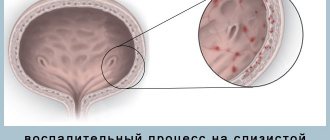
Bladder detrusor
(from lat. detrudere to push out) - the muscular membrane (tunica muscularis) of the organ, consisting of three mutually intertwined layers, forming a single muscle that expels urine (m. detrusor urinae). Its contraction leads to urination. The outer layer of the detrusor consists of longitudinal fibers, the middle layer consists of circular fibers, and the inner layer consists of longitudinal and transverse fibers. The most developed middle layer is in the area of the internal opening of the urethra. It forms the sphincter of the bladder neck. The circular fibers covering the orifices of the ureters are also more developed than the adjacent ones.
When urination is impaired as a result of bladder outlet obstruction, first the detrusor hypertrophies, and then trabecularity of the bladder wall develops, it becomes thinner and, as a result of high intravesical pressure, ischuria paradoxa occurs.
Bladder detrusor - what is it?
When the bladder fills with urine, its walls begin to stretch and intravesical pressure increases. The nerve receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system send signals to the brain along the sympathetic nerve fibers. There is a urge to urinate. If everything is in order with the detrusor, there are no problems with the innervation of the bladder, the person is able to restrain urination. If there are disturbances in its functioning, urinary incontinence occurs.
The detrusor is the muscular layer of the bladder . If there is a malfunction in its operation, a person has problems with urination. Functional disorders are of the following types:
- Hyperreflexive . The excitability of the organ is increased. A small volume of urine is enough to trigger the urge to urinate. Patients suffer from frequent urge to go to the toilet. Sometimes several drops of urine come out during one act. Subsequently, trabecularity of the urinary wall develops.
- Hyporeflexory . To excite the receptors in the bladder, a large volume of urine is required. The muscles do not contract enough during the urination process. Therefore, the liquid does not flow out completely and with weak pressure.
It happens that the detrusor is in normal condition, but a person has problems with urination. The reason is a malfunction in the nervous system.
Kinds
The detrusor muscle of the bladder is a set of muscles that facilitate the excretion of urine. The disruption of its functioning is influenced by many factors (age, weight, presence of chronic diseases, previous operations, etc.).
Organ dysfunction is divided into two types:
- hyporeflex;
- hyperreflexia.
Types of detrusor dysfunction:
| Kinds | Description |
| Hyporeflexory | Pathology associated with detrusor hypotonia at the time of emptying. The muscle tissue relaxes, stretches, the organ increases in size, causing the urinary tract to lose its ability to excrete urine, and fluid stagnation occurs in the body. Urine flows weakly, and patients complain of a feeling of incomplete emptying. |
| Hyperreflexia | The condition is associated with damage to the part of the brain that supplies impulses to vocalization. With this problem, the patient cannot independently control the process of urination. This condition can occur even with a normally functioning detrusor. With the slightest accumulation of urine, involuntary urination occurs. Another cause of hyperreflexia can be a spasm of the sphincters, which narrows the lumen of the urethra, thereby preventing the removal of urine from the canals. When urine is completely accumulated, the detrusor spontaneously contracts, causing the organ to involuntarily empty itself. |
When the bladder is completely filled, the detrusor relaxes, leading to spontaneous emptying. The phenomenon can be considered normal if these are isolated cases.
Causes
Detrusor pathology can be caused by various reasons. They are divided into two groups:
- Neurogenic . They develop as a result of innervation disorders and pathologies of the nervous system. These include mechanical damage to the brain or spinal cord, sclerosis and Parkinson's disease.
- Without affecting innervation . They are less common than neurogenic ones. Typical for older people. This group includes pathologies of the blood supply, atony of the walls of the bladder, tumors in the bladder or nearby organs.
Detrusor dysfunction can develop due to changes in its structure. Hyperactivity is often caused by sensory innervation of peripheral afferent nerves ending in the bladder.
When to see a doctor
Bladder detrusor is a problem that depresses and disrupts a person’s quiet lifestyle. Detrusor dysfunction often impairs professional, social and even family life. Despite the discomfort caused by the problem, patients are in no hurry to seek medical help. It is not right.
In the early stages, you can completely eliminate the pathology and move on with your life in comfort and good mood. But when the forms are neglected, doctors often resort to surgical treatment, and the problem cannot always be completely eliminated.
When the first warning signs appear, you should undergo an examination and receive qualified medical care. The treatment of urinary detrusor disease is carried out by a urologist; if necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to other specialists (gynecologist, nephrologist).
During the examination, the doctor will find out the following points:
- when the patient first began to feel unpleasant symptoms;
- Do close relatives have similar problems?
- number of movements per day;
- what sensations does the patient experience during bowel movements?
Even minor violations cause discomfort in a person, suppress his libido, and provoke irritability. The more you let the problem take its course, the greater the risk of irreparable consequences.
