MCD is not considered an independent disease. This is a condition in which an excess of uric acid accumulates in the body of a sick person. This substance has a tendency to crystallize. At the same time, during the process of urination, small salt crystals are washed out of the body. Uric acid diathesis of the kidneys at the beginning of development does not cause any discomfort to the patient and is asymptomatic. In the urine you can notice a precipitate of uric acid salts, which looks like small grains of reddish sand. But such sediment can only be noticed when you empty your bladder into a special container.
Causes of MCD
This pathological condition is diagnosed in both adults and children.
This pathological condition is diagnosed in both adults and children. Quite often, MCD is found in women during menopause. In the male population, this disease is diagnosed more often after 40 years of age.
Among the reasons for the development of uric acid diathesis are the following:
- unhealthy diet, namely an excess of meat foods;
- genetic predisposition;
- stressful situations;
- pancreatitis;
- diabetes;
- hepatitis;
- radiation therapy in the treatment of malignant neoplasms;
- passion for alcoholic beverages;
- disorders of the kidneys (abnormalities in protein production);
- In children in the first year of life, this condition occurs due to poor nutrition. If parents feed their child meat, believing that it is very healthy. In fact, your diet should be dominated by vegetables and fruits.
- improper drinking regime (due to a lack of fluid in the body, the amount of urine excreted decreases);
- abnormalities in the structure and activity of the kidneys;
- increased physical activity;
- general intoxication of the human body;
- bacterial agents that cause problems with the liver and kidneys;
- long fasting.
It’s worth knowing: sometimes pregnant women are diagnosed with uric acid diathesis in the first weeks of pregnancy. However, this condition does not require treatment, since it goes away on its own after the first trimester.
What is renal parenchyma?
The term “parnechyma” itself is defined as a collection of cells that perform an organ-specific function. Parenchyma is the tissue that fills the organ.
The parenchyma of the kidney consists of the medulla and cortex, which are located in the capsule. It is responsible for all functions performed by the organ, including the most important one – urine excretion .
Examining the structure of the parenchyma using light microscopy, you can see the smallest cells densely intertwined with blood vessels.
Normally, the thickness of the kidney parenchyma of a healthy person ranges from 14 to 26 mm, but can become thinner with age.
For example, in elderly people, the normal size of the kidney parenchyma is no more than 10-11 mm.
Interestingly, kidney tissue has the ability to regenerate and restore its functions. This is a big plus in the treatment of various diseases.
Important!
To treat kidney diseases, our readers successfully use Galina Savina’s method .
>>>
Many people do not know where their kidneys are, so sometimes they do not even realize that they may have impaired kidney function.
Kidney pain can indicate various diseases. Read our article about how kidneys hurt in various pathologies.
Uric acid is a consequence of the breakdown of purines
The concentration of UA (uric acid) in the human body is directly related to the level of purines in it.
The concentration of UA (uric acid) in the human body is directly related to the level of purines in it. Purines themselves are not pathological substances; only their concentration is important. Thus, in the male body the normal concentration of uric acid is no more than 7 mg/100 ml of blood, and in women this figure is 5.7.
A normal amount of uric acid is needed by the body as an antioxidant and to maintain the normal state of the vascular system. To normalize the level of purines in the body, low-purine diets are indicated.
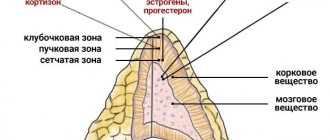
Structure
The renal parenchyma consists of two layers:
cortex , located immediately below the renal capsule. It contains the renal glomeruli, in which urine is formed. The glomeruli are covered with a huge number of vessels. There are more than a million glomeruli themselves in the outer layer of each kidney; medulla . Performs an equally important function in transporting urine through a complex system of pyramids and tubules into the calyces and further into the pelvis. There are up to 18 such tubules, grown directly into the outer layer.
One of the main roles of the renal parenchyma is to ensure the water and electrolyte balance of the human body. The contents - vessels, glomeruli, tubules and pyramids - form the nephron, which is the main functional unit of the excretory organ.
The thickness of the renal parenchyma is one of the main indicators of its normal functioning, since it can fluctuate under the negative influence of microbes.
But its size can also change with age, which must be taken into account when conducting an ultrasound examination.
So, in young and middle-aged people, the kidney parenchyma (normal value) is 14-26 mm.
In persons over 55 years of age, the kidney parenchyma (size and normal) is no more than 20 mm. The normal thickness of the kidney parenchyma in old age is up to 11 mm.
Parenchymal tissue has a unique ability to recover, so it is necessary to promptly treat diseases.
Clinical picture
Among the main symptoms of this disease, it is worth listing such signs as severe headaches.
If you have been diagnosed with ICD of the kidneys, we have figured out what it is, now we will look at the signs of this condition. Manifestations of the disease can be varied. It should be noted that the symptoms of MCD affect the activity of various organs, as well as the mental state of children and adults.
