General information
With the help of the kidneys, a person filters the fluid passing through them around the clock. When a baby suffers from hydronephrosis, the kidney does not fully cope with the task assigned to it, not all metabolic products are removed, and toxic substances are retained. If hydronephrosis in newborns is not treated in time, there is a risk of deterioration in health, kidney failure, and problems with the central nervous system.
Hydronephrosis has another scientific name - hydronephrotic transformation. Often the disease accompanies a person throughout his life and does not bother him in any way. According to statistics, this disease is diagnosed more often at the age of 40-50 years. It is important to diagnose hydronephrosis using ultrasound in the womb to provide timely treatment to the newborn. But if hydronephrosis is diagnosed in a newborn, it is important to start therapy as soon as possible, then the baby will recover sooner.
Congenital hydronephrosis, stages of hydronephrosis
In adults, hydronephrosis is classified into congenital and acquired. But if we talk about a newborn baby, there is only one option - the first. Hydronephrosis of the left kidney, right kidney, and both kidneys is distinguished. Congenital hydronephrosis in infants has the following stages:
Congenital hydronephrosis can affect one or both kidneys.
- First. The medical name is pyeloectasia. Due to impaired evacuation of urine, urine accumulates, gradual compression of the kidney walls begins, it continues to function normally, but slightly increases in size.
- Second. In science it is called hydrocalycosis. Occurs several months after pyelectasis. The kidney enlarges even more and begins to function inadequately. Occurs in both one and both kidneys due to the accumulation of urine in the parenchyma channels.
- The third is terminal. The kidney becomes huge, and the parenchyma transforms. A baby's kidney may fail.
Return to contents
Causes of kidney hydronephrosis in newborns
As already stated above, the causes of hydronephrosis in newborns are only congenital. Often this disease is diagnosed in the womb, since already at the 4th week of pregnancy the embryonic kidney is practically no different from the newborn kidney. The lifestyle of its mother has a very detrimental effect on the health of the fetus. The main cause of hydronephrosis is the structural characteristics of the child’s body. These include:
- narrowing of the bladder neck;
- the outflow of urine occurs the other way around - from the bladder to the ureter;
- interruptions in the passage of nerve impulses from the kidney to the brain and back;
- high ureteral discharge;
- problems with the pelvic ureter.
Return to contents
Symptoms of the disease
Depending on the stage of the disease, different symptoms are distinguished. At the first stage there are no manifestations as such. A slightly swollen tummy can happen, but this does not always happen, and an enlarged belly in a baby may indicate another disease. Hydronephrosis provokes a lethargic state of the baby, which will eat poorly, sleep a lot, and will be passive towards toys.
If a baby scratches or scratches itself, or behaves excitedly, this is a symptom of hydronephrosis such as itching. It appears as a result of the accumulation of toxic substances in the newborn’s body that irritate the skin. And toxins appear due to a violation of the outflow of urine. The diagnosis is also confirmed by the presence of blood streaks in the baby’s urine.
If hydronephrosis progresses, the newborn is at risk of developing inflammatory processes. Then more obvious symptoms appear. These include pain when urinating and fever. By palpation, the doctor detects a tumor in the child. Therefore, you should carefully monitor the baby’s condition.
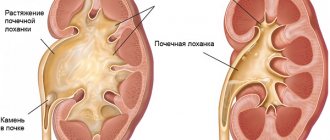
Symptoms of hydronephrosis
In the photo on the left there is a healthy kidney, and on the right there is hydronephrosis.
Often the development of kidney hydronephrosis occurs unnoticed. The disease has no specific symptoms. In the early stages, the clinical picture is determined by the cause that caused the development of hydronephrosis. For example, with urolithiasis, attacks of renal colic may occur, characterized by severe acute pain along the ureters.
As the pathology progresses, the patient complains of the following problems:
- dull pain in the lower back,
- independent of the time of day and body position;
- painful sensations are most clearly manifested in the area of the affected kidney: if the left side of the lower back hurts, then the left kidney is affected and vice versa;
- in some cases, pain appears in the right side of the abdomen;
- often painful sensations are accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
If renal hydronephrosis progresses and there is no treatment, then the following symptoms of hydronephrosis appear:
- pronounced pain from the problematic kidney;
- a painful attack is accompanied by nausea, and in some cases, vomiting;
- blood pressure increases;
- flatulence increases, the patient complains of discomfort due to bloating;
- when infection penetrates the kidney, body temperature rises - the most dangerous sign;
- there is blood in the urine - this applies to those patients who have been diagnosed with urolithiasis.
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney is one of the most common complications of urolithiasis, which can also occur on the right. Hydronephrosis of the left kidney increases the internal pressure of the calyces and pelvis. The walls of these organs “fight” high pressure for some time. Unable to withstand the pressure, the pressure gradually acts on the kidney itself, which in turn prevents urine from being released. This process can affect the tissue of the left kidney. The tubules and glomeruli atrophy and shrink. As a result, the layer of the organ in which urine was formed decreases.
The first symptoms of urinary stagnation are: acute pain in the lateral abdomen, radiating to the leg on the affected side. If hydronephrosis of the left kidney is observed, the pain will radiate to the back area.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis of the left kidney:
- pain in the kidneys, intensifying towards the damaged area;
- nervous overexcitation, anxiety;
- symptoms of intoxication of the body with nitrogenous products - loss of appetite, dizziness, migraines, vomiting and nausea, insomnia;
- back pain that radiates to the groin and under the shoulder blades;
- pain in the abdomen (stretching of the walls of the ureter due to the size of the stone);
- small amount of urine excreted per day.
- There may also be a small amount of mucus and blood when urinating.
If the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner, as well as unqualified treatment, the tissue of the left kidney can be severely damaged. This process leads to partial loss of organ functionality or even complete loss of the ability to perform its functions.
