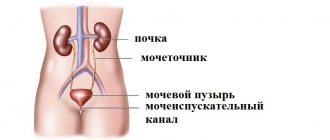
Older cats are susceptible to diseases of the excretory system. In addition to inflammation of the bladder and kidneys, pets often suffer from urolithiasis. (ICD). The cat's waste is eliminated in the form of salts in urine. Their solubility has its limits.
An increase in salt concentration, a change in pH, and the appearance of crystallization nuclei lead to the formation of solid deposits that impede the outflow of urine. Concretions are grouped into grains of sand or stones. They can clog the urinary duct, which poses a threat to the animal’s life.
Stones of different chemical compositions are formed in the urine of cats, but most often Struvite is formed. Therefore, the term is used when it comes to uroliths in general.
Types of uroliths
There are two types of urinary stones observed in cats:
- Struvites (Tripelphosphates).
- Oxalates are compounds of oxalic acid.
Struvite
Formed in alkaline urine. They represent a complex mixture of salts, in which ions of trivalent Phosphorus, as well as Calcium, Ammonium, and Magnesium predominate. Crystallization may be caused by dehydration.
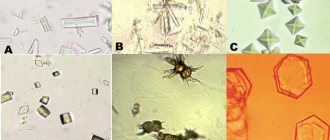
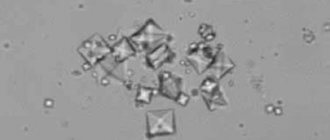
Up to 80% of uroliths in cats are represented by Tripelphosphates. These are loose or hardened formations of yellow or cream color. Under a microscope, crystals with diamond-shaped edges are observed in the urine.
Struvite can be dissolved with medication and is radiopaque, which makes conservative treatment of cats possible.
Oxalates
They are formed at acidic pH of urine, rapidly crystallize, and have a complex structure with sharp edges. Stones of increased hardness are difficult to dissolve, so conservative treatment is ineffective.
Conditions for struvite formation
Struvite is formed under the influence of the following factors:
- Sufficient amount of mineral salts.
- Duration of stay in the lumen of the urinary canal.
- Ph urine > 7.0.
- There is protein in the urine.
Struvite
These formations belong to the category of phosphate stones.
The formations contain ammonium magnesium phosphate and carbonate apatite.
Struvite can form only in an alkaline environment affected by infection.
Thus, the main reasons for the formation of struvite stones are:
alkaline urine reaction; the presence of certain bacteria in the urinary tract.
Struvite is characterized by its ability to quickly increase in size, filling the entire cavity of the kidney and causing complications such as sepsis and acute renal failure. It is also worth noting that struvite tends to form in women.
Experts note that this category of formations is the most difficult to treat. The only way to get rid of the stone is to use shock wave lithotripsy.
During therapy, it is important that the smallest particles of stones leave the body. Otherwise, the disease will reappear.
Causes
The formation of stones provokes alkalosis. This condition of urine is caused by the following reasons:
- Unbalanced cat nutrition.
- Pathology of water and salt exchange.
- Congenital predisposition.
- Hormonal imbalance in a cat.
- Adynamia.
- Infectious diseases.
- Chronic pathologies.
Unbalanced diet
Excess protein with a shortage of energy supplied, mainly from carbohydrates, is utilized by putrefactive intestinal microflora, forming toxins that change the properties of urine. An important role is played by ensuring the need for essential amino acids, for example, Taurine, as well as vitamin A.
Pathology of water and salt metabolism
Fluid deficiency, its poor quality, and dehydration lead to an increase in the concentration of urinary salts. Chemical compounds precipitate from saturated solutions.
Congenital predisposition
Outbred cats, Persians, and Birmans are susceptible to urolithiasis.
Hormonal disbalance
Hypersecretion of Parathyroid hormone is accompanied by an increase in calcium concentration and an increase in urine pH, which provokes crystallization.
Adynamia
A sedentary existence leads to stagnation of fluids, increasing the risk of precipitation of sparingly soluble urine salts. Such cats are prone to obesity, diabetes, and pancreatitis. The indirect cause of adynamia is castration. Cats deprived of sexual motivation are prone to decreased mobility.
Infectious diseases
The penetration of conditionally pathogenic microbes from the blood, lymph or genitals causes inflammation of the excretory canals. Necrotic cells become crystallization nuclei.
Why does the disease occur and how does it develop?
The main cause of the pathology is a violation of protein and mineral metabolism. Depending on which substances are not metabolized and crystallize, stones are of the following types:
- Struvites, also known as tripelphosphates. They consist of magnesium, ammonium, and phosphate salts. These are the most common types of stones in cats (80% of all cases). Most often they occur in animals aged 3 to 6 years due to poor nutrition.
