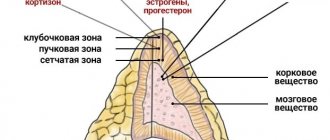
Thanks to medical experiments, it has long been reliably known that a large number of various diseases arise due to nervous overstrain. The fact is that when the human body is under constant stress and a person is always worried about something, then the surrounding information is simply not able to be perceived adequately, which leads to loss of attention and concentration. Such symptoms begin to appear due to a large amount of cortisol, and this is a hormone that responds to the function of the hippocampus. As a result, disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands begin, this is also influenced by the unregulated amount of hormones, and the hypothalamus is already responsible for this.
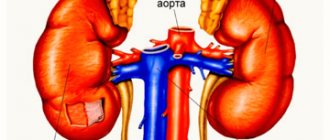
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex
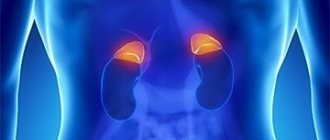
A pathology such as adrenal insufficiency begins to develop if the process of protein transport connections is disrupted. It is they who take an active part in the hormonal production of cortisol, which occurs in this area. In order for the body to grow and develop, it needs the hormones that the adrenal glands secrete. If such a process has certain disturbances, then hereditary diseases develop. Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex is sometimes called hyperplasia or adrenogenital type syndrome. Among hereditary diseases, it is one of the most dangerous; it can be triggered by various factors, including hormonal deficiency.
The disease, first of all, is characterized by the fact that the cortisol level decreases, which means the secretion of the adrenocorticotropic hormone begins to increase, as a result of which the cortex begins to become thicker. If we talk about gender, then this disease equally often affects both boys and girls. Such a congenital pathology as adrenal insufficiency is divided into six variants of the clinical form. Among them there are such options when the human body is simply deprived of the ability to function normally. And this becomes the reason that such a disease as adrenal insufficiency often becomes the cause of death of newborn children.
In the vast majority of cases, all of these forms of illness are caused by the protein effect of 21-hydroxylase. It is noteworthy that the prevalence of the disease is largely influenced by nationality.
Treatment of congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Basically, hormone replacement therapy is carried out. Doctors adjust the concentration of steroid hormones produced by the adrenal cortex and mineralocorticosteroids. Hormone therapy can also be prescribed to pregnant women if the diagnosis is made during gestation. Thanks to early diagnosis, abnormal development of the genitals in girls can be prevented. True, such treatment is still not recognized by everyone, because a pregnant woman may experience: swelling, high blood pressure, and excess weight. There is no reliable information yet about the effect of therapy on the fetus.
In addition to hormone therapy, surgical intervention can be used to eliminate the defect in the development of the genitals. Doctors recommend surgical correction as early as possible, but it all depends on the individual case, as well as on the decision of the parents.
What are the causes of the disease and its sequence
Congenital dysfunction of the adrenal cortex has a hereditary form, however, there are certain factors, the presence of which significantly increases the risk of developing the disease:
- one of the parents has a pathology;
- parents are carriers of a gene that is caused by a defect in transport type proteins.
If both parents have such a gene, then the child is at risk of getting the disease in 25 percent of cases. When the protein transport process is disrupted, there is an acute lack of cortisol, and there is also a lack of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex. As a result, adrenal insufficiency begins to develop, which is accompanied by an increase in the production of certain hormones.
If hyperplasia is observed, then male hormones called androgens begin to be produced in an enhanced mode. If there are too many of these male hormones in the human body, hyperadrogenism may develop. And this consists in modification of the genital organs, as well as too much hair begins to grow on the face and body, and in the most unexpected places.
Symptoms
Symptoms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in children are usually noticeable immediately after birth.
Most often, a child is born with increased body weight. One cannot help but notice the abnormal size of the genital organs - for example, boys have an enlarged penis, but the testicles may be too small. In girls, the clitoris is almost always large, and the labia can resemble the male scrotum in structure. As you get older, other symptoms of the disease are observed:
- Early deepening of the voice;
- Untimely appearance of hair on the genitals and body;
- Increase in body weight disproportionate with age;
- Acne on the skin in childhood;
- Cessation of skeletal formation by age 16;
- Short stature;
- Constant thirst;
- Muscle numbness;
- Decreased memory;
- Psychoses;
- Late onset of menstruation in girls.
In a child with a salt-wasting form of pathology, the clinical picture is complicated by disruptions in water-salt metabolism. This leads to vomiting, loose stools, and dehydration with all the ensuing consequences. Without treatment, this condition can cause the death of the patient.