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney
Hydronephrosis of the right kidney must be treated. If this is not done, kidney failure may develop. Stopping kidney function can lead to intoxication and result in the death of the patient. Another possible outcome is urolithiasis, which can be made worse by infection. The most common complication in this case is cup rupture.
Depending on the level at which the long-term blockage occurred, hydronephrosis of the right kidney occurs with various symptoms. The most common cause is urolithiasis. Urinary stones, larger in size than the natural tracts of the excretory system, get stuck in places of narrowing, and therefore completely or partially disrupt the outflow of urine.
Symptoms and signs:
- At the initial stage of the disease, a person usually complains of renal colic; In the evening, as a rule, there is a dull pain in the lumbar region, which goes away by night.
- Attacks can be caused by physical exertion or general fatigue.
- The presence of blood in the urine is observed with increased pressure in the calyces, as well as with the presence of kidney stones.
- Another characteristic sign is an enlarged kidney. In people with an asthenic physique, it can even be felt through the anterior wall of the abdomen.
Diagnostics
The disease can be diagnosed by ultrasound in the fetus at 20 weeks of gestation. Then the pregnant woman is constantly examined, and sometimes hospitalized for preservation. If the pelvis has increased in size by more than 7 millimeters, hydronephrosis is suspected. In such cases, a pediatric urologist monitors the fetus and waits for its birth. The baby’s body is so unpredictable that the disease can disappear on its own. But there is a risk of rapid deterioration, when the operation may no longer be necessary... Therefore, during the first month of life, the baby undergoes an ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys. Further studies are carried out after three months using scintigraphy, excretory urography and cystography. Subsequently, ultrasound is repeated to monitor the dynamics of the disease.
Treatment of hydronephrosis in Israel
Patients with hydronephrosis will be admitted to one of the largest clinics abroad - at the Top Ichilov Clinic medical center, at the Tel Hashomer clinic.
The child’s operation can be done in Assuta - it will be more expensive there; it can be done in the children’s clinic at Ikhilov in Dana. The department there is headed by the famous pediatric surgeon, urologist Ben Haim. Treatment at a children's clinic will be cheaper.
The cost of treatment largely depends on the duration of the operation, which can last from 2 and a half to 4 and a half hours.
Abdominal surgery will cost less than laparoscopy. Laparoscopy lasting 4 hours - the most expensive surgical option will cost $17,300.
A consultation with Ben Haim in Dana will cost $350, in Ikhilov - 700, Scinti with isotopes without anesthesia - $900, 1400 with anesthesia.
Treatment methods
Treatment of hydronephrosis in newborns often comes down to simple systematic observation. Many babies are born by caesarean section or prematurely. The organs of such a child (kidneys are no exception) are not yet fully formed and do not have the ability to function like those of children born at term. In this case, you will need systematic careful monitoring by a doctor with quarterly ultrasound. If the dynamics are positive, the duration of therapy is 3 years.
Hydronephrosis can also be detected in a child during intrauterine development. But the body of a newborn is so unpredictable that in the first months of life this disease has a chance to simply evaporate without a trace. If, after all, hydronephrosis was confirmed as a result of complex diagnostics, then treatment is required. But this does not mean that the newborn should be immediately sent for surgery. Depending on the stage of the disease, alternative methods of therapy are used.
At the first stage, all measures are aimed at accelerating urine output. During this period, the baby’s body is greatly weakened, and there is a risk of contracting an infection. If this happens, the doctor carries out symptomatic therapy with anti-inflammatory drugs. At the second stage, the doctor looks at the dynamics. If it is positive, then the therapy does not require any adjustment. If it is negative, the condition of the kidney and the general well-being of the little patient worsens, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Surgery and postoperative period
The operation used to treat hydronephrosis is called pyeloplasty. Its essence lies in the removal of damaged ureteral tissue and the further formation of a new, larger connection between the ureter and the pelvis. The most commonly used pyeloplasty in medical practice is laparoscopic pyeloplasty. Laparoscopic pyeloplasty is a gentle treatment method that will not even leave scars. The operation is based on the use of a laparoscope - a tube-shaped device with a camera located at one end. It is used to broadcast live to the screen.
Laparoscopy is one of the safest operations, because it does not even involve incisions, only small punctures. Prescribed for varying degrees of disease in children of different ages. But for newborns there are several contraindications. These are primarily small infants, premature infants, and children who have severe concomitant diseases.
The operation is so simple that after a week the newborn is ready for discharge, and the first postoperative period does not include a stay in intensive care. After this, the child must be examined by a urologist every 3 months, and a course of medications is prescribed to restore all kidney functions. In 80−90% of cases, the operation is successful. But, unfortunately, a newborn’s kidneys will not always be completely healthy; most require constant medical support.
The birth of a child brings joy and happiness to parents. It can be overshadowed by various diseases. Of particular concern is the diagnosis of renal hydronephrosis, which occurs in newborns. However, there is no reason to panic - modern medicine can quickly cure the disease.
Treatment with folk remedies
In the presence of a disease such as renal hydronephrosis in newborns, treatment with folk remedies involves eliminating the obvious symptoms of this pathology.
Recommended herbal teas:
- 50 g each of Adonis grass, oat grain, horsetail, bearberry, nettle leaves and 150 g of birch leaves;
- 100 g each of birch buds, sedum grass, horsetail, adonis, oat grain, bedstraw and hop cones;
- 250 g each of bearberry and birch buds, 50 g each of hoofed grass, horsetail and knotweed, 75 g each of bean leaves and corn silks;
- 150 g each of juniper fruits, birch leaves and dandelion roots.
To prepare the tincture, 100 g of any collection is poured into a liter of boiling water, boiled for 10 minutes, then poured into a thermos along with the green mass and left overnight. Strain and drink 100 g of tincture before meals. The course of treatment lasts 4 months, with a break of 2 weeks, after which it is continued.
