Urolithiasis (urolithiasis) is a chronic urological disease characterized by the formation of kidney stones due to metabolic disorders and inflammation in the urinary tract.
It is usually asymptomatic, but may also be accompanied by hepatic colic or lower back pain. Urolithiasis can develop at different ages, but from 20 to 55 years it is more common. Men are more susceptible to urolithiasis; they experience symptoms of urolithiasis several times more often than women. In the latter, complex forms of this disease with the formation of stones inside the kidney are more common.
Stones can appear in any organ of the excretory system. Elderly patients are characterized by the formation of deposits inside the bladder; in younger people, the formation of insoluble structures often occurs in the ureters and kidneys. In the kidney on the right, neoplasms form more often than on the left.
Concretions can be single, but sometimes their number reaches several thousand. Their size varies - from 1-5 mm to huge ones, reaching a weight of 1 kg.
Urolithiasis in women - what is it?
Urolithiasis (symptoms and treatment in women will be discussed in the article) is characterized by the presence of stones in one of the sections of the urinary system. In women, coral-type stones most often form; they are distinguished by their ability to block the entire renal pelvis. If the pathology was diagnosed only in the later stages, partial removal of the kidney may be required.
The exact causes of the development of the disease could not be established.
The following danger factors are identified that significantly increase the likelihood of urolithiasis:
- Insufficient physical activity.
- Frequent stressful conditions.
- Having excess weight.
- Congenital diseases of the urinary system.
- Frequent consumption of meat products.
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Disturbances in metabolic processes.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Living in an environmentally unfavorable area.
In most cases, the disease develops due to congenital pathologies, as well as in the presence of diseases such as polycystic disease.
Causes
There are many causes of urolithiasis, the main ones are as follows:
- drinking water with plenty of minerals. It is also called hard water. Water supersaturated with calcium salts most strongly contributes to the development of the disease;
- a menu rich in high-protein foods, as well as too sour and spicy dishes;
- deficiencies of individual vitamins - most often belonging to group B and vitamin A;
- physical inactivity – that is, an insufficiently active lifestyle also contributes to urolithiasis;
- some bad habits. Thus, the development of stones is promoted by excessive alcohol consumption;
- taking certain medications not according to instructions, in excessive quantities;
- structural features of the urinary system. We are talking about anomalies such as a narrowed lumen of the urinary tract;
- various inflammations, including urethritis, cystitis, etc.;
- metabolic disorders;
- severe and regular dehydration;
- increased acidity of the body itself.
Many of these causes of urolithiasis can act in combination, in a complex manner - it all depends on the situation.
Classification of stones
There are several types of kidney stones. They differ from each other in location, shape and quantity.
The following groups of stones are distinguished:
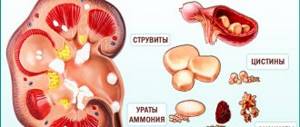
- Oxalates . Formation occurs from salts of oxalic acid. In appearance, the stone resembles a crystal, the size of which can vary up to quite large. Most often they form in people who abuse sweets and coffee. They can also form due to diabetes mellitus and vitamin B deficiency.
- Phosphates . They contain salts of phosphoric acid. Most often diagnosed by X-ray examination. The stones do not injure internal organs, as they have a smooth surface. The main reason for their appearance is considered to be infectious diseases.
- Urats . They are distinguished by their ability to be localized in absolutely any part of the urinary system; the location depends on the age of the person. They are formed due to the use of low-quality water and when the metabolic process is disrupted.
- Struvite . They can only appear in an alkaline environment during infection. They appear in the presence of certain types of bacteria and in alkaline urine.
- Cystine . They are one of the rarest types of stones, most often appearing in people at a young age. The main component is amino acid. They are characterized by severe pain that is not relieved by painkillers.
It is possible to determine the type of stones only after undergoing a special study. The symptoms of each of them are different, so there is no universal treatment for all categories of stones.
Classification
The types of stones that are found in urolithiasis are classified according to etiology, location, composition, risk of re-formation, radiological characteristics, and quantity.
According to localization, stones of the kidneys, bladder and ureter are distinguished. Depending on the quantity, stones can be multiple (sand) or single. According to the chemical composition, stones can be phosphate, oxalate, urate, cystine, uric acid, xanthine, 2,8-dihydroxyadeine, struvite.
Most often, patients are diagnosed with the following four types of stones:
- Calcium. In patients with urolithiasis, in 80% of cases calcium stones are found, which can have different texture, size and shape. Such stones for urolithiasis in men are diagnosed in cases where the patient’s age exceeds 50 years. There are phosphate, oxalate and carbonate stones. Calcium phosphate stones are less common in their pure form.
- Urate. They are detected in only 6-10% of cases. Such stones consist of uric acid salts: ammonium and sodium urate, as well as uric acid dihydrate.
- Struvite. These stones are formed due to infections of the urinary system and consist of waste products of infectious agents - magnesium-ammonium phosphates. Struvite stones are diagnosed in 10% of cases.
- Cystine. Such stones are detected in 1% of all cases. They often form in patients with a genetic pathology, which is characterized by a violation of the process of excretion of the amino acid cystine.
Symptoms of the disease
Urolithiasis (symptoms and treatment in women depend on the causes of the pathology) manifests itself with pronounced symptoms, which may differ depending on the type of stones and the stage of the pathology.
The following manifestations of the disease are distinguished:
- Pain syndrome localized in the abdomen or spine. The pain is intense and periodically intensifies.
- The pain may be accompanied by gagging.
- Inability to stay in the same position for a long time.
- Urinary disorders.
- The stream may be interrupted during urination, but the urge itself remains.