- Oxalates are stones made from calcium salts and ammonium oxalate. They are found mainly in adult cats over 6 years of age.
- Cystines are formations that arise due to cystinuria (impaired absorption of amino acids). Often the pathology is hereditary. The disease manifests itself mainly in cats older than 5 years.
- Urates are solid formations of uric acid. They are rarely detected, but cause the most severe suffering to cats (such stones have sharp edges and injure the walls of the urinary tract, causing bleeding, inflammation, and suppuration).
Congenital predisposition and external factors lead to the formation of stones. The most common catalyst for the development of the disease is an unbalanced diet, when the animal receives an excess of proteins, phosphates and magnesium salts and at the same time does not receive enough carbohydrates, iodine and vitamins A, D. Other factors for the development of the disease are:
- Physical inactivity of the animal leads to obesity, deterioration of blood supply to internal organs and slowdown of metabolism.
- Improper drinking regime (lack of absorbed fluid) or drinking low-quality water with a large amount of foreign impurities.
- Natural predisposition. Most often, the disease develops in Maine Coons, Persian, Siamese, Burmese, Himalayan, and Carthusian cats.
- Increased calcium concentration in the blood. It occurs not only with an unbalanced diet, but also as a consequence of injuries, osteomyelitis, and osteoporosis.
Stones are found six times more often in cats than in cats. The fact is that male animals have a narrowed S-shaped urethra (this shape helps retain solid formations in the ducts). There is an opinion that castration of cats is a factor for pathology. In fact, the operation itself does not contribute to the appearance of stones in any way - this is only affected by the fact that the owners do not properly care for and feed the operated animal.
Fat cats often suffer from urolithiasis, since obesity and urolithiasis have common prerequisites - impaired metabolism, unbalanced diet, physical inactivity
Symptoms
The onset of stone formation is difficult to notice. The cat's appetite worsens, it becomes lethargic, and it experiences discomfort when urinating. Clinical manifestations develop gradually:
- The abdomen swells and becomes painful.
- The cat becomes annoying and rubs against its owner’s legs.
- When landing on the tray, a plaintive meow is heard.
- The cat begins to relieve himself anywhere.
- The filler becomes pinkish and hematuria develops.
- Observe thirst.
Recurrent cystitis becomes a constant companion of a sick cat. If stones block the lumen of the urinary canal, the cat stops drinking and eating. he experiences anuria, vomiting, and convulsions. The condition is life-threatening.
What is important to know when using ready-made food
Medicinal food is available only in the premium class. Each package indicates that this food is intended for cats with urolithiasis. It also says what type of stones can be used for it. The composition of your pet's stones can be found out at the veterinary clinic after examination.
If the cat has not been given dry food before, it should be introduced into the diet gradually. The main task is to accustom your pet to it, because due to the specific smell and taste, many animals refuse to eat it.
Water should always be within the cat's reach. Pour only filtered water and change it twice a day. Monitor how often your cat drinks water. If he doesn’t go near a bowl of water, or drinks rarely, then you can moisten the cat food with water, but not much. There is no need to dilute it to the point of porridge.
If your pet has a good appetite, he eats the entire portion and asks for more, do not follow his lead. Excessive gluttony leads to excess weight, which is unacceptable in case of urolithiasis.
It happens that animals get bored with monotonous food. In this case, you can choose a different brand of food, or replace dry food with wet canned food. But in both cases, purchase only medicinal, premium food.
A special word should be said about feeding from the table. No matter what pitiful face your prankster makes, no matter how he rubs against your legs, there should be no concessions. If you want to treat him with something, or he deserves some encouragement, give him a piece of his food. Over time, the cat will get used to this and will accept such a treat with gratitude.
If there are no veterinary pharmacies near your home, make sure that your kitchen always has a supply of medicated food for your pet. If suddenly the food runs out, you cannot give natural food even temporarily. Keep special canned food for such cases, they have a long shelf life.
Diagnostics
The presence of struvite in a cat is determined taking into account clinical signs, as well as additional information about the animal:
- Breed. Domestic cats, as well as Persians, their hybrids, and Birmans are susceptible to pathology.
- Age. Mostly animals over 6 years old are affected.
- Floor. Among cats, the disease occurs 6 times more often, which is due to anatomical features.
- Is the animal sterilized and at what age? When a cat is castrated early, the urethra remains underdeveloped, so the risk of blockage increases.
- Composition of the diet. The use of cheap ready-made food, natural food, especially with an abundance of fish and foods unusual for cats, increases the risk of urolith formation.
