What are the reasons for the violation of the integrity of the urea
Often, an injury received by a person can provoke an organ rupture. If the bladder is empty, then damage is caused by a strong blow or a penetrating wound. If the bladder contained a sufficiently large amount of urine, then even a minor blow can cause harm.
Damage to the organ occurs due to a sharp and strong impact in the lower part of the abdominal cavity. Due to intra-abdominal trauma or fracture of the pelvic bones, there is a high risk of organ damage from bone fragments.
The following factors can cause a bubble to burst:
- falling from height;
- Road accident. The situation is especially dangerous when the victim is a pedestrian with a full bladder;
- abdominal injury received during sports, street fights, or at work.
The opinion that the bladder can rupture if the process of urination is not carried out for a long time is erroneous. When the amount of urine contained in the bladder approaches its maximum, urine begins to rise back to the kidneys. Because of this, after a short time, intoxication of the body and loss of consciousness occurs, which contributes to the involuntary process of urination and a decrease in pressure on the walls of the bladder.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=JtGZLgXnz_s
Reasons for the breakup
Violation of the integrity of the bladder due to its overflow occurs quite rarely. This will require several years of constant overcrowding and delays, as well as the presence of comorbidities. In this case, the walls become overstretched and can tear, but even here some mechanical action from the outside is required. In addition, most bladder diseases, such as chronic cystitis, on the contrary, contribute to thickening of the walls. Factors that most often lead to rupture should be considered:
- The most common cause of a burst bladder is a single-stage impact directly on the site of its projection. This could be a kick, a fall from a height, a gunshot or knife wound. You should not think that in this case the organ bursts like a balloon. Its integrity is simply violated and the contents leak out.
- The bladder can burst in an accident. In this case, prolonged compression of the abdominal organs occurs. The rupture occurs due to tissue decomposition. Often in accidents, fractures of the pelvic bones occur and fragments can damage the organ.
- Tumors of the urethra and bladder. Violation of integrity occurs in a benign process due to an increase in tumor volume, and in a malignant process - as a result of the development of wall necrosis and cell death.
- During the operation. If surgery is performed on neighboring organs (rectum, uterus, etc.), then accidental damage is possible.
Bladder burst: symptoms
Violation of the integrity of the walls of the bladder is an extremely dangerous phenomenon for human health. To avoid the development of severe complications and intoxication of the body, urgent hospitalization of the patient and surgical intervention are required to restore the damaged walls of the bladder. Self-healing of a rupture is possible only in the case of microdamage to the bladder, as well as in the presence of proper drug treatment with mandatory physiotherapy.
Bladder damage can be recognized by the following signs:
- Inability to independently carry out the process of urination.
- Frequent urge to urinate.
- No urge to urinate.
- Lower abdominal pain. The pain can be completely different: dull, sharp, weak or strong. Painful sensations are localized in the lower abdomen and often radiate to the lower back, kidneys or other organs.
- Increase in body temperature.
- Traces of blood in urine.
A sure sign of a violation of the integrity of the bladder walls is the appearance of swelling in the lower abdominal cavity or perineum. If you have any of the above symptoms, it is important to call an ambulance as soon as possible. Symptoms of the disease may also differ depending on the type of injury a person has. The table below provides a detailed description of the patient's condition when receiving two types of injury.
Typically, there is one type of rupture, but in rare cases a combination of these two different types is possible. This type of injury occurs when bones are broken. The patient's condition may be complicated by low blood pressure, pale skin and tachycardia.
What will happen and what are the consequences if a person’s bladder bursts?
Sometimes the symptoms of bladder rupture are not too intense. However, even mild symptoms should alert a person and prompt them to seek medical help. Injury to the lower abdomen of a person and rupture of the bladder can provoke a deterioration in health, as well as a number of irreversible changes in the urinary, reproductive and other systems.
Bleeding
If bleeding is severe, the patient may go into shock. He falls into an unconscious state, his pulse is rapid, his blood pressure is below normal. If emergency assistance is not provided to the patient in the near future, death is possible.
