Planning pregnancy with urolithiasis
In most cases, urolithiasis does not have a clinically significant effect on pregnancy management and does not cause complications.
Women are advised to cure the disease before conceiving (planning) a child. Stones may cause kidney pain, reddish urine, or dysuria. If urolithiasis is detected during pregnancy, you need to consult a doctor.
It is important to know! You should consult your doctor if symptoms persist for a long period of time or are associated with serious medical conditions. You should rush to see a specialist if you detect blood in the urine or urination problems.
Failure to contact a specialist in a timely manner can lead to serious complications - urethral injury or infection. It is important to follow all doctor’s recommendations as in the acute phase. People who are already suffering from chronic kidney disease should call an ambulance. Women at risk – leading an unhealthy lifestyle and eating a high-fat diet – should consult a dietitian.
Preventive measures
Pregnant women who have chronic urolithiasis or metabolic disorders, renal abnormalities, need to pay special attention to preventing attacks and exacerbations.
To do this, adhere to the following rules:
- eat right;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- do not eat spicy, salty and fatty foods;
- adjust the daily volume of fluid you drink;
- are not overloaded physically and mentally;
- at night they get full rest.
If pain occurs during pregnancy and the woman does not know what to do, she needs to urgently visit a doctor or call emergency help. To safely carry a baby if you have urolithiasis or are predisposed to it, you need to follow the rules of prevention. This will ensure that there are no exacerbations, and will allow you to give birth to a baby independently and without complications.
Complications
Urolithiasis of the kidneys during pregnancy is not a good condition. There will be no harm to the baby, but the woman’s health can be seriously undermined. Often this pathology leads to complications:
- The risk of developing infection in the genitourinary system increases.
- The mucous membranes of the ureters become inflamed and damaged.
- The normal functioning of the kidneys is disrupted.
- Kidney failure may develop.
But the most terrible complication of urolithiasis during pregnancy is the risk of premature birth or miscarriage. Such processes develop very rarely, but the risk increases significantly with prolonged and painful renal colic. This happens because pain stimulates sensory neurons, which leads to contraction of smooth muscles, and, as a result, contraction of the uterus.
Any disease is easier to prevent and prevent. That is why, when planning a pregnancy, a woman needs to undergo examination. If the disease was diagnosed during pregnancy, then during pregnancy and childbirth with urolithiasis, any changes in the stone should be monitored and monitored at all times. Women should not self-medicate, as this can lead to dangerous consequences. At the first manifestations of the disease, you should consult a doctor.
Causes of the disease
Most often, urolithiasis develops in a woman even before pregnancy. However, the disease can occur for a long time without visible manifestations, so a woman often has no idea about the presence of the disease. Changes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman aggravate the course of the disease.
But, in some situations, urolithiasis during pregnancy develops directly under the influence of internal and external causes.
Internal factors in the development of nephrolithiasis
Internal causes of ICD include:
- pathologies of metabolic processes in the body;
- prolonged immobilization;
- acquired diseases and congenital abnormalities of the excretory organs that disrupt the normal flow of urine and
- provoking its delay;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- urine acidity disorders;
- asymptomatic bacteriuria and chronic pyelonephritis.
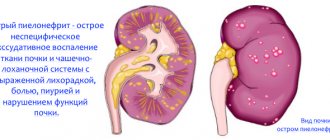
Pyelonephritis
In addition, internal factors in the formation of urolithiasis include disorders of the nervous regulation of the functioning of the excretory organs.
External causes of urolithiasis development
External reasons for the formation of stones include:
- insufficient fluid intake;
- hot climate conditions;
- diet violation;
- the effects of certain medications.
In addition, the development of nephrolithiasis can be caused by insufficient physical activity.
Diagnosis of urolithiasis in a woman
The purpose of diagnosis is to identify the cause of stone formation. The specialist determines the type, size and location of crystals in the urinary system; this is important for subsequent therapy.
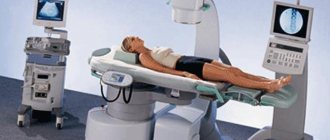
The urologist will ask about symptoms, type, location and frequency of pain, and lifestyle habits. During a physical examination, he will examine the stomach and side of the body, among other things. Using ultrasound (ultrasonography), stone formations can be detected with high accuracy. Other possible imaging modalities for diagnosing crystals in the kidneys include computed tomography (native spectral CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and excretory urography.