Among the main symptoms of this disease are the following:
Symptoms of drug-induced kidney damage and treatment
- severe headaches;
- increased irritability, aggressiveness and anxiety (sometimes such symptoms turn into prolonged depression);
- high blood pressure;
- vomit;
- asthma attacks;
- sleep problems;
- frequent constipation;
- temperature increase;
- sudden changes in weight in one direction or another;
- loss of appetite;
- general loss of strength, weakness;
- When you breathe, you can smell acetone.
All of these symptoms may not appear constantly, but only periodically at times when the patient’s condition worsens.
Focal changes
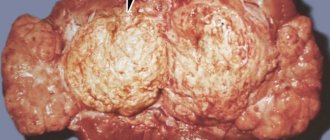
Focal changes are neoplasms that can be either benign or malignant. In particular, a simple cyst is benign, while solid parenchymal tumors and complex cysts are most often carriers of cancer cells.
A neoplasm can be suspected based on several signs:
blood impurities in the urine; pain in the kidney area; a tumor noticeable on palpation.
The listed symptoms, if present together, unmistakably indicate the malignant nature of the pathology.
Unfortunately, they usually appear in an advanced stage and indicate global dysfunction.
The diagnosis is made based on research:
Ultrasound; computed tomography; nephroscintigraphy; biopsies.
Additional methods for studying focal changes that allow us to determine the presence of a blood clot, the location of the tumor, and the type of vascularization necessary for effective surgical treatment:
aortography; arteriography; cavography.
X-ray and computed tomography of the bones of the skull, spine, as well as CT of the lungs are auxiliary examination methods if the spread of metastases is suspected.
For malignant tumors in the kidney parenchyma, treatment is usually surgical, which often involves removing the affected organ. For benign tumors, organ-preserving operations are performed, the purpose of which is to excise the tumor with minimal harm. After surgery, cancer patients are given radiation therapy.
Single metastases in the spine and respiratory organs are not a contraindication for
nephrectomy
, since they can also be excised.
Possible complications
If MCD in adults or children is not treated for a long time, then this condition can lead to the development of acute nephropathy.
If MCD in adults or children is not treated for a long time, then this condition can lead to the development of the following diseases and problems with the functioning of the body:
- Since uric acid salts resemble sand at the beginning of their appearance, over time they can form large stones, that is, lead to the development of urolithiasis.
- The risk of kidney failure increases.
- Acute nephropathy may develop against the background of uric acid diathesis.
- There is a risk of uric acid infarction.
- Disturbances in the activity of the gastrointestinal tract.
If uric acid diathesis is not detected and treated in time, then over time this condition can lead to malfunctions of all organs and systems. In this case, a person’s mental health will suffer significantly. The good news is that all complications of MCD are easily treated without the need for surgery.
Signs and symptoms
With diffuse changes, the walls of the parenchyma thicken, the sinuses of the kidneys enlarge, and the organs differ in size from each other. In the early stages of negative changes, the signs are weak, but as the pathological process develops, symptoms appear that must be paid attention to.
Characteristic manifestations:
- swelling of tissues against the background of increased intracapillary pressure;
- pain during urination;
- violation of the frequency and volume of fluid excreted while maintaining the usual drinking regimen;
- discomfort in the lumbar region, in most cases, is bilateral. Pain syndrome develops when the renal capsule is stretched;
- Doctors detect cysts in the sinuses and parenchyma, the size of the bean-shaped organs increases;
- As the cyst grows, the blood supply to the tissues is disrupted, and a dangerous condition develops—renal failure.
Based on the results of an ultrasound examination, doctors diagnose the following abnormalities:
- poor visualization of the renal veins;
- reduced echogenicity;
- fluid in the renal pelvis;
- tumor thrombosis;
- the parenchyma has unclear outlines;
- decreased sinus thickness;
- thickening of the parenchyma;
- venous thrombosis;
- echo signal from the area of the kidney sinuses;
- reverse circulation in the renal arteries.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, the patient must be examined by a urologist.
To make a diagnosis, the patient must be examined by a urologist. You will also need additional consultation with a nephrologist. The patient will have to undergo the following tests:
- KLA will reveal the concentration of acid (uric acid) in a person’s blood.
- OAM is needed to detect sediment from uric acid salts.
- Daily urine tests will help assess how the composition of urine changes throughout the day.
- Ultrasound of the urinary system.
No less important in diagnostic terms is collecting anamnesis. The patient must talk about the symptoms of the disease, their lifestyle and diet, as well as other points that will help identify the cause of the disease.
Additional diagnostic procedures and laboratory tests may be necessary to exclude the possibility of concomitant inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system.
