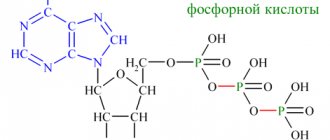
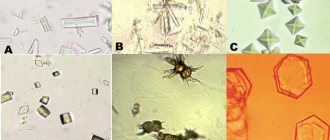
What it is? Oxalates in urine are salts of oxalic acid, which are organic dibasic compounds. Such components are present in small quantities normally, but most often their presence indicates hidden diseases of the body.
The level of oxalates in urine can be determined using a biochemical analysis; the biological material is blood; urine is less commonly used.
The most dangerous consequences of oxalates are kidney and bladder stones. Only 25% of formations in the urinary system dissolve independently in organic liquids. The remaining 75% must be removed surgically. This explains the relevance of the “oxalate” issue.
Indications for testing for the presence of oxalates in urine are frequent urination, increased volume of urine (polyuria). Pain can be observed in the lower abdomen - in the bladder area, above the lumbar segment of the back and in the side - renal colic.
- Unpleasant sensations are often accompanied by weakness and fatigue. Such clinical signs require an oxalate study.
What do oxalates in urine mean?
Oxalate salts are present in moderate amounts in the urine of adults and children. Calcium oxalate enters the body not only with certain foods, but is also produced in small quantities in the small intestine during the oxidation of vitamin C and glyoxylic acid. Within normal limits, oxalates do not exhibit harmful effects; microcrystals are present in the urine of any healthy person.
Under the influence of provoking factors, with excessive consumption of foods containing a lot of oxalic acid, oxaluria develops, the functioning of the bladder and kidneys worsens, and there are abnormalities in urine analysis.
Among the unpleasant consequences:
- painful renal colic;
- deposition of salts in various organs;
- excess or decreased urine production;
- severe intoxication due to stagnation of urine;
- nephrocalcinosis.
Oxaluria ICD code – 10 – E74.8 (Other specified pathologies of carbohydrate metabolism).
Find out how to prepare a millet infusion for the kidneys and how to use the folk remedy.
Instructions for using the drug Nephrosten from Evalar for the treatment of kidneys are described in this article.
Reasons for the accumulation of salts in the body
The accumulation of oxalic acid salts occurs in the following cases:
- persistent oxaluria;
- congenital disorders of metabolic processes of aldehyde acids;
- bacterial kidney infections;
- diabetes;
- poisoning from consuming technical fluids containing ethylene glycol;
- excessive consumption of ascorbic acid (more than 5 mg per day);
- decreased activity of enzymes that break down substances in the small intestine;
- renal tubular acidosis.
Provoking factors and diseases:
- pyelonephritis;
- diabetes;
- poor nutrition;
- history of nephrolithiasis;
- intestinal diseases, operations on this part of the digestive tract;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- lack of Oxalobacter formigenes bacteria in the intestines;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive system;
- deficiency of vitamin B6 and magnesium;
- chronic pathologies of the large intestine;
- development of candidiasis with oxalate deposits in the lungs.
Nephrologists pay attention to the acidity of urine: at a pH level of 5 to 7 (normal), oxalates do not accumulate; changes in levels above 7 or below 5 provoke precipitation. For control, tests are prescribed several times at certain intervals: sometimes the pH level changes briefly to remove excess acidic metabolic products. If the content of calcium oxalate is several times higher than the optimal values, then nephrologists talk about the development of oxaluria.
Diagnostics
Oxalates in daily urine can be detected using diagnostic measures. If a pathology is suspected, the doctor orders the patient to undergo laboratory tests. Urine is submitted for general and biochemical analysis. With their help, you can determine the number of leukocytes and whether a lot of salts have appeared. Using laboratory tests, you can detect the bacteria that caused the inflammatory process. If the results indicate two pluses or more, then they mean the presence of oxalaturia. If urination is impaired, the patient is recommended to undergo ultrasound diagnostics of the kidneys. If the disease is detected in a timely manner and treatment is started, it is possible to avoid pathological processes in the kidneys that arise due to the accumulation of urine and stones.