If urolithiasis is suspected, urine and blood are tested in the laboratory. Blood cell counts, electrolytes, creatinine, urea, coagulation values and signs of inflammation (eg C-reactive protein) are determined. The healthcare professional also evaluates the urine (blood cells, nitrite, pH). Sometimes it is necessary to collect and analyze urine within 24 hours.
- What is kidney hydronephrosis during pregnancy and why is the pathology dangerous for mother and child?
Acceptable treatments
Initially, painkillers are prescribed and possible urinary stagnation is eliminated. Kidney stones usually pass away in the urine on their own. Women should take plenty of fluids, move and use antispasmodics in moderation. If the stone does not pass spontaneously, it can be removed using minimally invasive surgical methods. The expectant mother will need to undergo additional laboratory and instrumental tests before surgical treatment.
With extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy, the doctor destroys kidney stones from the outside under ultrasound or X-ray guidance. The remaining parts are usually passed out in urine over the next 3 months. Percutaneous nephrolithotripsy is mainly used for the treatment of large stones. The endoscope is inserted through a tiny incision in the skin, then the stone is crushed and removed. In this case, the doctor inserts a special loop into the ureter.
Because the type, size, and prevalence of stones vary, there are different therapeutic approaches. The urologist selects the best individual treatment regimen based on the patient's symptoms, location and composition of the crystals. Smaller stones may be removed during cystoscopy (urethrocystoscopy).
Small urinary stones often go away naturally on their own. Spontaneous release can be stimulated by exercise and constant fluid intake. Colic is treated with analgesics - paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs allowed during pregnancy.
Sometimes alpha-blockers are prescribed, which relax smooth muscles and accelerate the removal of crystalline deposits. Indications and contraindications for the use of the medicine are determined by the attending physician depending on the trimester of pregnancy.
To prevent kidney stones, you need to take 2000-3000 ml of fluid daily. Water, diluted juices, fruits and herbal teas are suitable for rehydration. The diet should be balanced and not contain too much animal fat, salt, purines and proteins.
If serious clinical symptoms occur - hematuria, dizziness, nausea, fever or vomiting - the patient requires hospitalization. If complications occur during pregnancy, the following treatment options are available depending on the type and location of the stones:
- Litholysis: Administration of certain medications can dissolve urate and small cystine stones.
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy: Crystals in the urine are detected by ultrasound or x-ray. Subsequently, fragmentation is carried out using shock waves.
- Ureterorenoscopy: An endoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder and then advanced to the ureter and into the renal pelvis. This procedure is used to remove large stones when other methods do not work.
- Percutaneous nephrolithotripsy: To remove crystals located in the kidneys, a special needle is used to create a thin channel. Then the optical device is introduced. After this, the urinary stones are crushed or removed using a pair of instruments through the canal.
Open surgery is currently performed only in exceptional cases. Minimally invasive surgery is also rarely necessary during pregnancy.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is resorted to only if conservative therapy is ineffective and the woman’s condition is rapidly deteriorating. This situation can lead to the threat of miscarriage. Only in this case, the possible harm from surgical intervention is much less than the risk of losing the baby in the absence of prompt, timely assistance.
To remove stones, surgeons use the most gentle methods and techniques. As a rule, the operation is performed under local anesthesia.
If an attack of urolithiasis occurs at 36 weeks, then first a cesarean section is performed, and only then the kidney stones are removed.
What to do if you have symptoms of renal colic?
If you feel a sharp pain in your side or lower back associated with kidney stones, it is very dangerous to endure it. It will progress, and the patient’s condition will worsen. If treatment is not started promptly, infection may occur and sepsis may develop. Therefore, it is necessary to immediately call an ambulance and establish an accurate diagnosis. This may require additional examinations in a hospital.
There are many pathologies that can give similar symptoms, for example, appendicitis, acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis, nephroptosis, ectopic pregnancy, gastric ulcer, etc. Even if a woman has already been diagnosed with urolithiasis before pregnancy, self-diagnosis is very dangerous. You need to consult a doctor as soon as possible and determine the cause of the ailment.