Purulent formations
Due to inflammatory processes, purulent formations form along the perimeter of damaged tissues. If treatment is not started in time, this condition will lead to blood poisoning and serious consequences. Without treatment and medical intervention, death is possible.
The disease is one of the most severe complications of urinary rupture. It can be recognized by a number of characteristic signs, among which the most common are pain in the abdomen, constant muscle tension of the anterior abdominal wall, nausea and vomiting, absence of stool for a long time and hyperthermia.
The patient's condition will continue to deteriorate until, due to inflammation, poisoning of the body begins, as well as a malfunction of various organs and systems.
Osteomyelitis
The impetus for the development of the disease can be an injury received by a person. With osteomyelitis, a purulent-necrotic process develops, which affects the bones, bone marrow, and nearby soft tissues. Surgery and antibiotic treatment are required.
To avoid these complications, the patient is carefully examined to detect hidden damage and begin therapy in a timely manner. In this case, it can be ensured that the patient will recover quickly and be able to return to his normal daily routine.
How is the disease diagnosed and treated?
During the examination of the patient, the specialist makes a diagnosis based on the symptoms present, as well as the results of laboratory tests, which are carried out urgently. Insertion of the catheter will reveal the presence of a very small amount of urine with traces of blood. Cystography is considered the most informative method for diagnosing the problem. This method involves the use of contrast. A special illuminating substance is injected into the urinary system. Next, the specialist observes the dynamics of the advancement of the injected substance. If it was discovered that at the stage of contrast entering the bladder, the substance leaked out of the bladder, we can conclude that there was a violation of the integrity of the walls of the organ.
Depending on the severity and complexity of the injuries received by a person, appropriate treatment is prescribed. If there has been extra-abdominal damage, then during surgery the damaged tissue is sutured without involving the bladder mucosa in the process. If the resulting damage turns out to be minimal, treatment is prescribed with antibacterial drugs, drugs whose action is aimed at eliminating signs of intoxication of the body, as well as therapy with the use of hemostatic drugs. Conservative treatment begins only after the bladder has been completely emptied. To do this, the patient is given a catheter, which will remove from the organ all blood clots and urine residues present there.
Penetrating injuries also require immediate catheterization, as well as surgery to restore the integrity of the bladder and repair damage to adjacent organs. When the operation is completed, the catheter is left in place for some more time. If treatment is successful, it is removed after two weeks, when the bladder is already able to function independently and perform the tasks assigned to it. In parallel, antibiotic therapy is carried out to prevent the development of inflammation.
Can a person's bladder burst? It will not be possible to consciously hold back urination until the organ is overstretched and injured. The bladder is able to withstand severe loads and not burst from overflow in the absence of mechanical obstacles to the drainage of urine. External physical influences on the abdominal wall are dangerous.
When filled, the bladder stretches, the walls become thinner, it begins to protrude beyond the boundaries of the bone and becomes vulnerable to external influences. Especially if it's filled with urine. A blow to the stomach or a fall from a height can cause the bladder to burst. Empty, on the contrary, is elastic and is not injured by shaking.
Let's consider what happens if the bladder bursts, for what reasons this happens, what symptoms will help recognize a dangerous condition.
Treatment
After receiving data from the laboratory, the doctor will be able to judge the severity of the disease and select appropriate treatment, which often requires surgery. However, with minor damage to the bladder and provided that the urine contained in it has not entered the peritoneum, there is a high probability that the rupture will heal on its own, thereby restoring its integrity.
In such cases, to prevent the damaged area from stretching and urine leaking out of it, a catheter is installed in the patient until he or she recovers completely.
A timely diagnosis of bladder rupture will help avoid serious consequences and complications.
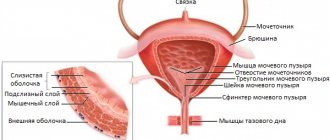
The bladder is represented by an unpaired muscular organ, which is located in the pelvis and performs only two functions: the accumulation of urine and its periodic excretion from the body through the urethra. At the entrance and exit of the bladder there are sphincters that regulate the passage of urine from the ureter to the bladder and from it to the urethra.
