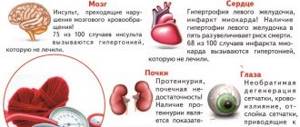
Many people are interested in the question: is beer harmful to the kidneys? Opinions on this matter are quite varied. Beer increases the load on the organ when consumed. But some believe that the drink is not harmful because it has a low alcohol concentration. What negative effects does drinking beer have on a person or, conversely, can the drink be consumed in unlimited quantities?
The effect of beer on the body
Benefits of drinking the drink
Beer is prepared on the basis of natural products - hops, malt and brewer's yeast. In general, the drink contains vitamins B and PP. As well as minerals - selenium, copper, iron, phosphorus. If you drink the drink in moderation, up to a glass a day, the benefits are noticeable. The drink strengthens the musculoskeletal system, dilates blood vessels, increases the number of red blood cells, calms the nervous system and tones. The benefits of beer are obvious if you use it externally. It has a good effect on the hair structure and has a beneficial effect on the facial skin in the form of masks. It also helps as a lotion for boils.
Harm from beer
However, beer is more harmful to the kidneys than beneficial. The drink contains a small amount of alcohol. Long-term use, even in small quantities, can lead to beer alcoholism, which is almost incurable. Even non-alcoholic drinks are dangerous. In addition, intoxicating liquid increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, varicose veins, oncology, liver cirrhosis, and kidney failure. The hops from which the drink is brewed contain morphine. This is an addictive drug. Hormonal imbalance in men and women also indicates the dangers of intoxicated drinking. Regular leaching of magnesium and potassium salts from the body leads to edema, low stress tolerance, a tendency to depression and excessive aggression.
Composition and production technology
The reason for the popularity of non-alcoholic beer is the ability to drive a car after drinking a couple of glasses. The origin of the drink is connected with the introduction of a ban in the 1970s in Europe on driving under the influence of alcohol (previously it was punishable only if a drunk driver committed a crime). Because of this, manufacturers and sellers of alcoholic products began to suffer losses - sales fell by more than 32%. Manufacturing companies found a way out - they began selling a non-alcoholic product (Clausthaler was the first to do this).
The soft drink is made from the same ingredients as regular beer: water, malt, hops, and maltose molasses. The chemical composition is no different: of the macro- and microelements it contains the most calcium, potassium, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamins A, PP and B. These substances are useful, but there is one harmful chemical - cobalt. It is added to obtain lush foam, but with excessive consumption of a cobalt-containing product, pathologies of the liver and heart develop.
The nutritional value of the non-alcoholic product is almost similar to that of fortified beer. For comparison, in 100 grams of drinks:
- calorie content – 37 kcal in non-alcoholic beer and 43 kcal in traditional beer;
- protein – 0.2 and 0.5;
- carbohydrates – 7 and 3.6;
- fats – 0 and 0;
- glycemic index – 90 and 110.
Non-alcoholic beer is produced in one of 4 ways. The first is interruption of fermentation (pasteurization or filtration of yeast). The procedure is not easy, so it is practically not used now. More common is the addition of yeast strains that consume simple glucose and leave maltose alone (because of this, fermentation slows down on its own, without human intervention). The downside is the characteristic sweetish taste, which not everyone likes.
The third way to make a soft drink is to add lactic acid bacteria to a product with 10% strength. When boiling, microorganisms neutralize the resulting ethyl alcohol, reducing the temperature by 9–10 times. The process is long and labor-intensive, but it allows you to get beer that does not differ in taste from fortified beer.
Another method is evaporation of alcohol in distillation units. The taste and color of the beer is watery, but manufacturers use this method to reduce the price of the product.
How does beer affect the kidneys?
Beer is an alcoholic drink, which means it causes inflammatory processes in the kidneys, intoxication and micronutrient deficiency.
Beer has a negative effect on the filtering properties of the kidneys.
The bean-shaped organ cleanses the body of toxic substances. In addition to a small amount of useful substances, alcoholic liquid contains many poisons. These are aldehyde, ketone, several types of alcohol, esters. All these poisons pass through the excretory organ and poison it. The effect of beer on the kidneys is harmful due to its diuretic properties. If you drink beer in large quantities, the nephrons, where the incoming liquid is filtered, work at full capacity and die. Because of this, the natural filter decreases in size and does not fully perform its function. This can lead to a pathological condition such as kidney failure. When the kidneys become inflamed and painful, the symptoms appear as follows:
- nagging pain in the lumbar region and radiating throughout the back;
- temperature increase;
- blood impurities in urine;
- increased hydrosis at night;
- loss of appetite;
- urination accompanied by pain.
Benefits and harms
Although beer contains vitamins and minerals, they are not beneficial. To make up for the daily requirement, you need to drink more than a liter, and this amount is unsafe - you end up with an excess of calories and fast carbohydrates. Several bottles of the foamy drink raise blood sugar, which is dangerous for diabetics.