Using ultrasound or radiography, the location, type, shape, and number of stones are determined. Chemical analysis of urine, as well as crystallographic research, makes it possible to determine the type of stone and develop control measures.
Treatment
The therapeutic concept is developed based on clinical symptoms. If the urethra is blocked and the cat's condition is life-threatening, surgery is indicated. Responsible fellinologists deliver the pet to the clinic in a timely manner, and the veterinarian prescribes conservative treatment, which consists of dissolving the stones.
Surgical treatment
The following medical techniques are in demand:
- Catheterization. Emergency care for anuresis.
- Cystostomy. Removing stones from the urinary bladder.
- Urethrostomy. Elimination of obstruction of the urethra.
Conservative treatment
Measures to combat struvite in cats are as follows:
- Diet therapy.
- Organization of watering.
- Drug therapy.
With balanced feeding of the cat, the optimal pH of the urine is ensured, which prevents the precipitation of its components. To compose a diet from natural products that have a healing effect, the high professional skill of a fellinologist is required. Therefore, it is better to use ready-made food for a cat suffering from urolithiasis. Treating a sick pet to unusual food should be stopped - only dietary food.
It is necessary to pay attention to the organization of watering. It is better to drink bottled drinking water. The bowl needs to be washed daily, changing the drink 1…2 times a day.
Drug treatment consists of the following:
- General strengthening agents:
- To ensure the proper water-salt ratio, polyion mixtures are used.
- At the same time, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, detoxification therapy is carried out.
- Antispasmodics - Drotaverine.
- Stone-breaking drugs:
- Erwin the cat. Extract from medicinal plants. It has a diuretic effect and destroys stones.
- Stop Cystitis. Phytosuspension. Prevents the formation of stones and dissolves existing ones.
- Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents prescribed by a veterinarian.
What to feed a sick animal?
There is food made specifically for cats suffering from urolithiasis. However, only manufacturers producing premium food for animals have such lines. The cost of medicated food is often too high for cat owners.
Natural food, at first glance, seems to be a cheaper option, but when owners get acquainted with the list of permitted products, they realize that this is not so. In addition, preparing food for your cat will take extra time. It is for this reason that preference is often given to medicated food.
Dietary lines of dry food were developed by veterinary specialists. They are well balanced and contain only the components necessary for sick animals. When consumed regularly, this food promotes the dissolution of struvite and prevents the formation of oxalates. The rating of the most popular holistic-class foods for the treatment of urolithiasis includes the following brands:
- "Orijen"
- “Acana” (“Akana”);
- "Golden Eagle Holistic" ("Innova");
- "Cat Holistic" (Eagle Pack);
- “ANF holistic” (“ANF Holistic”);
- Earthborn Holistic.GO and NOW Natural holistic.Felidae;
- "Chicken Soup"
| Manufacturer | Ruler | Indications |
| "Royal Canin" | "Urinary S/O Feline" | Treatment of struvite urolithiasis, idiopathic cystitis, prevention of oxalate formation. |
| "Hill's" | "Prescription Diet™ Feline s/d" | Dissolution of struvite, acidification of urine. |
| "Prescription Diet™ Feline c/d Multicare" | Therapy of urolithiasis at the initial stage, dissolution of struvite formations, prevention of relapses of urinary tract diseases. | |
| "Purina Pro Plan" | "Veterinary Diets Urinary (UR) St/Ox" | Acidification of urine for the purpose of prevention and treatment of struvite stones, prevention of the formation of oxalates, treatment of idiopathic urination pathology. |
The exact serving size and types of foods that will be included in your pet's diet are determined depending on its age, condition and level of activity. However, there are a number of products that experts recommend giving to cats with urolithiasis. As you know, calculi in cats can be soluble or insoluble.
- boiled meat (chicken, beef, veal);
- vegetables, fresh or boiled (carrots, pumpkin, zucchini, cucumber, beets, broccoli, cauliflower);
- porridge (rice, millet, wheat, buckwheat).
With struvite, the diet will be slightly different. If phosphate formations are present in the urinary system, then the following products are recommended for cats:
- boiled rabbit, chicken, veal;
- boiled chicken or beef liver;
- porridge (oatmeal or rice);
- boiled egg white.
If a pet is diagnosed with urolitic pathology, the owner needs to determine what he will feed his cat. Diet planning is one of the main stages of treatment. The diet can include both natural products and ready-made food.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of uroliths, the following actions are recommended:
- Replace low-quality drinking water with bottled or filtered water.
- Monitor urine pH using special tests.
- Keep the tray clean. A cat would rather wait until a walk than use a dirty toilet.
