Sodium and potassium salts, deposited in the urine in large quantities, often appear due to poor nutrition. Deterioration of test results is a reason for a serious examination by a nephrologist or urologist.
Do not panic if large quantities of urate are detected in the urine. "What does it mean?" – the specialist will explain. You need to contact a nephrologist or urologist as soon as possible, get tested, do an ultrasound of your kidneys, and find out the cause of the deviation. Modern methods of therapy make it possible to quickly restore the health of the urinary tract.
Reasons for education
Excess urates are the result of excessive consumption of pickles, processed foods, meat products, addiction to coffee, chocolate, and fatty sea fish: cod, mackerel, herring. Protein products, especially of animal origin, should form part of the diet, but not dominate the menu.
Regular inclusion of smoked meats in the menu causes swelling, interferes with the removal of fluid, and creates additional stress on the kidneys. The habit of adding salt to dishes provokes not only the accumulation of urates, but also swelling, increased blood pressure, diseases of the urinary system, and gout.
Other causes of uraturia:
- taking certain medications;
- urinary tract infections;
- stones in the kidneys;
- glomerulonephritis;
- frequent intake of B vitamins (excessive amounts);
- kidney dysfunction;
- abuse of painkillers;
- renal failure;
- disruptions in metabolic processes;
- low fluid intake throughout the day.
Look at a selection of effective methods for treating cystitis with folk remedies at home.
Read useful information about how and how to treat urethritis in men at this address.
Signs and symptoms
A visit to a nephrologist or urologist to clarify the diagnosis is required if certain symptoms appear:
- discomfort, mild or severe pain in the lumbar region;
- increased blood pressure;
- the appearance of blood clots in the urine;
- development of weakness, nausea often occurs, and in severe forms of uraturia - vomiting;
- When urinating, pain and pain are bothered.
Sometimes patients experience the phenomenon of brown-pink urine. The reason for the incomprehensible phenomenon is a significant accumulation of amorphous urates or uric acid salts in the body. The norm is a few units, a sharp increase in indicators is a sign of the following diseases: glomerulonephritis, fever, acute or chronic renal failure.
Proper nutrition for pathology
To reduce the amount of uric acid salts in urine, the patient is advised to radically review his menu. It is also important to control your water balance - drink enough fluid per day. The urate diet prohibits the consumption of salty, fatty, smoked, and fried foods.
In case of such a violation, it is strictly forbidden to add the following products to your diet:
- alcohol;
- mineral water;
- canned food and spices;
- offal;
- concentrated meat broths;
- trans fats and margarine;
- natural dark chocolate and coffee;
- beef, pork and veal.
The urate diet requires strict adherence to nutritional rules. In this case, it is recommended to limit the intake of: various seasonings; fresh onions, cabbage; legumes; bread and baked goods.
The patient's menu for urate in the urine must include a list of the following products: oatmeal; fresh vegetables and fruits; fermented milk products; eggs; white grapes; baked or stewed potatoes; bell pepper; citrus. If you follow the rules of dietary nutrition, recovery occurs very quickly, and the effectiveness of therapeutic measures increases significantly.
Diagnostics
To confirm abnormalities in the tests, the patient gives urine again. If the indicators are the same (increased urate levels), the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the kidneys and a blood test.
To determine the cause of deviations, it is important for the doctor to know whether a person excessively consumes foods that accelerate the accumulation of potassium and sodium salts, and how much liquid he drinks per day. The doctor finds out what diseases the patient has suffered, whether there are any complaints: pain in the lumbar region, difficulty urinating.
Based on the results of tests and ultrasound examination, the urologist/nephrologist makes a diagnosis, recommends a diet, and selects medications. Neglecting the advice of a specialist and refusing to change eating habits over time leads to urolithiasis and gout - the deposition of uric acid salts in the joints.
How to treat such an ailment?
What to do if symptoms of uraturia develop? In such a situation, the main part of treatment is maintaining a proper diet. The diet helps stop the progression of the pathology, which subsequently leads to the complete disappearance of urea crystals from the patient’s urine.