Mechanisms of development of urolithiasis
The main cause of urolithiasis is considered to be a violation of water-salt metabolism. Often the disease is hereditary, occurring in several generations of patients. Lifestyle, especially nutrition, is also of great importance. Conditions such as vitamin deficiency, chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines, kidney disease, and gout provoke the development of the disease. Together, all these factors lead to the appearance of stones in the kidneys and ureter, which cause all the main symptoms of the disease.
Urolithiasis is quite rare in pregnant women. The development of an attack can be triggered by a sedentary lifestyle (especially in late pregnancy), as well as various metabolic disorders against the background of unstable hormonal levels. For expectant mothers, the only danger is a sudden exacerbation of the disease while waiting for the baby. Chronic urolithiasis, which does not manifest itself in any way during pregnancy, does not pose any threat to the woman and her child.
Etiology of pathology
Treatment of any disease first of all begins with eliminating the causes that give rise to it. That is why, despite the onset of urolithiasis even before the period under review, it is important to identify and exclude provoking factors. An important role in the etiological mechanism is played by the hereditary factor.
However, in addition to this, a number of other reasons should be highlighted:
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of spicy and sour foods that increase uric acidity, as well as excessive consumption of animal proteins and refined sugar;
- vitamin deficiency;
- diseases that disrupt metabolism;
- bone pathologies and injuries;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal system of a chronic nature (enteritis, pancreatitis);
- pathologies of the kidneys and genitourinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis).
Diet
Diet plays a major role in the treatment of urolithiasis. Allowed to eat: cereals, apricots, watermelons, peaches, pears, meat, vegetables. In limited quantities you can consume: potatoes, dairy products, legumes, eggs. Salty, spicy, smoked and fried foods should be completely excluded from the menu. The diet should contain as much plant food as possible.
- Urolithiasis: causes, features of the course, diagnosis and methods of treating the disease
Diet for kidney stones
Treatment of urolithiasis is carried out comprehensively, so doctors always accompany the pharmacological course with a specially designed diet. Following a diet facilitates the functioning of the urinary system, cleanses the body and improves the prognosis for recovery.
Dietary recommendations for urolithiasis depend on the type of stones found:
- For urate stones, restrictions apply to meat products. Sausages, wieners, and frankfurters are especially harmful to uric acid salts. For pregnant women, it is important not just to exclude meat, but to choose an equivalent substitute based on fish, vegetable proteins and dairy products.
- If calcium salts predominate, then the basis of the menu should be cereals, meat and fruits. Buckwheat and millet groats are especially useful. Chicken eggs, milk, beans and tomatoes should be completely avoided.
- If you have oxalate stones, it will be useful for a pregnant woman to eat 2-3 apples every day. Fruits such as bananas and watermelons have a beneficial effect on kidney function.
Regardless of the type of stones, fried foods, smoked foods and soda are excluded from the diet. It is harmful to abuse flour products and chocolate.
What are the dangers of urolithiasis during pregnancy?
In pregnant women suffering from urolithiasis, pyelonephritis often occurs against the background of this pathology. The expansion of the collecting system and the presence of stones creates all the conditions for the rapid development of kidney inflammation. Treatment of these diseases is carried out simultaneously, taking into account all the features of the course of pregnancy.
Urolithiasis in itself is not an indication for termination of pregnancy. It does not have a negative effect on the fetus, does not lead to the formation of developmental defects and does not interfere with the growth of the baby. Even with the development of renal colic, in most cases, doctors manage to stop the attack without consequences for the woman and child. In rare cases, severe urolithiasis can cause spontaneous miscarriage or premature birth.
Disease prevention
During pregnancy, attention should be paid to preventing the development of attacks. What needs to be done to prevent the disease?
- Complete nutrition.
- Refusal of spicy, salty, smoked foods.
- Drinking regime.
- Complete cessation of cigarettes and alcohol.
- Get enough sleep, follow a routine.
- Regular gymnastics and exercise.
Compliance with basic recommendations will help avoid the development of exacerbation of urolithiasis during pregnancy. But, if the acute form could not be avoided and the first signs of attacks appear, you should immediately consult your doctor.
Dangers and Risks
Urolithiasis during pregnancy often provokes the development of pyelonephritis. The expansion of the renal pelvis and the presence of stones create favorable conditions for rapid inflammation of the kidneys. Treatment of the disease takes into account the course of pregnancy.