Norm and deviations of indicators
To monitor the level of calcium oxalate crystals, a urine test is prescribed. A nephrologist studies the results, gives recommendations for correcting the diet, selects medications and herbal decoctions, and indicates how much fluid the patient should drink per day.
| Patient age | Norm of oxalates (volume of salt excretion during the day) |
| Children under 1 year | 1 to 1.3 mg |
| Adults | Up to 40 mg |
Important! Deviations (increases in the amount of oxalates) necessarily require correction with the help of medications and diet.
Normal values
The level of oxalates in the urine of any adult should not exceed 40 mg/day. If we are talking about small children or patients of preschool and school age, then the concentration of the substance in them is 1-1.3 mg/day.
It is necessary to understand that the level of oxalaturia is assessed not according to the data of a single study, but according to the results of diagnostics of 24-hour urine. In this case, the acidity of urine is necessarily assessed, which is considered optimal when {amp}gt; 5 pH
A certain concentration of oxalic acid salts (oxalates) is present in the urine of even an absolutely healthy person
How to get your numbers back to normal
Treatment of oxaluria is carried out after diagnostic measures. To confirm the diagnosis, an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder and a urine test are prescribed. Mandatory points: clarification of general health, eating habits, drinking regime.
Doctors identify five components of therapy:
- taking medications;
- correct drinking regime;
- strict diet;
- lifestyle correction;
- treatment of chronic pathologies.
Diet and nutrition rules
The rate of decrease in the concentration of calcium oxalate in the body depends on compliance with the recommendations. It is important to strictly adhere to the diet for oxalates in the urine, indicated by the nephrologist. Doctors warn: oxalates dissolve worse than urates, therapy is long-term.
Recommendations:
- drink from 2 to 2.5 liters of liquid: water, vegetable soups, compotes, herbal teas, mineral waters as prescribed by the doctor;
- bake and cook dishes;
- Smoked and spicy foods are prohibited from being consumed: it is important to reduce the load on the kidneys, intestines, stomach, and liver;
- minimal salt consumption, especially with pronounced swelling;
- dairy diet;
- reduce the intake of fats and carbohydrates;
- Items with synthetic flavors, dyes, and preservatives are prohibited.
Authorized products:
- rice;
- White bread;
- non-acidic berries and fruits;
- egg white;
- minimal amount of lightly salted herring;
- pasta;
- cucumber, squash and pumpkin juices (combine with antihypoxic drugs);
- sour apples, sea buckthorn;
- lean fish, lean meat;
- borscht and soups made with vegetable broth (do not fry).
Learn about the symptoms of bladder stones in men and the treatment of the pathology.
How to take Canephron for kidney diseases? The rules of application are described in this article.
Follow the link to read about the signs and symptoms of acute kidney failure in women.
Exclude from the diet:
- citrus;
- eggplant;
- tomatoes;
- red grapes and dark plums;
- sorrel;
- parsley;
- buckwheat;
- wheat bran;
- celery;
- spinach;
- oats;
- rhubarb;
- beets;
- rosehip decoction;
- peanut;
- legumes;
- chocolate.
Drug therapy
Recommendations:
- consumption of magnesium (Asparkam, Magnesium +, Magne – B6) and pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6);
- preparations for dissolving oxalates. Cyston is an effective herbal remedy, Cholestyramine is a modern synthetic drug. Uronefron, Xidifon, Potassium Citrate actively dissolve salts;
- vitamin complexes: Riboflavin, Fitin;
- If urine stagnates, diuretics are prescribed to remove excess fluid.