For therapeutic purposes, medications are also used for this disorder. They help quickly remove salts from the body or completely dissolve urates formed in the urine. Treatment should begin as quickly as possible, before stones appear in the urinary organs. Otherwise, drug therapy will no longer be effective. For this purpose, medications are used:
- Asparkam, Panangin - are excellent for removing excess salts from the body. These medications are used for oxalaturia and uraturia. But if the patient is diagnosed with phosphaturia, taking these medications is strictly prohibited! They can be used in childhood.
- Allopurinol - causes urates to dissolve in secretions. At the same time, the amount of urea excreted by the kidneys sharply decreases.
- Canephron, Urolesan - they do not cause the dissolution of urate stones, but they are good at removing excess salts from the body. As a result, the process of urination is significantly improved.
- Blemaren - this drug comes in tablet form. It is very convenient to use as it easily dissolves in water. The medication has an alkalizing effect. After consuming it, the pH of the urine changes and the uric acid crystals present in it disintegrate. Dissolved salts are quickly eliminated naturally.
- Half-fallow decoction is a folk remedy that copes well with various disorders of urinary functions. This plant has a mild diuretic effect and eliminates excess salts.
Large amounts of urate in the urine are not formed immediately, but after a certain time. It is impossible to detect such a disorder at an early stage of development - which is why it is so important to regularly visit your urologist and periodically take urine tests. Timely examinations, a healthy lifestyle and proper diet will protect you from urolithiasis and other serious consequences of uraturia.
General rules and methods of treatment
An integrated approach to therapy is the key to recovery. It is important to treat kidney pathologies and infectious diseases, against the background of which abnormalities in urine tests appeared.
Recommendations:
- a strict diet with restriction of foods that provoke the accumulation of uric acid;
- taking herbal preparations to dissolve and remove urates;
- increasing the volume of fluid consumed per day to standard levels;
- taking herbal decoctions to cleanse the kidneys and remove harmful salts;
- physical activity, prevention of urinary stagnation;
- preventive measures, follow-up examinations with a doctor, ultrasound of the kidneys once a year.
On a note! Men often consume meat products in excess. The result is that the stronger sex suffers from urate accumulation 4 times more often than women.
Medications
Main groups and names:
- increase the outflow of urine, remove urates with herbal preparations: Canephron, Urolesan, Fitolysin;
- the drug Allopurinol reduces the production of uric acid, breaks down urate formations in the kidneys and ureters;
- Blemaren effervescent tablets are prescribed for the active dissolution of urates and oxalates, but if phosphates are detected, the medicine cannot be used;
- dissolves and removes uric acid salts with the drug Asparkam (a combination of magnesium and potassium).
Diet and nutrition rules
In the absence of severe renal pathologies, dietary correction returns the urate level to normal. Compliance with nutritional rules in combination with a drinking regime throughout life prevents repeated violations of indicators and normalizes water-salt metabolism.
Prohibited products:
- fatty meat, especially red varieties: veal, beef;
- strong meat, fish, mushroom broths;
- chocolate in any form, cocoa;
- beer, strong alcohol, wine;
- canned food;
- offal;
- smoked and boiled sausages;
- mineral water with calcium salts;
- animal fats;
- canned fish;
- mackerel, cod, herring, sprats;
- margarine;
- mushrooms;
- smoked meats, pickles, pickled vegetables.
Permitted names:
- potato;
- light grape varieties;
- eggs;
- fruits;
- marmalade, marshmallows;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- bran, sprouted grains of wheat;
- cucumbers;
- apples;
- pumpkin;
- eggplant;
- citrus;
- dried apricots;
- pears;
- watermelons;
- oatmeal;
- peaches;
- apricots;
- Bell pepper;
- cherries.
Learn about the signs of kidney inflammation in women, as well as treatment for the disease.
Effective methods for treating neurogenic bladder in women are collected in this article.
Go to https://vseopochkah.com/bolezni/simptomy/bolyat-pochki-ili-spina.html and read about why your kidneys hurt and how to distinguish symptoms from back pain.
Noticeably limit:
- lean fish;
- bread (white and gray);
- onion;
- legumes;
- cabbage of all varieties;
- salt;
- spices, seasonings;
- spinach.
