The most common test taken by visitors to medical institutions is a general urine test. One of the indicators is salts in the urine.
Normally, the form contains 1–2 pluses, but sometimes there are 3–4. If the levels of salts in the urine are exceeded once, the doctor has the right to suspect a pathology. In this case, a repeat urine sample is prescribed. But repetition of the results or an increase in salt concentration means pathology of the excretory system. To accurately determine the disease, differential diagnosis is carried out.
Salts in urine analysis
Let's remember the laws of chemistry: salts are formed when alkalis and acids combine.
According to their biochemical composition, the fluids of the human body contain both. Many substances pass through the kidney filter in the form of a salt solution. The total concentration, together with other solutes, maintains the desired osmotic pressure.
To regulate it, some of the components are excreted in the urine.
The salt composition of urine changes, compensating for excesses received from food and various deviations in mineral metabolism. Therefore, based on its study, certain disorders can be suspected in diagnosis.
The greatest concern is the detection of salts in the urine in the form of crystals. Their formation is evidenced by excess of normal concentration and precipitation. Gradually, stone structures (salt stones) form in the urine, which can cause clinical signs of the disease.
Mechanisms of protection against stone formation
In a healthy person, urine has a slightly acidic reaction. Metabolic disturbances lead to a shift (acidification or alkalization). When the acid-base balance is disrupted, salts in the urine turn into crystals.
In addition, antagonist substances provide protection against excess crystallization. They control biochemical reactions in the body and, if elevated, bind individual components. The following have a similar effect:
- enzymes that act as catalysts during chemical transformations;
- magnesium ions;
- pyrophosphate compounds;
- citrates.
Performing a preventive function, they prevent the attachment of crystals to the mucous membrane of the urinary tract (bladder, kidneys, ureters).
Salts in a urine test are detected by examining the sediment under a microscope. Based on the shape and arrangement of the crystals, the laboratory assistant makes a conclusion about their chemical properties.
It should be noted that the electrolytes, antioxidants, and some vitamins necessary for the body exist in the blood only in the form of a salt solution. Without them, basic biochemical reactions and the removal of accumulated toxins are impossible. Therefore, insoluble compounds in urine are considered clinically significant.
If single crystals are visible in the field of view of the microscope, they are called amorphous. They are harmless because they do not participate in the formation of rocky structures. However, they are important in the prevention of further metabolic disorders.
According to the acid composition, the most common are:
- oxalates;
- urates;
- phosphates.
Crystals are found much less frequently:
- ammonium urate;
- hippuric acid;
- sulfates in combination with calcium.
A targeted urine test for salt is more informative if it is carried out from a previously collected daily amount. It allows you to eliminate fluctuations in the concentration of chemical compounds in the blood during the day.
Features of the appearance of salts in urine in adults and children
The causes of salts in urine at different ages of a person may differ.
For an adult, the main ones are:
- disruption of the supply of essential minerals from food (indulgence in overly salty and spicy dishes, smoked meats, fried meat foods, overeating sweets, chocolate, drinking alcohol and strong coffee, incorrect choice of mineral water);
- inflammatory diseases of the urinary and genital organs, in which salts are found in the urine with an increased content of red blood cells, leukocytes, bacteria and pathogens of sexually transmitted infections;
- dehydration of the body (lack of fluid) leads to an artificial increase in the concentration of all substances in the blood, including salts; they form a crystalline precipitate in the urine; the condition occurs with a lack of drinking in the heat, with increased sweating and fever, with loss of fluid during vomiting and diarrhea , due to bleeding and large surface area of skin burns.
A child can only be given one slice of this tile.
The child may:
- violations in the diet, premature introduction of “adult” dishes, insufficient drinking regime;
- up to two years of age, the functional inferiority of the filtration mechanism of the kidneys plays a role;
- connections with daily fluctuations in acid-base balance;
- inborn changes in metabolism.
Older children are sensitive to dehydration and have a harder time with not drinking. Increased salt residue in the urine disappears more easily under the influence of sufficient fluid administration and dietary measures.
Inflammatory diseases of the urinary organs and their consequences are less important than in adults, since they often occur acutely and do not have time to cause serious problems.
Violation of neuroendocrine regulation of water balance is characteristic of diseases of the endocrine system:
- diabetes mellitus;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- hypothalamic-pituitary brain lesions (tumors).