Prevention
To avoid the disease in men and women, it is necessary to take preventive measures. First of all, you should limit your intake of acidic foods and reduce the amount of vitamin C in your diet. The daily fluid intake should be increased to 2 liters. To avoid pathology, you should lead an active lifestyle and take breaks during sedentary work so that urine does not accumulate and stagnation does not occur. When the first unpleasant symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Oxalates in the urine of a child
Accumulation of calcium oxalate occurs even in newborns with genetic disorders: primary hyperoxaluria develops. The progression of the disease causes brittle bones, the appearance of stones in the bladder, blood stagnation, and chronic renal failure.
One of the factors that provokes the accumulation of oxalates is problems with intestinal function:
- partial fusion of the short intestine;
- poor absorption of bile cholic acids from the digestive tract;
- malabsorption in the small intestine.
The active development of the pathological process begins at 5 years and older with an expansion of the diet. Parents often provoke problems with the kidneys and bladder, often including foods containing calcium oxalate in the menu of preschoolers and schoolchildren.
Do not overload your diet with the following dishes and products:
- blackcurrant juices and jelly;
- green apples;
- jellied meats, strong broths;
- chocolate, cocoa-based drinks;
- salads with sorrel, parsley, spinach, beets.
In adolescence, the disease progresses, new signs appear, and the main symptoms are more pronounced:
- increased blood pressure;
- overweight, clearly visible accumulations of fat;
- allergies of various kinds;
- headache;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- change in the color of urine: the shade is more saturated;
- general weakness;
- frequent urination;
- discomfort in the abdominal area;
- urine volume is higher or lower than normal.
Treatment:
- diet correction is similar to the diet for adults;
- prescribing medications with magnesium and vitamin B6;
- potassium citrate with meals;
- diuretic teas for poor fluid discharge. According to the doctor's recommendation, brew horsetail, corn silk, and black elderberry (flowers) for the young patient. The leaves of mint, lingonberry, strawberry, and knotweed are useful. All medicinal plants are selected by a nephrologist taking into account the child’s age;
- sufficient amount of liquid. Depending on age, children should receive fluid (measurement - ml per 1 kg of weight): six months - 140, 1 year - 125, 7 years - 95, 14 years - 55 ml. The best option is to drink water half an hour before meals or 60–90 minutes after meals.
Preventive recommendations
Basic rules for preventing relapses:
- moderate consumption of foods containing a lot of oxalic acid: spinach, celery, sorrel, tomatoes, beets. You should not eat a lot of sour fruits and vegetables, citrus fruits;
- monitor your alcohol consumption, make sure you don’t accidentally swallow brake fluid and antifreeze instead of strong drinks (such cases are periodically recorded by doctors in toxicology departments). High load on the kidneys negatively affects the condition of the nephrons;
- control of the condition of the small intestine: in some diseases, calcium oxalate actively accumulates when the absorption of oxalates fails;
- treatment of chronic pathologies occurring against the background of metabolic disorders. Persistent oxaluria and diabetes require increased attention;
- compliance with the drinking regime: to flush out salts from the body you will need 2–2.5 liters of water per day;
- contact a nephrologist if signs of oxaluria appear.
Doctors pay attention to an important nuance: many patients with high levels of oxalates in the urine for a long period do not have obvious signs of pathology. The accumulation of oxalic acid salts against the background of chronic diseases is more difficult to recognize: the clinical signs of the underlying pathology are often brighter than the manifestations of oxaluria. For this reason, every person should have a urine test twice a year to monitor their kidney function. A simple diagnostic method reduces the risk of severe disorders of the urinary system with high concentrations of harmful salts in the kidneys, joints, and bladder.
Magnesium preparations, pyridoxine hydrochloride, diuretic teas, and compositions that dissolve calcium oxalate help in identifying oxalates in the urine. Mandatory elements of therapy: proper drinking regimen, diet, treatment of chronic pathologies. If you strictly follow the recommendations, you can get rid of oxaluria and bring the level of oxalic acid salts to normal.
Video about urine analysis in children and features of correction of indicators when oxalates are detected, Dr. Komarovsky: