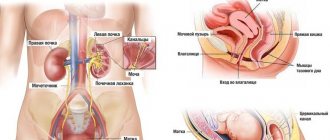
Disorders of the urination process are also called dysuria in medicine. This disease is said to occur when a person has difficulty accumulating urine in the bladder, and also has problems with its excretion. Difficulty urinating in women occurs against the background of various gynecological diseases in almost 35% of cases. The disorder may also be associated with pathologies of the kidneys and ureters. Regardless of what caused the problem, this is an alarming signal that should make you think about your health. Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help avoid serious complications.
Physiological and pathological factors
Any reasons that provoke problems with urination in women can be divided into two broad subgroups: physiological, that is, resulting from natural causes, and pathological.
Among the first are aspects such as:
- Gestational period. Due to hormonal imbalances, as well as significant pressure on the organs of the excretory system, difficulty urinating in women is more often observed during pregnancy. As a rule, after the onset of childbirth, a problem of this kind disappears by itself and does not bother the woman. Typical symptoms that worry the expectant mother at this stage are weak urine pressure, slow release of fluid, and a constant urge to go to the toilet.
- General hypothermia of the body. Sluggish urination in this case is a completely natural physiological reaction of the body, expressed in the appearance of spasms, to exposure to low temperatures.
- Drinking small amounts of alcohol or medications with psychotropic properties. The action of these substances also leads to the appearance of reflex spasms.
Pathological causes
It should be noted that physiological reasons provoke the development of difficulty urinating in women without pain. As for pathological factors, the list of such factors is much more extensive:
- A weak stream during urination, associated with a burning sensation, discomfort, pain, may be the result of urolithiasis. As a rule, such a problem is the result of blockage of the canals with sand or large stones.
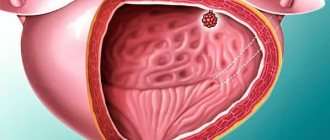
- Diseases of the reproductive system in the acute stage: fibroids, endometriosis.
- The inability to go to the toilet on time, which provokes stretching of the bladder tissue.
- The appearance of malignant or benign neoplasms in the area of the bladder itself or in the urethra.
- Inflammatory diseases resulting from damage to the body by viral or bacterial microflora.
Also, the occurrence of problems with urination in women can be the result of the negative influence of external factors, which include mainly mechanical injuries and other types of damage. For example, a weak stream of urine and painful sensations may be the result of a blow or bruise with subsequent tissue swelling.
Important! The causes and treatment of dysuria or disruption of urine outflow processes are inextricably linked. To select the optimal therapeutic tactics, it is important to identify the factors contributing to the occurrence of problems and take measures to eliminate them.
Establishing diagnosis
With such a phenomenon as dysuria in women, treatment of the underlying disease is necessary. This is the only way to cope with an unpleasant symptom. Difficulty emptying the bladder in itself is not a separate disease, so examinations and a correct diagnosis are necessary.
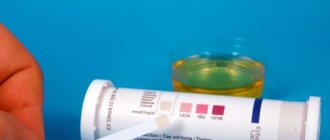
Laboratory diagnostics play an important role:
- general urine analysis;
- urine according to Zimnitsky;
- Reberg's test;
- blood test (general and biochemistry);
- urethral smear.
A general analysis can reveal signs of infection and inflammation: bacteriuria, pus and mucus in the urine. According to Zimnitsky, the degree of impairment of the excretory function of the kidneys is determined: the amount of urine, its share of the total amount drunk is assessed, and the predominance of daytime diuresis over nighttime or the opposite phenomenon is diagnosed. The Rehberg test allows you to find out the state of the renal parenchyma (assess the processes of reabsorption and filtration of the tubules) by endogenous creatinine in the blood and urine.
A blood test visualizes the inflammatory process by increasing ESR and leukocytes. A biochemical study will tell you in detail about the functioning of the kidneys (the amount of nitrogen compounds, protein). Urine culture and urethral smear with biomaterial inoculation on nutrient media reveals the type of infection and also helps to choose the right antibacterial therapy.
The indicated methods of differential diagnosis, when urination is difficult, complement instrumental methods:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, abdominal cavity, pelvis;
- contrast urography.
By combining their data with the conclusions of laboratory tests, you can get a holistic picture of the disease. The listed methods make it possible to accurately assess the processes of impaired filtration and reabsorption of urine by the kidneys, its excretion, and also show places of narrowing, compression by a stone or tumor, and stricture. If difficulties arise, the doctor may recommend a CT or MRI to clarify the diagnosis.
Clinical manifestations
Regardless of the etiological factors, stranguria or disturbance of urination processes in women has certain symptoms that become more pronounced as the pathology progresses. These include:
- Patients note splashing of urine in separate drops.
- The duration of the act of urination increases significantly, while the urine flows in a thin, intermittent stream, and there is no pressure of the discharged liquid.
- The outflow of urine is accompanied by the appearance of pain, burning, itching or other unpleasant sensations, which can also spread to the lower abdomen.
- If the difficulty in urinating was caused by inflammatory diseases, symptoms that are characteristic of the underlying disease that caused complications of this kind are observed. For example, the appearance of blood or pus in the urine, pain, deterioration in general health.