This partly explains why an increase in salts is found in women during pregnancy. Pregnant women must have their urine tested as regularly as required by the obstetrician.
Detection of salts in the urine of an infant may indicate:
- non-compliance with the mother's diet during breastfeeding;
- unsuitable artificial food.
We will consider whether there are any differences in the reasons for the appearance of different types of salts using specific examples.
Origin and significance of oxalates
Oxalate salts are derivatives of oxalic acid. Their presence is confirmed by beautiful pointed star-shaped crystals.
Stones formed from oxalates have the greatest traumatic potential
They injure the vessels and mucous membrane when moving, and dig into the wall of the ureter. Therefore, the symptoms of renal colic most often cause: sharp paroxysmal pain in the side, lower back, radiating to the abdomen, groin, and thigh. In this case, blood is found in the urine.
Diet for oxalates in urine
Many salts of oxalic acid are formed if the diet contains:
- strong tea, coffee, cocoa;
- chocolate;
- asparagus;
- sorrel;
- rhubarb;
- kiwi;
- spinach;
- gooseberry;
- mango;
- currant;
- juniper;
- dog-rose fruit;
- beet;
- Bell pepper;
- nuts.
It should be noted that some of these products are recommended in therapeutic and cleansing diets for various diseases. In addition to the above factors, oxalaturia is detected due to poisoning with brake fluid (antifreeze) containing ethylene glycol.
Urates are the sodium and potassium salts of uric acid (purines). Under a microscope they always have a brick color. The following foods are rich in these salts:
- baked goods and products made from yeast dough;
- canned fish (especially sprat, sprats, sardines);
- legumes;
- meat and fish broths;
- pork spleen;
- White mushrooms.
Of the specific accumulation factors, it is necessary to emphasize the importance of drinking too hard, unfiltered water in areas with a deficiency of iodine and fluorine in the soil.
Hard water causes corrosion not only of metal pipes, but also accompanies the deposition of salts in the human urinary organs
Urate crystals are detected in urine when:
- gout in adults;
- uric acid diathesis in infants;
- blood leukemia.
What influences the formation of phosphates?
The phosphate group includes salts and esters of phosphoric acid. Phosphorus is very necessary for children to build bones, ensure safety and mobility in adulthood, and support tooth enamel. It is constantly associated with calcium.
Both elements are necessary in the processes of excitation of muscle tissue, for the cells to obtain energy. Phosphate stones have a porous structure and are susceptible to destruction. They do not cause traumatic injuries like oxalates and are much easier to treat.
Amorphous phosphates in urine are detected against the background of:
- predominantly dairy food;
- using oatmeal, buckwheat and pearl barley porridge too often to feed a child or adult;
- hobbies for pasta;
- uncontrolled consumption of baked goods, chips, sweet soda.
Phosphaturia is one of the symptoms:
- inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system;
- increasing the functioning of the parathyroid glands;
- Fanconi syndrome.
Tripelphosphate salts include not only phosphates, but also various combinations of dead bacteria residues. Compounds are formed only in alkaline urine. The chemical composition must include:
- ammonium salts;
- microelement – magnesium.
Infectious components are:
- staphylococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Helicobacter;
- mushrooms.
A qualified specialist will prescribe the necessary tests to clarify the cause of the appearance of salts in the urine
Therefore, tripelphosphate salts in the bladder always indicate the presence or past inflammation of the kidneys (pyelonephritis), cystitis. Their concentration increases rapidly during steroid therapy. Failure to take timely measures can lead to urinary incontinence.
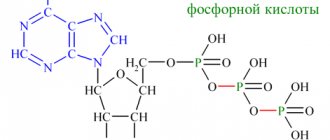
How are sulfates formed?
Calcium sulfate salts are quite rare. May appear with significant consumption of products containing salicylic acid compounds:
- melons;
- fresh blackberries, blueberries and jam from these berries;
- apricots and dried apricots.
A product rich in benzoic acid, lingonberries, has similar capabilities.
Hippur salts indicate overeating of the same foods and appear when:
- liver damage;
- overdose or long-term treatment with salicylates (Aspirin, painkillers);
- processes of increased fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines.
How to get rid of salts in urine?
