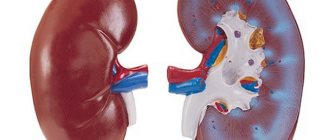
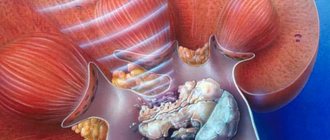
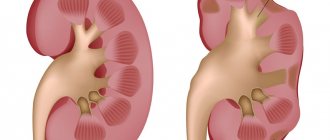
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic pathology. It can appear at any age - during the formation of the fetus in the womb or after 60 years, but most often occurs at 30-40 years of age. With this disease, multiple cysts form in the kidneys, which leads to disruption of their functions, as well as other complications. The prognosis depends on the type of genetic inheritance, age of manifestation of the pathology, and concomitant diseases. There is no specific treatment for polycystic disease in medicine.
Causes of polycystic disease
In adults, the disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner and manifests itself between the ages of 3 and 50 years. Polycystic kidney disease in children has autosomal recessive inheritance. This disease is one of the most common hereditary disorders.
In most cases (about 90%), it is transmitted from parents, and only in 10% is the result of gene mutation. Inheritance of polycystic disease occurs regardless of gender.
How does it manifest clinically?
With a disease such as polycystic kidney disease, the symptoms are as follows:
- There is pain in the area of the projection of the kidneys, varying in intensity, which often radiates to the side and intensifies with palpation. The pain is most often bilateral, and is caused by an increase in the size of the kidneys, stretching of the capsule, and compression of blood vessels and nerves.
- Organs increase in size, which can be confirmed by bimanual examination and ultrasound.
- Urolithiasis often occurs, blood appears in the urine, and is accompanied by symptoms of renal colic.
- Complicated by pyelonephritis, suppuration or rupture of the cyst, as well as hypertension.
- Heart rhythm disturbances appear, extrasystoles are detected. This is due to the fact that with polycystic disease the electrolyte composition of the blood changes and anemia develops.
- Renal failure develops with characteristic symptoms of constant dry mouth, itching, thirst, severe weakness and polyuria with a decrease in urine concentration. The patient has no appetite, and signs of exhaustion are increasing.
Prevention
Polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disease, it cannot be cured and almost impossible to prevent. Preventive measures, like therapeutic measures, consist in combating symptomatic manifestations and general relief of the pathology. To prevent relapses of the lesion, doctors recommend that patients follow a diet, take vitamin and mineral complexes, and regularly consult a specialist at the first symptoms. A set of therapeutic and preventive measures - diet, alternative medicine and official medications - can restrain the formation of cysts within acceptable limits; without them, the patient is extremely likely to “acquire” disability and death.
Types of complications
Polycystic kidney disease is dangerous not so much in itself, but because of the possible complications that lead to disability or can even cause the death of the patient.
Hematuria
Blood in the urine appears as a result of the fact that the cyst may rupture. Usually this phenomenon does not occur with heavy blood loss, but in some cases urgent surgical intervention may be necessary.
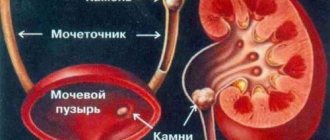
Urolithiasis disease
It develops as a result of metabolic disorders in the kidney, as well as stagnation of urine due to the difficulty of its excretion. Occurs with large cysts. Stones at the outlet of the ureter block the outflow of urine, and this aggravate the condition. They can also cause bleeding.
Hypertension
It develops as a result of compression of kidney tissue and disruption of the release of substances responsible for regulating blood pressure. At the same time, blood flow becomes less, and substances that contribute to the development of hypertension begin to be released.
Infections
Changes in urodynamics and pronounced stagnation of urine contribute to the attachment of pathogenic microflora and its reproduction. Therefore, polycystic disease is often accompanied by a disease such as pyelonephritis.
Failure
The gradual death of renal parenchyma cells leads to the fact that it cannot perform its main functions. Since the cysts grow gradually, organ failure becomes chronic. Gradual poisoning of the body develops as a result of the accumulation of toxic substances.
What are the causes and mechanisms of development?
Polycystic disease is characterized by inheritance, and during intrauterine development 2 genes can mutate:
- on chromosome 4;
- on the short arm of chromosome 16.
Multiple kidney cysts can be passed on from one or both parents. Polycystic disease develops inside the womb and progresses throughout life. With a mutation in the fourth chromosome, the prognosis is favorable, the outcome is more positive, since organ failure develops only in old age. In the second case, polycystic disease progresses faster, and the death of the patient, due to multiple cysts and kidney dysfunction, occurs at an early age.
Diagnosis of the disease
With a diagnosis such as polycystic kidney disease, the diagnosis must be carried out in full. The doctor first listens to the patient’s complaints and finds out when the first symptoms of trouble began. An important point is to determine the presence of such a disease among close relatives.
A general blood test for polycystic kidney disease will show the presence of inflammation and iron levels in case of anemia. Blood biochemistry will determine the presence of deficiency based on the level of urea and creatinine. It will also allow you to find out the level of protein, potassium, iron and sodium. Urinalysis can detect hematuria, white blood cells (with pyelonephritis), small stones and sand (with ICD).
Instrumental methods can reliably verify the presence of polycystic disease. For this purpose, ultrasound and excretory urography are used. If necessary, the specialist refers the patient to a CT scan. If the rhythm is disrupted, a cardiogram is taken. Since cysts can be located in other organs, the liver, lungs and pancreas are also examined.