In adults, all signs of the disease are caused by malfunctions of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, as well as, in fact, the adrenal glands. In women, CAH without treatment leads to sexual dysfunction, cycle disruptions, infertility, and the development of osteoporosis. In men, blood pressure often increases, muscle atrophy occurs, and diabetes mellitus develops. Among adults, diseases of the digestive system, urinary system, dysfunction of the immune system, hair loss, and skin diseases are widespread.
How does dysfunction manifest itself?
As for the clinical picture, everything here is directly dependent on the degree of impairment and all this has three forms:
- Salt-wasting type form.
- The form is simple virial.
- The shape is non-classical.
If we talk about the degree of prevalence, then the first place belongs to the salt-wasting form, which occurs in 75 percent of cases. It is this form that causes the blockade of the 21-hydroxylase protein. All this is accompanied by a disruption in the production of glucocorticoids. Moreover, the onset of pathology occurs even when the child is in the mother’s womb, and all the symptoms are clearly visible almost always immediately after the baby is born.
Among the primary signs the following can be noted:
- adrenal insufficiency;
- androgen excess.
If we are talking about girls, then their genitals develop like those of men:
- the clitoris becomes larger;
- the labia begin to fuse and become similar to the scrotum.
As for the internal genital organs, they do not undergo any special changes, that is, their anatomical shape remains normal, and no other signs are observed. If such a pathology is not treated in a timely manner, then girls will not have a menstrual cycle, and the hormonal sphere will not be regulated.
If all this begins to develop in boys, then their penis becomes larger, and the scrotum undergoes increased pigmentation. Here it is very important to begin the process of correcting hyperandrogenism in time, then the disease will not progress quickly. If everything is left to chance, the growth plates of the bones will begin to quickly close, and this leads to an extremely short mouth of children. Moreover, boys who are only 2-3 years old may have an unnaturally rough voice, muscles develop abnormally, and the groin area begins to become covered with hair.
When the simple virile form develops, the enzymatic activity is partially preserved, then adrenal insufficiency does not begin to actively develop, and as for the transformation of the genital organs, everything is similar to the salt-wasting form. It happens that hydroxyclase enzymes have certain deviations, usually of a minor nature. However, this can lead to the development of a post-pubertal form of the disease, which is accompanied by decreased hormonal levels, and as for the concentration of adrenocorticotropic hormone, it increases, but not much. As for infants, in such cases they do not have adrenal insufficiency or changes in the genital organs. This problem is often identified only after a woman consults a doctor due to infertility or she has menstrual dysfunction.
And often the cause is the growth of body hair, like in men. But it also happens that a genetic defect is so insignificant that a person may not know about it throughout his life.
Non-classical form of P450c21 deficiency
Clinical manifestations:
- hirsutism - 60%
- oligo- or amenorrhea - 54%
- acne - 33%
- infertility - 13%
There is no virilization of the external genitalia
Available:
- accelerated growth
- advance of bone age relative to passport age
- early closure of growth zones
- early initiation of pubic and axillary hair growth
Laboratory diagnostics:
- 17-OH-progesterone may be within normal limits (basal values of 170–300 ng/dL can be used as screening markers);
- the gold standard is a diagnostic test with 1-24 ACTH (Synacthen).
Currently in Russia a modification of this test is used with 1 mg of 1-24 ACTH (Synacthen-Depot).
The physiological level of rise in cortisol and its precursors should exceed the basal level by 2-3 times.
Test with Sinatken
- Determination of basal levels of 17-OH-progesterone.
- Administration of 0.125 mg 1-24 ACTH.
- Determination of 17-OH-progesterone after 60 minutes.
- VDKN is indicated by an increase in 17-OH-progesterone to 1500 ng/dl;
- in older patients, non-classical CAH may also be indicated by an increase of 1000-1500 ng/dL.
Test with Synacthen-Depot
- Determination of basal levels of 17-OH-progesterone.
- Administration of 1 mg 1-24 ACTH.
- Determination of 17-OH-progesterone after an hour.
- VDKN is indicated by an increase in 17-OH-progesterone more than 4-5 times (>45 nmol/l).
- A similar increase in 17-OH-progesterone and 11-DOC may indicate 11-β hydroxylase deficiency.
- An increase in DHEA-S by more than 3 times is a non-classical variant of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency. Extremely high levels of DHEA-S that do not change after stimulation - androgen-secreting adrenal tumor .
The final confirmation of the diagnosis is molecular genetic analysis.
What are the symptoms of the pathology
If a person has disorders of this kind, the following symptoms are observed:
- a person constantly feels weak, gets tired quickly, and without spending significant effort;
- problems with appetite begin, sometimes a person does not want to eat at all;
- there is pain in the abdominal area;
- the person often feels sick and vomits;
- rapid weight loss;
- the skin becomes covered with strong pigmentation, the same can happen with the mucous membrane;
- bowel function begins to be disrupted;
- the person becomes irritable and apathetic;
- often feel dizzy for no apparent reason;
- taste sensations change, as well as hearing and smell.
