Neurogenic bladder in children is a functional inability to control urge. This is caused by a disruption of nervous regulation. In this case, the bladder may behave differently and cause frequent uncontrollable or difficult urges. The possibility of infection of the urinary canals is also possible.
Most often, neurogenic bladder dysfunction in children occurs in infancy, in approximately 9-12% of children. The disease can be congenital or acquired over time, this moment depends on the causes of the disorder of the nervous system.
What does an enlarged bladder mean?
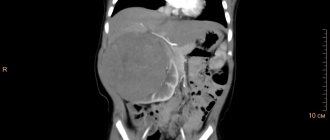
An enlarged bladder indicates diseases of the urinary system, for example, urinary retention (ischuria), hydronephrosis, and upon palpation it is mistakenly mistaken for a tumor formation in the abdominal cavity, a cyst, or intestinal volvulus.
In some cases, during ultrasound diagnostics, an enlarged bladder in the fetus is detected in a pregnant woman. If the size of the organ increases beyond 8 mm , then the doctor diagnoses megacystis . But to accurately determine the disease, the woman is offered to undergo a vesicocentesis test, in which the wall of the bladder is pierced through the placenta to examine the baby’s urine. Early detection of the disease prevents its further development.
The urinary system of the fetus is located in the lower part of the body, resembling a pear or a circle. The size increases as the child grows and by full term reaches up to 30 ml . A child has a bowel movement once every 30-40 minutes. If it is not detected or is enlarged in the baby, a repeat ultrasound is prescribed.
The bladder is formed in the fetus on days 25–27 of pregnancy, and finally at 21–22 weeks. Defects arise against the background of chromosomal abnormalities.
Why does a child develop this pathology at an early age?
The neurogenic bladder in children and its symptoms are associated with 2 functions, evacuation and reserve. Based on statistics, more than 10% of children of different ages living in the CIS countries suffer from pathology. It is very important to pay attention to the deviation in a timely manner, as it can gradually provoke the occurrence of other diseases of the genitourinary system.
It will not be possible to diagnose the pathology earlier than at the age of 3-4 years, since only starting from this period are children able to completely control urination.
Information for parents! Instilling neatness skills in a child is not enough. It is necessary to monitor the full level of development of the brain, namely the subcortical and cortical centers. They are responsible for controlling this function.
To decide how to treat a neurogenic bladder in a child, you need to familiarize yourself with the causes of the deviation. They may be as follows:
- Injury received during childbirth.
- Congenital defects.
- HIV.
- Problems with the functionality of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Hernia.
- Diabetes.
- Stroke.
- Brain injuries, as well as injuries affecting the sacral spine.
- Hernias and neoplasms of the spinal cord.
- Damage to the nervous system from the regulatory side.
- Hormonal imbalance.
If a child receives many injuries at an early age, gets a strain on the bladder muscles, and also if he has inflammatory processes in the ureters, malignant or benign tumors, this can also lead to a neurogenic bladder in the child. Treatment in this case will be difficult.
Most often, the disease affects girls, since their hormones have a different, more sensitive effect on the organ’s receptors. It is also worth paying attention to the fact that school-age children against this background cannot control their emotions, as a result they develop nervousness and depression.
What are the dangers of an enlarged bladder in a fetus?
Diseases of the urethra and bladder in the fetus are detected in rare cases, they are distinguished:
The disease exstrophy is understood as the absence or underdevelopment of the anterior wall of the bladder, which leads to defectology of the lower abdominal wall. The disease is detected due to the absence of an image on the scanogram, while the structure of the kidneys and their size do not change. The defect is diagnosed at 16-20 weeks and is treated surgically.
exstrophy
At the end of pregnancy, examination reveals ureteroceles , characterized by dilation of the ureter; the disease is accompanied by cystitis, pyelonephritis, and urethritis. The newborn is sent to a special medical facility for therapy.