Even when the organ is full, the sphincters are closed. Their activity is regulated by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, but with age this function weakens and it becomes difficult to hold back large amounts of urine. And in older people (especially those with diseases of the nervous system), urination occurs involuntarily.
The walls of the organ are also abundantly supplied with nerve endings, so when it enlarges, the muscle layer is stretched, and information is sent to the brain that it is time to empty. We feel this in the form of heaviness in the lower abdomen and tension in the external urethral sphincter. There is a feeling as if the bladder is bursting.
Types of injuries
Bladder injuries are divided into open (as a result of wounds, road accidents), closed (internal) and bruises. Internal complete bladder rupture is classified into 2 types:
- extraperitoneal (accompanied by heavy bleeding, the lower part of the organ is damaged, urine pours into adjacent tissues);
- intraperitoneal (occurs more often when the organ is full, characterized by minor bleeding, the upper part of the bladder bursts, urine pours into the abdominal cavity, flooding the internal organs);
With fractures of the pelvic bones, the gap can be mixed. With closed injuries, the process begins with the inner layer, then affects the muscles and, in extreme cases, the peritoneum.
Warning signs
If a bladder rupture occurs, the symptoms are very characteristic and impossible for a conscious person to ignore:
- pain in the area below the navel, above the pubis;
- severe swelling in the groin;
- feverish state accompanied by chills, deterioration of general health;
- acute urinary retention (AUR) and ineffective urge; if urine is excreted, it is with blood;
- sometimes the pain goes to the lumbar region.
For doctors, an important diagnostic step is the insertion of a soft catheter. There will be almost no urine, despite the patient's prolonged absence of urination. Or the fluid is much larger than the capacity of the bladder and is a mixture of urine, blood and exudate.
Next, laboratory tests of biological fluids, hardware, ultrasound, computer, and X-ray contrast diagnostic methods are used.
A characteristic symptom confirming an intraperitoneal rupture of the bladder will be acute pain when pressing on the anterior abdominal wall, if the hand is quickly removed.
Acute urinary retention
This is an unpredictable condition in which it is impossible to empty the bladder on your own due to frequent urges to do so (difference from anuria).
- disruption of nerve impulses;
- mechanical blockage of the urethra;
- injuries of the urinary organs;
- psychogenic urinary retention;
- poisoning with chemicals and medications.
The doctor will conduct a differential diagnosis to exclude conditions that caused acute urinary retention that are not associated with bladder rupture. In men, urinary retention develops as a result of prostate adenoma and cancer, constipation, bladder tamponade, narrowing of the lumen of the urethra, neurological and infectious diseases, and stones.
In women, the causes of acute urinary retention can also be pregnancy, oncology, and diabetes mellitus.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to use laboratory diagnostic methods, which include:
- cystoscopy – examination of the bladder cavity through a special optical device;
- Cystography is an x-ray using a contrast agent.
With their help, it will be possible to obtain information about the location and size of the gap.
Due to its structure, a foley catheter can be installed in a patient for a long period of time
Consequences of injuries
If a ruptured bladder is left untreated, the consequences are the same for men and women.
- In case of intraperitoneal injury to an organ, the leaked urine is partially adsorbed, causing irritation of internal organs, non-infectious inflammation and peritonitis (urinary) in the future.
- With an extraperitoneal complete rupture, blood and urine permeate the nearby tissue to form a urohematoma. Next, the urine breaks down, salt crystals fall out, and purulent inflammation (phlegmon) of the pelvic and retroperitoneal tissues develops. The process spreads to the entire wall of the organ with the transition to necrotizing cystitis.
If measures are not immediately taken to hospitalize the victim when the bladder bursts, the consequences will be irreversible, including death.
The process will involve the blood vessels of the pelvis with the formation of blood clots, blockage of the lung artery, infarction of its tissues, and pneumonia. Purulent pyelonephritis will develop in the pelvis, turning into acute renal failure.
Very rarely, the inflammatory process with minor ruptures leads to a slowdown in the development of the purulent-inflammatory process with the formation of ulcers in the tissue.
Treatment of complete closed injuries is only surgical. If the bladder bursts slightly or a bruise occurs, urine does not flow beyond its boundaries. Layer-by-layer hemorrhages are formed with deformation of the outlines of the organ.
