Creatinine (1-methylglycocyamidine, cre) is the final metabolite of creatine phosphate, which provides muscles with energy. Creatinine is a completely burned-out waste product of metabolism and is not suitable for reuse by the body. In high concentrations, 1-methylglycocyamidine is toxic. Therefore, it enters the bloodstream for transport to the kidneys and excretion with urine. When creatinine in the blood is increased, they speak of the inability of the kidneys to fully perform filtration functions.
The diagnostic information value of determining creas by assessing the condition of the kidneys is not limited to. The level of the metabolite is used to judge the intensity of muscular activity and the balance of the diet in terms of the quantity and quality of protein.
Norm
The level of creatinine in the blood of people of different ages and gender is not the same. The unit of measurement is mmol/l.
Blood creatinine levels are shown in the table for children, men and women:
| Gender and age | mmol/l |
| Infants | 76±29 |
| Pupils | 46±19 |
| Men | 93±18 |
| Women | 63±17 |
The creatinine level changes regularly. A decrease in creatinine levels in a school-age child is explained by a decrease in metabolic rate. The age-related accumulation of muscle volume and the deterioration of the completeness of amino acid nutrition are indexed by the rise in the concentration of the slag of biological combustion of creatine phosphate. Concentration is directly proportional to muscle volume, which explains the advantage of men in this indicator. If blood creatinine has increased, what does this mean?
A high creatinine level should not be unambiguously associated with pathology, because a distinction is made between a physiological increase and a pathological one. Interpretation of analysis data is the responsibility of the therapist.
Complications with low and high levels of creatine in the blood
Deviations of creatinine from the norm, in any direction, without treatment may be accompanied by the development of complications:
- constant pain in the lumbar region;
- dysfunction of the urinary tract and kidneys;
- swelling of the face and limbs (spoils the appearance and can interfere with work);
- pathologies of the cardiovascular and pulmonary systems;
- constantly high blood pressure;
- fatigue will be present in the morning;
- in severe forms, convulsions and loss of consciousness are possible;
- sudden weight loss, without weight gain.
Creatinine is an important indicator of muscle metabolism. A change in its concentration in the blood may be a symptom of the development of severe pathologies. If such a change is triggered, then failure of the liver, kidneys or heart is possible, which will lead to death.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Mila Friedan
Promotion
The following reasons influence the creatinine content in the body:
- Gender. The muscle volume of women and men of the same age differs;
- Age. In infants, creatinine levels are high. In schoolchildren it falls, simultaneously with a decrease in metabolic rate. In an adult, it grows again, in parallel with an increase in muscle volume;
- Level of muscle load. For athletes and heavy physical labor workers, the creatinine rate is adjusted upward;
- Hormonal changes. Growing up, pregnancy. Women are more susceptible to variability;
- The muscular mass of weightlifters and bodybuilding fans;
- Balanced nutrition. Excess proteins lead to a decrease in their digestibility, which provokes an increase in creatinine and other toxic nitrogen-containing components;
- Fasting leads to rapid depletion of carbohydrate and lipid energy sources. The body has to extract calories from proteins. This process, which is the most unfavorable from an energy point of view, leads to the formation of a large amount of nitrogen-containing waste, the first of which is creatinine;
- Using protein supplements to “pump” muscles that contain creatine.
The use of protein to pump up muscles physiologically increases cratinine.
These features, the specifics of the way of life, should be taken into account by the doctor.
High creatinine or hypercreatinemia is considered the main diagnosis of many diseases. The degree of hypercoreatitisnemia is important in deciphering the biochemical blood test.
Analysis
What is the indication for the test?
The symptoms for which a specialist usually prescribes samples are as follows:
- The need for a particularly thorough medical examination when a patient decides to undergo a donor kidney transplant.
- There is a suspicion of poor kidney function or changes in the muscular system.