Urethral atresia is called a rare disease, discovered at 14-15 weeks. The images reveal a significant size bladder in the child, which leads to an enlarged abdomen in the fetus, and the mother has no amniotic fluid.
Bladder diverticulum is characterized by thickening of the walls of the organ due to the inferiority of the muscle layer. In the image, the doctor determines a cystic formation of a round or oval shape. The defect is more common in boys. Large formations are removed promptly.
Prune-Bell syndrome combines 3 pathologies: congenital hypoplasia or insufficiency (absence) of the abdominal wall muscles, megacystis, dilatation of the ureter and prostatic urethra (abnormal phenomena) and bilateral cryptorchidism. Each category manifests itself in all patients to varying degrees, and peritoneal lesions vary.
Abnormal development of the urinary tract interferes with the normal functioning of the entire urinary system in the baby, and the disease can be fatal for the fetus.
Diagnosis of OAB in children
There are also a number of causes of urinary incontinence that are related to the child's behavior. These include the child's laughter or enthusiasm.
Overactive bladder is not age-related, although many children outgrow the condition. Most children outgrow the condition by about 7 years of age. Urinary incontinence or frequent urination in young children under 3 years of age is normal and should not be considered a problem.
If your child still has signs of an overactive bladder by the time they reach 7 years of age, they should see a doctor. Your doctor will perform a series of diagnostic tests to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. These tests may include a urine test to check for infection and an ultrasound to look for bladder problems.
Prevention
In medical practice, there are no preventive measures to prevent enlarged bladder syndrome in the fetus. Doctors advise women planning to conceive a child to fully prepare: undergo all tests, be examined by all specialists, and take a complex of vitamins. If any disease is detected, be sure to start treatment.
Pregnant women are advised to follow and comply with all doctor’s instructions in order to avoid serious complications.
In boys, during diagnostic ultrasound, a phenomenon such as a stream of turbulence into the amniotic fluid can be observed. Due to the overcrowded bladder of the fetus, it is easily mistaken for hydronephrosis, ovarian cyst, multicystic disease, or megacystis. Repeated examination provides an accurate description of the organ.
How to prevent relapse
Prevention of bladder deformation is facilitated by simple rules that can be easily incorporated into your everyday lifestyle:
- healthy eating;
- drinking up to 2 liters of fluid per day;
- emptying the bladder at the first urge;
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases;
- refusal of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- physical activity.
Moderate sports are the most important because they allow you to maintain muscle tone, and muscles are the main support that keeps the bladder in the correct position and in the required shape. If you notice the first signs of deformation, consult a specialist.
A child has a cold in the bladder, how to treat it
Treatment for cystitis is prescribed only by a doctor. Since antibiotics are used to eliminate foci of inflammation, only a specialist can calculate the dosage, as well as prescribe exactly those medications that are suitable for the child, taking into account his state of health and previous diseases. Most often, Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Co-trimoxazole, Ciprofloxacin and other drugs are prescribed to combat infection and inflammation. If necessary (in the presence of acute pain), antispasmodics are prescribed, which should also be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
To treat cystitis with folk remedies, use sitz baths with decoctions of calendula and chamomile (a tablespoon of water per liter of boiled water, leave for half an hour, add to the bath). Treatment must be combined with the ingestion of such general strengthening and anti-inflammatory drugs as rosehip decoction (4 tablespoons of fruits, fresh or dry, pour 500 mg of boiled water, leave for a quarter of an hour; give the baby half a glass four times a day), chamomile. Cranberries perform well – both fresh, frozen, and in the form of jam. Cranberry has an excellent anti-inflammatory effect, and therefore is recommended for any health problems in the baby.
You can also use coltsfoot decoction (a tablespoon of chopped herb in 2 cups of boiling water, simmer over low heat for 5 minutes; leave for 10 minutes; strain and take 1/4 cup four times a day).
