helix.ru/kb/item/02-011
Determination methods
The breakdown product of creatine can be measured in the blood and urine, and the indicators provide insight into the functional functioning of the excretory organs at different stages of purification. To obtain comprehensive data, a combination of diagnostic techniques is used, and to conduct a routine examination and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment for various pathological conditions, the results of one of the tests are sufficient. Calculation of creatinine clearance is carried out by establishing blood and urine parameters, as well as using the Rehberg test.
Analysis of urine
According to this method, urine is collected in a clean container throughout the day, then mixed and the portion is delivered to the laboratory to determine creatinine clearance. Urinalysis is not always convenient, but it can reflect changes at the level of renal nephrons and allows one to evaluate the filtration work of the urinary system.
Blood analysis
The formation of endogenous creatinine in muscles is accompanied by an increase in its level in the blood, which is determined using biochemical analysis. Calculation of clearance to assess the excretory function of the kidneys is carried out using a special formula or using index calculators. To obtain the results, you need to enter the creatinine level in the blood, the weight and age of the person in the specified fields.
Rehberg's test
Creatinine clearance can be calculated with a high degree of accuracy using a test that simultaneously determines parameters in urine and blood. The Reberg test is considered a reliable research method and does not require long preparation and waiting. To stimulate diuresis, you need to drink half a liter of water. The first portion of urine is drained, and during the second urination a blood sample is taken. The joint assessment helps calculate creatinine clearance.
Physiological reasons for high levels of natural metabolite
The reasons for increased creatinine in some situations are not pathology. These are conditions in which muscle mass increases:
- Intensive sports activities. Its amount may be at the highest permissible limit or higher.
- When changing your lifestyle to a more active and mobile one.
- When taking certain medications: tetracycline antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and others. As a result of biochemical reactions, creatinine is formed and penetrates into the blood.
- Eating large amounts of meat also contributes to the excessive entry of this substance into the blood.
Preparing for analysis
Blood, Urine Standard conditions: In the morning, on an empty stomach. Toilet the external genitalia. The first morning portion of urine is in the toilet, drink 200 ml of water, an hour after drinking the water, take blood into a vacutainer with a separating gel, after another hour the patient must urinate, collecting the entire portion of urine in a plastic container. Important: Be sure to indicate the volume of urine collected.
To obtain reliable data, simple rules must be followed when preparing and conducting samples to assess creatinine clearance:
- To conduct a urine test, it is necessary to eliminate coloring substances one day before, as well as reduce the consumption of salty, smoked and pickled foods.
- Urine is collected in a sterile container and delivered to the laboratory no later than 2-3 hours after the sample is taken.
- Before the blood test, excessive physical activity is excluded for 2-3 days, and fatty, sweet, and salty foods must be removed from the diet.
- For all types of studies, protein and fluid intake standards are required.
Against the background of infectious diseases, creatinine levels increase due to blood thickening and increased breakdown of creatine at high temperatures. It is better to wait for complete recovery or achieve stabilization before testing creatinine clearance.
Preventive actions
In order to avoid deviations of creatinine from the norm, doctors recommend providing the child with:
- timely treatment of colds;
- adequate physical activity;
- proper nutrition;
- regular visits to the doctor and passing the necessary tests;
- stable emotional state;
- restoration of water balance.
The kidneys are an important organ that plays a large role in the functioning of blood circulation, the development of the entire individual’s body, as well as the volume of muscle tissue. The creatinine level in children is one of the important indicators when making a diagnosis. Diseases that affect its level are quite serious and require long-term therapy.
Normal indicators and calculation formula
You can make calculations using formulas that allow you to determine the degree of functional activity of the kidneys based on creatinine clearance yourself, focusing on age standards and gender. When conducting diagnostics on different types of equipment and depending on the research methodology, the units of measurement are:
- mg/dL – creatinine weight indicator is rarely used,
- µmol/l is a generally accepted biochemical standard.
A translation between two calculation systems can be carried out using a calculator on any specialized website or using a reference book.
It is not difficult to calculate clearance using the formula; you need to substitute the data obtained from blood and urine tests.