Without treatment, an incomplete rupture resolves without a trace, or leads to tissue inflammation, necrosis and the transition of the process to the stage of complete rupture with the release of urine and further, as described above. An incomplete rupture can occur from the outside when the wall of the bladder is injured by bone fragments.
A bruise with an incomplete rupture is treated conservatively. Strict bed rest must be observed, medications are prescribed to eliminate inflammation, stop bleeding, antibiotics, and analgesics. To prevent the development of a two-stage rupture and independent scarring of the bladder wall, a catheter with permanent urine drainage is installed for 7-10 days.
Internal incomplete rupture with venous bleeding stops. When the arteries rupture, the blood does not clot and tamponade develops.
Hemorrhages
Bladder tamponade, what is it? This is a state of AUR (complete cessation of its excretion) due to the filling of the urinary cavity with clots of coagulated blood. The causes of hemorrhage are various: diseases of the kidneys and urinary tract, trauma, tumors, prostate adenoma, rupture of its capsule, bleeding from varicose veins of internal organs.
Each new portion of blood increases the number of clots. Bladder tamponade is characterized by a painful and unsuccessful urge to urinate, increasing pain when pressing on the suprapubic area, and patient nervousness. If you manage to get portions of urine, they are mixed with blood.
Despite the fact that the bladder capacity in men is 250-300 ml, blood loss during tamponade is much greater, which is manifested by obvious anemia (pallor of the skin, rapid heartbeat, increased blood pressure, dizziness).
By introducing a catheter it is possible to partially alleviate the patient’s condition, but the lumen of the tube also becomes clogged with clots. It is not possible to completely empty the bladder. If an attempt to wash away blood clots is unsuccessful, treatment for tamponade is surgery.
If, as a result of an abdominal injury, the victim exhibits characteristic symptoms (the bladder has burst, or the pelvic bones are fractured), it is necessary to urgently call an emergency team, and the victim should put an ice pack on the stomach.
Bladder rupture is not a common occurrence. The organ is very elastic and can accumulate urine for a long time, “bothering” a person only with an active urge to urinate. But in an overcrowded state, the bubble becomes vulnerable: this is facilitated by the thinning of the stretched walls. As a result, any mechanical impact can provoke a rupture. What are the signs that indicate your bladder has burst? What to do in this case?
Prevention
Rupture of a hollow organ, such as the bladder, is a serious injury, in some cases capable of leading to death. Do not ignore medical attention if you notice signs of this injury. The leakage of urine outside the organ causes severe complications - peritonitis, phlegmon of the peri-vesical space.
Surgery should be performed as quickly as possible to repair the rupture. Preventive measures for this condition are avoidance of traumatic situations, compliance with safety precautions, timely treatment of infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, and regular urination.
This phenomenon is quite rare, however, it is no exception. The structure of the organ is elastic; it can stretch when filled with urine, but spontaneous rupture cannot occur, for example, with prolonged abstinence from going to the toilet.
However, when exposed to external influence, a violation of integrity is quite likely, because in an overfilled state, the bladder becomes vulnerable and can burst. How to understand that this happened and what measures need to be taken is described in this article and in a video specially selected on this topic.
Below we will talk about how to understand that the bladder has burst. Clinical signs are not always specific and clear, so the victim may misinterpret the signs that appear.
You need to pay attention to the following:
- discomfort or pain in the navel area or below, sensations vary - from mild, aching to stabbing and sharp;
- in rare cases, severe pain in the back or lower back;
- the appearance of swelling or edema in the pubic area;
- temperature;
- possible development of fever;
- urinary dysfunction consists of frequent urges, during which the patient cannot urinate or they are absent altogether;
Important. The bladder cannot burst without a reason. Even with prolonged and strong-willed suppression of the urge to urinate, this is impossible. In extreme cases, uncontrolled urine leakage will occur. Human physiology is designed in such a way that he cannot endure for so long that it would provoke a violation of the integrity of the membranes of the bladder.