Special treatment for salt in the urine may not be required if, after following a diet excluding the richest foods, a control test shows the norm. If there are bacteria in the urine, in addition to salts, leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, casts, mucus, bacteria, it is still better to undergo an examination. After all, salt deposition is possible against the background of sluggish inflammation.
The first step is to ensure that the volume of water is at least 1.5 liters per day
A diet for salts in the urine must include a sufficient amount of fluid to drink. It is necessary to limit or completely eliminate the products listed above. And in the diet, products that have a binding effect and maintain energy balance are recommended.
If urates are present, it is recommended to use purine-free products and fortify food:
- dairy products;
- poultry meat;
- eggs;
- fruits;
- vegetables;
- cereals;
- nuts.
For oxalaturia, the daily menu should include:
- beans;
- liver meat;
- sprouted wheat or bran;
- seaweed;
- pumpkin seeds;
- potato.
The products will provide the necessary salts of oxalic acid:
- magnesium;
- vitamin B6, E, A.
Recommended fruit drinks and compote from:
- cranberries;
- cherries;
- lingonberries;
- flax seed decoction;
- pear leaves.
Cranberry juice - a drink recommended by experts
For phosphaturia the following are indicated:
- brown rice products;
- meat soups and broths;
- drinks made from berries and fruits;
- boiled vegetables.
The effectiveness of the diet can be assessed by a control urine test after 2-3 weeks of dietary restrictions. Lack of results will indicate the need to prescribe medications. The dietary approach should be maintained throughout life.
In addition, each person should carefully understand their habits and proper nutrition. An indicator such as salts in the urine can be a warning of more significant disorders in the form of urolithiasis.
Source: https://2pochki.com/diagnostika/soli-analize-mochi
Salts in urine: causes of salt crystals in urine and treatment with folk remedies
Urine, excreted by the body during bowel movements, is filled with various chemicals and waste products. This liquid also reflects any changes occurring in the human body. Often, it is thanks to urine analysis that it is possible to promptly determine the presence of pathologies or diseases.
Causes of salt in urine in adults
It is believed that the formation of crystals in urine is much more common in people beyond childhood.
This is associated with three main reasons, and one of them is a change in the colloidal characteristics of this physiological fluid.
This disorder can be caused by a predisposition at the gene level, diseases of the genitourinary system (which cause organ dysfunction), as well as problems with the blood supply to the kidneys.
The next reason is considered to be an increase in the concentration of salts in urine. This phenomenon occurs due to the consumption of excessive amounts of foods enriched with proteins, as well as dehydration of the body (which increases the density of urine) and metabolic disorders (which is typical for uric acid diathesis, gout, xanthinuria, oxalosis and Wilson's disease).
The last common cause is a violation of the acid-base balance (pH) of urine.
The manifestations differ depending on exactly how the pH is disturbed: when the acidity of urine increases, the solubility of salts worsens, and when the balance is more alkaline, the solubility of phosphates is impaired.
In this case, crystals of sediment (salts) present in the excreted urine almost always signal the development of serious diseases, which threatens a gradual deterioration of the condition and serious consequences, and this makes it necessary to quickly find out what such a change in urine means and how to get rid of it.
In many cases, the precipitation of salts into an amorphous sediment is caused by a change in the daily menu or diet, after which food products begin to predominate in it, which during metabolism cause the formation of urates (meat, mushrooms), oxalates (sorrel, parsley, celery) or phosphates in the body (fish, caviar, dairy products).
If the diet is not oversaturated with any of the listed types of food, but a high salt concentration in the urine remains, the following diseases may cause this:
- acute infection;
- diseases of the urinary system (cystitis, pyelonephritis);
- dehydration of the body.
Salts in a child's urine
The appearance of crystals in children's urine is considered a fairly common ailment, and the reasons here are almost the same as in adults.
First of all, this is due to the physiological characteristics of the body: children’s kidneys are not yet working at “full capacity”, and therefore cannot completely dissolve large amounts of salts entering the child’s body.
When such a symptom is detected, most doctors prescribe the child to follow a special diet, and parents must strictly ensure that the child adheres to it.
However, this is not true in all cases.
Since the formation of salt sediment in the urine is directly related to the acid-base balance of this fluid (normal levels of which should be from 5 to 7 pH), this phenomenon is observed in cases where the balance is shifted.
In this case, the doctor must prescribe an additional examination in order to accurately establish the acid-base balance, and, based on the information received, detect the development of pathology in the child’s body, if any.
