Urine is a human waste product, a liquid formed by the kidneys in the process of filtering plasma and reabsorbing some of its components. It consists of 97% water, the remaining 3% comes from decay products and impurities.
The detection of salts in a urine test is not always a sign of any disorder. A small concentration is indicated in the laboratory by one or two pluses (“+” or “++”) and can occur normally in a healthy person. As a rule, this is a temporary phenomenon associated with physiological characteristics.
A significant amount of salts (“+++” and “++++”) most often indicates metabolic disorders, water-salt metabolism, diseases of the urinary system, endocrine diseases and other pathologies.
Types of salts
Most often phosphates, oxalates, urates, nitrites are found in urine, less often - calcium sulfate and carbonate, hippurates, etc.
1.1. Urats
These are salts of uric acid. With constant release, they can form stones in the kidneys, bladder, and also near the joints (gouty tophi).
The appearance of urates in the urine may be associated with poor diet (excess in the diet of red meat, strong meat broths, coffee, tea, liver, legumes, canned food, mushrooms), high physical activity, gout and impaired purine metabolism. Leukemia and other malignant tumors are also accompanied by an increase in the concentration of uric acid and its salts in the blood and urine.
In children, urates are observed in large quantities during uric acid diathesis, infections accompanied by fever and dehydration.
1.2. Oxalates
Salts of oxalic acid form insoluble compounds. Calcium oxalate crystals have sharp edges that irritate and damage the lining of the urinary tract.
Almost 80% of all kidney stones are formed from oxalates!
Oxalic acid salts are found in large quantities in the following products:
- 1 Spices (black pepper), herbs (parsley, dill), sorrel.
- 2Sugar beets, chocolate, cocoa beans.
- 3 Beans, lentils.
- 4 Blackberries, gooseberries, currants, cranberries, lingonberries, kiwi, mango, grapes, tomatoes.
- 5 Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts.
- 6Tea, coffee.
Excretion of oxalates in the urine is observed in cases of impaired oxalate metabolism in the body, urolithiasis, various poisonings, neoplasms, and excessive consumption of ascorbic acid.
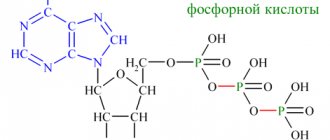
1.3. Phosphates
Phosphoric acid salts may indirectly indicate a dietary disorder, namely vegetarianism. With a complete abstinence from meat and protein products, the urine becomes alkalized, which leads to the appearance of ammonium phosphates in the urine.
Their level also increases with the predominance of fish, dairy products, cereals, caviar, and mineral water in the diet. In children under 5 years of age, rickets and an overdose of vitamin D can cause the excretion of phosphates in the urine.
The concentration of these salts increases with inflammation of the bladder, hypofunction of the parathyroid glands, prolonged fever or vomiting, and acid-base imbalance.
The clinical picture is blurred
It is almost impossible to recognize the disease in the first stages, since there are no obvious signs.
If symptoms exist, they can be confused with other health problems.
However, the importance of detecting the disease is great
Indeed, in the early stages, treatment occurs much faster and will prevent serious consequences.
You should pay attention to lower back pain, which we often attribute to sciatica or hypothermia. You should be alerted to frequent and painful urination, high blood pressure, and a small amount of urine excreted.
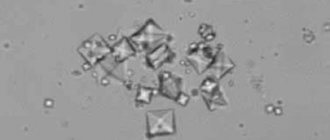
The most distinctive symptoms of crystalluria include cloudy urine with bloody discharge and a strong, unpleasant odor.
You can test your urine for crystals at home. Place morning urine in a place protected from light for a day. And watch.
If a white coating remains on the walls of the glass jar, this indicates an increased concentration of phosphates, alkaline and potassium salts.
Red crystals indicate excess uric acid. A black or reddish sediment indicates that oxalates have accumulated in the body.
The most pronounced symptoms include acute pain in the groin and under the navel, as well as in the lumbar region. High temperature. Swelling of the limbs.
Causes and risk factors
Today, some factors are known that lead to the precipitation of salt crystals.
2.1. Eating disorder
If salts are detected as a result of a urine test, you need to reconsider your diet:
- 1 Diet abuse (ketogenic or, conversely, vegetarian vegetable diet).