Symptoms
Problems with the detrusor are manifested by the following symptoms:
- Sharp and strong urge to urinate.
- Inability to hold urine (fluid is released immediately after the urge to urinate)
- Frequent urge to go to the toilet (more than 8 times a day)
- Change in jet pressure (becomes stronger or weaker)
- Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Prevention
The prognosis for recovery from bladder detrusor disease depends on the complexity of the problem. After treatment, the doctor gives general recommendations to patients, which they must strictly follow in order to eliminate the risk of relapse.
This:
- examination by a gynecologist every six months;
- timely diagnosis and consultation with a doctor when the first signs of a urinary system disorder appear;
- diet (excluding spicy, salty, fatty foods);
- excluding the use of strong tea and coffee;
- compliance with the drinking regime (water consumption per day is 1.5 liters);
- limiting water consumption before bed;
- losing excess weight;
- performing exercises to strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor and back;
- control of water consumption (liquid is taken according to a special schedule);
- using double emptying (after the first voiding, wait 1-2 minutes and force yourself to go to the toilet again);
- urination on a schedule (force yourself to go to the toilet every 2-4 hours);
- bladder training (hold the urge for about 30 minutes in order to further accustom yourself to bowel movements on a schedule).
In most cases, the problem can be completely eliminated if treatment is started in a timely manner. Therefore, the main thing in preventing urinary detrusor disease is to be attentive to your health, excluding severe stress and hypothermia.
Diagnostics
To identify detrusor pathology, the doctor listens to the patient’s complaints, interviews him, and collects an anamnesis of the disease. It is important for the doctor to know whether the person has recently experienced severe stress or been exposed to the cold. Existing diseases are identified. Particular attention is paid to disorders in the nervous and genitourinary systems.
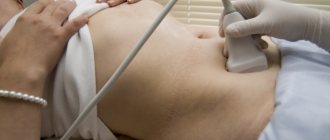
After communicating with the patient, the doctor gives a referral for examination. First you need to take a general analysis of urine and blood. Ultrasound diagnostics are performed. These studies exclude pathologies of the bladder or kidneys, which can cause symptoms similar to signs of detrusor dysfunction.
If it is difficult to make a diagnosis based on the above examinations, the doctor will direct the patient to undergo:
- Cystometry . It is performed by catheterizing the bladder. The organ is filled through a tube with gas or a special liquid. The method shows what maximum amount of urine a bladder can hold, what pressure is created at different degrees of bladder fullness.
- Profilometry . The procedure is used to determine the functioning of the sphincters and pressure in the urethra. A system of tubes is inserted into the urethra. Then they are gradually taken out. In this case, the device records the pressure exerted by the muscles of the urethra.
- Uroflowmetry . The patient should urinate into a special container. The method shows the speed and volume of urine excreted.
Structure of the urinary system
The kidneys filter blood plasma. During this process, it is freed from metabolic products, the final compounds of drugs.
The resulting urine passes from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder.
The main function of the bladder is to store and periodically excrete urine. Its wall consists of three layers:
- protective external;
- middle, which is represented by smooth muscles (detrusor);
- internal, which consists of transitional mucous epithelium.
The mucous membrane forms well-defined folds on the inner surface of the bladder, which straighten as urine accumulates.
There are no folds only at the bottom of the bubble. There is the so-called vesical triangle. It got its name due to its resemblance to this geometric figure.
In two corners there are the mouths of the ureters, and in the third there is the internal sphincter, through which the bladder connects to the urethra.
The detrusor consists of three layers of smooth muscle - external and internal longitudinal and middle - circular or circular. The circular layer is most developed around the internal sphincter.
When the detrusor muscle contracts, the volume of the bladder decreases and urine is expelled from the body through the urethra.
Treatment
The most common diagnosis is detrusor overactivity. This pathology is treated using the following methods:
- Conservative (diet, physiotherapy, muscle exercises, herbal medicine)
- Surgical.
- Medication.
If innervation disorders lead to a malfunction of the detrusor, then the doctor selects therapy to treat pathologies of the nervous system. For detrusor hyperreflexia, doctors prescribe the drugs Sibutin, Proroxan, Driptan, Novitropan. These drugs affect the detrusor receptors and relax it.
Antispasmodic tablets Spazmex or No-shpu . The medications Proserin and Kalimin are indicated, which reduce the effects of acetylcholine. For a speedy recovery, it is recommended to combine drug therapy with physical procedures that facilitate urination.
Consequences and complications
Disturbances in the detrusor function change a person’s usual way of life and reduce social adaptation. Without treatment, hyperactive bladder can lead to the following complications that require long-term therapy:
- Secondary inflammatory and dystrophic pathologies of the urinary organs (inflammation of the urinary tract, pyelonephritis, vesicoureteral reflux)
- Myofascial syndrome.
- Pelvic venous congestion syndrome.
The consequences of these complications are nephrosclerosis, chronic renal failure and persistent hypertension.