Symptoms of the disease
In some cases, salt crystals are released along with urine even in healthy people - this is due to changes in the menu, environment and physical activity; over time, the body adapts to new conditions.
If the formation of salts becomes permanent, this may become a sign of the development of pathological processes in the body.
This condition is also accompanied by the following symptoms (usually they are not pronounced, but they do occur):
- cloudiness of urine and the appearance of sediment;
- change in urine color;
- weakness and pain in the lower abdominal cavity;
- increased frequency of urination (polyuria);
- itching, irritation and burning in the organs of the reproductive system, due to the fact that accumulated salt corrodes the mucous membrane, which means a gradual deterioration of the condition;
- problems with bowel movements (dysuria).
Many patients suffering from an illness that causes the appearance of salt crystals in the urine report increased fatigue, drowsiness, and lethargy. In some cases, high blood pressure, problems with the heart, blood supply, and pain in the right side of the abdominal cavity are recorded.
External manifestations become noticeable - rapid weight changes, difficulties during long walks, breathing problems, shortness of breath.
These symptoms should be given special attention, since they are the primary signs of the development of diseases in the body, which, in the absence of adequate treatment, lead to serious consequences.
Classification
Urine consists of approximately 95% water, and another 5% of various chemicals that give it a characteristic color, smell, and also affect the appearance of sediment. Detection of salts during clinical urine analysis is carried out using a special scale with 4 marks.
In the analysis of urine belonging to a healthy person, salts are not determined at all, but the acceptable norm is a one-time increase of up to 2 levels.
If too much salt is detected (marks 3 and 4), an additional examination is prescribed (for example, a urine test according to Zimnitsky). Such a daily test allows you to accurately determine which salts are concentrated in the urine.
In cases where, in addition to salts, bacteria are found, we are talking about the development of infectious inflammation in the urinary tract. The normal indicators are the following values:
- the content of visible leukocytes in a urine particle during microscopy should not exceed 3 and 5 in men and women, respectively;
- epithelium, red blood cells and casts should be absent.
The salts themselves are divided into three types: urates, oxalates and phosphates. The type of salt that precipitates into the crystalline sediment contained in urine depends on the factors that caused this phenomenon.
Urates in urine
The appearance of salts of this type is the most common, and is usually accompanied by an acid reaction. In this case, the characteristic factors causing the appearance of salts will be fever, excessive physical exertion, lack of fluid in the body, urinary tract diathesis, gout and leukemia.
Oxalates in urine
This type of precipitate is ammonium compounds, the formation of which is caused by the course of two different chemical reactions.
Most often, patients with this type of salt in the urine suffer from the following diseases: hormonal imbalance, pyelonephritis, intestinal diseases, ulcers. When consuming foods rich in oxalic acid, a disruption in its absorption in the body becomes noticeable.
In rare cases, these salts become signs of the appearance of malignant neoplasms (tumors) in the body.
Phosphates in urine
The formation of salts of this category in urine is associated with the occurrence of an alkaline reaction (which is accompanied by a decrease in acidity).
The most common culprits that cause this condition of the body are the following: cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), hormonal imbalance (hyperparathyroidism), excessive consumption of food (especially calcium-rich food), fever, chills, dehydration (associated with poisoning) and functional ability of the stomach or intestines.
Therapeutic measures
Since education is only a consequence, and not the disease itself, therapeutic measures must be aimed at treating the disease that caused such a change in the composition of urine. In case of incorrect selection of products in the daily menu, food for which the patient has contraindications should be excluded, or even better, a dietary menu should be drawn up.
The easiest way to correct dehydration is to simply increase your daily fluid intake. But with pathology of the genitourinary system, serious (and most often inpatient) treatment will be required, prescribed by a doctor and accompanied by taking medications.
Upon completion of planned therapy, a repeat test for the presence of salt crystals almost always has a negative result.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies
First of all, it is worth understanding that the effectiveness of traditional treatment methods has not been clinically confirmed, and therefore you can resort to them only at your own peril and risk. One of the recipes aimed at preventively cleansing the body of salts is as follows:
- pour five grams of bay leaf into a glass of boiling water;
- Bring to a boil in a water bath and keep for another five minutes;
- leave the resulting decoction for 3-4 hours;
- strain this liquid and take several sips throughout the day;
- These procedures should be carried out for 3 days in a row, 1-2 times a year.