Features of polycystic disease in childhood
Polycystic disease in newborns and children before they reach one year of age is a very serious disease with a poor prognosis for recovery and future life. Violation of the basic function of the kidneys (filtration) usually leads to death. If you believe the statistics, then out of a thousand newborns one has this pathology.
Modern diagnostics have the ability to detect diseases in a baby not only at birth, but also in the womb. Therefore, treatment becomes possible at the earliest stages. Depending on the severity of the lesion, conservative therapy is used or surgery is performed.
If the diagnosis of polycystic disease is not made in a timely manner, then the rapidly progressing pathological condition becomes fatal. The fact is that in young children this disease occurs with the formation of very small cysts, which do not manifest symptoms for a long time. But as they grow and develop, they increase. And when signs of polycystic disease develop, it is almost impossible to take action at this stage.
For this reason, the baby should be examined in advance, especially if there are relatives suffering from this disease. This will allow you to start treatment early and avoid the severe consequences of polycystic disease.
Cyst forms
In kidneys affected by polycystic disease, 2 types of cysts form:
- closed. Such cysts are closed and do not communicate with the lumen of the tubules, thereby not providing excretory function. This type of formation is more common in newborns;
- open. This type of formation is represented by diverticulum-like extensions of the tubules, which communicate with the pelvis and calyces. If such formations have formed, then the excretory function of the organ is preserved for a long period of time.
Giving help
With a disease such as polycystic kidney disease, treatment can only be symptomatic, since it is not possible to influence the cause of its occurrence:
- For severe pain, NSAIDs or analgesics are used.
- The addition of pathogenic microflora requires the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, of which the doctor recommends those that are excreted through the kidneys in the urine.
- If you have hypertension. Which often accompanies polycystic kidney disease, antihypertensive drugs and sometimes diuretics are used.
- If the level of hemoglobin is reduced, then special medications containing iron should be used.
- If the cysts become large and cause a tendency to bleeding and severe pain, then surgical intervention is recommended to improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Damage to most of the renal parenchyma with the development of organ failure in polycystic disease is the reason for removal of the kidney. If the second organ is preserved, it takes on the entire main function of removing toxins and metabolic products from the human body. If the second kidney is also affected, the patient undergoes hemodialysis (three times a week for 5 hours) and a transplant is recommended.
In the initial stages of polycystic disease, it is recommended to undergo a control ultrasound examination and tests at least twice a year. Usually such a patient is registered and observed by a nephrologist.
Treatment of the disease
Only the attending physician can tell you how to properly treat polycystic kidney disease, based on the data of the initial examination and the test results obtained. It is worth noting that it is impossible to completely cure the pathology, therefore all therapy provided is symptomatic.
Therapeutic treatment of polycystic kidney disease includes:
- antibacterial therapy;
- antihypertensive treatment;
- getting rid of anemia;
- correction of disorders that may arise due to a lack of minerals, in particular phosphorus;
- getting rid of pain - antispasmodics are prescribed.
Surgical techniques for treating polycystic kidney disease:
- kidney transplantation;
- puncture of cystic formations;
- laparoscopic removal of exudate from cystic formations.
Kidney transplant
Features of nutrition in polycystic kidney disease
A high load on the kidneys with such a pathology is completely contraindicated, therefore, in addition to conservative and surgical treatment, a diet for polycystic kidney disease is important. Without its observance, no therapy can be effective. The basic nutritional rules for this disease are as follows:
- Sharp salt restriction will help normalize blood flow in the kidney and reduce blood pressure.
- In case of polycystic disease, foods containing potassium (bananas, potatoes, dried fruits) are subject to restrictions.
- The products of protein metabolism place a huge burden on the kidneys. Therefore, dishes containing them are not recommended to be placed on the table.
- In the absence of edema, he recommends consuming at least 2-3 liters of fluid.
- The menu of a patient with polycystic disease also excludes fatty, fried and smoked foods. It promotes the production of biologically active substances, which can worsen the patient’s condition.
- If cysts in the kidneys lead to the development of urolithiasis, then, depending on the composition of the stones, the diet should exclude or sharply limit some dishes.
- Protein deficiency is compensated by taking special medications, while animal protein in food remains prohibited.
Folk remedies for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease
It should be noted that the use of treatment with natural and herbal remedies does not replace the main treatment, and is only an auxiliary method of providing assistance for polycystic disease.
Some herbs have proven themselves to be beneficial for kidney pathology. They help improve a person’s quality of life and can significantly alleviate the course of polycystic disease.
Before use, you should consult with a specialist, since some products may help one patient and harm another.
Most often, to help with polycystic disease, it is recommended to make your own tinctures, which include echinacea, mullein, freshly picked burdock leaf, calendula, and walnuts. Kidney teas, which can be brewed and drunk instead of regular drinks, also help.
loading…
Traditional methods
It is worth immediately noting that folk remedies should in no case become dominant. They can be used only after receiving permission from your attending physician, and in tandem with the methods of official medicine. Polycystic disease cannot be cured with folk remedies. With their help, you can only support the functioning of organs and eliminate some symptoms, such as hypertension, swelling, etc.
Folk remedies for the treatment of this disease are prepared from:
- burdock leaves;
- garlic;
- mullein;
- calendula;
- licorice;
- chicory;
- ferules;
- walnuts;
- beans.
Most doctors do not allow the treatment of polycystic disease with folk remedies, since their uncontrolled use may not only not improve a person’s condition, but also worsen it. Certain folk remedies can be taken, but only in precise dosage and under the constant supervision of a doctor.