- Usually, a referral is given in cases that suggest a change in the level of the substance: the appearance of difficulty breathing, the presence of aching pain in the lumbar region, when a feeling of heaviness and fatigue appears.
- For symptoms of dysfunctional disorders: complaints of insomnia, constant weakness, fatigue, lack of appetite, swelling of the limbs and face, problematic urination, accompanied by burning, intermittency, discoloration, as well as foaminess, etc.
- Indications also include shock and sepsis.
A test is required before undergoing dialysis.
Preparing for analysis
When ordering a creatinine test, you need to prepare for it. To eliminate errors when conducting research, you should:
- Avoid exercise for two days before taking samples. This means that fitness classes, dancing, all kinds of workouts, running, and weight lifting are excluded. Even when going to the clinic, you should not run up stairs or expose yourself to any other stress.
- In the evening meal, any fatty foods should be excluded from the diet. In addition, foods containing large amounts of protein are also undesirable. During the day before taking samples, you should not drink alcohol, and also reduce the amount of coffee and strong tea to a minimum.
- Blood is drawn on an empty stomach. This means no food intake in the last 8 hours. But it is more effective to exclude food intake for 10-12 hours before the analysis.
- Before this, under no circumstances should you drink tea or coffee, only clean water.
- If possible, stop taking medications before taking the sample as this may also affect the results. This point must be agreed upon with the attending physician. The same applies to various pain medications, which can also change the test result. In particular, this applies to aminopyrine, phenacetin and other anti-inflammatory drugs.
- It is also necessary to refrain from smoking for at least an hour or two before blood sampling.
- It is also necessary to overcome anxiety at the time of blood sampling; immediately before taking the test, you should sit quietly for at least 15 minutes.
This preparation lists a standard set of requirements that are observed when taking any blood tests in order to eliminate errors in obtaining the result.
Carrying out analysis
There are several methods to determine creatinine levels:
- using test strips;
- Cockcroft-Gault House;
- m-house Jaffe;
- Rehberg's breakdown.
Using test strips
get results the fastest. You can buy them at a pharmacy and conduct the test yourself by applying only a drop of blood to the strip. The level of the substance will be determined by the number of horizontal stripes corresponding to its concentration in the blood. The result is obtained in just a couple of minutes. But there is a big minus here. The accuracy of such a test is not very high, so this method is not used for various diseases due to the large error.
According to Cockcroft-Gault
The Cockcroft-Gault formula is used to calculate the rate of glomerular filtration of blood in the kidneys. In other words, the efficiency of the kidneys' excretion of various substances.
Jaffe method
In this method, sequences of chemical interactions are selected in which the amount of a substance in both the blood and urine can be determined.
This method is most often used in laboratory research.
Reberg-Tareev test
This analysis helps to calculate how quickly creatinine is excreted by the kidneys. In this case, it is the level of the substance whose concentration is measured simultaneously in two substances that is calculated. As a result, you can calculate how efficiently your kidneys are working.
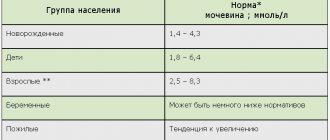
Different norms for men, women, pregnant women, children
Acceptable standards differ between different sexes, and they also change with age and lifestyle. The indicator is influenced by physical activity and hormonal processes, as well as the human constitution. In a healthy person, creatinine levels remain stable, increasing slightly with muscle contraction caused by physical activity. But sudden changes are an alarming signal indicating pathologies in the kidneys.
Level of substance in blood serum:
- For women - 53-98 μmol/l;
- For men - 55-116 μmol/l.
With proper kidney function, the rate of excretion of the substance in the urine per day is:
- For men - 8.8-17.6 m mol (1.0-2.0 g);
- For women - 7.2 15.8 m mol (0.8 -1.8 g).
In children, the norm is:
- age up to one year - 18 -36 μmol/l in blood serum;
- age up to 14 years - 27 -63 μmol/l.