Another recipe, and a rather harmless one, is to use rice using this method:
- soak the grain by soaking 2 tablespoons in cold water for a day;
- the next day, porridge is cooked from this cereal for breakfast (eaten without salt, sugar or other seasonings);
- After an hour, you are allowed to have a snack with regular foods.
Of course, treating yourself on your own is far from the best idea; it is better to entrust this matter to doctors.
Source: https://MpsDoc.com/diagnostika/analiz-mochi/soli-v-moche/
Diagnostics
A general clinical urine test allows you to detect the presence of salts and determine its concentration. In order for the analysis to be reliable, it is necessary to follow a set of preparatory measures before collecting and submitting urine for research.
It is recommended to exclude from the diet foods rich in oxalic and ascorbic acid (fruits and berries with bright colors) one day before. For an objective study, you should not drink alcohol or diuretics the previous day. Before collecting urine, you need to wash yourself and prepare a clean container for urine. Approximately 100 ml of morning urine should be provided to the laboratory.
To find out the type of salts and the cause of their appearance, a more complete examination of the body is required.
Diagnostics:
- Clinical blood test.
- Blood chemistry.
- Bacteriological culture of urine.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary tract.
- Urography.
- In some cases, a blood test to check glucose levels.
Increased salt in urine, what does this mean?
The meaning of most medical tests for people unfamiliar with medical science is a “dark forest”. A general urine test is no exception. In particular, indicators of the level of salts, because, in fact, it should be present in this biological fluid.
What then is bad if the analysis has three or four pluses opposite the corresponding parameter, when the norm is 1-2? In principle, there is nothing bad if the advantages appeared once. If, during repeated tests, salts in the urine are in the same amount or their concentration increases, you should think about health problems.
Among the salts that urine contains are urates, oxalates and phosphates.
Possible diseases and symptoms
Often, an increase in the amount of salts in the urine is a sign of the development of some pathology. When making a diagnosis, we focus on the symptoms characteristic of a particular disease.
- Urolithiasis disease. This urological disease is characterized by acute paroxysmal pain in the lower back, frequent false urge to urinate, as well as the presence of large amounts of creatinine and urate in the urine.
- Kidney diseases. In inflammatory kidney diseases - nephritis or pyelonephritis - there is increased body temperature, pain in the lumbar region, nausea, difficulty urinating, cloudy urine. The amount of urates and oxalates has been increased.
- Joint diseases. Gout and arthritis are manifested by attacks of crippling pain, inflammation and swelling of the joints. The disease is caused by the deposition of urate in the tissues of the joints, an increased amount of which is also found in the patient’s urine.
- Diabetes. Symptoms (subjective sensations) of diabetes are a constant feeling of thirst and frequent urination, signs (objective evidence) are increased levels of blood sugar and oxalates in the urine.
Why does this happen to women?
High salt content in women occurs, first of all, due to poor nutrition, especially among diet lovers, when the menu is selected inappropriately and at the wrong time. Excess salts can be associated with metabolic disorders, diabetes, and oncology. If, in addition, bacteria are detected, then an infection in the woman’s genital organs is likely - this is a warning about a pathology developing in the body, which is dangerous for infertility. During pregnancy, a urine test is the most reliable way to monitor the health of the unborn child and mother, so the doctor requires this to be done regularly. Sometimes, salt is the result of sexually transmitted or infectious diseases, as well as the effects of harmful substances on the female body, for example, ethylene glycol or any paints and varnishes. In such cases, immediate medical attention is needed.
A healthy lifestyle and varied diet prevent the appearance of salts in the urine.
Return to contents
The appearance of salts in a urine test - what does this mean?
The fluid that is excreted by the urinary system consists of various chemical elements, including salt. When a high concentration of salt is found in the urine, this indicates an imbalance of acids and alkalis in the body.
Its appearance does not always indicate the presence of pathology, because it should be present in small quantities in urine. Together with proteins, salt makes up 5% of the volume (the rest is water).
Only in cases where, based on certain signs, there is a suspicion that you have increased salt in your urine, you need to consult a specialist.
Based on the results of the analysis, the urologist or nephrologist will decide how to reduce its level to a normal value. The occurrence of salt in urine has various reasons, and treatment is prescribed in accordance with these points.