Non-alcoholic beer is bad for the kidneys and liver. The cardiovascular system receives a greater load. A hormonal imbalance occurs - the product increases estrogen in the blood, which for men threatens testosterone deficiency.
Beneficial features
Claims about the benefits of non-alcoholic beer are still only hypotheses. For example, since 2020, Japanese scientists have been conducting research on the increased anti-carcinogenic resistance of the body when consuming products with hops that have not undergone complete fermentation. Experiments on laboratory mice drinking a small amount of weak drink daily showed a stop in the growth of cancerous tumors by 5–18%. But no such effect was found in humans, so it is impossible to say that beer can save you from cancer.
Another scientific study on whether drinking non-alcoholic beer is beneficial or harmful is being conducted in Copenhagen. The journal “Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases” published an article about the progress of an experiment with 220 participants - scientists are studying how the product affects the brain, blood vessels and heart. In the control group, consuming the product 2-3 times a week, there was an improvement in brain activity, as well as a decrease in the growth rate of atherosclerotic plaques. But the research has not yet been completed and it is impossible to say with certainty what exactly is the reason for the positive dynamics.
Negative Impact
A small glass every 5-6 days will not do any harm. A dangerous effect on the body occurs with excessive use (more than 1.2 liters per week). Unlike alcoholic beer, you cannot get used to a non-alcoholic product (there is no physical dependence). The danger of abuse is as follows:
A decrease in testosterone levels in the male body and its replacement with phytoestrogens leads to serious changes. Men gain weight according to the female type (deposits appear on the sides, abdomen, buttocks, arms), the mammary glands enlarge, and potency deteriorates.
- Load harmful to the cardiovascular system.
Non-alcoholic beer has increased diuretic properties. This is harmful because excessive stress on the kidneys leads to increased blood pressure and increases the likelihood of a heart attack and stroke.
- Joint destruction.
Substances from beer are processed by the body into uric acid. If there is a lot of it, the synovial fluid begins to corrode. The result is arthritis, arthrosis, gout.
Important: non-alcoholic beer poses a great danger to the liver. The drink contains fusel oils. In non-alcoholic varieties there are 5 times less of them than in alcoholic ones, but they tend to accumulate in tissues. At increased concentrations, the destruction of hepatocytes begins. Oils can also corrode the gastric mucosa, which leads to gastritis and ulcers.
Beer ailments
The intoxicating drink causes natural filters to wear out. Because of this, dangerous diseases such as protein excretion in the urine, degenerative changes in the kidneys (nephrosis), complications of pyelonephritis, renal failure (kidney failure), and cancer can develop. If necrosis of the renal tubules occurs under the influence of alcohol, the patient may fall into a coma and die.
The most common disease caused by drinking foam is kidney stones. This causes calculous pyelonephritis, which leads to serous inflammation of the parenchyma of the excretory organs. With urolithiasis, there is a risk of urosepsis. This condition threatens the death of the patient, since pathogenic microflora spreads through the bloodstream to all systems and organs and poisons the body. Therefore, beer cannot be good for the kidneys.
Consequences of treatment
Long-term consumption of alcoholic beverages is addictive, and a person gradually increases the daily “norm”. Excessive consumption of drinks of this kind leads to the destruction of internal organs, especially the kidneys and liver. The causes of destructive processes are metabolic failure and prolonged intoxication. Toxins from alcohol accumulate in tissues and are released into the body long after consumption.
The increase in size and flabbiness of internal organs is explained by granular dystrophy, which develops against the background of alcohol abuse. Ignoring the problem for a long time and continuing to drink alcohol can cause kidney necrosis. Treatment of urolithiasis with alcoholic beverages can lead to the development of toxic necronephrosis, which gradually turns into the form of pyelonephritis. In the kidneys, the metabolic rate decreases and the circulation of uric acid is disrupted.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=lnnHt2qIEJ4
Urolithiasis disease
As already mentioned, drinking alcohol increases the load on the kidneys, therefore, with frequent consumption of alcohol-containing drinks, an insoluble sediment of protein origin is formed in the urinary tract. Initially, it is microscopic crystals, which over time increase in volume, merge with each other and turn into stones.
Drinking large amounts of beer leads to an imbalance in the acid-base balance in the human body, which is a predisposing factor to the formation of kidney stones. Therefore, every glass of beer you drink accelerates the development of urolithiasis, which often manifests itself as severe pain in the lower back.
Another danger of this drink lies in the fact that many manufacturers do not follow the technology for making beer, as a result of which its composition can often contain a large number of various impurities that are deposited in the urinary tract in the form of salts. And if the kidneys are already weakened due to regular increased load, then the chances of developing urolithiasis are close to 100% - it’s only a matter of time.
When the filtration capacity of an organ is impaired, the flow of fluid through the tubules slows down, creating favorable conditions for sedimentation, including in the form of those substances that are contained in ordinary food products.