- Bloody traces appear in the urine.
- Increased urge to urinate.
- General deterioration in health, manifested by fever, weakness and chills.
Urolithiasis: causes, symptoms and treatment in women in various ways will help you learn everything about the disease.
If at this stage the disease has progressed to an advanced form, in the absence of treatment, all of the above symptoms begin to intensify. Against this background, the development of renal failure is also possible.
Renal colic
Renal colic is characterized by debilitating cramping pain.
The following symptoms are identified:
- The pain is predominantly characterized in the lumbar region.
- The pain syndrome does not decrease with a change in position, and is also poorly relieved by painkillers.
- Pain can appear at any time and is sudden.
- The attack is not associated with physical or mental stress.
Renal colic can occur for the following reasons:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Harmful working conditions.
- Polycystic kidney disease.
- Chronic dehydration.
- Stagnation of urine and the presence of inflammatory processes.
- High physical activity.
In most cases, renal colic occurs due to urolithiasis.
Hematuria
Hematuria is a process characterized by the presence of blood in the urine.
The symptoms of this condition are as follows:
- General weakness.
- The appearance of low-grade fever.
- Presence of blood in urine.
- Pallor of the skin.
- Constant feeling of thirst.
Hematuria has many causes.
These include:
- Infectious processes in the genitourinary system.
- Mechanical injuries.
- States of intoxication, severe poisoning.
- Medicines that affect the blood clotting process.
- Diseases of an autoimmune nature.
- Low blood pressure.
Often, hematuria indicates severe inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system, so if blood is detected in the urine, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic test.
Coraloid nephrolithiasis
Coral nephrolithiasis is considered an independent disease; it does not belong to the group of other pathologies associated with the formation of stones. Coral-type stones are diagnosed more often than other types. The disease is divided into 4 stages, with the transition to each stage the symptoms worsen.
Initially, the pathology manifests itself as headache, weakness and increased body temperature. As it progresses, the pain syndrome, localized in the lumbar region, intensifies.
The disease develops for the following reasons:
- Long-term living in hot climates.
- Unbalanced diet, vitamin A deficiency.
- Increased protein content in the blood.
- Infectious processes in the urinary tract.
In most cases, the disease develops due to a combination of several causes.
Associated infectious processes
Infectious conditions are manifested by the following symptoms:
- A sharp increase in body temperature, accompanied by fever.
- Weakness, excessive fatigue.
- High blood pressure.
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
- Headache and dizziness.
Infectious processes in the urinary system have several causes of development.
These include:
- Diabetes mellitus of any type.
- Reduced immunity.
- Anemia.
- Inflammation in other systems and organs.
- The appearance of kidney stones.
In some cases, infectious processes develop due to dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as due to diseases of the uterus in women.
How are stones formed?
There are several theories regarding how kidney stones form and what causes them to appear. According to the latest data, stone formation is a complex process that is influenced by many factors:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Bad ecology;
- Nutritional features;
- Region of residence - in some areas the water is hard and contains a lot of salts;
- Hormonal imbalance, especially parathyroid disorders;
- Metabolic disorders, in particular mineral metabolism;
- Anatomical features of the structure of the kidneys and urinary tract (weakness of the ligaments supporting the kidney);
- Deficiency of substances that slow down crystallization (citrate, pyrophosphate, nephrocalcin, uropontin);
- Inflammation in the renal pelvis;
- Taking sulfonamides and tetracyclines, nitrofurans together with ascorbic and other acids.
The combination of several of these factors leads to the patient developing chronic crystalluria , a pathology in which crystals of various salts appear in the urine. Stone formation is a complication of this condition. Depending on the pH of the urine and the type of salts, various stones (clusters of crystals) begin to form. Usually their place of birth is the collecting ducts and pelvis.
The process of stone formation begins with the concentration of salts in the urine increasing and them becoming insoluble. The salts crystallize around a colloidal “core,” a large organic molecule that forms the basis of a kidney stone. Subsequently, new crystals form and grow on this matrix.
Recent studies have found that almost all stones (97%) contain nanobacteria , so named because of their small size. These atypical gram-negative (not stained by the Gram method) microorganisms produce apatite (calcium carbonate) during their life processes. This mineral is deposited on the walls of kidney cells, promoting crystal growth. Nanobacteria infect the epithelium of the collecting ducts and the areas of the renal papillae, creating centers of calcium phosphate crystallization around themselves, and thereby contribute to the growth of the stone.
Diagnosis of urolithiasis
Several methods are used to diagnose kidney stones; a comprehensive examination is necessary to make a diagnosis.
The methods and their characteristics are presented in the table:
| General blood and urine analysis. | Laboratory tests can detect the inflammatory process in the body. A urine test allows you to choose the right treatment method, as it determines sensitivity to antibiotics. |
| Ultrasound | It is a priority examination technique for pregnant women, as it does absolutely no harm. Ultrasound helps determine not only the presence of stones, but also their exact location. |
| Radiography | An x-ray also allows you to determine the location and size of the stones. Cystine and urate stones are invisible on the image. |
| CT scan | It is used quite rarely, only when other methods are not informative. Most effective for coral-type stones. |
| MRI | It is one of the most informative methods, but due to its high cost it is used quite rarely. Helps determine the location, size and type of stones. |
In most cases, an accurate diagnosis is made after laboratory tests, ultrasound and x-rays. This diagnostic complex allows you to accurately determine the location of the stone, its type and size.
Treatment
Both surgical treatment methods and conservative therapy are used. Treatment tactics are determined by the urologist depending on the age and general condition of the patient, the location and size of the stone, the clinical course of urolithiasis, the presence of anatomical or physiological changes and the stage of renal failure.