Analysis of urine
Checking the content of urine to ensure that all its elements are within the normal range is called a urine test. Normal urine has a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. Sudden changes in the balance of acids and alkalis (pH) will indicate precipitation of salts.
It is difficult for people far from medicine to decipher any analysis. If the doctor ordered a general urine test, and it showed that the norm of salts in it was significantly exceeded, this means that the patient will undergo treatment.
The result is considered bad when 3-4 plus signs appear opposite the salt parameter (it’s normal if there are 1 or 2). But this only matters if such salt content indicators are repeated repeatedly in a urine test.
If excess salt is detected in the urine once, this may be a consequence of incorrect testing, and not of health problems. A urine test for salt will give a reliable result if you prepare correctly for submitting the material according to the instructions and carefully follow all its points.
If, even when collected in a container, it is clear that the liquid is dark in color and there is sediment in it, a high salt content can be assumed.
To find out why the urine is salty, the patient may be referred for additional diagnostics. If the acid-base balance is disturbed, too much salt is found in the urine.
Most often, the imbalance appears due to poor nutrition (increased production of uric acid is affected by purine and oxalic acid, found in many foods).
Classification of salts
There are different types of salts in urine. Most often they are represented by urates, phosphates and oxalates. Sometimes crystals of other salts are found in the urine, for example, ammonium urate.
Typically, the following salts are found in a general urine test.
Urats
The most common uric acid salts that are found in the urine of people suffering from leukemia, fever, and gout.
A high salt content in this type of urine also indicates poor nutrition with excessive consumption of protein foods, dehydration, and heavy physical activity. Urate in the urine is reduced with the help of a certain diet and taking medications that affect these salts.
Phosphates
The presence of salts according to the results of urine analysis indicates its alkaline reaction (alkalization of the acidic environment). Inflammation of the bladder (cystitis), gastrointestinal dysfunction, dehydration due to poisoning, hyperparathyroidism (hormonal disorder), Fanconi syndrome will be indicated by phosphates in the urine.
Often, their high content is found in healthy people when they overeat or abuse foods rich in phosphorus.
Oxalates
If oxalates, the so-called salts of oxalic acid, are detected, then you should be wary. The presence of this salt in the urine is indicative, which means the patient has a metabolic disorder. His body does not absorb oxalic acid well.
This leads to peptic ulcers, pyelonephritis, and intestinal problems. Such salts can come from certain plant foods or result from biochemical reactions in the body.
In urine sediment, these types of salts are visible under a microscope, and they look like crystals. Their shape can be used to determine their chemical composition.
The concentration of salt in urine is indicated by pluses (the norm is 0-2). If an increased concentration of urates or oxalates appears in the results of a urine test, this often means the development of pathological processes in the kidneys and other organs.
Reasons for the appearance of salts in urine
There are many factors in the presence of which a urine test for salts shows their high content. The most common causes of high salt content in urine are:
Poor nutrition
This is the main reason for the appearance of salts. To get rid of them, products that contain oxalic acid, which usually causes an imbalance in the acid-base balance, are excluded from the menu.
These are sorrel, tomatoes, chocolate, sour berries. Salts also appear during dieting, fasting, and monotony of food consumed.
Urogenital infections
The appearance of salts is often caused by infections such as chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, and thrush.
Blood supply disorders
The lack of beneficial substances transmitted through the blood negatively affects the processes in the kidneys. They are very dependent on proper blood supply.
If it is violated, then signs of salt appear in the urine. Blood transmission becomes problematic in the presence of vascular pathology. When they narrow and become blocked, the kidneys do not receive enough blood, and diseases arise (nephrosis, pyelonephritis, etc.)
Taking medications
Some strong medications, especially antibiotics, can provoke the appearance of urates in the kidneys, through which they are excreted.
Lack of fluid
Salts occur when there is insufficient fluid intake, dehydration caused by illness, diarrhea. When the body lacks water, salt precipitation occurs in the urine.
Additional reasons
Salts in the urine are more common in adults and children for the reasons listed above. The education process is aggravated by a history of concomitant diseases. The reasons may be impaired metabolism in the body, long-term use of certain medications.
Contribute to the appearance of urates:
- frequent consumption of meat, mushrooms, spinach, tomatoes, fish;
- presence of stress;
- taking antibiotics.