If there is physical impact on the organ, it may burst. The more urine there is, and therefore internal pressure, the higher the likelihood of injury.
The thing is that as it fills, the walls stretch and become thinner, which increases the vulnerability of its walls. In this case, the bladder extends beyond its normal location, so the protective functions of the pelvic bone tissue are leveled and the organ will be less protected.
In this case, the danger is:
- blows or jolts to the middle or lower abdomen;
- external pressure, for example, in a crowded vehicle, when diving to depth and any other;
- a fall;
- perforation in the late stages of bladder cancer, when the tumor destroys its walls (in this case, palliative surgery is indicated).
Simply put, any traumatic impact on an overfilled bladder can lead to a violation of its integrity. This may be minor physical pressure or serious injuries, such as injuries from a car accident caused by a gun or a knife.
In any case, only a doctor can help the victim, because self-medication can be very dangerous. The cost of neglect and carelessness towards one's health can be too high, for example, the patient can die from peritonitis.
How do you know if your bladder has burst?
Symptoms of a ruptured bladder appear very clearly, and it is unlikely that the patient will be able to remain in the illusion that everything is in order with the body. The main signs of a burst organ include:
- Pain in the lower abdomen (under the navel and near the pubis). Its character can be different - from mild aching to acute.
- A bulge or swelling localized in the groin or above the pubis.
- Increased temperature, fever, chills, general discomfort.
- Hematuria is the appearance of blood in urine.
- Problems with urination - the urge is felt, but urine is not excreted from the body. In some cases, the desire to urinate does not arise at all.
- Sometimes there is severe back pain.
One thing to understand about the bladder is that it does not burst without a reason. Even enduring the urge for a long time will not become a reason for rupture: the organ is designed for serious “load”; in the worst case, the person will simply wet himself.
It's another matter if the filled bubble has been subjected to mechanical stress. Since, due to accumulated urine, the walls of the organ are tense, and its size is increased compared to the norm, the “urea” slightly protrudes beyond the area of its usual location and loses the protection of the pelvic bones. In this state it is extremely dangerous:
- a fall;
- shaking in transport;
- a push to the stomach.
Each of these “events” can be a decisive factor that leads to a breakup. We should not forget about more obvious injuries - gunshot or knife wounds, as well as injuries received as a result of an accident.
If the symptoms described above occur after an event that is “stressful” in terms of a full bladder, then you should urgently consult a doctor. In this case, there is no way to do without the help of a specialist.
Preventive actions
The main prevention of bladder rupture is to empty it in a timely manner. This prevents its walls from stretching and thinning and makes it more resistant to damage. It is also useful to exclude from the diet excessively salty, fried, smoked and other unhealthy foods.
Take care of yourself, take care of yourself and be healthy.
Can your bladder burst? Few of those who are in normal health ask this question seriously. Most likely for the sake of winning an argument or a healthy sense of curiosity.
Even a person who unbearably wants to relieve himself is unlikely to start asking Google and Yandex whether the bladder can burst. Most likely he will try to think about it as little as possible.
But there are other categories of people, those who are interested and concerned about this issue quite seriously. For the most part, these are very shy and squeamish people, for whom even the thought of relieving their natural needs in a public toilet is unbearable. Especially for such people, we decided to answer this question - can the bladder burst?
Burst bladder: types of injuries and their symptoms
The signs of a bladder rupture can be detailed: each type of injury has slightly different symptoms.
Among all types of bladder injuries (including simple bruises), approximately 40% of injuries occur due to intraperitoneal rupture. It is typical for cases when the organ was either empty or poorly filled.
With intraperitoneal damage, everything is somewhat different: only a full bladder bursts, the upper part of which touches the wall of the abdominal cavity. Since urine splashes towards other organs, it is likely that they will become inflamed.
A combination of two types of ruptures is very rarely observed. Typically, such an injury is accompanied by bone fractures, and tachycardia, low blood pressure, pale skin, and cold sweat are added to the symptoms.
Bladder burst: how to treat it
Therapy is possible only under the supervision of a doctor. First, a diagnosis is carried out. Bladder rupture is confirmed after testing, including:
- Urine and blood tests.