General principles of treatment of urolithiasis:
- Drink plenty of fluids. Whatever the causes of urolithiasis, concentrated urine promotes the formation of new stones or the “growth” of existing ones. In case of nephrolithiasis, at least 2 liters of fluid per day is recommended.
- Diet. Depending on the nature of the pH and the prevailing salts, a diet is prescribed that helps dissolve small stones. The diet can either accelerate their dissolution or contribute to their formation and recurrence of urolithiasis even after the stone has passed.
- Physical activity. Inactivity and a sedentary lifestyle provoke the formation of stones, and walking, running, and jumping lead to the removal of microliths.
- Herbal medicine: diuretic, anti-inflammatory herbs.
- Stone removal (surgical and conservative methods).
Treatment of the disease
Urolithiasis (symptoms and treatment in women are individual, they depend on many factors) requires timely treatment.
The following general principles are used in treatment:
- Compliance with the drinking regime.
- Maintaining a balanced diet.
- Engage in moderate physical activity.
- Surgical stone removal.
- Drug treatment.
- Phytotherapy.
It is important to consider that the approach to treatment must be comprehensive. Self-medication is strictly prohibited; all medications can be taken only after a doctor’s permission.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is necessary when urolithiasis is accompanied by complications.
These include:
- Pyelonephritis, characterized by chronic inflammation of the kidneys.
- Vivid pain syndrome that is not relieved by painkillers.
- Hydronephrosis.
Traditional, endoscopic and minimally invasive methods are used for removal. Minimally invasive techniques occupy a leading position, as they do not require a long rehabilitation period.
This operation is accompanied by minor blood loss and almost always occurs without complications.
Surgery is the most effective treatment, as it allows you to completely get rid of stones. To avoid relapse, the patient must follow the doctor's recommendations.
Pyelolithotomy
This operation allows you to remove stones by cutting the renal pelvis. It is used when crushing stones is impractical; it is used for large and numerous stones.
The operation is performed in the following cases:
- For coral-type stones.
- For large stones located in the ureter.
- For large stones in the renal pelvis.
- For stones of a special type and shape that cannot be crushed.
Before surgery, the patient must undergo a series of diagnostic tests. Surgery is not performed for anemia, severe heart disease and any critical conditions.
Nephrolithotomy
The operation is characterized by dissection of the tissues of the pelvis. The intervention is carried out using a nephroscope, which allows a small incision to be made, so the method is minimally invasive.
Has the following indications:
- Coral type stones.
- Stones that are localized deep in the renal pelvis.
- If the stone size is more than 2 cm.
- Stones with a branched structure.
The rehabilitation period after surgery does not take a long time. During the first days, patients may experience pain.
Ureterolithotomy
The operation is an invasive technique. Used to remove stones located in the ureteral lumen.
This type of surgery has the following indications:
- Disturbances in the outflow of urine, which leads to expansion of the cups.
- Pyelonephritis in the acute stage.
- Large stones.
The operation requires a careful preparation period. It consists of laboratory tests, ultrasound, and in some cases an MRI may be required. After surgery, the patient must wear a special drainage and also avoid excessive activity and heavy lifting. They are discharged from the hospital no earlier than after 2 days.
X-ray endoscopic operations
The technique allows you to remove stones of various structures and sizes. It is performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia. All manipulations are carried out using a special camera, which allows you to see all the smallest details on the screen. Removal occurs with a high-precision laser.
The indications are as follows:
- Coral type stones.
- The appearance of renal colic.
- Disturbances in the outflow of urine.
- Acute pain in the kidney area.
- Acute pyelonephritis.
A distinctive feature of this method is rapid rehabilitation. After 4-5 hours the patient can leave the hospital.
Shock wave lithotripsy
This technique does not involve surgical intervention, since the destruction of stones occurs under the influence of shock waves.
Used in the following conditions:
- Difficulty in urinating.
- Pain localized in the kidney area.
- The stones available are large in size.
- Multiple stones.
This manipulation is prohibited for pregnant women, as well as for acute diseases of the urinary system.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatment involves the use of methods without surgery. It is carried out in cases where the stones are small in size and the pain syndrome can be relieved with painkillers.
Conservative treatment eliminates the symptoms of the disease and promotes the passage of stones in the urine.
In addition to medications, conservative methods include herbal medicine, diet and special physical exercises.
Antibiotics
Urolithiasis is almost always accompanied by an inflammatory process; symptoms and treatment in women depend on the stage of inflammation.
Antibiotics are most effective in the initial stages of pathology; they can be administered intravenously or taken orally. The course of treatment should not exceed 14 days. In order to choose the right drug, you need to take a blood and urine test.
The most commonly used drugs are:
- Pefloxacin. In the initial stages, take 2 tablets per day; if the disease progresses, the dosage can be doubled. Consume only before meals.
- Ampicillin . It is used in the middle stages of pathology. It is administered intramuscularly, the dose should not exceed 2 million.
- Levofloxacin . Available in tablet and injection format. The dosage varies from 200 to 700 mg per day depending on the stage of the disease.
It is worth considering that only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics; self-medication is not acceptable.
Methods of therapy
Achieving 100% recovery in chronic urolithiasis is very difficult. To eliminate the disease, both conservative (minimally invasive) and radical methods of therapy can be used.
There are general principles in the treatment of urolithiasis in women: destruction of stones and restoration of metabolic processes in the body.
Additional methods of treating urolithiasis in women are aimed at restoring blood circulation in the kidneys and optimizing water and mineral metabolism.