- Prevent obesity. Prepared high quality feed is used. Active games are played regularly. Avoid the consumption of treats and human food.
- Avoid hypothermia and overheating.
- Undergo regular diagnostic examinations twice a year.
If a cat develops uroliths, it will have to change its lifestyle. A responsible fellinologist is able to provide a sick pet with satisfactory health and a long life.
The detection of an increased content of phosphate stones in a urine sample almost always indicates the presence of a bacterial infection and an increase in urine pH. Triple phosphates are often formed in young children, pregnant women and the elderly. This selectivity is closely related to health problems and decreased immunity. Being a disturbing symptom, tripelphosphates themselves can cause serious harm to the human body.
Treatment methods for urolithiasis in dogs
Keeping dogs is quite a complex process. They require regular walks, properly selected nutrition, the introduction of vitamins and minerals into the food, as well as certain conditions of detention. If you think that only your dog’s comfort depends on this, then you are completely wrong. It is the diet that affects the health of your pet. A deficiency or, on the contrary, an excess of minerals can cause one or another pathology. The same applies to conditions of detention.
Animals that are often exposed to drafts or sleep on a cold floor (ground) without bedding are susceptible to inflammatory diseases. Urolithiasis occurs especially often in such conditions. This is a dangerous disease that can lead to disastrous consequences. That is why treatment of this disease in dogs must be timely and always effective.
Urolithiasis disease
Triple phosphates found in the urine are a sign of urolithiasis, a common urological disease. It is manifested by the formation of stones in the organs of the urinary system. Most often, phosphate stones form inside the bladder and structural kidney elements.
Kidney pathology can manifest itself as unpleasant symptoms even in newborns, but the disease is most often diagnosed in middle-aged people. There is a certain pattern:
- Triple phosphates form inside the bladder in older people and children.
- Phosphate stones form in the kidneys and ureters in people 20-45 years old.
Experts suggest that such selectivity is associated with insufficient immunity of the elderly and children. The prerequisites for the formation of tripelphosphates are a monotonous diet and unfavorable external factors. Unfortunately, the individual stages of pathogenesis, as well as the etiology of the disease, are not fully understood. The chemical reactions underlying the crystallization of tripelphosphates have found a scientific basis, and the infectious component of the pathogenesis has also been confirmed. But the overall picture explaining the formation of phosphate stones still has significant gaps at certain stages.
Oxalates
Oxalates are an inorganic type of kidney stones. They are crystals with sharp protrusions. The shade of such stones can be brown or dark brown.
Oxalate stones are formed as a result of chemical reactions involving oxalic acid and calcium.
Patients who prefer to eat plenty of foods that contain a sufficient amount of vitamin C often provoke the process of stone formation themselves.
Vitamin C is found in large quantities in many vegetables and fruits. To prevent oxalaturia, doctors recommend following a strict diet.
Citrus fruits, tomatoes, legumes, and sorrel are prohibited. Drinking coffee and chocolate is also prohibited.
Oxalaturia is also characteristic of those patients who have a deficiency in the body of B vitamins, potassium and magnesium.
Pathologies such as pyelonephritis and diabetes mellitus can act as provocateurs for the occurrence of oxalate stones in the kidneys.
The process of stone formation is also typical for those patients who have a failure of metabolic processes.
To eliminate uroliths, doctors recommend not only following a diet, but also increasing physical activity to counteract congestion. Doctors also direct patients to increase their drinking regime.
Tripelphosphates - what is it?
Triple phosphates, or struvites, are formed as a result of numerous chemical reactions and there is only one reason for their formation. Crystallization occurs due to metabolic disorders:
- The composition of the blood changes.
- There is an increase in salt content.
- The amount of fluid circulating inside the body decreases.
An increase in the concentration of salts in urine that cannot dissolve in water provokes crystallization processes, and this is a direct path to urolithiasis. Which chemical elements will form the basis of the calculus depends solely on the acidity of the urine. For example, with alkaline urine, stones crystallize from sulfur-containing amino acids, as well as uric acid and its compounds. Triple phosphates are formed when the pH shifts to the alkaline side, like calcium stones.
In order for tripel phosphates to begin to crystallize, the concentration of ammonium anions must increase. And this is only possible for one reason - the content of protein breakdown products in the urine will sharply increase, which always happens when an infectious focus forms in the body. So, having detected tripelphosphates in the urine, doctors diagnose the patient to identify hemorrhagic cystitis or pyelonephritis.
If a person’s health is fine, then his urine contains salts and minerals that prevent the crystals from sticking together to form larger conglomerates. Such inhibitors include:
By entering into chemical reactions with small crystals, they destroy them and (or) prevent them from settling inside the structural elements of the kidney. With a low content of crystallization inhibitors, the formation of stones is sharply accelerated.