During pregnancy, the level of creatine in women is 44-80 μmol/l.
Moderate hypercreatinemia
A moderate increase in creatinine in the blood (by tens of units) occurs with the following pathologies:
- Kidney diseases;
- Renal hypertension;
- Cirrhosis and toxicosis and inflammation of the liver;
- Extensive muscle and bone injuries;
- Burn disease;
- Gangrene of the limbs;
- Necrotic processes in organs;
- Graves' disease;
- Any type of diabetes mellitus that causes kidney damage;
- Hyperfunction of the adrenal medulla;
- Excessive muscle fatigue;
- Exposure to toxic substances;
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy;
- Purulent-septic situations;
- Severe injuries;
- Intestinal blockage;
- Peritognit;
- Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune pathologies;
- Side nephrotoxic effects of a number of medications;
- Dehydration;
- Heart failure;
- Toxicosis of pregnant women.
In heart failure, creatinine increases moderately
Urea is elevated in a child: reasons
In childhood, kidney pathologies are extremely rarely the cause of high urea. The main factor in increasing the indicator is acute viral-bacterial infections, which are accompanied by vomiting, fever, and intoxication.
In addition to infections, increased urea in children can be caused by:
- Lack of fluid in the body.
- Prolonged hunger.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Manifestation of diabetes mellitus.
- Burns.
- Diarrhea.
- Congenital genetic metabolic disorders.
Severe hypercreatinemia
A high increase in creatinine (by one hundred or more units) occurs with the following pathologies:
- Renal failure of the third and fourth phases;
- Breakdown of muscle tissue. Myopathy;
- Myositis generalized;
- Prolonged compression of muscle masses. Reperfusion syndrome;
- Leptospirosis. Other severe infections.
Creatinine is considered one of the main diagnostic tests for the functional capacity of the kidneys. In practical work, we have to deal primarily with this cause of hypercratinemia.
Purpose and circulation of creatinine
All chemical compounds circulating in the body can be divided into those that are constantly included in the metabolism in the form of various metabolites that transform into each other, and those substances that belong to the group of waste waste. The latter are subject to mandatory removal from the body. Blood creatinine is considered one of the few representatives of waste substances that exhibit toxic properties to tissues. Since its formation occurs constantly, it must be excreted just as regularly.
The central organs and tissues that regulate its metabolism are the kidneys, liver and muscles. Creatinine metabolism is designed in such a way that primary formation occurs in muscle tissue. It contains creatine phosphate, which breaks down during muscle contractions to produce a powerful flow of energy needed to perform movements and loads. Creatine phosphate is formed in the liver by combining the amino acid creatine with a phosphoric acid residue (phosphorylation process), from where it is sent through the bloodstream to the muscles. After the breakdown of creatine phosphate, creatinine is formed, which is excreted by the kidneys in urine.
Important to remember! The reasons for the increase in creatinine may be due to a violation of any of the stages of its circulation and metabolism!
Treatment
How to treat hypercreatinemia? It is necessary to eliminate the cause of the occurrence and reconsider the way of existence.
To do this you need:
- Conduct a computed tomography scan of the condition of muscle tissue and organs.
- Long-term persistent hypercreatininemia is the basis for treatment in a specialized medical institution.
- Strict adherence to the basic principles of the diet. Vegetarian food with the exception of seasonings, marinades and pickles.
- Dosed fluid intake. If you have kidney problems, limit water. In other situations, use high quality water as needed.
- Physiotherapy.
- Drugs that normalize protein metabolism.
- In severe cases, hemodialysis (surrogate kidney).