Diet therapy, spa treatment and physiotherapy also have a positive effect on recovery processes in the body. The optimal therapeutic method is determined after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Basic methods of stone destruction:
- drug litholysis;
- surgical removal of stones or kidneys along with them;
- ureterolitholapoxia;
- percutaneous nephrolithotripsy;
- instrumental removal of stones from the ureters;
- extracorporeal lithotripsy.
To improve the therapeutic result, some methods are combined. In modern medicine, percutaneous nephrolithotripsy, ureterorenoscopy and extracorporeal lithotripsy are most often used.
Diet and physiotherapy
Nutritionists recommend drinking at least two liters of water per day, as well as increasing the consumption of fiber-rich foods.
To select the correct products, it is necessary to take into account the chemical structure of the stones. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods rich in calcium, purine bases (adenine, guanine) and oxalic acid.
Effective methods of physiotherapy are:
- ultrasound therapy;
- inductothermy;
- sinusoidal modulated currents;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- amplipulse therapy.
Physiotherapy methods are indicated for latent disease and in remission.
Drug treatment
Medicines used to treat urolithiasis are divided into the following groups:
- analgesics (Baralgin, Tempalgin, Tramadol, Ketarol);
- antibacterial drugs (antibiotics, sulfonamides, nitrofurans, etc.);
- antispasmodics (Diprofen, Papaverine, Platifilin);
- hormonal agents (Prednisolone, Progesterone);
- immunostimulating substances (vitamins necessary for the kidneys);
- medications for the removal of urates, medications that promote the destruction of stones (Alopurinol, Solimok, Blemaren, Prolit, Fitolysin, Litovit, Hypothiazide, Asparginate, Boric acid, Magnesium asorbate, ascorbic acid, penicillamine).
The above medications prevent exacerbation of the disease, alleviate the general condition, and eliminate pain.
Surgical intervention
Radical treatment methods are used only when conservative therapy is powerless. Traditional surgery is performed under general anesthesia. This includes:
- Pyelolithotomy . The kidney stone is removed through a small incision in the renal pelvis.
- Nephrolithotomy . A surgical incision is made in the lumbar region and stones are removed from the kidney through it. This is the most difficult operation for the patient.
- Cystolithotomy . Removing stones from the bladder.
- Ureterolithotomy . Stones are removed from the ureter.
Folk remedies
Herbal medicine in combination with traditional methods of treatment will help get rid of urolithiasis, as well as recover during the rehabilitation period. To do this, you can use the following tools:
- decoction of flax, nettle leaves and rose hips;
- an infusion of half-palm herb perfectly crushes small stones;
- juice from beets, cucumbers and carrots (on an empty stomach);
- cabbage, watermelon, berries and strawberry leaves exhibit a diuretic effect;
- Cranberry juice is an excellent antibacterial agent.
In pharmacies you can buy combined herbal medicines: Prolit, Phytolysin, Cyston, Cystenal.
Drugs to lower uric acid levels
This group of drugs not only reduces uric acid levels, but also improves the patient's condition.
The following drugs are recommended:
- Febuxostat . Recommended for long-term use. The first results become noticeable after 2 months. Prohibited for severe liver diseases.
- Probenecid . Removes salt crystals from the kidneys. Take 1-2 tablets per day. The course of treatment is selected individually.
- Allopurinol . Take 1 tablet up to 4 times a day. The course of treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
Patients should note that all of the above drugs are prohibited for women during pregnancy.
Antispasmodics
Antispasmodics eliminate pain by relaxing smooth muscles and are most effective in the initial stages of the disease.
The following drugs are recommended:
- No-Shpa . A single dosage should not exceed 2 tablets; you are allowed to drink up to 240 mg per day. Without consulting a doctor, take no more than 2 days.
- Bencyclane . Allowed during pregnancy, but with caution. Take up to 4 tablets per day.
- Spasmalgon . The maximum dose is 4 tablets per day. Injections are used for acute renal colic.
Contraindications for each drug are different, so before use you must carefully read the instructions.
Painkillers
This group includes the following drugs:
- Pentalgin . Take 1 piece, the maximum dose is 4 tablets. Use is allowed for no more than 5 days.
- Nurofen . Drinking after meals is allowed with milk. The break between uses should be at least 4 hours. The maximum dosage is 4 tablets.
- Diclofenac . It is an injection; the therapeutic dose should not exceed 1 ampoule per day.
Painkillers should not be taken for a long time, as they negatively affect the condition of the entire body, in particular the kidneys.
Diuretics
Diuretics can only be used for small stones.
This group includes:
- Indapamide . Take 1 tablet per day. Mainly in the morning on an empty stomach. The course is selected individually.
- Klopamide . Start taking with 20 mg per day, if necessary, increase the dose to 40 mg per day.
- Arifon . Take in the morning, the initial dosage is 1.25 mg. If necessary, increase to 2.5 mg.
Diuretics must be taken in strict accordance with the course of therapy prescribed by the doctor. Long-term use can worsen the situation.
Painkillers
Therapeutic therapy for urolithiasis is not complete without the prescription of antispasmodics or analgesics, which are used to eliminate the pain syndrome that occurs during the passage of a stone or renal colic, by relaxing the muscle muscles. Their combination is considered most effective when administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Antispasmodics:
- No-shpa;
- Spasmalgon;
- Drotaverine;
- Scopolamine.
Analgesics:
- Papaverine with Analgin;
- Baralgin;
- Voltaren;
- Diclomax.
The combined action drug Maxigan is also used.
Patients with this disease are advised to have medications of this effect at home without fail, since the process of stone formation can repeat after treatment.
Preparations for dissolving urinary stones
They are used in the absence of complications and for small stones.