Study
Diagnostic procedures make it possible to determine the structure of the kidney tissue, examine the internal state of the organ, and timely identify diseases of the urinary system in order to quickly take measures to prevent their spread and aggravation.
Parenchymal tissue can be examined in several ways:
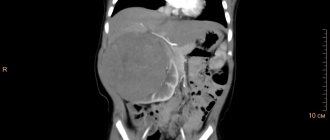
ultrasonic It is carried out for any suspicion of pathological processes. The advantages of the method include the absence of X-ray radiation and contraindications, and the affordable cost of the procedure. Using ultrasound, their number, size, location, shape and condition of the tissue structure are determined. In addition, an ultrasound examination can detect the presence of stones and detect signs of inflammation and neoplasms. Duplex scanning allows you to study renal blood flow; CT and MRI. Unlike ultrasound, they are more informative research methods that help identify congenital anomalies, parenchyma cysts of the left and right kidneys, hydronephrosis, and pathologies of blood vessels. They are carried out using contrast enhancement, which has a number of contraindications, so it is prescribed if additional, more in-depth research is necessary;
biopsy. It is carried out in stationary conditions. The essence of the method is the examination of microscopic kidney tissue taken from the patient using a special, thin medical needle. A biopsy can reveal: chronic, hidden diseases, nephrotic syndrome, glomerulonephritis, infectious diseases, proteinuria, malignant tumors, cysts. Contraindications: low blood clotting, one working kidney, allergy to novocaine, hydronephrosis, blockage of the renal veins, renal artery aneurysm.
If deviations in the size of parenchymal tissue from the generally accepted norm are detected, it is necessary to contact a specialist for further examination and treatment.
The decision on the choice of diagnostic method should be made by the doctor based on the medical history.
Treatment
Treatment of MCD consists of following a special diet
Treatment of MCD consists of following a special diet, which consists of the following:
Causes of prolapsed kidney: symptoms and treatment
- Reducing the amount of protein consumed. Not only an excess of protein foods is harmful to the body, but also its lack (especially for children, since protein is the main building material in a growing body). The amount of protein per day is determined from a person’s weight - for each kilogram of him there should be a gram of protein.
- You need to increase the amount of fluid you drink during the day. It should be at least two liters or more.
- It is important to reduce the amount of salt you consume to a minimum. It is better not to salt food at all during the cooking process, but only add a little salt to the food before eating.
Patients may also be prescribed medications whose main purpose is to:
- Reducing the acidity of urine. Asparkam removes oxalate and urate salts from the body. It is suitable for therapy even for infants.
- Reducing the amount of uric acid in excreted urine. For this purpose, Allopurinol is prescribed. This is an enzyme that is responsible for the hydrolysis of uric acid salts and helps reduce its concentration in the body.
- Preventing the process of crystallization of uric acid salts. The drugs Canephron, Urolesan and Fitolysin help improve the outflow of urine and accelerate the excretion of salts.
- Optimization of metabolic processes occurs with the use of vitamin and mineral complexes, namely germanium and selenium, as well as water-soluble vitamins C and B.
Important: good results are achieved by combining drug treatment and physiotherapy, namely magnetic therapy, darsonvalization, ultrasound therapy, ultraviolet irradiation, magnetic laser, laser and singlet oxygen therapy.
For the treatment of pregnant women and children, a simplified treatment option is used, but no less effective. The doctor selects the appropriate method after taking a 24-hour urine test and identifying the cause of the disease.
Parenchyma structure
So that a person ignorant of medicine can understand what parenchyma is, let us explain - this is the main renal tissue. There are 2 layers in this substance.
The first is cortical or “external”. There are complex devices here - renal glomeruli, densely covered with vessels. Urine is formed directly in the glomeruli. It is difficult to count the number of glomeruli in the cortex; each kidney contains more than a million of them. The cortex is located directly under the renal capsule. The second layer is the cerebral or “internal” layer. Its task is to transport the resulting urine through a complex system of tubules and pyramids, and collect it in the pyelocaliceal system. Each kidney contains from 10 to 18 pyramids, which grow into the cortex as tubules.
It is the kidney parenchyma that is responsible for the water and electrolyte balance of the body. Kidney parenchyma is a unique tissue. Unlike other tissue elements, it is capable of regeneration, i.e. restoration.
This is why treatment of acute renal pathologies is of great importance. The parenchyma tissue of both the left and right kidneys responds positively to health measures.
Glomeruli, pyramids, tubules and vessels form the main structural unit of the kidney - the nephron.
An important indicator of physiological structure is thickness. This is a variable value and changes with age, as well as under the influence of infections and other pathogenic agents.
Normal parenchyma thickness:
| From 14 to 26 mm, 20-23 mm on average | Up to 20 mm | 10 – 11 mm |
When examined by ultrasound, not only the thickness of the kidney parenchyma is important, but also other physiological characteristics of the organ.