Folk remedies and recipes
For uraturia, doctors recommend the herb half-palm. A natural diuretic rarely causes side effects, “gently” dissolves and removes salts. The urologist must definitely approve the herbal tea: it is important to know that the concentration of urates is increased, and not phosphates or, for example, calcifications. The herbal remedy acts effectively in the early stages of accumulation of uric acid salts.
Uraturia - what does it mean? The mechanism of pathology development
The reasons for the increase in urates can be different and depend largely on the condition of the person and his immunity.
Reasons for increased urate in men and women:
- poor diet, high consumption of salts in food;
- impaired renal function and impaired blood supply;
- insufficient amount of fluid entering the body;
- changes associated with medication use;
- infectious diseases associated with disorders of the urinary system;
- leukemia, but only certain types.
Pregnancy does not always have a positive effect on a woman’s body. Pregnant women experience urates much more often than others. This is especially true for pregnancy in the first trimester. Urates occur due to toxicosis or as a result of dehydration.
Causes of sediment in urine in pregnant women:
- a pregnant woman drinks little water;
- large amounts of meat and tomatoes;
- smoked food and chocolate;
- urates in the urine may appear if the body has a urinary tract infection.
If salts do appear, then the main recommendation remains dietary nutrition. After 2 weeks, when taking the test, there are no salt components, which means the main reason was poor nutrition. If the salt remains, then this is due to impaired kidney function.
If, during the test, urates are found in the child’s urine, then most often, a preliminary diagnosis may be leukemia or suspicion of gout. Only further diagnostics will allow a correct diagnosis to be made.
Causes of urate in the urine of a child:
- poor nutrition. The children's digestive system has not yet formed, and if it is not fed correctly, a uric acid precipitate will appear in the urine;
- you need to pay attention that the appearance of uric acid residues in the urine may indicate that on the eve of the test the child had a fever, vomiting, and diarrhea;
- the child consumes large amounts of chocolate.
On a note! If the child is taking antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, then the analysis may show sediment. Even antipyretic drugs affect the appearance of urate in the urine. If one of the signs was present before taking the test, then in case of a bad result you should not take the test seriously. It is worth refusing to eat food that affects the appearance of uric acid in the urine and only after two weeks have passed the test again.
Normalization of nutrition and avoidance of foods that provoke the formation of urates is a mandatory element of the treatment of uraturia. A diet for urate in the urine involves following the main rule - eating foods with a low salt content. The following principles must be adhered to:
- you should not allow yourself to go hungry or stick to a low-calorie diet;
- reduce protein content;
- completely stop eating canned food and offal;
- a ban is imposed on drinking bottled water.
Products excluded:
- fatty meats and fish;
- rich meat broths;
- cocoa;
- mushrooms;
- Black tea;
- beer;
- red wine.
It is necessary to limit consumption as much as possible:
- fish;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- spinach;
- of bread;
- Luke;
- salt, hot seasonings.
Citrus fruits are allowed, but only on the condition that their consumption does not lead to the formation of oxalates. Their content will be less if you eat dried apricots and apples, fresh pears and grapes. These fruits help remove excess fluid from the body and reduce particles of uric acid salts in the urine.
With uraturia, it is necessary to strictly limit the consumption of meat. All types of meat, except lamb and horse meat, must be kept in water for at least 3 hours before cooking. The first broth from white meat must be drained. Vegetables cooked with it should not be consumed. The daily intake of clean water should be at least 1.5–2 liters per day.
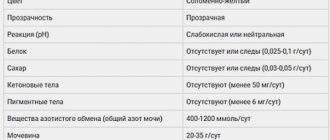
Urate salts are normally absent in urine. Their one-time detection is not a cause for concern. In such cases, doctors prescribe a repeat examination after a while. If urates are detected repeatedly, this indicates poor filtration capacity of the kidneys. The pH of the urine, which largely depends on the diet, is of decisive importance.
What are urates?
Urates are salts of uric acid. Protein and purine compounds enter the body along with food, which stimulate the formation of uric acid. If you abuse food rich in these compounds, urates are found in the urine. Normally, these salts are soluble, but with a significant increase in concentration, the filtration system of the kidneys ceases to cope with its function. Amorphous urates begin to be excreted in the urine. This pathology in medicine is called uric acid diathesis or uraturia.