This group includes:
- Blémarin. Alkalinizes urine. In addition to the capsules themselves, the package contains strips that allow you to independently determine the acid balance.
- Spilled . The composition contains natural ingredients, so there are practically no contraindications. Aimed at improving metabolic processes, designed for a long course of administration.
- Cyston . Has antimicrobial and diuretic properties. Dissolves oxalates and phosphates. Does not affect the acid-base balance.
Drugs for dissolving stones are effective only in the initial stages of the disease; their use in the future is not advisable.
Diagnosis of ICD
The urologist examined the patient, studied the medical history and found out the time of onset and the nature of the symptoms that bother him; he prescribes the following types of studies:
- to determine leukocytes and ESR you need to take a biochemical blood test;
- determination of the content of salts, protein and casts is carried out based on urine analysis. It allows you to set the pH level. If the indicator indicates an acidic environment, this is a sign of the presence of urates. In an alkaline environment, phosphates are formed, and in a slightly acidic environment, oxalates;
- urine culture tank to determine sensitivity to a specific group of antibiotics;
- Ultrasound and CT of the urinary system allows you to accurately determine the number of stones, their shape and size;
- urography is performed to detect the source of inflammation by administering a substance to the patient;
- ureteropyelography makes it possible to evaluate the structure of the ureters;
- In order to determine the location of the stone, an x-ray or endoscopy is prescribed.
Ultrasound is one of the methods for studying pathology
Cheap medicines for the treatment of urolithiasis
List of medicines in the table:
| A drug | Action | Price |
| Drotaverine | A drug from the group of antispasmodics. Relaxes smooth muscles, thereby achieving an analgesic effect. Recommended in the early stages of the disease. | 60 rub. |
| Furagin | It has an anti-inflammatory effect, as well as a mild diuretic effect. It is used for any infectious processes in the urinary tract. | 75 rub. |
| Canephron | It has anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic and antibacterial effects. It contains only natural ingredients, so the drug does not cause side effects. | 250 rub. |
| Uronephron | Used to dissolve kidney stones. Allowed only if the stones are small. The drug is also aimed at normalizing metabolic processes. | 100 rub. |
Herbal preparations
This group of drugs treats the female body in a more gentle way, in comparison with synthetic drugs. Their advantage is considered to be a minimum of side effects, as well as permission for use by pregnant women and young children. A negative point can be called intolerance to some herbs and plants that are part of natural medicines. Therefore, the use of plant-based drugs must be agreed upon with a doctor, who recommends the dosage and duration of treatment.
The most common drugs are:
- Canephron. This medicine, which contains several types of healthy plants, effectively copes with inflammation in the genitourinary system. Canephron is also often prescribed for the rapid removal of fluid, sand and crushed stones from the body. However, it must be taken carefully by people suffering from diabetes.
- Cyston. This antiseptic drug of plant origin quickly removes stones and sand from the inflamed organ of the urinary system. But before using it, you need to make sure that the woman is not allergic to the components of Cyston, otherwise she may experience signs of an allergy such as itching, spots on the skin or a red rash.
- Cystenal. It is used in the treatment of urolithiasis, since Cystenal has several healing properties, namely diuretic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
- Phytolysin. This is an antimicrobial agent that will help get rid of the disease in a short time. The plant components present in its composition help to successfully remove stones and sand from the body, and compliance with contraindications will minimize the occurrence of negative side reactions.
Every person should know that any treatment for a disease must be prescribed by a doctor, since self-medication not only worsens the course of the pathology, but also causes serious harm to the patient’s health.
Phytotherapy
Urolithiasis (symptoms and treatment in women depend on many factors that must be taken into account when selecting therapy) in some cases can be treated with herbal medicine. It is important to consider that this method is effective only in the early stages, while herbal medicine is used as an additional remedy.
Herbal infusions eliminate the inflammatory process in the urinary system, reduce the size of stones, and also help relieve pain.
Complications
Urolithiasis, if the patient is not treated in time, can lead to more serious consequences:
- penetration, development and spread of infections in the urinary tract;
- pyelonephritis and other kidney diseases;
- nephrosclerosis. These are transformations of kidney tissue that are associated with degenerative processes;
- problems with the intestines - in particular, paresis;
- accumulation of purulent formations;
- renal failure and bacterial shock.
If the stone is not removed, then as the disease develops the kidney may even die - this is extremely dangerous and risky, so the disease requires effective and thorough treatment.
Rose hip
Rose hips normalize the functioning of the urinary system. Due to its high content of vitamin C, it increases the body's protective functions.
For the treatment of urolithiasis, the following recipe is recommended:
- Grind 50 g of rose hips, then pour 200 ml of water into it.
- Put on fire and cook for 20 minutes.
- Strain the broth thoroughly.
Take 2-3 sips before meals, the course of treatment should be at least 1 month.
Drug treatment
The main clinical symptom of urolithiasis is pain due to renal colic. To stop an attack, the patient is prescribed analgesics and antispasmodics. In severe cases, when renal colic does not go away after taking the above drugs, the patient is administered narcotic analgesics.
Drugs that dissolve stones in the urinary system are prescribed in accordance with the chemical composition of the stones. The course of treatment is usually long, but not less than 1 month. If complications develop in the form of pyelonephritis or inflammation in the bladder and urethra, the patient is prescribed an antibiotic, the dosage of which is selected strictly individually for each patient.