Age is subtracted from 140 and multiplied by body weight in kilograms. The resulting figure is divided by the creatinine level in mg/dL, multiplied by 72. If the creatinine value is indicated in µmol/L, 0.8 is used instead of 72. For women, a factor of 0.85 is used to adjust the final value.
Normal clearance values for adults:
- men 70–110 mmol/min,
- women 45–95 mmol/min.
Indicators for children:
- up to one year 15–35 mmol/min,
- up to 15 years 25–75 mmol/min.
If you need to decipher test results, it is better to consult a doctor. He will not only carry out correct calculations taking into account all variable values, but will also help establish the reason for the deviation from the age norm of creatinine.
general information
By indicators such as urea and creatinine, metabolic processes occurring in the body are assessed. Creatinine and urea are the first to respond in cases of liver dysfunction, kidney disease, and muscle dystrophy. An increase in urea and creatinine above normal levels in children indicates a violation of the breakdown of substances in the individual’s body. Kidney function is directly assessed by creatinine levels. Often, deviations from the norm identified as a result of the analysis indicate renal failure. In addition, the following factors influence the outcome:
- large volume of muscle tissue;
- meat diet;
- failure of the kidneys.
Children's doctors advise taking the test several times to be sure of the result, since it is influenced by infectious and chronic diseases and fatigue. The concentration of red blood cells also affects creatinine levels. An overestimated number of red blood cells indicates an infectious process occurring in the body. In this case, treatment is primarily aimed at eliminating the infection and restoring red blood cells to normal.
Normal indicators and calculation formula
Promotion
High creatinine levels are determined in the following conditions:
- toxic effects,
- abnormalities in the functioning of the thyroid and pancreas,
- disturbances of water-salt metabolism,
- taking specific medications to gain muscle mass,
- increased physical activity and strength training before the test,
- excessive consumption of protein in food.
If an increased level of creatinine is detected, a repeat analysis is carried out in compliance with all and additional studies of the functional activity of the kidneys.
Demotion
The most common cause of decreased creatinine clearance is pregnancy and old age. These conditions are considered physiological and require correction only if there is a significant deviation from normal values. Other reasons for decreased clearance:
- loss of muscle mass due to diet, dystrophy, injury,
- liver diseases in which protein metabolism is impaired,
- vegetarianism and lack of protein in food,
- disorders in the functioning of the cardiovascular system,
- infectious, viral and autoimmune disorders,
- oncological diseases,
- hormonal disorders,
- prolonged dehydration.
After determining the exact cause of the deviation, treatment is carried out using medications and lifestyle changes.
Decreased creatinine in blood tests and its causes
Sometimes the creatinine level in the blood changes slightly or greatly. This happens for various reasons:
- When creatinine does not leave the body due to kidney damage (urolithiasis, renal failure, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, uremia), decreased blood supply to the kidneys, severe shock.
- When there is an increased level of creatinine in the blood. There are a lot of factors here - endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus), frequent irradiation of the body, excessive physical activity (weightlifting, bodybuilding, improper diet (large amount of protein consumption), abuse of sports nutrition, with an increased content of growth hormone in the body (gigantism), severe skin injuries and operations, destruction of muscle tissue (compression) due to car accidents, various infectious diseases, loss of large amounts of blood, internal ulcers and tumors, anemia.
Symptoms of elevated creatinine are fatigue, fatigue, difficulty breathing, a feeling of exhaustion, and confusion.
Treatment for increased creatinine depends on the degree of the indicator. If this does not particularly affect the general condition of the body and the indicator is within the acceptable norm, doctors recommend a special diet, reduced physical activity, increased consumption of clean drinking water, diuretics, antioxidants to remove waste and toxins, and normalization of sleep.
A low creatinine level is also a pathology and has a negative effect on the body. Its causes are as follows: low muscle mass, severe muscle injuries, a diet with low protein intake, cirrhosis of the liver, pregnancy, amputation of limbs, long-term treatment with allergy medications, a vegetarian diet, blockage of the urinary tract.
In this case, you cannot independently prepare a diet based on diets and hunger strikes, and reduce sports activities to a minimum. Taking medications under the supervision of a doctor.
An increase, as well as a decrease, in the level of creatinine in the blood has quite serious consequences if you do not pay attention. Therefore, try to check with your doctor during blood tests to see if there are any abnormalities.