For children, it is necessary to prepare the tincture in the following daily dose of the herbal mixture:
- up to 1 year – 0.5 tsp;
- up to 3 years – 1 tsp;
- 3-6 years – 1 dec. l.;
- 6-10 years – 1 tbsp. l.;
- over 10 years – 2 tbsp. l.
It should be remembered that some herbs may have contraindications.
What is hydronephrosis
The kidney filters any fluid that passes through it. If a child develops hydronephrosis, the organ cannot cope with its functions, as a result of which metabolic products and toxic substances are retained in the body. If left untreated, this condition can lead to serious consequences, including kidney failure and problems with the nervous system.
Often the disease accompanies a person throughout his life and does not manifest itself in any way, but is diagnosed after forty years. It is very important to detect hydronephrosis in the womb in order to quickly provide the child with the necessary help. If the disease is detected in a newborn, therapy should be started as soon as possible.
Classification, types, degrees of severity
Experts divide kidney hydronephrosis into types according to various characteristics. Among urologists, the classification according to ICD 10 is accepted (this is an abbreviation of the international classifier of diseases, which is also accepted in Russia and is updated every 10 years).
According to this classification, kidney hydronephrosis is primarily divided into congenital and acquired ailments. Thus, a disease initiated during the prenatal period is assigned code Q62.0 according to ICD 10.
Congenital hydronephrosis can occur both as a result of disturbances in the development of the fetus at the intrauterine stage, and due to various chromosomal abnormalities. However, a hereditary factor can lead to the development of this disease at any age. Acquired hydronephrosis also develops as a complication after a number of diseases and as a result of other pathogenic factors. It has been noted that between the ages of 20 and 60, the disease more often affects women; in old age, men are more affected, on the contrary.
And yet such a division - into primary and secondary - cannot be called complete. Pathology is also classified according to other criteria. Thus, they distinguish both hydronephrotic transformation of two kidneys and one - hydronephrosis of the right kidney or the left. Bilateral hydronephrosis is a fairly rare phenomenon; it is observed in no more than 9% of all cases of the disease.
Urologists distinguish between hydronephrosis and the degree of the disease. It can be acute or chronic. If the patient has acute hydronephrosis, treatment started on time can lead to the restoration of full kidney function. In the chronic stage, some kidney functions are lost forever. And yet, with proper treatment, it is possible to provide the patient with a normal quality of life.
Hydronephrosis is also classified according to the type of development. If the disease is complicated by an associated infection, then it proceeds according to the infected type. If not, such a disease proceeds aseptically, the symptoms in these two cases will be slightly different.
It should be noted that hydronephrosis has several degrees of severity:
- Hydronephrosis 1st degree. It can proceed quite easily. The patient sometimes does not notice the symptoms or they are not very pronounced. However, the renal pelvis (or pelvis) is already slightly stretched, the kidney is enlarged, although it still serves its purpose. At this stage, a little more than 10 ml of liquid accumulates in it.
- Hydronephrosis 2nd degree. It is characterized by further expansion of both the renal calyces and the pelvis. The tissues become thinner under the pressure of excess fluid, the kidney atrophies and copes with its functions much worse. However, it is still possible to correct the situation by tracking the symptoms in time.
- Hydronephrosis grade 3. It is considered irreversible. As a result of such advanced pathology, kidney death inevitably occurs.
Stages of the disease
In an adult, hydronephrosis can be congenital or acquired. In the case of children, only the first option is possible. The disease may affect both kidneys or one of them. The congenital disease has several stages:
- Pyeelectasia - as a result of the accumulation of urine, the walls of the kidney are compressed, it increases slightly in size, but still functions normally.
- Hydrocalycosis - the organ increases in size even more and begins to function defectively. The cause is the accumulation of urine in the renal calyces.
- Terminal - the kidney becomes large and deformed, as a result of which it may fail.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=QsDmlPcpB18
Causes of the disease
The disease is only congenital and, as a rule, is diagnosed in the womb. The main cause of pathology is the structural features of the child’s body:
- narrowing of the bladder neck;
- disturbance of urine outflow;
- disruptions in the transmission of nerve impulses from the kidney to the brain;
- hereditary predisposition.
The main factor provoking the development of hydronephrosis is narrowing of the pelvis and ureter. Most often this is due to the presence of an accessory artery, which can interfere with the outflow of urine. Sometimes the disease occurs due to an abnormality in the development of the renal vessels, due to the impact of negative factors on the body of the expectant mother.
Symptoms of the disease
Hydronephrosis in an infant may not appear immediately, which complicates diagnosis. As a rule, children with pathology become restless, and small streaks of blood can be seen in the urine. If you touch your stomach, you feel a strong tension. Itching may occur, which is associated with the accumulation of toxic substances in the body that cause skin irritation.
Often the disease is detected only when an infection is attached, which is manifested by such symptoms as high fever, vomiting, lethargy, and lack of appetite. As the disease progresses, the risk of developing inflammation increases. In this case, obvious symptoms appear: pain when urinating, high fever. On palpation a tumor is detected. If you suspect hydronephrosis, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. He will be able to make a diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Symptoms
Signs of renal dropsy at the initial stage of development are almost impossible to identify - they are weakly expressed.
Then, as the pathology progresses, the following symptoms occur:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, aches in the lumbar back, a feeling of fullness at the waist level
- Decreased amount of urine (noticeable discrepancy between the volume of liquid drunk and urine excreted)
- Dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, thirst)
- Weakness, decreased performance, dizziness, feeling of blood flowing away from the face when changing body position
- Increased blood pressure (due to compression of the renal artery)
- Bloating, tension in the anterior abdominal wall
Other signs: increased body temperature, fever, pallor, lethargy, an unpleasant strong odor from urine - a manifestation of an incipient bacterial infection.