Indications for surgical intervention are the following conditions:
- The size of the stones exceeds 5 cm in diameter;
- The calculus blocked the lumen of the ureter and the patient’s urine flow was disrupted;
- Ingrowth of a stone into the mucous membrane of the urinary tract;
- Constant attacks of renal colic that last more than 60 minutes.
knotweed
With regular use, it normalizes salt metabolism in the body and also promotes the passage of kidney stones. Dissolves stones, which reduces their size. Recommended not only for treatment, but also as a prevention of urolithiasis. Has antimicrobial and diuretic effects.
For kidney stones, use the following tincture:
- Grind the knotweed herb.
- Fill it with water, the mass should be liquid.
- Put on fire and boil for 30 minutes.
- Leave in a dark place for 2 hours.
Drink 50 ml daily, 2 times a day. The recommended course of therapy is 14 days.
Characteristic signs and symptoms
General signs of urolithiasis:
- pain syndrome. The intensity of discomfort and the area of localization depend on the location of the source of the disease;
- problems with emptying the bladder;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- renal colic;
- vomit.
The location of the stones is easy to determine by the characteristic symptoms:
- kidneys Aching, dull pain in the upper back, blood in the urine, problems with urination. Discomfort increases when lifting weights, after working out in the gym;
- ureter. The calculus disrupts the flow of urine and blocks the canal. Painful sensations appear in the groin area, hips, and genitals. When the stone is located in the lower part of the ureter, the patient feels that even after emptying the bladder is full, but the next attempt to urinate ends in minimal fluid release. A dangerous symptom in women is renal colic. Sharp pain affects not only the abdominal area, but also spreads to the hypochondrium, perineal area, and legs. The symptoms are similar to those of radiculitis and intercostal neuralgia;
- bladder. The main symptom of the disease is a frequent urge to urinate, discomfort intensifies after physical activity. Emptying the bladder is difficult, the urine becomes cloudy, and sometimes blood clots are visible in the fluid.
Grape
White grape juice is used as a diuretic. Doctors recommend that people suffering from kidney disease include grapes in their diet.
The following recipe is effective in the initial stages of the disease:
- Wash and dry 200 g of grape leaves, then chop.
- Pour 1000 ml of clean cool water.
- Leave to infuse in a dark place for 3 days.
- Strain thoroughly.
Use 50 ml daily. This recipe is not effective for large stones.
Prevention of stone formation
People who maintain an adequate drinking regime rarely suffer from urolithiasis. If women have a history of urolithiasis, relapses occur quite often, especially when concomitant pathologies are detected. But they should know that the recurrence of the disease in most cases is due to poor nutrition and metabolic disorders. Among the many recommendations for prevention, experts cite the following as the main ones.
- Limiting the consumption of protein foods in the daily diet, reducing the amount of table salt as much as possible.
- A balanced diet with a predominance of foods rich in vitamins, amino acids and microelements.
- Using purified water for drinking if it is of low quality and has a high degree of hardness.
- The daily fluid intake is within the normal range – 2 liters.
- Annual medical examination for the treatment of endocrine, hepatic and renal pathologies.
- Visit a doctor in a timely manner if your health worsens or symptoms of urinary tract inflammation appear.
- Elimination of stressful situations, nervous and emotional stress.
Doctors recommend leading a healthy lifestyle, strengthening the immune system, since moderate motor and activity, engaging in gentle sports, eating high-quality food, sufficient amounts of healthy fluids, and vitamin complexes will help avoid the development of not only urolithiasis, but also a number of other diseases.
One of the most effective preventive measures for female patients with kidney stones is considered to be sanatorium-resort treatment. During the period of remission, it is recommended to visit specialized centers for mineral water therapy. This should be done on the advice of a doctor, who will determine the type of stones and choose a suitable resort.
Chamomile
Chamomile is known as an anti-inflammatory agent. In the treatment of urolithiasis, it is used as part of medicinal preparations, as well as as an independent remedy. Due to its mild antispasmodic effect, chamomile helps relieve pain.
The decoction recipe is as follows:
- Finely chop 100 g of chamomile, pour a glass of hot water.
- Put on fire for 20 minutes.
- Leave to brew for 2 hours.
Drink 50 ml daily 3 times a day. It is recommended to drink before meals.
A little about urinary stones and classification
Removing a stone from the ureter without an incision
Every woman needs to know what kind of stones she has, since the specifics of treatment depend on this. The most common types of stones are:
- Oxalate nephrolites. Often occur against the background of chronic intestinal diseases, with frequent diarrhea. These are dark stones that have a high density and a spiky surface;
- Phosphate stones. They often occur against the background of chronic urinary infections, developmental defects, and hyperparathyroidism. This is a typically “female” stone: in men they are half as common. These are grayish and fragile uroliths, however, they can also be white;
- Urates are uric acid stones. These stones occur with gout, but can also occur with cancer if the patient is receiving chemotherapy. A very high risk of urate occurs if acidification constantly occurs in the urine. These uroliths are yellowish to terracotta in color, may be smooth, and are dense.
Cholesterol, cystine and xanthine stones are much less common.
Of course, in addition to localization, it is necessary to distinguish whether stones appear on one side, or whether there is a bilateral lesion. There are also special cases, for example, recurrent urolithiasis that occurs after treatment, urolithiasis in a single kidney, or urolithiasis in pregnant women.
Herbal infusions
For urolithiasis, the following herbs are recommended:
- Plantain . It has antiseptic properties and is most effective for coral-type stones.
- Cranberry . It has an anti-inflammatory effect, but in case of urolithiasis it is allowed in small quantities.
- Birch buds . They remove excess fluid and alleviate the general condition of urolithiasis.
- Yarrow . Relieves pain and facilitates the movement of stones.
A competent combination of components will help increase the effectiveness of therapy.