If you conduct a clinical examination, you can observe an increase in potassium in the blood, and nitrogen-type waste products also increase. As for the pressure, it decreases, there may be tachycardia. If we are talking about women, then they begin to experience certain irregularities in the menstrual cycle, and infertility occurs. There are cases when the symptoms of the disease have much in common with polycystic ovary syndrome, this can be found out by studying the results of a blood test. At the same time, women's genitals may have much in common with men's, but the internal genitalia remain normal. Babies nurse weakly, may become dehydrated, vomit frequently, and may have adynamia.
How can pathology be diagnosed?
Diagnostic methods may vary, however, it is very important that everything is done as early as possible. As for methods, they can be like this:
- in order to identify the development of the disease in the early stages, neonatal screening is often used, with which protein deficiency can be identified, then replacement therapy begins on time;
- it is necessary to collect anamnesis and find out whether such pathologies occur in family members, after which appropriate laboratory tests are carried out;
- if there is a salt-wasting form of the disease, then it is necessary to determine the level of aldosterone deficiency, and for this it is necessary to measure renin activity in the blood plasma;
- it is necessary to analyze the genetic type and identify a gene that damages transport type enzymes;
- In order to make the most accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to examine the ovaries using ultrasound.
Congenital pathology must be detected in time, then the disorders can be treated much more effectively.
Treatment methods and clinical recommendations
There are many ways to treat such a pathology, however, before prescribing a treatment method, it is necessary to clearly identify the causes of the disease. Most often, the patient is prescribed hormone replacement therapy, and this is for life. Thus, to a certain extent, the process of compensating for cortisol deficiency occurs, and androgen production in the adrenal glands is suppressed.
The drugs used must be dosed individually; everything here is directly dependent on how old the person is and the size of the body. If we are talking about treating adults, then they need to use prednisolone and dexamethosone. However, such drugs cannot be given to children, since they interfere with normal growth; it is best for them to be given a natural type of glucocortecoid, of which the modern market produces many. However, it is very important not to confuse it with the dosage; only a doctor can prescribe it, and he takes the test results as a basis.
If the pathology is diagnosed late, that is, the female organs are actively developing according to the male type, then a decision is often made on surgical intervention, which involves plastic surgery. If there is increased hair growth, then you need to resort to hair removal. If acne occurs, then hormonal contraceptives must be used.
What are the features during pregnancy?
If the dysfunction is post-pubertal, the following complications may occur:
- miscarriage;
- forced abortion or miscarriage;
- the fetus does not develop.
If a woman is pregnant, she may have the following symptoms:
- dehydration;
- electrolyte balance is disturbed;
- appetite worsens.
If you start taking hormonal medications in a timely manner, the woman will feel better within a month, however, this does not mean that treatment can be stopped. The fact is that disorders such as early placental abruption may occur, and the pregnancy may become overdue. You need to understand that for the adrenal cortex, childbirth and the period after it are stressful. To prevent serious complications, it is necessary to constantly monitor the hormonal levels in the blood.
Treatment
Treatment tactics in the vast majority of cases come down to taking certain hormonal drugs, which are selected based on test results. Hormone replacement therapy in young children involves taking or injecting Cortisone, while in older children and adults, corticosteroid levels are adjusted by taking Prednisone or Dexamethasone. As the required levels of hormones in the blood are achieved, the dosage of medications is reduced. Additionally, women are prescribed estrogens, men - androgens.
Timely hormonal correction in girls helps the genital organs to form correctly and prevent the problem of infertility. During pregnancy, taking hormones can be discontinued, which is decided individually in each case. With the development of arterial hypertension, treatment is carried out with special drugs in a certain dosage and combination. For children with signs of water-salt imbalance, salt intake increases.
Typically, such intervention is performed no later than one year of age. Adrenal hyperplasia of the nodular type is treated only by removal of this organ, since partial resection quickly leads to relapse. Subsequently, hormone replacement therapy is carried out until the end of life.
Preventive measures
It happens that with adrenal dysfunction, infertility is observed for 3 years or more, and treatment does not show positive results. Then there is a need for surgical intervention, however, glucocorticoids must be continued. If the disease is detected early, then most often we can talk about a favorable prognosis, but it is very important to correctly select the hormonal dose.
As for special nutrition, it is not provided here, however, if there is a lack of aldosterone hormone, then salt-type depletion may occur. And when the blood experiences a salt deficiency, you need to eat more table salt. If this is not done, the potassium level in the blood begins to increase and blood pressure decreases. Once again, it should be said that it is necessary to respond to all negative symptoms in a timely manner and seek medical help, otherwise VDKN can lead to the most negative consequences that are irreversible. Here, adrenal insufficiency and other complications can cause big problems.