Chronic form
A long period of time occurs in a hidden form. Main signs of the condition:
- Discomfort in the lumbar region (after eating, drinking water, minor physical activity, changing body position)
- Asthenovegetative disorders (fatigue, weakness, decreased performance)
- The appearance of blood in the urine. The presence of red blood cells, depending on the degree of urine staining, can be determined visually or using a microscope
If the clinical picture worsens, the combination of symptoms forces the patient to sleep in a supine position. The action helps to reduce intra-abdominal pressure and, due to this, improve the outflow of urine.
Attention! If body temperature rises, hospitalization is indicated, since hyperthermia is one of the signs of pyelonephritis (inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system). To confirm chronic hydronephrosis, exclude the presence of ectopic pregnancy, pancreatitis, colitis, peptic ulcer, and spinal diseases
To confirm chronic hydronephrosis, exclude the presence of ectopic pregnancy, pancreatitis, colitis, peptic ulcer, and spinal diseases.
Acute form
It develops rapidly, the pain syndrome is characterized by paroxysmal unpleasant sensations of high severity. Localization - lumbar back with transition to the groin area, perineum. The urge to urinate becomes more frequent, and pain occurs during the release of urine. During the day, dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting) are observed.
Hydronephrosis on the left
It is manifested by a number of symptoms, including pain, a feeling of fullness in the back, changes in daily diuresis (urine volume in 24 hours). Additional signs are frequently recurring increases in blood pressure and the appearance of blood in the urine. Without hardware diagnostic methods, it is impossible to confirm the presence of hydronephrosis. Differentiation is carried out with diseases of the intestines, spine, and heart.
Bilateral hydronephrosis
Occurs only in 5-10% of cases and almost always refers to congenital forms. Pathological expansion is observed simultaneously in both kidneys. Clinical manifestations are pain syndrome of the shingles type, the presence of protein in the urine, hypertension, nausea, reduction in daily diuresis.
Differentiation is carried out with pancreatitis, spinal diseases, pyelonephritis.
Therapy methods
Most often, treatment of hydronephrosis in newborns comes down to systematic observation. Many babies are born by caesarean section or prematurely. Their organs are not fully formed, so they cannot fully function. In this case, constant monitoring by a pediatrician and an ultrasound examination every three months are required. If the dynamics are positive, the duration of therapy is three years.
The disease can be detected during intrauterine development. In the first months of the baby’s life, it may disappear without a trace, but if the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment will be required. At the first stage, therapeutic measures are aimed at normalizing the process of urine excretion. During this period, the baby’s body is weakened, which increases the risk of contracting an infection. If this cannot be avoided, anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out. At the second stage, the dynamics are assessed: if it is positive, the therapy does not change. If it is negative, the condition of the kidney worsens, and surgery is prescribed.
To treat hydronephrosis, pyeloplasty is performed. During the operation, performed by laparoscopy, the damaged tissue of the ureter is removed and a new connection is formed between it and the pelvis. This is the least traumatic treatment method that leaves no scars.
For the operation, a laparoscope is used - a device made in the form of a tube, at one end of which there is a camera - it transmits the image to the screen. Laparoscopy is considered a safe operation since it does not involve incisions, only small punctures.
Surgical intervention is prescribed for children of any age, but for newborns there are certain contraindications. First of all, these are infants with low body weight, premature babies with concomitant severe diseases.
The operation is easily tolerated by newborns: at first it does not require a stay in intensive care, and after a week the baby is discharged. After this, every three months the child should be examined by a urologist, and a course of therapy aimed at restoring all kidney functions is also carried out. In 90% of cases, the operation is successful, but complete recovery is not always possible. Many children require constant medical support.
The success of treatment largely depends on how quickly the disease is detected. If the pathology affects both kidneys, the likelihood of complications increases. With unilateral hydronephrosis, therapy is more effective.
The most common consequence of the disease is pyelonephritis, which develops against the background of an associated infection. The disease may also be accompanied by intoxication of the body, which occurs due to insufficient elimination of toxic substances. The most serious complication is renal failure, which requires lifelong hemodialysis or a donor kidney transplant.
Hydronephrosis is a serious disease that requires immediate treatment, without which the child may remain disabled.
Therefore, if there is any suspicion of pathology, the baby should be shown to a doctor. Prevention of the disease is timely examination of the mother during pregnancy and the newborn in the first months of life, a healthy lifestyle to avoid negative effects on the fetus, as well as contacting a doctor if problems arise and following his instructions.
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys in newborns occurs with a frequency of one percent among all babies born. However, the danger of this disease requires special attention to its treatment. Hydronephrosis of the kidney in children is a pathology that is characterized by expansion of the pyelocaliceal system due to the accumulation of fluid in it. It develops much more often in male children than in girls.
Hydronephrosis: treatment of the disease without surgery
Renal dropsy or hydronephrosis is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the pelvis of the organ, which leads to stretching of the latter and compression of the functional tissue of the kidney. The reason for the development of this condition is the impaired flow of urine through the ureter into the bladder. An effective treatment for this pathology is an operation during which the outflow of urine is restored and plastic surgery is performed on the walls of the pelvis to reduce its size. But many people want to avoid surgical intervention, so the pressing issue is the possibility of treating hydronephrosis without surgery, using traditional medicine recipes at home. How effective such therapy can be for hydronephrosis, and what specific drugs will be needed for this, read in the article.
A few words about hydronephrosis
This disease is chronic, lasting for a long period, but at the same time constantly progressing.
This disease is chronic, lasting for a long period, but constantly progressing. During development, the disease goes through several stages, so doctors divide the development of hydronephrosis into several degrees. The first stage of the disease is asymptomatic, without causing significant inconvenience to the patient. During this period, the wall of the pelvis, despite the insufficient outflow of urine and its accumulation in the renal cavities, is practically not stretched, so the functional tissue of the organ where urine is formed does not experience any noticeable pressure. The insidiousness of the pathology is that at the first stage, when the changes are reversible, the disease can only be diagnosed by chance during an ultrasound scan of the kidneys, for example.