- Ultrasound of the bladder, which determines the presence of blood and clots near the organ and directly in it.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, performed to identify disturbances in the outflow of urine.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, necessary to assess the condition of the internal organs, namely the presence of blood in the abdomen.
- Retrograde cystography. Needed to find out what type of damage you are dealing with. The condition of the pelvic bones is also assessed. During the examination, a special substance is injected into the patient’s bladder through the urethra, visible on x-rays.
- Intravenous urography. Designed to assess the complexity of the injury and its location. An X-ray-positive drug is injected into a vein, and after a few minutes it is excreted by the kidneys. During this time period, several images are taken, which serve as the basis for making a diagnosis.
- MRI. The procedure is focused on layer-by-layer examination of the bladder, thereby achieving high accuracy in studying the affected area. Additionally, the condition of neighboring organs is determined.
- CT. Used to obtain a 3D image of the bladder. Computed tomography, like other studies, allows you to assess the condition of the organ - the location of the damage, the volume of blood and urine.
The greatest danger is intraperitoneal rupture. In this case, surgical intervention is indicated. The peritoneum is cut, and the doctor sutures the damaged walls of the organ. After the operation, the patient is given a catheter for several days, which promotes tissue restoration. With an extraperitoneal type of injury, there is a chance to get by with conservative treatment, which involves bed rest, taking medications (antibiotics, hemostatic and anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers). It is also necessary to install a catheter to ensure a constant flow of urine and allow the wound to heal on its own. If conservative therapy does not work, surgery is performed.
After completion of treatment, the patient has to recover for quite a long time. First of all, you need to normalize the intestinal microflora, improve the functioning of the liver and kidneys, not to mention the bladder itself. A strict diet without smoked, fatty and salty foods is indicated. Alcohol and cigarettes are prohibited. Active sports activities and overheating/hypothermia are not recommended.
A burst bladder can cause severe bleeding, which can be fatal. There are known cases of osteomyelitis and peritonitis resulting from trauma. Therefore, if you suspect a rupture, you should immediately go to the hospital. The countdown often goes by minutes.
Happy is the one who has never had to rush around looking for a toilet. A full bladder makes itself felt at the most inopportune moment, and after the long-awaited relief, the thought creeps in: what if it burst? Can this happen and under what circumstances?
Treatment
If signs of a ruptured bladder appear, the victim must be urgently taken to the nearest medical facility. It is better if an ambulance does this, but if it is not possible to call doctors, you need to transport the person yourself.
There is practically no way for a non-specialist to alleviate the condition of the victim. To reduce pain, you need to lay the person on his side and bend his knees. This reduces tension in the abdominal wall muscles. It is permissible to give a tableted painkiller.
If there is an open wound, you need to apply a bandage, if possible sterile. You should also try to stop the bleeding by applying pressure to the wound.
To determine treatment tactics, the doctor examines the victim and identifies the type of organ damage. Table. Types of therapeutic tactics for various bladder injuries.
| Type of damage | Treatment methods |
| Non-penetrating single | Conservative tactics are preferable: Bed rest for at least a week; catheterization of the bladder for a period of 7-8 days; use of antibacterial drugs, analgesics and hemostatics |
| Intraperitoneal closed | Surgery required. To do this, a laparotomy is performed - a dissection of the anterior abdominal wall. The doctor examines the internal organs and assesses the degree of damage to the bladder. The wound is sutured, the organ is drained by performing a cystostomy. The cavities are washed with an antiseptic solution |
| Extraperitoneal closed | A laparotomy is performed, the condition of the abdominal and pelvic organs is assessed. The bladder cavity is examined, the damage is sutured. A cystostomy is performed. The space around the organ is drained. |
| Open | Anti-shock measures are carried out - the administration of saline solutions intravenously, medications to maintain the functioning of the heart and lungs. Antitetanus serum must be administered. Surgical treatment consists of identifying and eliminating the source of bleeding and suturing injuries to all organs. The abdominal cavity is washed with antiseptic solutions. |
In the presence of skeletal injuries, the integrity of the bones is restored. After the operation, the person is under medical supervision for 10-14 days. Strict bed rest is prescribed until the sutures are removed. The patient is given antibiotics to prevent the development of infection. A light fortified diet is prescribed.
