What role do adrenal hormones play?
The adrenal glands produce certain hormones that are necessary for the human body. They perform various functions.
| Name | Description |
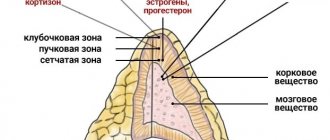
| Aldosterone | A mineralocorticoid hormone produced in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal glands. It controls mineral metabolism in the human body. Maintains electrolyte balance, maintains blood pressure and is responsible for ion transport in the sweat, salivary glands, and intestines. |
| Glucocorticoids | Hormones are produced by the stratum fasciculata of the adrenal glands. They have anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects, take part in various metabolic processes of the human body. |
| Adrenosterone | Hormonal substances are produced in the zona reticularis of the adrenal glands. This includes testosterone, estrogen, pregnenolone. |
| Catecholamines | The adrenal medulla is responsible for the production of hormones. These are adrenaline and norepinephrine. |
All hormones produced by the adrenal glands are vital for the proper functioning of the human body. With their excess or insufficient production, serious pathological changes appear, including serious complications.
Tests to measure hormone levels
Hyperfunction or hypofunction of the adrenal glands is characterized by a decrease or increase in the production of certain biologically active substances that take part in various metabolic processes of the human body. A doctor, as well as an additional comprehensive examination, will help you establish an accurate diagnosis and select the most effective treatment method.
Patients are prescribed the following tests:
| Name | Description |
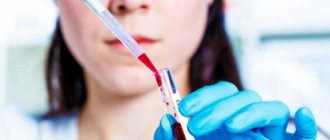
| General blood and urine analysis | The results of the study will help determine the level of hormones in the human body. |
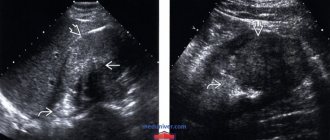
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | The doctor examines the adrenal glands, assesses their size and shape, and identifies pathological changes. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | Maximum diagnostic examination methods that will help to visually and thoroughly examine the adrenal glands, hypothalamus, pituitary gland and evaluate their anatomical structure. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | |
| Electrocardiography (ECG) | A diagnostic method that helps to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. |
It is recommended to take tests in the morning and on an empty stomach. Before collecting the material, patients must refrain from eating harmful foods. The same goes for physical activity and emotional outbursts.
It is important to differentiate the disease and start treatment in a timely manner to prevent possible consequences. Similar clinical signs are accompanied by chronic pancreatitis, gastric ulcer, dermatomyositis, pellagra.
Hyperthyroidism: diagnosis
Pituitary dysfunction is diagnosed when the patient undergoes tests. When examining the material in the laboratory, the specialist initially determines which hormone is in excess in the body. Next, the biochemical indicator of the material is tested.
If the doctor does not have enough data obtained in the laboratory to make a diagnosis, he may prescribe other types of examinations using special equipment. This:
- X-ray.
- Tomography.
After an accurate diagnosis and identification of the causes of dysfunction of the pituitary gland, the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy.
How does adrenal hyperfunction manifest itself?
Hyperfunction of the adrenal glands is observed in the case of increased production of hormones that support the vital functions of the human body. There are numerous situations where the functioning of the endocrine system is disrupted. In this situation, a person needs to consult an endocrinologist and undergo a thorough examination.
Causes
The adrenal glands (hyperfunction and hypofunction occur against the background of numerous provoking factors) affect the functioning of the entire human body.
Pathological processes trigger various changes in the body:
- hormonal imbalance;
- prolonged stress, overexertion;
- oncological diseases of the kidneys or peripheral organs (malignant tumors);
- gland hyperplasia;
- severe inflammatory process in the adrenal glands;
- overweight;
- development of diabetes mellitus;
- period of bearing a baby.
Benign neoplasms also provoke increased production of hormones and hyperfunction of the adrenal glands as a result. The same applies to the growth of the cortex.