Picture of baby and bladder
The drug is available in the form of white or almost white coated tablets. The tablets are round, biconvex, odorless; at the fracture, the core and film shell are visible, both layers are white or almost white. Indications for use of SPAZMEX:
- urinary incontinence, imperative urge to urinate (with idiopathic detrusor hyperreactivity; with neurogenic hyperactivity / hyperreflexia / detrusor against the background of multiple sclerosis, spinal injuries, congenital and acquired diseases of the spinal cord, strokes, parkinsonism);
— detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia against the background of intermittent catheterism;
— in the complex therapy of cystitis accompanied by imperative symptoms;
- nocturnal and daytime enuresis;
- mixed forms of urinary incontinence.
Urinary incontinence is a fairly common pathology, especially among young children, which, if not treated in time, can traumatize the child for many years. Many women in the prime of life suffer from this disease. Because of it, they cannot go out anywhere and limit themselves in literally everything, they are afraid to leave the house for a long time, and limit themselves on travel. They are literally tied to the toilet. You should always see a doctor and consult with him. After all, medicine has so many wonderful drugs in its arsenal, among which SPAZMEX is far from the last place!
The dosage regimen and duration of treatment are set individually depending on the clinical picture and severity of the disease.
The tablets should be taken before meals, without chewing, with plenty of water.
The description of the drug SPAZMEX is based on the officially approved instructions for use of the drug SPAZMEX for specialists and approved by the manufacturer for the 2010 edition.
The site was created to inform people suffering from the disease. Also on the site there is a phone number and email address of a doctor who will provide free advice on the problem (https://www.vtualetbegom.net/specialist/ or https://www.gampu.net/specialist/). You can include this link in your post.
the article does not say anything about the fact that in most cases, incontinence occurs not from a chronic infection, but from prolapse of the pelvic organs, as a result of childbirth, heavy lifting or predisposition. And it should be treated not with medications, but with special exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles or in severe cases, surgically. Kegel exercises help a lot, just don’t be lazy!
Thursday, April 07, 2011 16:13link
Prolapse does not play any role, consult a urologist. And I support exercise! You can always do without medications. Almost always.
A child has a cold in the bladder: treatment
First of all, you need to go to see a doctor. The diagnosis must be carried out by a doctor, taking into account laboratory data - only in this way can the cause and location of the problem be accurately determined, and treatment prescribed accordingly.
Laboratory testing of urine is most productive if you follow the following rules:
- urine is collected in the morning, immediately after waking up, but preferably after the morning toilet;
- the urine collection container must be pre-disinfected;
- It is advisable to transfer the collected urine to the laboratory within an hour and a half after collection, or send it to the refrigerator.
During the study, urine biochemistry is studied, an antibiogram and culture are performed. If necessary, an ultrasound examination of the bladder is also prescribed.
Parents should always remember that self-medication and refusal of medical care in case of cystitis can lead to extremely negative consequences. Treatment with unauthorized antibiotics, in turn, can reduce the effectiveness of the drugs, as well as very quickly transform the disease into a chronic form.
Types of diseases that occur in a child
There are 2 types of cystitis according to the degree of spread - primary and secondary. The primary type develops in a healthy bladder, which has not previously been subject to inflammation by infection. Secondary cystitis appears as a result of inflammation of the body, which causes the development of the disease. Often this form manifests itself after disruption of the genital organs or urinary tract.
The course of the disease is also divided into two types - acute and chronic. Acute cystitis, when developing, affects the mucous membrane of the bladder, spreading to its surface. In the presence of a chronic form, changes are observed in the muscular and submucosal layer, which disrupt the structure of the organ and its basic functions.
Depending on the type of pathology, the following names of inflammation are distinguished:
- bullous;
- necrotic;
- interstitial;
- granular;
- polyposis.
Important: today the disease occurs from improper use of medications or abuse of traditional methods of treatment. In this case, the disease is of the allergic type, which affects the mucous membrane and causes irritation of the urethra. This type of cystitis should be treated under the supervision of a doctor so as not to aggravate the course of the disease or cause complications.