The appearance of these salts in excreted urine requires observation and periodic examinations.
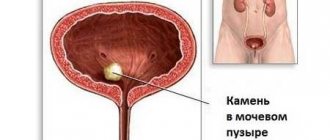
- Amorphous urates in urine in large quantities are a harbinger of the development of urolithiasis. Accumulating in the body, they are eventually converted into urate stones. Stones can cause renal colic, which is expressed in severe unbearable pain that is localized in the lower back.
- The second serious complication of uraturia is gout. With this pathology, urate salts gradually accumulate and are deposited in the tissues of the body. The disease is accompanied by severe pain, which occurs against the background of damage to the patient’s joints. Treatment of pathology takes a long time.
Once uraturia is detected, treatment should begin immediately. The course of therapy is selected by the doctor individually. First, the specialist finds out the peculiarities of the patient’s diet. In some cases, it is possible to reduce the concentration of salts by adjusting the usual menu. The main task of the patient is to fully comply with medical prescriptions, recommendations, and undergo recommended examinations.
The main goal pursued by doctors for uraturia is the dissolution and removal of excess salts from the body. They approach the problem in a comprehensive manner. Often, along with the normalization of salt concentrations, other chronic pathologies are treated. In some cases, improvement can be achieved by simply adjusting the diet, so doctors begin collecting anamnesis by studying the patient’s menu.
1. Herbal medicines that help remove urates from the body:
- Urolesan;
- Canephron;
- Phytolysin.
2. Agents that reduce the production of uric acid and promote the dissolution of urates:
- Asparkam;
- Allopurinol;
- Blemaren.
Diet for uraturia
A diet for urate is a mandatory component of effective therapy. In most cases, normalization of salt concentration can be achieved already at the stage of nutrition correction.
Doctors advise consuming less:
- fish;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- Luke.
Nutrition should be balanced. The number of meals should not be less than 4, ideally 6. After eating, there should be a feeling of slight hunger: overeating has a bad effect on the general well-being and metabolic processes in the body, and increases the load on the patient’s digestive system.
The term uraturia is used in medicine to denote an increased content of urates in human secretions. This phenomenon indicates a change in the composition of urine and metabolic disorders.
What are urates? These are crystalline substances that are formed in the fluid secreted by the kidneys from uric acid. Urea itself is produced by the body during the metabolism of purines - specific compounds that form the DNA structure of each cell. The level of uric acid also increases after consuming certain foods and certain medications.
The mechanism of development of such a disorder could not be fully studied, because urine is a complex and multicomponent liquid formed by the filtering system of the kidneys. A change in the chemical composition of secretions does not always lead to the appearance of salts. These components can remain dissolved in urine for a long time without forming a sediment. In this case, organic substances prevent the formation of urate in the urine.
What is the norm of uric acid salts? In a healthy person, urates, as well as phosphates or oxalates, should not be detected in the secretions. But a small amount of these crystals in urine is acceptable. Therefore, if the study results show 1 or 2 pluses, this indicator is the norm and indicates a small amount of urates.
Urate salts in a child’s urine
Main reasons:
- unhealthy diet (distortions in the menu, like in adults);
- congenital pathologies of uric acid metabolism;
- consequences of past illnesses;
- dysbacteriosis;
- stones in the kidneys;
- helminthic infestations;
- gout;
- starvation;
- frequent body overheating;
- lack of fluid throughout the day.
Children whose relatives suffer from diabetes, pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, obesity, heart disease, and blood vessels have a tendency to accumulate uric acid salts.
To exclude pathological changes, the pediatric nephrologist prescribes a diet, and after a while the child takes tests again. If there is no improvement, then an in-depth examination will be needed to identify the causes of abnormalities in the composition of urine. An ultrasound of the kidneys, bacterial culture and a general urine test are required.
In the treatment of uraturia in children, many types of drugs are used that improve urine output in adults. For example, Asparkam is prescribed even to children.