Diagnostics
To confirm the presence of urolithiasis, assess the general condition of the paired organ, determine the parameters of the stone (size, location), the following is carried out:
- Biochemical, clinical examination of blood and urine. An increase in ESR and leukocytes in the blood are signs of inflammation, but with urolithiasis they indicate an ongoing complication. A decrease in hemoglobin levels indicates the need to compensate for the iron removed from the body during hematuria.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys. A quick and simple method for confirming the presence of stones, clarifying their parameters, and localization.
- Excretory urography. A solution containing iodine is administered intravenously to the patient. Then a series of x-rays are taken (often after 15 and 40 minutes). An iodine-containing solution fills the ureters, making it possible to visualize the condition of the urinary system as a whole.
- Survey X-ray examination. Provides a general clinical picture, including the relative position of the kidneys. This type of diagnosis is carried out simultaneously with excretory urography.
Other research methods are prescribed only when there is doubt regarding the size, type of stones, or their location; blood supply and general condition of the kidneys.
Diet for urolithiasis
A diet for kidney stones does not require serious restrictions.
Several principles must be followed in nutrition:
- Drinking enough liquid.
- The diet should be varied and balanced.
- It is necessary to give up spices and reduce salt consumption as much as possible.
- Portion sizes need to be reduced.
- Avoid foods that contribute to the formation of kidney stones (such as fatty meats, fish and legumes).
- Completely abstain from alcoholic beverages.
Patients should note that fasting is strictly contraindicated, as this can significantly aggravate the situation. It is recommended to eat food 4-5 times a day, but in small portions. It is advisable to focus your diet on fresh vegetables and fruits.
Stone crushing methods
There are several types of their destruction - through the use of ultrasound, laser or through abdominal surgery. The choice of a specific method depends on the individual equipment of the clinic where the intervention is planned; size and location of the stone.
Characteristics of each operation:
- Ultrasonic lithotripsy (stone crushing). Provides standard preliminary preparation - cleansing the intestines with an enema, refusing to eat food on the eve of the operation. Involves the use of ultrasonic vibrations. Allows you to crush the tumor into the smallest fragments, and then wash it out of the body with saline solution. The risk of damage to the parenchyma is eliminated.
- Laser lithotripsy. Preparation involves refusing to eat food (the evening before the operation) and water (on the day of the intervention). The tumor is crushed using a high-precision beam. In this case, the image of the kidney condition is transmitted to the monitor screen of the laser unit. This type of lithotripsy provides a favorable outlook. The possibility of injury to the organ is excluded.
- Abdominal surgery (open). It is a traditional surgical procedure (with tissue dissection). It is carried out only for large, multiple neoplasms. It involves a long recovery period, restrictions on physical activity and nutrition.
In modern urology, the method of open surgery is used only when there are serious reasons. Abdominal surgery is not the primary option for eliminating urolithiasis.
Only a urologist can prescribe a specific method of lithotripsy. The specialist takes into account the diagnostic results and factors related to the patient’s health status.
Drinking regime and “water shocks”
The so-called “water shock” technique is permissible only in the initial stages of the disease. Its essence is that in the morning you need to drink 1.5 liters of liquid within 10 minutes. It doesn't have to be clean water. It is allowed to drink herbal infusion or fresh juice. It is also possible to use a watermelon as a “water blow”.
Before using this method in treatment, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound scan, since stones larger than 10 mm are a contraindication. The break between such procedures should be days.
Principles of treatment of kidney stones in women
First of all, you need to deal with emergency urology - relief of renal colic. If the patient knows that she is “passing a stone” and has all the signs of the disease, thermal procedures are needed, for example, a hot bath. This relaxes the smooth muscles, the ureter becomes wider, and the pain decreases or disappears completely.
There must be complete confidence that this is renal colic: in case of appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, heat is prohibited.
In addition, antispasmodics (Baralgin, No-Shpa), anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs (Xefocam, Ketanov), and herbal preparations, for example, Fitolysin, are used intramuscularly.
In case of recurrent colic, the patient must be hospitalized in a specialized urological department, where catheterization of the ureter is performed, a stent is installed, or the kidney is unloaded during ureteral obstruction by applying a nephrostomy using the percutaneous puncture method.
Basic principles of planned treatment
Diet and drinking regimen are important components of treatment!
Naturally, eliminating an attack of colic does not cure urolithiasis: the formation of stones continues, the passage of urine is periodically disrupted, and inflammation occurs. Modern urology does not always resort to surgery.
Quite often, stones can be dissolved, expelled or crushed without resorting to incisions. But, even if the stones are removed, they still will not stop forming. Therefore, the main focus of preventive treatment is proper nutrition.
Diet for kidney stones, nutrition principles
The diet for kidney stones is highly dependent on the chemical composition of the stones. That is why we described their varieties in such detail. Let's consider the main options for therapeutic nutrition, depending on the predominance of one or another type of stones:
- Urate stones. We refer patients to a diet for gout and hyperuricemia, eliminating sources of purines, from liver and legumes to aged cheeses and red wine. A dairy-vegetable diet and drinking alkaline mineral waters are preferable;
- Oxalates. A natural source of oxalate crystals is oxalic acid and its calcium salts. Sorrel, spinach, rhubarb, celery and parsley, onions, carrots and tomatoes, and beets are sharply limited. Limit cottage cheese and milk as a source of calcium. Shown are sweet fruits (melons and peaches), cabbage, cucumbers;
- Phosphates. In order to cope with this type of uroliths, increased consumption of meat and fish foods, butter, cereals, and pasta is provided. Honey and lemon juice are beneficial. The goal is to acidify the urine, which helps dissolve phosphate stones. Sauerkraut is recommended for the same purpose, but eggs, sour cream, fruit and milk are sharply limited.