Urolithiasis is not a reason for artificial termination of pregnancy; it, as a rule, does not have a negative effect on the child and does not lead to the formation of defects and developmental anomalies. Even when renal colic occurs, in most cases doctors manage to cope with the pain without consequences for the pregnant woman. Only in the most severe cases can urolithiasis cause premature labor or miscarriage.
Fruits and vegetables
Traditional methods of treatment involve the use of fruits and vegetables:
- Watermelon has a good diuretic effect. To be effective, you need to consume up to 2 kilograms per day. Pear, barberry, melon, and gooseberry have an excellent diuretic effect.
- Urine stagnation is prevented by regular white cabbage or strawberries.
- Cranberry is a natural antibiotic; you can also eat fruit drinks.
- Dill and a decoction of it are successfully used to remove excess fluid and salts from the body.
Herbal preparations
For the treatment of urolithiasis in pregnant women, plant-based preparations are more often used, since their effect is milder and does not contain substances toxic to the child. Popular drugs in this group of medications are the following:
- Cystenal;
- Canephron;
- Phytosalin;
- Cyston (helps crush kidney stones, gently eliminates spasm and inflammation of the urinary tract).
Cystenal is prescribed to prevent stone deposition, and sometimes in combination with other drugs. Used in the acute phase of the disorder. Canephron accelerates the crushing and removal of small solid deposits - sand. The drug Fitolysin prevents the formation of large stones and removes excess salts. Cyston helps crush kidney stones, gently eliminates spasm and inflammation of the urinary tract.
Herbal-based medications have two disadvantages: firstly, they can often cause allergic reactions, and secondly, such medications are powerless in exacerbating urolithiasis.
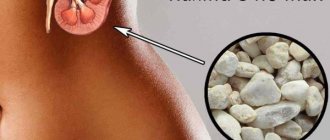
Symptoms
Stones form in the urinary organs due to changes in the chemical and physical composition of urine. They can be single or multiple; their size varies greatly: from small (less than 3 mm) to large formations (more than 10 cm). The severity of KSD symptoms is directly dependent on the size, number, position and behavior of kidney stones.
At an early stage, the pathology occurs in a latent form, without causing any unpleasant manifestations. A doctor may suspect the disease due to abnormalities in urine tests or an ultrasound of the kidneys, so all pregnant women should undergo these types of examinations.
Symptoms of kidney stone disease in the acute stage have a pronounced clinical picture. Classic renal colic causes severe cramping pain in the side or lower back, which radiates to the perineum. Often an attack occurs after physical activity, taking diuretics, or drinking plenty of fluids.
The pain is caused by the stone blocking the urinary tract. As it progresses, the source of pain moves from the lower back down the abdomen, to the inner thigh.
In addition to severe pain, kidney stones give the following symptoms:
- frequent, painful urination;
- presence of blood in the urine;
- sand discharge;
- nausea, vomiting;
- general weakness;
- fever, chills.
Some pregnant women are characterized by an atypical manifestation of renal colic. In this case, patients may experience symptoms of an acute abdomen.
A feature of the course of KSD during pregnancy is that hormonal changes in the body cause relaxation of the abdominal muscles, including the ureters and renal pelvis. As a result, stones can pass away on their own, damaging surrounding tissues, as evidenced by blood impurities.
Treatment of urolithiasis in pregnant women
The main goal of treating urolithiasis during pregnancy is to quickly and accurately separate and remove stones - hard deposits - from the excretory system, as well as relieve inflammation of the mucous membranes of the urinary tract.
- Urolithiasis symptoms and treatment in men
For this, various kidney teas based on diuretic, anti-inflammatory and disinfecting herbs are prescribed, as well as visits to mineral water resorts.
Sometimes, in the acute course of the disorder, elimination of spasm of the renal canals, pain relief, and therapy for infectious diseases are also required. Drugs with this focus cannot be chosen independently, since most antispasmodics and painkillers cannot be used by pregnant women, since their active substances pass the placental barrier. Medicines are prescribed only by a doctor.