Oxalates appear if you have the following diseases:
- kidney diseases;
- diabetes;
- colitis;
- urolithiasis disease;
- Crohn's disease;
- oxalosis (congenital pathology).
They also occur with a lack of vitamin D, a high content of foods containing oxalic acid in the diet, and ethylene glycol poisoning.
Common causes of excess phosphate:
- vegetarianism or foods containing a lot of phosphorus;
- diabetes;
- genitourinary infections;
- stones in the kidneys;
- kidney diseases.
These facts are the answer to the question of why salt appears in the urine.
Treatment
After identifying the reasons why a large amount of salts appears in the urine, appropriate treatment is prescribed. If they arise due to a serious illness, then salts must be treated with the use of medications and various procedures.
If the cause is poor nutrition or dehydration, then this can be corrected by following a certain diet and drinking more water. When the norm of salts in the urine is exceeded, medications that regulate metabolism, a complex of vitamins A and E, and others are usually prescribed.
The basis for the treatment of all types of salt in the urine is nutritional therapy. It should include healthy foods and exclude foods containing harmful substances. Treatment will be more successful if you focus on the type of salts.
The easiest way to get rid of oxalates. It is enough to establish proper nutrition and avoid eating foods that contain oxalic acid.
If urates are detected, you will need to reduce your intake of foods containing purine, drink a lot of clean water (1.5-2 liters) every day, and take medications prescribed by your doctor to improve salt metabolism. The appearance of phosphates in urine is a reason to reduce (completely eliminate) the consumption of foods that contain a lot of phosphorus.
If stones (calculi) have already formed in the kidneys due to excess salts in the urine, doctors decide what to do next.
Diet and medications cannot help here. The stones are broken or removed using a laser or ultrasound. For large stones, the problem is solved by surgical intervention. Concomitant diseases that provoke the appearance of salts are treated separately.
Diet
In the initial stages, salts can be removed by following a diet. Diet therapy is an important part of treatment. By adhering to its rules, you can improve the functioning of your body.
Advice from nutritionists for problems with high levels of different types of salts in the urine is as follows:
- balanced meals, fractional (more often, but reduce portions), preferably separate;
- You should eat food every day at one specific time;
- limit meat consumption (weekly no more than 100-150 g);
- drink enough water every day.
These measures will lead to the improvement of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract without the help of medications.
Different types of salts can be found in urine. Know their type in order to correctly add or remove certain types of foods from the diet.
If urates are present, then it is recommended to eat foods containing vitamins A, B, potassium, magnesium, zinc (vegetables, nuts, poultry, fruits). Alkaline mineral water is useful.
If you have oxalates, the menu should include other foods: potatoes, liver, boiled meat, poultry, fish, seaweed, wheat sprouts, beans, peas, lentils.
Drinks allowed: cranberry, cherry, lingonberry juice and compotes, flaxseed decoction. You should exclude foods with excessive amounts of oxalic acid (sorrel itself, figs, beans, spinach, beets, etc.).
You can reduce the salt content in urine with phosphaturia by eating eggs, broths and soups with meat, boiled vegetables, liver, and other foods with a lot of vitamin D and calcium.
Diet recommendations apply to everyone, only in women the symptoms of salt in the urine are more pronounced. The effect of a diet that must be followed throughout your life will be shown by a control test taken after 3 weeks. If there are a lot of salts in the urine even after a diet, then drug treatment is prescribed.
Prevention
The human body reacts to excess salt not only by its appearance in urine, but also by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in tissues (spurs on the heels, growths).
You can prevent their formation by avoiding foods that cause these pathologies, switching to a balanced diet, and playing sports.
It is important to know that a high salt concentration in a urine test often warns of dangerous diseases of internal organs that do not have symptoms at the initial stage. Therefore, do not be lazy to take a urine test twice a year, it is necessary for your health!
Source: https://propochki.info/diagnostika/soli-v-moche-chto-eto-oznachaet
Prevention measures
Not a single person is immune from the appearance of sediment in excreted urine; however, by observing the rules of personal hygiene and some other generally accepted canons, it is possible to minimize the occurrence of this pathological condition.
The rules consist of the following points:
- Maintaining personal hygiene rules
- Protected sexual intercourse
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- hand washing to prevent helminthic infestation
- preventive measures to prevent the formation of kidney stones
- proper and healthy nutrition.