Seeing a doctor occurs when the first manifestations of the disease appear:
- single renal colic;
- the appearance of red blood cells in the urine (urine turns a characteristic pinkish color);
- sudden increases in blood pressure.
Even at this stage, it is difficult to diagnose hydrocele of the kidneys, since these symptoms are characteristic of many renal pathologies. The correct diagnosis is established only through additional instrumental studies (ultrasound, tomography) and analysis of the functional state of the excretory organs.
If the diagnosis turns out to be incorrect and the patient does not receive proper treatment, the pathology moves to the next stage, when the pelvis is severely deformed (enlarged), and the function of the organ is significantly reduced, that is, renal failure occurs. Hydronephrosis diagnosed at this stage requires immediate treatment, and surgical treatment. It is impossible to treat third-degree hydrocele with medication, especially using traditional methods. Such attempts will lead to aggravation of the situation with the threat of losing the kidney, therefore, regardless of the patient’s desire (or reluctance), at this stage of the development of the pathology, surgery is needed. During surgery, plastic surgery of the pelvis (pyeloplasty) is performed and the obstruction to the outflow of urine from the kidney is removed.
When are folk remedies effective for renal dropsy?
Traditional medicines can be considered as adjuncts in the preoperative period along with medications
Traditional medicines can be considered as adjuncts in the preoperative period, along with medications used to relieve the symptoms accompanying hydronephrosis. But traditional medicine recipes are especially useful in the postoperative period, when a gentle rehabilitation program is necessary. At the stage of recovery of the body, folk remedies promote tissue healing, normalization of metabolic processes after chronic azotemia, and a moderate anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect.
Herbal medicines work great during recovery after surgery for hydronephrosis in combination with dieting and limiting fluid intake. This complex prevents the development of relapses of the disease and postoperative complications, including in patients of early childhood.
Important! Even the use of folk remedies for renal dropsy requires prior consultation with the attending physician, especially when it comes to hydronphrosis in childhood. Not all plants are harmless, so it is important to follow the correct dosage when preparing potions and taking them.
Some rules for treatment with folk remedies
The drugs are taken in long courses (several months), after which they take a two-week break
There are several compositions of herbal (plant) preparations that are used for hydronephrosis at home. The drugs are taken in long courses (several months), after which a two-week break is taken. It is recommended to alternate the composition of the preparations, taking after a break infusions made according to a different recipe.
Care should be taken to select the dosage when treating children. For a child under 3 years of age, the “adult” drug is diluted with purified water 5-6 times; in the period of 3-10 years, a three-fold dilution is used and a two-fold dilution for older children.
For children and adults, plant-based kidney infusions are recommended to be taken half an hour before meals. The frequency of appointments depends on the general condition of the patient, the severity of the pathology, and the stage of its development. All herbs and other plants used for traditional treatment are usually known to traditional medicine doctors. Many plants are included in pharmacy kidney preparations; some drugs are prepared based on herbal extracts, so consult a doctor before taking traditional medicines. It is possible that some components of infusions (decoctions) are contained in medications prescribed by a doctor, and this can lead to an overdose when taking pharmaceutical and folk remedies at the same time.
Preparing herbal teas
Plants dried in the shade are first crushed, mixed in the indicated proportions, then measured with the indicated measure
All fees, the composition of which will be presented below, are prepared in approximately the same way. Plants dried in the shade are first crushed, mixed in the indicated proportions, then measured with the indicated measure. Pour two tablespoons of herbal mixtures into a glass of boiling water and leave for 24 hours in a warm place or thermos. After straining the infusion, adults take a quarter glass (50 ml) of the drug; for children, the drug is diluted in the above proportions with water. The frequency of administration usually corresponds to the amount of food consumed (3-4 times during the day). Here are the compositions of the most effective remedies for the treatment of hydronephrosis and recovery after surgery.
- Birch leaves, dandelion root, and juniper fruits are mixed in equal parts. The collection has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and moderate diuretic effect, reduces blood pressure in hypertension of renal origin.
- Currant leaves (red currant), knotweed grass, raspberry leaves, meadowsweet flowers, calamus root, chamomile flowers, a succession are mixed in equal proportions. The infusion has an analgesic and antispasmodic effect (helps with renal colic), promotes the excretion of nitrogenous bases by a healthy kidney.
- Burdock root, wormwood, chamomile (flowers), bearberry and celery root plus rose hips are mixed in a 1:2 ratio. The collection cleanses the blood of toxins, relieves inflammation and has an antibacterial effect in the genitourinary system (works as a uroseptic).
- Horsetail, hop cones, adonis, birch leaves in equal parts. The collection effectively relaxes the spasmodic walls of the ureters and facilitates the passage of urine through the outlet channels. Additionally, it has an anti-inflammatory effect and relieves low-intensity pain.
- The following are taken in equal volume fractions: knotweed grass (young plant), alder cones, celandine grass, aerial part of the grass, peppermint leaves (can be replaced with lemon balm). The infusion has an antispasmodic effect, relaxing the smooth muscles of the ureters and thereby improving the outflow of urine from the pathologically altered kidney. In addition, the drug promotes the elimination of toxins, slightly increases diuresis, while reducing blood pressure.
In addition to herbal infusions, traditional medicine recommends taking herbal teas based on one plant. To prepare a medicinal drink, use cornflower petals or heather inflorescences. An infusion of parsley root and cumin seeds is effective for many kidney ailments, including dropsy.
Traditional medicines from the garden
For hydronephrosis, traditional healers recommend using drugs from pumpkin petioles and bean leaves
Sometimes effective medicines are just under your feet, all you have to do is pick them up and prepare them. We are talking about some plants traditionally grown in gardens. For hydronephrosis, traditional healers recommend using drugs from pumpkin petioles and bean leaves.