Classification of adrenal hyperfunction
Considering the area of development of pathological processes, in medicine there is a certain classification of adrenal hyperfunction:
Hypercortisolism
| Name | Description |
| Hypercorcytism | A pathological condition in which the production of cortisol increases. |
| Hyperaldosteronism | Adrenal hyperfunction is characterized by increased production of aldosterone. |
| Adrenal hyperandrogenism | Functional disorders occur in the zona reticularis of the adrenal glands, where male sex hormones are produced. Excessive production of steroids is observed. |
| Pheochromocytoma | An increase in catecholamine levels is observed. |
In each individual case, a person develops characteristic signs that indicate an increase in the concentration of certain hormones. It is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination and tests to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms
The adrenal glands (hyperfunction and hypofunction of the paired gland negatively affect a person’s daily life) when working hard cause characteristic symptoms with which it is necessary to go to the hospital.
The endocrinologist, taking into account the patient’s complaints, will prescribe an examination. Also guided by the signs of disorders, he will be able to determine the degree and stage of development of pathological processes.
Adrenal hyperfunction is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- adenomas are formed;
- there are sharp changes in blood pressure parameters;
- the menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- hands and legs are shaking;
- the size of the adrenal glands increases;
- acne appears on the skin;
- pigmentation occurs;
- tumor processes develop;
- the patient complains of constant weakness in the body, rapid fatigue.
Accompanying signs are also atrophying phenomena associated with muscles, a sharp change in body weight. Tests show high levels of glucose in the blood.
Treatment
Therapy for damage to the adrenal glands in each case is selected according to an individual scheme. Not only the results of a comprehensive examination are taken into account, but also the person’s condition and associated pathologies. It is important to first eliminate the provoking factor. Complex treatment allows the use of folk remedies if there are no medical contraindications.
Adrenal glands (hyperfunction and hypofunction of the gland are the result of serious disorders in the human body), with increased production of hormones, must be treated primarily with medication:
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Glucocorticoids | Dexamethasone, Hydrocortisone | For adult patients, the drug is prescribed in a dosage of 0.5 to 9 mg per day. |
| Antagonists | Metyrapone, Mitotane | The medicine should be taken orally. Adult patients are prescribed 750 mg every 4 hours (6 doses). |
| Antihypertensive drugs | Nifedipine, Eplerenone | The drug is taken orally with a sufficient amount of liquid (250 ml). The recommended dosage for an adult patient is 10-20 mg 3-4 times a day. |
Additionally, all patients are prescribed vitamin complexes and immunostimulating agents that will help increase the body's defenses. In cases where the cause of adrenal hyperfunction is a tumor, surgery is indicated for the patient.
Consequences and complications
Increased concentrations of hormones produced by the adrenal glands rarely provoke negative consequences or relapses. The patient must strictly adhere to all doctor's recommendations and take medications.
Otherwise, without treatment, a person will face the following complications:
- development of malignant processes;
- failure of the endocrine system;
- dysfunction of the liver and kidneys.
Complications provoke the development of serious concomitant diseases, including Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of hair throughout the body, the process of thermoregulation is disrupted, and the risk of bone fractures increases.
Oxytocin
Structure
It is a peptide consisting of 9 amino acids and a half-life of 5 minutes.
Synthesis
Carried out in the hypothalamus. The hormone enters the secretion point - the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland - along axons with the carrier protein neurophysin.
Regulation of synthesis and secretion
Secretion is stimulated by irritation of the breast nipples (breastfeeding), pregnancy, increased frequency of sex, stress, sleep, serotonin.
Mechanism of action
Not known exactly. Associated with the regulation of the amount of prostaglandins in the cell and changes in the flow of Ca2+ and Na+ ions.
Targets and effects
Uterus
By changing the ion flows in the myometrium of the uterus, it causes its contraction. As pregnancy progresses, the sensitivity of the uterus to the hormone increases.
Breast
In the myoepithelial cells of the alveoli, it stimulates spasm of the ducts and milk secretion.
Adipose tissue
Increases glucose consumption and, consequently, the synthesis of triacylglycerols.
Pathology
not noted
Hypofunction of the adrenal glands
Hypofunction of the adrenal glands is characterized by insufficient production of certain hormones.
As pathological processes progress, the internal organs of the human body gradually cease to function normally.
Causes
In most cases (98%), the cause of adrenal hypofunction is abnormal autoimmune reactions in the human body. Pathological changes provoke destruction of the paired gland.
But there are other negative factors that disrupt the functioning of the adrenal glands:
- tuberculosis in the active stage;
- hereditary predisposition;
- genetic abnormalities;
- damage to the cardiovascular system;
- tumor in the pituitary gland;
- adrenal hyperandrogenism.