On the tenth day, the stitches are usually removed and, if there are no signs of complications, the person is discharged. It is recommended to limit physical activity for 12 weeks after surgery.
A little anatomy and physiology
The bladder, also called the “urethra,” is located in the small pelvis under the reliable protection of the pelvic bones. Its main function is the reception, accumulation and timely excretion of urine coming from the kidneys.
The outer lining of the bladder is made up of three layers of smooth muscle tissue that is highly stretchable, holding about 500 ml of urine.
The organ's ability to stretch has certain limits, so a natural question arises: can the bladder burst during sleep? When the bladder is full, the nerve receptors that send a signal to the brain are irritated, and the person feels the urge to urinate even in his sleep.
In a state of severe alcohol or drug intoxication, when the body loses the ability to reflexively respond to stimuli, at best, involuntary bowel movement occurs. Confusion does occur, and there is no need to worry about the integrity of the organ, but sometimes excessive pressure provokes rupture of the bladder wall. However, more often the reasons are not so prosaic and are the result of diseases of the genitourinary system or a tragic accident.
What can cause a bladder to burst?
In healthy people, the wall thickness of the empty urine reservoir is 12-15 mm. Even taking into account that when filled, muscle tissue stretches up to 2-3 mm, there is no need to worry whether the bladder may burst if you endure it for a long time: nature has provided it with elasticity and a sufficient margin of safety.
Another thing is injuries and diseases accompanied by inflammation, ulceration, decreased muscle tone and chronic urinary retention. Damage to an overfilled bladder can occur in people suffering from cystitis, atony, leukoplakia, malignant and benign bladder tumors.
In reality, organ rupture occurs infrequently and is the result of external factors:
- injury to a strained bladder when falling flat from a height or onto protruding objects;
- a strong blow to the stomach, for example during sports or in a street fight;
- damage from fragments of the pelvic bones in serious accidents;
- penetrating wounds to the abdomen: knife and gunshot wounds.
Patients who don't trust doctors worry whether their bladder could burst as a result of medical error? Surgical interventions sometimes cause damage to the bladder, in particular when the urethra is dug or forced emptying.
Like any injury, urethral rupture has its own characteristics and, according to the classification, is divided into 2 main types: intraperitoneal and extraperitoneal.
Possible complications
It is useful to know what will happen if the bladder bursts - this will prevent complications. The main consequences of injury include:
- leakage of urine into cavities and tissues - this causes purulent-inflammatory processes (peritonitis, peri-vesical phlegmon);
- general intoxication of the body - urogenic sepsis;
- purulent-necrotic cystitis;
- formation of a neurogenic bladder accompanied by urinary incontinence;
- hemorrhagic shock with the development of heavy bleeding;
- if the bladder bursts, frequent infections of the urinary system are possible in the future;
- with a concomitant pelvic fracture, the development of osteomyelitis is possible;
- formation of fistulas in the peri-vesical tissue;
- separation of part of an organ.
In some cases, you can even die from a ruptured bladder if help is not provided in a timely manner. The causes of death can be:
- inflammation of the abdominal cavity with the development of severe peritonitis;
- sepsis;
- great blood loss.
The development of complications can be prevented by correct diagnosis of injury and prompt assistance.
Intraperitoneal rupture
In this case, damage to the bladder occurs in the most vulnerable upper-posterior part. This is an extremely dangerous injury when urine from an overfilled damaged organ leaks into the peritoneal area. The victim experiences sharp pain in the abdomen, which intensifies when lying down.
Increasing persistent pain, persistence of urge when it is impossible to empty, sudden bloating of the abdomen are the main signs of urine entering the abdominal cavity, so a person with this type of injury requires emergency medical care.
What can the disease lead to?
If help is not provided in a timely manner or if it is treated incorrectly, damage to the bladder can have its own complications. The consequences of a break include:
- peritonitis when urine enters the abdominal area, as well as other organs;
- large loss of blood, in the presence of bleeding can lead to death from bladder rupture;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases, blood poisoning;
- purulent deposits that, when ruptured, form passages to the internal organs, which is dangerous due to bacteria and microorganisms.