Pumpkin is used for many diseases by consuming its juice or raw pulp. For renal dropsy, pumpkin stalk is used. It is first crushed, after which a tablespoon of the resulting mass is measured and poured with half a liter of purified (spring) water. The mixture is not boiled, but gradually heated in a water bath for half an hour, then covered with a heat-saving cloth and infused for several hours. After filtering, the prepared drug is consumed warm, four times a day, half a two-hundred-gram glass. The infusion has a strong analgesic effect in renal pathologies and promotes the outflow of urine through a narrowed ureter (relaxes the smooth muscles of the canal wall).
Simultaneously with the drug described above, it is recommended to take an infusion prepared from bean leaves. This remedy is taken for many diseases accompanied by metabolic disorders and endointoxication. The infusion is also indicated for hydronephrosis accompanied by renal failure. To prepare the product, take 4 large spoons of chopped bean flaps and add a liter of water. Next, the cooking process involves heating for two hours in a water bath. The cooled and strained drug is taken 100 ml up to 6 times a day.
Types of hydronephrosis
There are congenital and acquired hydronephrosis. Hydronephrosis in children is usually congenital.
It is also divided into 3 degrees according to severity of manifestation:
- The first degree does not show any symptoms, kidney function is not impaired, only the pelvis is dilated, but only slightly.
- The second degree is characterized by a decrease in kidney function by approximately 40%, the pelvis expands significantly, and the kidney grows in volume.
- In the third degree, kidney function
and is impaired, the excretory function suffers, kidney failure may develop, and the organ becomes very large compared to its original size.
Causes of hydronephrosis in children
With the normal functioning of the urinary system, all urine from the kidney is regularly removed from the body through the ureter and bladder. An additional vessel that puts pressure on the ureter can interfere with the excretion of urine. Also, disturbances in urine output may be associated with a change in the normal structure of the ureter (excessive narrowing), as well as its location. As a result, fluid remains in the kidney and significantly stretches it.
Numerous studies have shown that hydronephrosis in newborns is closely related to the fact that the mother smokes and drinks alcohol during pregnancy.
Uncontrolled use of drugs also has an impact on the development of kidney pathology. There is an opinion that hydronephrosis can also be caused by harmful environmental effects on a woman.
Nutritional features and therapeutic diet
Doctors require switching to a balanced and high-calorie diet, including enough amino acids and vitamins.
As with other kidney diets, the menu is selected to reduce the load on the kidneys.
Only then will they be able to perform functions and use their reserves of strength to fight hydronephrosis naturally
It is important to exclude the consumption of dangerous microelements from the diet
The attending physician can correctly create a menu, taking into account:
- Presence of swelling;
- Arterial pressure;
- General state;
- Accompanying illnesses;
- Urine tests;
- The effect of medications taken.
Nephrologists pay attention to 2 important elements that can aggravate the patient’s condition with hydronephrosis:
Protein. Its processing requires serious work from the kidneys. Violation of the excretory function does not allow the body to get rid of toxins remaining as a result of metabolic processes. But the complete exclusion of protein foods causes even greater harm to a person. Recovery (especially in old age) is long and associated with many problems
Doctors agree that patients should focus on easily digestible proteins (lean meat, dairy products) and limit their daily dose to 0.5 grams per kilogram of body weight. Salt. In each specific case, the norms of its daily consumption are calculated individually.
Patients with hydronephrosis need nutrition that promotes urine excretion, so their diet should include fasting days with:
- Compote diet: compotes from fresh berries or fruit are prepared by adding sugar (drink every 3 hours);
- Fruit diet: every 3 hours eat 300 grams of fresh fruit (particular preference is given to watermelon);
- Vegetable diet: all 5 meals during the day are replaced with a 300 gram portion of salads.
List of harmful and healthy foods
Each patient who wants to restore health must give up various broths, chocolate, legumes, fatty meats and fish, canned foods, carbonated drinks and alcohol.
For successful treatment you need to prepare dishes from vegetables. Spinach, pumpkin and cauliflower are healthy.
It is useful to include rice and buckwheat porridge in the menu. It will be cooked in water or milk with the addition of pieces of pumpkin and fruit.
Lean meat, fish and poultry remain in the diet only if they are served boiled. Sugar in reasonable quantities and dairy products are not prohibited.
Diet taking into account concomitant disease
Hydronephrosis of the kidneys is accompanied by other pathologies of the organ.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, adjustments are made to his menu:
- Combination with pyelonephritis during an exacerbation. The consumption of fresh berries and fruits is increasing. The amount of liquid you drink per day is at least 2 liters.
- Combination with uremia. The emphasis is on the consumption of baked potatoes and eggs. Protein and sodium intake are kept to a minimum. High blood pressure requires complete exclusion of salt during treatment.
- Development against the background of kidney stones. You need to drink plenty of fluids.
- With phosphaturia, it is necessary to limit the consumption of fruits and dairy products due to the high calcium content and alkalizing effect. Increased urine acidity is achieved by eating cereals, bread with lean meat.
- With uraturia, foods that are sources of purines are prohibited. Their most prominent representatives are coffee, cheese, and poultry.
- For oxaluria, reduce calcium intake with ascorbic acid. Chocolate, milk, legumes, and sorrel are subject to serious restrictions.
Kidney hydronephrosis is a dangerous pathology. Following a diet for kidney hydronephrosis can reduce the rate of its progression, reduce the damage caused, and help the body recover during and after therapy.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of hydronephrosis at an early stage are absent or mild, especially for a unilateral process. In this case, a healthy kidney works for two. If hydronephrosis is bilateral, then signs may appear in the first degree. First of all, pain occurs in the lumbar region; when bacteria are introduced, an increase in body temperature is possible.
There may be blood in the urine. As the process worsens, an enlarged kidney can be felt in the lumbar region, and the newborn’s tummy becomes larger. While the child urinates, he cries and screams. As a result of a violation of the outflow of urine, metabolic products accumulate in the baby’s body. What causes severe itching of the skin.