Treatment
During pregnancy, treatment is a complex process. Many effective medications used normally cannot be used. All remedies, including traditional medicine, are selected by the attending physician. Conservative therapy for kidney stones is aimed at relieving the woman of pain and cramps, preventing the development of the inflammatory process, and, if possible, dissolving and removing the stones. For this purpose, antispasmodics, analgesics, and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Preference is given to mild herbal medicines. If the pain does not subside, a novocaine blockade is made in the uterine ligaments, and urine is removed using a catheter.
A prerequisite for conservative therapy is proper drinking regimen. The daily volume of fluid is selected individually. It is necessary for the formation of urine, the passage of stones, and the replacement of an acidic environment with an alkaline one. Herbal medicines, decoctions and infusions of diuretic herbs, and mineral water are used regularly for a long time.
A woman can try to adopt a position that reduces pain. To alleviate the condition, do not apply a warm compress or heating pad to the back and lower back, or take a hot bath.
If conventional therapy is ineffective, the condition of the expectant mother worsens and surgical intervention will be required. The indication is a developing purulent process, bleeding or symptoms of acute renal failure. From 36 weeks, labor is artificially stimulated, and after the baby is delivered by caesarean section, the stones are removed.
The most suitable period for planned surgical intervention is 15–18 weeks. From the lower and middle sections of the ureter, stones are removed through the bladder using an endoscope. Blockage of the pelvis requires emergency assistance. It is carried out in a gentle percutaneous way - kidney puncture through the skin.
Kidney stones during pregnancy sometimes have to be removed surgically
To restore the flow of urine, a temporary stent can be installed. After delivery, the ureter is dissected and stones are removed. Grinding kidney stones in pregnant women using a laser or ultrasound is not permitted.
Homeopathic treatment for urolithiasis has also been used for a long time. The natural herbal composition improves metabolic processes in a woman’s body, without causing harm to the baby. Ready-made homeopathic preparations and herbal teas include many different plants. All of them have certain contraindications and side effects. It is not recommended to use these products on your own; consultation with a specialist is necessary.
One of the components of therapy is proper nutrition, both in acute and chronic forms of the disease. The diet must be balanced and contain the necessary set of minerals and vitamins. The diet menu is selected after determining the chemical composition of the stones. Any diet must be adjusted by a doctor.
If oxalates are detected, products containing oxalic acid are prohibited. Spinach, legumes, parsley, tomatoes and celery are excluded from the menu. Dairy products and eggs are not recommended. Fruits and berries with a high content of vitamin C are subject to restrictions. Dishes with a large amount of plant fiber will be beneficial. You can eat a variety of cereals; flaxseed or olive oil is used for dressing. Vegetables: pumpkin, zucchini, cucumbers.
A decoction from the peels of pears, apples, and quinces removes oxalates. Alkaline mineral water is recommended.
If the stones consist of calcium salts, it is necessary to exclude or reduce as much as possible the amount of potatoes and legumes. Limit milk and eggs. In the diet, preference should be given to meat products, cereals and fruits. You can eat pasta and baked goods. If the stones are of urate nature, reduce the amount of meat to a minimum, exclude rich meat broths and offal. The basis of the diet should be plant foods, dairy dishes, non-sour berries and fruits.
For all types of stones, spicy, salty, fatty, smoked and fried foods are excluded from the pregnant woman’s diet. The diet includes lean meat and fish, boiled or baked, as well as steamed. Cranberry juice is useful; it has a diuretic and bactericidal effect. Watermelons, gooseberries, melons, and white cabbage have a diuretic effect.
Nature of pain and accompanying symptoms
Depending on the stage of the disease and its nature, a pregnant woman acutely feels pain symptoms, and sometimes does not feel them at all. If the problem does not manifest itself, then its effect on the body of the mother and unborn child is insignificant and does not lead to frightening consequences. If the symptoms are felt acutely, then it is urgently necessary to alleviate them and stop the exacerbation.
Prolonged pain in pregnant women is an alarming symptom that signals that you need to see a doctor.
Based on what caused the pain, its nature and location are different. It can be tolerant (mild), cutting, dull. The sensation may be localized under the ribs or in the spine. Often a pregnant woman has pain in the right side or lower abdomen. With sudden movements and physical activity, the pain intensifies or occurs suddenly. Attacks may appear and subside in cycles throughout the day. The nature of pain in the ureters is completely different in each individual case, so it is difficult to diagnose the disease.