Autoimmune disorders also contribute to adrenal hypofunction. The immune system produces antibodies that attack its own cells, mistaking them for foreign microorganisms.
Classification of adrenal hypofunction
Taking into account the course of pathological processes, the following types of adrenal hypofunction are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Spicy | A person experiences an Addisonian crisis, which is characterized by a complex of severe disorders. The pathological condition is also accompanied by periodic disruptions in the functioning of internal organs and low vitality. |
| Chronic | When the adrenal tissue is directly damaged, a person develops a secondary form of hypofunction. In most cases, disorders are diagnosed in older people. |
| The tertiary chronic form of adrenal hypofunction occurs as a result of insufficient production of corticoliberin, the production of which is responsible for the hypothalamus. Pathological processes provoke gradual atrophy of the tissues of the paired gland. |
Symptoms at each stage of development of pathological processes differ, depending on the area of localization and the degree of their spread.
Symptoms
The adrenal glands (hyperfunction and hypofunction require mandatory medical care) with insufficient production of hormones provoke the appearance of specific symptoms. The clinical picture will allow the doctor to identify disorders and establish a preliminary diagnosis. Also prescribe the most informative examination for the person.
Adrenal hypofunction is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
- the skin in the neck, arms and face darkens (the intensity of the color depends on the degree of development of pathological processes);
- the mucous membrane of the gums, tongue, lips becomes covered with brown spots;
- there is a feeling of general fatigue in the body;
- muscle weakness gradually increases;
- skin rashes and acne appear;
- women's menstrual cycle is disrupted;
- sebaceous glands become inflamed;
- body weight increases sharply;
- blood pressure increases;
- stretch marks appear on the human body;
- the functioning of the digestive system organs is disrupted;
- nausea and vomiting regularly;
- metabolism slows down due to damage to the endocrine system;
- pain occurs in the abdominal area.
Hypofunction of the adrenal glands is also accompanied by nervous irritability and a person’s apathy towards the world around him. Memory deteriorates, absent-mindedness appears, and concentration decreases. Bruises appear on the body, even with minor physical impact.
Treatment
Complex therapy for adrenal hypofunction involves patients taking special medications for life. A diet is also selected for the person. It is necessary to avoid all kinds of factors that provoke a malfunction of the adrenal glands. This applies to increased physical activity, emotional outbursts, and stress.
The endocrinologist selects drug therapy based on the patient’s condition and test results.
The patient is prescribed replacement therapy using the following drugs:
| Name | Application | Contraindications |
| Triamcinolone | The initial dosage for adults is 4-40 mg per day. After achieving a therapeutic effect, the amount of medication is reduced to 1-2 mg every 2-3 days. |
|
| Cortineff | Adult patients are prescribed 100-200 mcg per day. It is recommended to take the tablets in the morning, swallow them whole and drink enough liquid. |
|
Hospitalization is necessary for the patient if an acute period of adrenal hypofunction develops. In a hospital setting, antishock therapy is carried out, and medications are administered intravenously. In the absence of positive dynamics after drug therapy and in the event of serious complications, surgical intervention is indicated for patients.
Consequences and complications
With timely and properly selected therapy, many patients with hypofunction continue to live normally. The course of the disease in this case is favorable.
In other situations there is a serious risk of complications:
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- cerebral edema;
- collapse.
The most dangerous complication is death. Chronic adrenal insufficiency is treated with medications throughout life. Patients are assigned a certain disability group, depending on the degree and severity of the disease.
Hyperfunction and hypofunction of the adrenal glands require careful diagnosis and properly selected therapy. An endocrinologist prescribes medications to patients that will not only help eliminate existing symptoms, but also restore the functioning of the paired gland.
Patients should additionally strictly adhere to dietary nutrition. The prognosis for adrenal gland dysfunction depends on the patient. Failure to comply with medical prescriptions will lead to serious consequences, including death.
Causes of pathology
Hyperfunction of the pituitary gland can manifest itself due to two main factors:
- Congenital.
- Purchased.
In the first type of pathology, it is transmitted from parents to children at the genetic level. Acquired hyperfunction can be caused by:
- Infectious diseases.
- Head injuries.
- Using medications for a long time.
- Stress.
- Blood flow disorders.
- Autoimmune processes.
- Tumors.