Physical therapy will help normalize creatinine levels
How to lower creatinine
Creatinine can be effectively reduced only by eliminating the cause of its increase and correcting lifestyle. To do this you need:
- It is imperative to conduct a thorough diagnosis to determine the condition of internal organs and muscle tissue;
- For long-term and persistent hypercreatininemia, hospitalization in medical institutions of a certain profile is indicated, where treatment will be prescribed depending on the disease and cause;
- Selection of proper nutrition. Protein foods of animal origin and fats, salt, marinades, smoked foods, seasonings, whole milk and alcohol are almost completely excluded. The diet is enriched with vegetable oils, vegetables and fruits;
- Correction of the amount of fluid consumed. If creatinine is high due to renal pathology, water intake is minimized. In all other cases, high-quality water consumed in the right quantity will help reduce this indicator;
- Correct motor mode. Adjusted depending on the general condition of the person;
- Traditional medicine: various mixtures of medicinal herbs and plants, rice water;
- Taking medications that affect protein metabolism (lespefan, ketosteril, lespinefril);
- Methods of extracorporeal detoxification and hemodialysis (artificial kidney). An extreme measure required if creatinine is elevated to critical levels.
Creatinine is a reliable indicator of the functional abilities of internal organs. Its assessment and correction should be carried out exclusively by specialists.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies and potions from the following plants that have a diuretic effect will help bring creatinine to normal:
- Nettles;
- Calendula;
- knotweed;
- Sage;
- Burdock;
- Lingonberries;
- Rosehip;
- Dandelion;
- Chamomiles;
- Mint;
- Oak;
- Birches.
Nettle recipe
Nettle leaves have a diuretic and restorative effect. Pairs well with knotweed and calendula. Two spoons of the mix are poured with boiling water (a glass), infused, and filtered. Drink it in a couple of days.
Medicinal collection
Three spoons of a medicinal mixture containing sage, burdock, dandelion leaves, birch bark, pour boiling water (a glass), filter and drink three spoons before bed.
Infusions
Lingonberry foliage (60g) is poured with boiling water (a glass), kept in a water bath for 30 minutes, and cooled. Drink 1/3 glass three times a day. You can make a collection of lingonberries, motherwort, chamomile, dandelion, string, and violets. An infusion of chamomile and mint is prepared in the same way.
Lingonberry infusion
Four tablespoons of a mixture of dandelion root, aerial parts of St. John's wort, celandine and violet flowers, pour water (two glasses), boil, leave for an hour, filter. Drink 5 ml three times a day, half an hour before meals for 30 days.
Oak bark is used in a mixture with bearberry grass. In the first option, take two spoons of the mixture. Fill with water (glass). Bring to a boil, strain. Drink 6 tablespoons three times a day.
Another option is oak bark, birch bark, birch buds. Four spoons of the mixture are boiled for one hour. Cool, infuse, filter and drink 100 ml six times a day.
Fruit mixture
A mixture of fruits, leaves of rose hips, hawthorn, parsley root, and dill seeds has a good effect. A spoonful of the mixture is poured into a glass of boiling water and left overnight. Dosage: seven doses of five spoons per day.
The use of folk remedies is combined with adherence to the water regime. You need to drink at least one and a half and no more than two liters of fluid per day. Lack and excess of water prevents the excretion of excess creatinine.
What to do to prevent high creatinine? Promote moderation in lifestyle. Avoid excessive physical activity, exhausting religious fasts and weight loss diets. Regular examinations, morning exercises, and a balanced diet will help you avoid troubles caused by a distortion of nitrogen metabolism.
Creatinine is considered a reliable indicator of the functional capabilities of internal organs. Assessment and correction of the situation caused by hypercreatinimia must be carried out by medical professionals.
Clearance - what does it mean?
Clearance is an indicator of the rate of purification of biological fluids and body tissues from substances that are in the process of transformation, redistribution and removal from the body. Negative clearance is characterized by a negative value and indicates the retention of the substance in the blood plasma.
The test evaluates:
- excretory and metabolic function of organs;
- the amount of local blood circulation;
- metabolic processes.
In medical practice, laboratory testing of clearance makes it possible to diagnose pathologies of the hepatobiliary and urinary systems.