Extraperitoneal (retroperitoneal) rupture
Can a person’s bladder burst without him feeling it? Yes, if the lower or anterior walls of the organ are slightly damaged. In this case, urine does not enter the peritoneal cavity, but fills nearby tissues.
Common signs of extraperitoneal rupture are localized pain in the lower abdomen, swelling and bluishness of the skin in the pubic area. It is worth noting that extraperitoneal rupture is often provoked by trauma to the pelvic bones. In this case, the characteristic symptoms will not go unnoticed by traumatologists.
Even if the injury seems minor and there is no cause for concern, late diagnosis of a retroperitoneal rupture can lead to serious complications. Therefore, you should not ignore any manifestations of a violation of the integrity of the bladder walls.
Classification
Depending on the intensity of the lesions and their location, rupture of the excretory organ is divided into the following types:
- Bruise - there is no violation of the integrity of the bladder, while blood is removed using a catheter.
- Extraperitoneal - observed with injuries caused by knife wounds or bone fragments, while urine does not pour into the abdominal cavity,
- Intraperitoneal - observed when an organ ruptures in a place not protected by the pelvic bones, urine accumulates in the abdominal cavity.
- Combined - receiving several injuries to the bladder leads to the accumulation of urine in the peritoneum and pelvis at the same time.
Bladder burst: main symptoms
Internal organ injuries are not universal. Their clinical manifestations depend on the severity of the injury, the person’s health status, the degree of their pain threshold and other factors. For example, can the bladder burst from excess urine in a healthy person? With a strong blow to the abdomen, the case may be classified as a combined bladder rupture.
Also, the symptoms of the pathological condition in people with similar injuries vary greatly. Some experience unbearable cutting pain in the lower abdomen, others experience dull, paroxysmal pain. In severe trauma, a state of shock may blur the clinical picture, but the following symptoms are present to varying degrees:
- difficult, painful urination, with intraperitoneal rupture anuria (lack of urine with persistent urge);
- urine turns pink (hematuria);
- tension (hypertonicity) of the abdominal muscles;
- signs of internal bleeding: a sharp decrease in pressure, tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), pallor, chills, fever.
There is no need to guess whether the bladder may burst as a result of the injury; you need to urgently send the victim to the hospital. Delay can have the most dire consequences.
What happens when the bladder bursts
In many cases, toxins entering the blood and tissues cause inflammation of the internal organs and pelvic bones. Even if the victim suffers pain and shock, there is a high probability of peritonitis and even death.
With minor damage, scarring of muscle tissue goes away on its own. However, this takes time, and in order to do without antibiotics, you need to have a very strong immune system.
Therefore, if you suspect a violation of the integrity of the bladder membrane, it is necessary to call an ambulance and alleviate the condition of the victim.
Diagnostics
Determining the symptoms of a burst bladder is made difficult by the fact that more than half of the victims go to doctors in pain and hemorrhagic shock, and it is difficult to obtain any information from them. Signs of bladder rupture at this stage are similar to acute appendicitis and intestinal obstruction.
The necessary studies to make a diagnosis are:
- objective examination;
- CT and MRI;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity and pelvis;
- cystography with contrast.
If internal bleeding is suspected, an examination is not carried out; a laparotomy is immediately performed, during which a violation of integrity is detected.
First aid methods
Before doctors arrive, the person must be placed on his back. Place an improvised cushion under your knees bent and legs spread apart: a pillow or a folded jacket. The main danger when any internal organs are damaged is a state of shock. In this case, the legs and pelvis are raised above the head.
If a penetrating injury occurs, it is important to stop the bleeding and prevent blood poisoning. To do this, the wound is treated with an antiseptic and a bandage is applied.
In case of internal injuries, cold is applied locally to the abdomen, and the victim is covered with a rug, blanket, or outer clothing.
If possible, it is better to avoid painkillers and hemostatic drugs. This way, doctors will be able to objectively assess the clinical picture and make the correct diagnosis.