Drug litholytic therapy (dissolving stones)
To dissolve stones, different means are used for different types of stones. For phosphate stones, methionine is prescribed (to acidify the urine), and to prevent phosphates from being absorbed in the intestines, aluminum hydroxide is given orally.
If the stones consist of urates, then the drugs “Uralit-U”, “Blemaren”, “Magurlit” are prescribed. In case of severe hyperuricemia, allopurinol is prescribed - for a long time and under the control of tests.
For oxalate stones, other types of treatment are used, since they dissolve extremely poorly. But, nevertheless, diet helps prevent their formation.
Can stones come out on their own? Banishing stones!
If it turns out that the size of the stones does not exceed 4 mm, then there is an 80% chance that they can leave the body naturally. To remove kidney stones, the following are prescribed:
- Diuretics, drink plenty of fluids, watermelons;
- Exercise therapy options such as jumping, walking and running;
- Analgesics and antispasmodics are prescribed to dilate the ureters and pelvis;
- The process is stimulated by prescribing physiotherapy under the guise of uroseptics.
It is important before starting this therapy to make sure that the stones are small and do not obstruct the flow of urine. Otherwise, they need to be destroyed or removed. But don't take it out!
Breaking up stones, or lithotripsy
Currently, various types of crushing of stones are shown, which are carried out under the control of X-ray or ultrasound guidance, or navigation.
Stones can be crushed through close contact (endoscopically), remotely at a distance, through the skin (with the introduction of an endoscope into the pelvis). The energy for destruction is generated by laser, pneumatics, water hammer, and ultrasound. This way you can destroy stones of any size in a few sessions.
That is why, at present, open operations are performed very rarely, and kidney removal is carried out in the complete absence of its function, or in cases of massive purulent foci interspersed with stones (with calculous pyonephrosis).
What should you not do if you have kidney stones?
In RuNet, the answers to this question come down to dietary recommendations. But there are universal contraindications:
- You cannot start trying to expel stones on your own by using diuretics and watermelons, without accurately diagnosing their size, position and permission from a doctor;
- You should not go to the bath unless you are sure that it is renal colic (nausea, vomiting, fever);
- You cannot engage in active sports (boxing, wrestling, jumping) if you have urolithiasis without clarifying the diagnosis and recommending a urologist to avoid blockage of the urinary tract with stones.
If you do not take these simple recommendations into account, you can get serious complications.
Therapeutic exercises for women with urolithiasis
Exercise therapy for urolithiasis is allowed only during the period of remission. In this case, the lesson should not last more than 30 minutes, the load must be moderate. Do not use weights during exercise.
Therapeutic gymnastics has the following functions:
- Helps remove kidney stones.
- Helps normalize renal excretory function.
- Normalizes metabolic processes.
- Reduces the severity of pain.
Contraindications:
- State of fever.
- Acute period of the disease.
- Localization of the stone in the pelvis apparatus.
- Kidney failure.
- Infectious diseases.
Exercises are selected individually by the doctor in each case; they depend on the stage of the disease, age and general condition of the woman. Particular emphasis is placed on bending and twisting, and it is recommended to exclude swings and jumps.
Differential diagnosis
Modern techniques make it possible to identify any type of stones, so it is usually not necessary to differentiate urolithiasis from other diseases. The need to carry out differential diagnosis may arise in an acute condition - renal colic.
Usually, diagnosing renal colic is not difficult. With an atypical course and right-sided localization of a stone causing obstruction of the urinary tract, it is sometimes necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of renal colic in urolithiasis with acute cholecystitis or acute appendicitis. The diagnosis is based on the characteristic localization of pain, the presence of dysuric phenomena and changes in urine, and the absence of symptoms of peritoneal irritation.
There may be serious difficulties in differentiating between renal colic and renal infarction. In both cases, hematuria and severe pain in the lumbar region are noted. We should not forget that renal infarction is usually a consequence of cardiovascular diseases, which are characterized by rhythm disturbances (rheumatic heart defects, atherosclerosis). Dysuric phenomena during renal infarction occur extremely rarely, pain is less pronounced and almost never reaches the intensity that is characteristic of renal colic due to urolithiasis.
How to relieve an attack at home
In order to relieve an attack at home, you must perform the following steps:
- Drink plenty of liquid.
- Place a heating pad on the lumbar area or keep warm with a woolen blanket. You are allowed to take a hot bath in a sitting position for 10 minutes.
- Take painkillers or antispasmodics. It is recommended to drink No-Shpu, Papaverine or Baralgin.
- If the attack does not stop, take a Nitroglycerin tablet under the tongue.
It is strictly forbidden to take painkillers in large quantities, and it is also necessary to avoid overheating the lower back. If the attack does not subside, you will need to call an ambulance.
Urolithiasis progresses quite quickly, symptoms and treatment in women depend on the stage of the pathology. An acute attack indicates complications of the disease and requires immediate medical attention.
Article design: Oleg Lozinsky
Prevention
Not every person develops stony deposits during their lifetime. Their formation requires a long-term unhealthy lifestyle. The following will help reduce the risk of developing urolithiasis:
- Normalization of nutrition and drinking regime. It is not recommended to consume sour, spicy, salty snacks, fast food, carbonated drinks, and unfiltered water.
- Increasing the volume of physical activity.
- Timely elimination of inflammation of the urogenital tract.
- Regular medical examinations and a more attentive attitude to health if there is a hereditary predisposition to urolithiasis.
It is also important to stop dysfunction of the digestive organs, normalize body weight, avoid a monotonous diet, and stop drinking alcohol.