- 2Therapeutic or any other fasting.
- 3 Sharp limitation of fluid intake (especially clean drinking water).
- 4 Predominance in the diet of smoked meats, canned foods, marinades, as well as alcohol, strong coffee or tea, chocolate, cocoa, mushrooms, and meat broths. Salts are formed when eating sour berries, sorrel, and tomatoes.
2.2. Physiological factors
A temporary increase in salt concentration in a healthy body is possible due to intense physical activity and training, after insolation (exposure to direct sunlight during the hot season), as a result of dehydration (loss of fluid due to vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature).
Physiological factors include pregnancy, during which biochemical processes and hormonal balance change, which can lead to excessive excretion of metabolic products by the kidneys, including salts.
Toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy is accompanied by dehydration, which can also increase the concentration of salts (urates or phosphates) in the urine.
2.3. Urinary tract infections
Intensive reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms contributes to the formation of salts - metabolic products, changes in the acidity of the environment and the precipitation of salt crystals.
Pathologies such as pyelonephritis, cystitis, prostatitis in men often occur with typical changes in the parameters of a general urine test. With such infections, nitrites, ammonium phosphate, and ammonium urate are more often detected.
2.4. Other reasons
Intestinal infections can also be accompanied by an increase in the concentration of salts (urates, phosphates) due to biochemical changes, dehydration, fever, and changes in enzyme function.
Other possible reasons include:
- 1Diabetes mellitus.
- 2Rheumatoid arthritis.
- 3Gout.
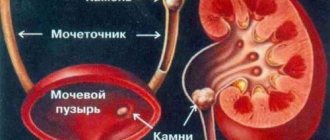
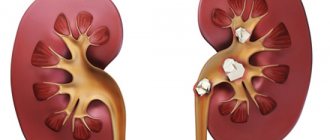
- 4Nephrolithiasis.
- 5Intestinal diseases (colitis, ileitis).
- 6Oncology.
- 7Chronic renal failure with impaired filtration function of the kidneys.
- 8Stress, genetic metabolic defects.
2.5. Taking certain medications
Long-term treatment with certain medications (acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, antibiotics, vitamin D or C), poisoning with ethylene glycol, heavy metals are also accompanied by changes in urine analysis.
Algorithm of the doctor's actions
The disease is characterized by the severity of pain and its localization. First of all, during diagnosis, a general urine test is taken; it is by its results that deviations can be judged.
If the urine is acidic, then most likely it contains an increased amount of oxalates and urates. With a saturated alkaline composition, phosphates are usually found, the presence of which leads to urolithiasis.
Our readers recommend!
For the prevention of diseases and treatment of the kidneys and urinary system, our readers recommend Father George's Monastic Tea. It consists of 16 of the most beneficial medicinal herbs, which are extremely effective in cleansing the kidneys, in the treatment of kidney diseases, urinary tract diseases, and in cleansing the body as a whole. Doctors' opinion. »
High oxalate levels are caused by excessive consumption of acidic foods. It could be sorrel, apples, oranges. Therefore, the doctor must find out what food the patient consumed before taking the test over the past 4-5 days.
After a general urine test has shown that deviations from the norm exist, an X-ray of the urinary tract and cystoscopy are performed. as well as ultrasound of the bladder.
With a comprehensive combination of all test results, a course of treatment is prescribed.
What symptoms might there be?
The excretion of salts in the urine is not always accompanied by any symptoms. Even their high concentration does not manifest itself in any way for a long time, but from the appearance of the collected portion one can suspect the presence of impurities:
- 1Sample turbidity.
- 2Formation of sediment in the container during prolonged standing.
- 3 Strong odor, mucus discharge, or significant color change.
The patient may complain of a burning sensation when urinating, abdominal and lumbar pain, headache, fever, frequent urge to urinate and difficulty urinating.
In children, pregnant women, and in the physiological conditions listed above, the appearance of salts in the urine may not be accompanied by any symptoms. They disappear on their own after some time.