- For the first portions of urine to appear in women at the beginning of intercourse, it is necessary to tense the muscles of the lower abdomen.
- After visiting the toilet, the patient complains of a lack of feeling of emptying the bladder.
- The woman experiences an increased desire to urinate.
- There may be a slight, but noticeable to an outsider, increase in the volume of the lower abdomen. At the same time, the patient’s weight remains within the usual range.
Urinary retention problem
Difficulty urinating most often in men. Poor urination is caused by:
- the patient is forced to strain hard to get urine out of the urethra;
- there is pain when urinating, constant discomfort, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- The urine stream is weak, it may split, and urine may be released in drops.
In addition to inflammation of the prostate, obstruction of outflow can cause an increase in the size of the gland due to hypertrophy and adenoma. It mechanically blocks the urinary canal, squeezing the urethra.
The causes of urethritis and cystitis can be:
- irritation from chemicals (products for treating catheters, cystoscopes);
- diabetes;
- bladder stones;
- complications of traumatic injury;
- prostate cancer;
- damage to nervous regulation due to strokes, head and spinal cord injuries;
- unprotected casual sexual relationships;
- congestion in the pelvis due to circulatory failure.
Prostatitis develops more often in men who have previously had sexually transmitted infections
The initial symptoms of prostatitis are:
- general weakness;
- impaired erection;
- weakening urine stream in the morning.
Specific male diseases that contribute to urinary retention are inflammation:
- testicles (orchitis);
- foreskin and glans penis (balanitis, balanoposthitis);
- epididymis (epididymitis).
Diagnostics
To identify the causes of difficulties with urine separation, various diagnostic options are used. Among the first tests that are recommended for the patient to undergo as soon as possible are urine and blood tests performed in a laboratory. The use of these techniques will help to identify the presence or absence of inflammatory processes and infections in the body.
To diagnose the consequences of previously received mechanical injuries, incorrectly performed surgical interventions, as well as if there is a suspicion of the growth of malignant or benign tumors, additional instrumental methods are required. The most commonly used methods are ultrasound, radiography,
What problems will we talk about?
Urinary disorders can be divided into:
- frequent urges of an imperative nature (which cannot be restrained by willpower), in the worst case – urinary incontinence;
- pain during urination;
- difficulty excreting urine up to acute retention.
The formation of problems may be based on functional or age-related changes. This is more common in children. In adults, impaired urination is more often associated with diseases, physical and emotional trauma.
You can read about each type of disorder in separate articles in more detail. We will examine the origin of the mechanism of loss of control and the possibility of its restoration.
Treatment methods
If a woman experiences difficulties with the free outflow of urine, treatment should be carried out immediately, since there is a high probability of progression of the existing disease, which directly provokes a violation of urine flow. The choice of a therapeutic regimen is made after a full diagnosis.
So how to treat stranguria? As a rule, the patient is first prescribed drug therapy, which can be supplemented with diet and folk remedies. In the absence of positive dynamics, as well as against the background of the development of complications, it is possible to use surgical manipulations aimed at restoring the physiological functions of the organs of the excretory system. Surgery is a necessary measure if difficulty urinating is caused by a reason such as blockage of the excretory ducts with stones or the development of tumor-like neoplasms.
Medication
Drug therapy used to normalize the outflow of urine is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease and clinical signs that bother the patient:
- If the cause of problems with the free outflow of urine is the formation of stones or sand in the organs of the excretory system, it is necessary to take medications that promote their destruction and subsequent removal naturally. The following types of medications are especially often used: Canephron, Enatin, Cyston. These drugs have an identical dosage regimen. To obtain a therapeutic effect, it is recommended to take two tablets of the selected product three times a day.
- If a bacterial or viral infection occurs, a woman may be prescribed antibiotics, such as Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin.
- If the patient is bothered by unpleasant sensations during the act of urination, pain, burning and itching, then the use of medications is required, the main task of which is to eliminate symptomatic manifestations. Drugs in this group include No-Shpu, Papaverine, Buscopan.
- To stimulate the outflow of urine, which, for example, is necessary when stones form in the organs of the excretory system, it is necessary to take medications that have diuretic properties. More often, products are used that are based on components of plant origin, for example, licorice root or corn silk.
Is there a way to prevent urinary problems?
By taking preventive actions you can prevent not only your own illnesses, but also the suffering of your children.
- To prevent incontinence and the correct formation of the baby’s personality, expectant mothers should take a responsible approach to bearing the fetus, their regimen, and nutrition.
- At a young age, it is necessary to dress according to the weather, avoid hypothermia of the legs and pelvis.
- Sex education requires the responsibility of adults and experienced people for introducing adolescents to contraceptives and sexual hygiene.
- You cannot take any medications, dietary supplements, or succumb to advertising tricks on your own.
- General strengthening of the immune system and playing sports allows you to avoid age-related problems.
Urinary problems should not be left untreated. The process quickly enters the neglected stage. This disease is difficult to treat and takes a long time, and the possibilities of successful surgery are significantly reduced. Therefore, it is better to consult a doctor if initial signs are detected.