Important! Refusal to adjust the diet, indulging the child’s whims accelerates the accumulation of harmful salts, leads to the development of urolithiasis, impaired uric acid metabolism - gout develops.
Why do salts accumulate?
The cause of the accumulation of urates is considered to be an unbalanced, monotonous diet, along with its excessiveness and irregularity. Here is an approximate list of products whose consumption affects the concentration of urates:
- red meat;
- all types of canned food;
- offal sausages;
- offal, smoked meats;
- spices, herbs.
The reasons may be related to the following situations:
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary system;
- the effect of stress on the body;
- taking medications (antibiotics, painkillers);
- violation of metabolic processes.
The causes of uraturia are associated with dehydration of the body, when poisoning or infectious diseases are accompanied by frequent diarrhea and vomiting.
During pregnancy, small amounts of urate accumulate in the urine due to dehydration of the body that occurs during toxicosis.
When the levels of these substances exceed the norm, it is necessary to exclude infectious diseases of the genitourinary organs. To minimize the development of this situation, it is necessary to maintain water-salt balance and adhere to a diet.
Urate salts accumulate in a child’s urine mainly for the same reason as in adults – poor nutrition. Eating large amounts of meat, fish, cheese, tomatoes, and chocolate leads to the accumulation of salts. Normalizing your diet will help eliminate this problem.
Certain diseases of the child can cause this condition: if before the discovery of this fact the child had a fever, vomiting with diarrhea, then the antibacterial drugs or antipyretics used could affect the results of the analysis. This condition is temporary and does not cause concern to parents.
Urates in urine during pregnancy
Causes:
- intoxication due to dehydration, especially in the first trimester;
- an excess of red meat, fish, chocolate, coffee, smoked meats, tomatoes, spicy foods in the menu;
- daily fluid intake is lower than normal - less than two liters;
- kidney diseases;
- urinary tract infections.
If urine tests worsen or negative symptoms appear, the woman should visit a nephrologist and tell the gynecologist about the problems that have arisen. For mild uraturia in pregnant women, therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis; the safe herbal drug Canephron is often used. In case of pronounced toxicosis, the doctor gives a referral for inpatient treatment.
Preventive recommendations
Patients experiencing manifestations of uraturia should know how to prevent a re-increase in indicators. A proper diet in combination with a drinking regime significantly reduces the risk of relapse and prevents the accumulation of harmful salts.
Basic preventive measures:
- moderate consumption of animal protein;
- more vegetables and fruits in the diet;
- offal, veal, sprats, cod, mackerel - items that can be consumed no more than once a week;
- refusal of strong coffee and tea, chocolate, sweets;
- drink up to two liters of liquid per day (more in hot weather), half the volume is clean water, which flushes the kidneys;
- eat smoked meats, pickled vegetables, pickles, canned food, sausages, fatty fish and meat less often;
- replace strong broths with light vegetable soups;
- on the recommendation of a doctor, take courses of medicinal herbs that have a beneficial effect on the kidneys;
- move more: “sedentary” work provokes stagnation of urine, varicose veins, swelling, venous insufficiency;
- stop taking uncontrolled medications;
- treat acute inflammatory diseases in a timely manner and prevent renal pathologies from becoming chronic;
- do an ultrasound of the kidneys annually, take a general urine test every three months to monitor acidity levels;
- If you experience problems with urination, changes in the color of the liquid, the appearance of foreign impurities, mucus, or blood, contact a urologist or nephrologist.
The accumulation of urates is a problem faced by many meat lovers and people who are skeptical about fluid intake standards. The accumulation of uric acid salts also occurs in kidney diseases.
If the level of urate in the urine increases, you should not hesitate to visit a doctor. Taking medications, diet, drinking regimen, and healthy herbs return the indicators to normal. Ignoring recommendations provokes the development of gout, severe pathologies of the urinary tract, including nephrolithiasis, and renal failure.
In men
In men, increased urate levels and associated complications are more common than in women. This is due to the peculiarities of hormonal levels, which also affect metabolism.
stones usually form , which are not capable of causing serious damage to the organs of the excretory system, and often pass on their own, even without treatment. Problems associated with an increase in salt concentration in men usually arise after 35-40 years.