Hydrocele of the kidney on the left does not differ clinically from the right-sided process.
Degrees
There are three degrees of hydronephrosis:
- Hydronephrosis in 1st degree. At this stage, the pyelocaliceal apparatus of the kidney is enlarged, but this is not accompanied by an increase in the organ itself. Kidney function is preserved; the clinical picture can manifest itself with symptoms such as aching pain in the lumbar region. Sometimes hematuria (blood in the urine) may occur. In the tests, protein may be slightly increased; with hematuria, red blood cells will also be present.
- Hydronephrosis in 2 degrees. At the second stage, simultaneously with the pelvis, the kidney itself enlarges. On average, it increases by 10 - 20 percent of its original volume. However, it is worth understanding that the enlargement of the kidney does not occur due to an increase in its tissue or function, but due to the stretching of the pelvis and the accumulation of urine in them. The kidney function itself is reduced by 30–40 percent. Protein (proteinuria) begins to appear in the urine, and toxic metabolic products - creatinine and urea - increase in the blood. At this stage, the first signs of renal failure begin to appear - blood pressure rises, and renal edema appears in the morning.
- Hydronephrosis grade 3. Represents renal failure. At this stage, the kidneys almost double in size, while their function decreases by more than 60 to 70 percent. The kidney parenchyma (its tissue) almost completely atrophies, and large cavities form in its place. The kidney takes on the appearance of a multi-chamber cavity, which, in turn, is filled with urine residues. Arterial hypertension becomes resistant (difficult to treat) and blood pressure is constantly elevated. Protein continues to be lost by the body; at the terminal stage, proteinuria reaches 3 grams per liter of urine. Such a massive loss of protein provokes large swelling. Patients at this stage are very swollen, swelling is observed not only in the eye area, but throughout the body.
Hydronephrosis is also classified according to the type of development. If the disease is complicated by an associated infection, then it proceeds according to the infected type. If not, such a disease proceeds aseptically, the symptoms in these two cases will be slightly different.
Diagnosis of renal hydronephrosis in children
Hydronephrosis of the left kidney in a child develops in more cases than hydronephrosis of the right kidney. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo routine tests: blood, urine and biochemistry.
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound, and it makes it possible to detect hydronephrosis in newborns in the womb starting from the 15th week. The main symptom is an increase in the size of the kidney. If the doctor detects this sign, then the baby is observed in utero on an ongoing basis. If there are signs of hydrocele of the kidney after the birth of the baby, he is prescribed specialized treatment.
In addition, for diagnosis, the method of excretory urography is used to compare the excretory capacity of both kidneys. There is also a diagnostic technique called voiding cystourethrography. The essence of the technique is the introduction of contrast, which absorbs X-rays well, into the bladder. While the child is urinating, photographs are taken, on the basis of which one can judge the structure of the organs and the presence of reverse urine flow. And if in doubt, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is used.
How to treat?
Treatment of hydronephrosis in children consists only of surgical intervention, with the help of which the normal outflow of urine is restored. In newborns, hydronephrosis can resolve on its own within one year. That is why the baby is examined every three months. However, this monitoring method is used only for the first and second degrees of hydronephrosis. In the third case, urgent treatment is necessary. Most often, surgery for hydronephrosis is performed using an endoscopic technique. With this method, two small incisions are made through which the endoscope and the necessary devices are inserted. Endoscopy is less traumatic than the abdominal technique.
If the obstruction is located at the level of the ureter, then plastic surgery is performed. The effect of such surgical intervention is quite high. If there is a large volume of fluid inside the kidney, it is removed using catheterization.
After the operation is completed, the child is given a drainage system; it can be external or internal. If the surgeon installs an internal drainage system, the baby will be discharged from the hospital on average within a week. And with an external system, the baby spends about a month in the hospital. During the rehabilitation period after hydronephrosis, antibiotics and uroseptics are indicated. The baby must be registered with a urologist. A general urine test after surgery should be taken once every two weeks for six months. Even after 6 months, there may be leukocytosis in the urine, however, this is not a cause for concern.
Sometimes the operation is performed on a child in the womb, but this technique is very dangerous and can lead to miscarriage.
Free consultation with a urologist
Congenital hydronephrosis is an enlargement of the kidneys or pyelocaliceal system of the fetus, diagnosed during a prenatal (prenatal period) ultrasound examination of the child in the womb. Prenatal ultrasound of the fetus is a method that diagnoses various fetal anomalies in 1% of pregnant women, of which 20-30% are anomalies of the genitourinary system, 50% of which are manifested by hydronephrosis. In the absence of this research method, anomalies of the genitourinary system may not be diagnosed in time, and then after birth and at a later age they manifest themselves as pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidney), urolithiasis, hypertension, or even end-stage renal failure.
The formation and degree of hydronephrosis depends on the stage of pregnancy and the reasons that caused it. With an ultrasound examination, the bladder and kidneys of the fetus can be detected at the 15th week of gestation, and the kidneys and their structure (renal sinuses) can be examined in more detail at the 18-20th week of gestation. At 20 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus is larger and abnormalities are easier to detect. Congenital hydronephrosis has received significant attention since the advent of prenatal ultrasound, the main method for screening, however, the management and treatment of patients remains controversial. It is a known fact that early diagnosis of hydronephrosis can lead to significant anxiety for parents during subsequent pregnancies.
Pathophysiology (development of the genitourinary system in the fetus)
The ureteric sprout develops from the mesonephric (Wolfian) duct, starting from the fifth week of pregnancy. Most nephrons (functional units of the kidneys) develop by the middle of the second trimester, and their complete differentiation occurs by 36 weeks of gestation.
Embryologically, the ureter begins development as a solid cord, which then elongates and canalizes. Distal (below) the ureter, the urogenital sinus differentiates into the development of the bladder and urethra from 10 weeks to 12 weeks of gestation, respectively. Current technologies do not allow visualization of the renal parenchyma until nephrogenesis (kidney development) is complete.