Uric acid level
Uric acid levels vary among children, women, men, and the elderly. Acceptable indicators:
- in the child’s urine the level of uric acid should be from 120 to 300 µmol/l;
- in males, the value should not be lower than 200 and exceed 420 µmol/l;
- the female body is expected to have a norm of 160-320 µmol/l;
- after both sexes reach the age of 60, the acceptable level of uric acid is the same and is 210-430 µmol/l.
Diagnostic methods
It is quite simple to detect urates, oxalates and other salts in the urine of both adults and children. To do this, you need to collect morning urine in a sterile container and submit it to the laboratory for general analysis. In the result form, their number is indicated by plus signs (from + to ++++)
Salts can also be detected at home using special test strips. The concentration is determined by a chemical reaction and a change in the color of the indicator.
If a large amount of salts is detected, the analysis must be repeated. If the result is similar to the previous one, the doctor assesses the need for further examination: ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, blood tests to clarify the type of metabolic disorder.
What accompanies the appearance of sediment in the urine?
Single one-time increases in the amount of salts that form a precipitate are completely asymptomatic in humans.
If the abnormal salt ratio is caused by urolithiasis, infection in the urinary system or diseases in the bladder, kidneys or liver, then in addition to the constant presence of sediment, the following signs will be observed:
- pain when urinating and frequent pain of various types in the pelvis, abdomen or lower back;
- difficulty and prolonged urination;
- nausea, general poor health;
- constant or periodic increase in body temperature.
Treatment approaches
Therapeutic measures depend on the cause of the appearance of salts. If physiological factors are to blame (intense physical activity, sun exposure, heavy sweating), then the level of crystals decreases over time on its own.
In other cases, it is necessary to take measures to prevent the loss of urinary sediment, since a constantly high salt concentration contributes to the development of nephrolithiasis.
5.1. Diet
The basis of therapy is a therapeutic diet, which normalizes the acidity of urine and helps remove excess salts from the body.
| Salts | Food |
| Urats | Berries, fruits, dried fruits |
| Vegetables (pumpkin, potatoes, eggplant, cauliflower) | |
| Cereals, grain bread | |
| Flour and confectionery products | |
| Alkaline mineral water | |
| Oxalates | Drinking water up to 3 liters per day |
| Apples, pears, apricots, vegetable soups, potatoes | |
| Porridge with milk. White bread, loaf, pasta | |
| Butter or vegetable oil, cottage cheese, eggs | |
| Phosphates | Mineral water up to 3 liters per day. Juices |
| Berries and fruits are sour. Legumes. Vegetables: cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin, potatoes | |
| Cereals, porridges, pasta | |
| Meat fish |
Table 1 - Recommended food products
Folk remedies
First of all, it is worth understanding that the effectiveness of traditional treatment methods has not been clinically confirmed, and therefore you can resort to them only at your own peril and risk. One of the recipes aimed at preventively cleansing the body of salts is as follows:
- pour five grams of bay leaf into a glass of boiling water,
- Bring to a boil in a water bath and keep for another five minutes.
- leave the resulting decoction for 3-4 hours,
- strain this liquid and take several sips throughout the day,
- These procedures should be carried out for 3 days in a row, 1-2 times a year.
Another recipe, and a rather harmless one, is to use rice using this method:
- soak the grain by soaking 2 tablespoons in cold water for a day,
- the next day, porridge is cooked from this cereal for breakfast (eaten without salt, sugar or other seasonings),
- After an hour, you are allowed to have a snack with regular foods.
Of course, treating yourself on your own is far from the best idea; it is better to entrust this matter to doctors.
Physiotherapy for gout
Experts often recommend that patients resort to physiotherapeutic procedures during the treatment of gout. Gout is a disease in which uric acid crystals are deposited in joints, primarily the big toes. One of the physiotherapeutic procedures is pasmophoresis, which cleanses the blood of the increased salt content of acidic urine. It should be remembered that the effectiveness of plasmaphoresis does not last for a long period of time if, in parallel with it, the patient does not follow a special diet.
The diet allows not only to increase the excretion of uric acid from the body, but also to improve the general condition of the patient and his organs. It is important for a person to strictly follow the prescribed healthy diet and exclude from the diet all foods that have been prohibited by the doctor. Since gout is a chronic disease, the patient will need to maintain a balanced diet that excludes foods containing purine throughout his life.