The placenta, not the fetal kidneys, functions as hemodialysis for the fetus, maintaining homeostasis (constancy) of salt and water; however, between the fifth and ninth weeks of pregnancy, the fetal kidneys begin to produce hypotonic urine, increasing the amount of urine with increasing gestational age, reaching 50 ml/hour. Underdevelopment of almost any part of the genitourinary tract can contribute to the development of transient (temporary) or permanent partial or complete obstruction of the urinary tract, leading to expansion of the proximal (overlying) collecting system, which ultimately manifests itself as antenatal hydronephrosis.
This obstructive process may not be a pathology, but the result of normal development. However, if significant and persistent urinary tract obstruction is present, renal tissue may be damaged, resulting in varying degrees of cystic renal dysplasia or impaired renal function.
Most urinary system anomalies diagnosed in the prenatal period appear to be hydronephrosis or dilatation of the upper urinary tract. Generally, congenital hydronephrosis is considered to be the result of urinary tract obstruction; however, dilatation of the renal collecting system may be the result of a non-obstructive process, such as uretero-vesical reflux, non-reflux non-obstructive megaureter, plum belly syndrome (triad: congenital underdevelopment or absence of muscles of the abdominal wall; abnormalities of the urinary tract - dilatation of the ureters, megacystis; bilateral cryptorchidism). The obstructive process, especially bilateral, causes great harm to the development of the kidneys, and urine produced by the kidneys is the main component of the amniotic fluid necessary for the normal development of the fetal pulmonary system and the functioning of the fetus in general. Thus, differentiating between obstructive and non-obstructive renal disease is extremely important in determining fetal outcome. However, this is not always possible before the baby is born.
There are many reasons that can lead to congenital hydronephrosis. Congenital hydronephrosis without concomitant urinary tract abnormalities in the vast majority of cases (79-84%) is isolated congenital hydronephrosis . Researchers believe that isolated congenital hydronephrosis is the cause of physiological dilatation of the ureters at some stage of development.
As discussed in Pathophysiology, the ureters begin development as solid cords that then gradually canalize, allowing urine to flow freely from the kidneys into the bladder. Urine production begins around the 8th week of pregnancy, before the ureters are drained. This circumstance leads to temporary obstruction with hydronephrosis . By the time complete drainage of the ureters occurs, the obstruction has been relieved and hydronephrosis should resolve. At the moment, factors that disrupt the sewerage process can lead to permanent hydronephrosis .
Therefore, it is very important to differentiate benign physiological ureteral dilatation from significant obstructive disease or vesicoureteral reflux.
Prevalence of antenatal hydronephrosis
Congenital hydronephrosis is the most common congenital anomaly of the urinary tract diagnosed by prenatal ultrasound of the fetus in the womb, accounting for 50% of all anomalies of the genitourinary system. The incidence of hydronephrosis varies and depends on a number of reasons: the degree of dilatation of the pyelocaliceal system of the fetal kidneys and the stage of pregnancy at which ultrasound is performed. Typically, the incidence of significant uropathy associated with hydronephrosis is 0.2%.
Development of hydronephrosis depending on race, gender, age
Currently, there are no clinical studies proving the connection between the development of congenital hydronephrosis and race and gender. However, regarding age, numerous studies have shown that the stage of pregnancy at which hydronephrosis develops is very important. The prognosis of fetal development directly depends on the timing of the development of hydronephrosis.
Treatment of congenital hydronephrosis
Treatment depends on the severity of congenital hydronephrosis. In severe cases, surgical treatment of hydronephrosis is required. Hydronephrosis is considered severe, in which the renal pelvis is dilated to 15 mm or more. Most patients with moderate congenital hydronephrosis require a follow-up examination at 18 months of age to reassess the condition. With mild congenital hydronephrosis, the patient is under dynamic medical supervision without any treatment.
Surgical treatment of congenital hydronephrosis
Surgical treatment tactics for congenital hydronephrosis are controversial for various reasons. Firstly, the difficulty of accurate diagnosis, secondly, the cause of congenital hydronephrosis in some cases remains unclear, and finally, surgery is not always successful and complications of surgery can affect the effectiveness of treatment.
As with all fetal surgery, there is a risk of bleeding, infection or preterm labor and these should be discussed with your doctor.
Not all children with severe obstruction improve, even with successful surgery . This is because it is sometimes very difficult to determine the extent of damage to the fetal kidneys and lungs before surgery. Therefore, in almost all cases, you will need further surgical treatment after the baby is born to restore bladder drainage and protect kidney function .
After birth, a newborn with congenital hydronephrosis is recommended to undergo an ultrasound examination of the kidneys every 1-4 weeks, as well as monitoring by a neonatologist (newborn doctor) and a pediatric urologist.
The prognosis of congenital hydronephrosis directly depends on the reasons that caused the expansion of the renal collecting system. Many newborns with congenital hydronephrosis have a good prognosis . However, it must be remembered that severe bilateral hydronephrosis in combination with urinary tract obstruction and oligohydramnios, diagnosed in early pregnancy, is a precursor to an unfavorable outcome.
‹ Treatment of hydronephrosis Up Hydronephrosis during pregnancy ›
Outcomes of hydronephrosis in newborns
The outcome of the disease is greatly influenced by the timeliness of its detection. If the process is bilateral, then the frequency of complications increases. With unilateral hydronephrosis, treatment is very successful.
Among complications, the first place in frequency is occupied by pyelonephritis, which occurs against the background of an associated infection. Also, hydronephrosis is often complicated by intoxication of the body due to insufficient excretion of metabolic products. The most serious result of hydronephrosis is renal failure. It requires continued use of hemodialysis (a blood purification procedure using a special membrane) for life or a donor kidney transplant.