Tripelphosphates are formed in the upper part of the urinary tract, especially in the calyces and pelvis of both kidneys. For their crystallization, phosphorus, magnesium and ammonium ions are needed, as well as a shift in urine pH to the alkaline side. Experts often call phosphate stones infectious stones, since the emergence of a favorable environment for their formation occurs only in the presence of an inflammatory process. Tripelphosphate does not need much time to grow - within a few months a large stone will form inside the kidney.
At this stage, the patient usually undergoes nephrolithotomy - this is the removal of stones from the renal parenchyma by cutting it. If irreversible damage has already occurred inside the kidney, then it is removed.
Classification
Stones are formed from a mixture of minerals and organic substances. Modern medicine offers four main groups of kidney stones:
— Oxalates and phosphates . This is the most common category of education. Stones are diagnosed in 70% of patients diagnosed with urolithiasis. The basis of formations of inorganic origin are calcium salts.
— Struvite and phosphate-ammonium-magnesium stones. This type of stones occurs in 20% of patients. The cause of the formations is diseases of the urinary tract of an infectious nature. That is why they are called infectious.
- Urats . Diagnosed in 10% of all patients. The cause of the appearance is excess uric acid and some pathologies of the digestive tract.
— Xanthine and cystine stones . Quite rare formations. Occurs in 5% of patients. Experts associate their appearance with congenital pathologies and genetic disorders.
It is quite difficult to detect stones that are pure in composition; half of the patients are diagnosed with mixed type formations.
Reasons for the appearance of tripelphosphates in urine
Struvite is not capable of damaging the ureters during the outflow of urine to the bladder. They are soft, fragile and smooth, silver or gray in color. The shape of the stones resembles an elongated prism with smoothed corners, similar to the lid of a coffin. The appearance of small phosphate stones in the form of an amorphous sediment can occur due to sudden changes in diet. The urine of vegetarians contains an increased amount of tripelphosphates due to the refusal of animal proteins and the transition to plant foods.
Usually this should not be a cause for alarm, because, from a chemical point of view, everything is quite understandable. With the breakdown of animal protein, the acidity of urine sharply shifts to the acidic side, since the products of metabolism are acid anions and neutral cations. Plant protein, on the contrary, during metabolism shifts the pH to the alkaline side, which serves as a favorable environment for the formation of phosphate stones.
The amount of amorphous phosphates increases in urine if they predominate in the diet:
- plant food;
- dairy products;
- lean fish.
If, during a urine test, the amount of tripelphosphates is increased, but there are no symptoms of infectious diseases, then you need to balance your diet. After 10-14 days, you will need to retake biochemical tests to compare the results.
Very often, adherents of a one-component plant-based diet after losing weight begin to intensively treat urolithiasis. Nutritional errors provoked the formation of crystals inside the kidneys and their growth. When following such a diet, the body’s enzyme system malfunctions, the amount of vitamins and mineral elements decreases sharply, as well as immunity. An ideal environment is created for the formation of phosphate stones.
Signs of bladder stones
Struvite scratches the urethral mucosa, so blood may appear in the urine.
Stones in the bladder may not bother the animal for a long time. However, cat owners may experience the following symptoms:
- Frequent urination.
- Uncontrollable bowel movements.
- When walking on a “small” path, the pet becomes very tense.
- Urine usually comes out in a thin stream or drops.
- The presence of bloody impurities in the urine.
- Cloudy urine.
- Constant thirst.
Having noticed the first signs, you should not think about whether it is dangerous. It is better to immediately seek advice from a specialist.
Symptoms of tripelphosphate formation
Large phosphate stones in urine are rarely discovered by chance. Their accelerated formation in the calyces and pelvis is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. Tripelphosphate kidney stones provoke deformation of the inner lining of the urinary tract. A sign of significant damage is the appearance of blood clots or drops of blood in the urine. Urinary tract infections or other kidney problems can cause thick urine, difficulty urinating, and painful urination. One of the symptoms of the formation of tripel phosphates is a stagnant smell of urine.
The formation of crystals into large phosphorus conglomerates from chemical compounds occurs with the direct participation of pathogenic microorganisms and infectious agents, so patients are often diagnosed with the following symptoms:
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite.
- Hyperthermia, a feverish state accompanied by chills and cold sweat.
- Increased fatigue, apathy, weakness.
- Abdominal pain. Usually the pain is not pronounced and is dull and aching in nature.
One of the symptoms of tripelphosphate formation is increased fluid intake. Sometimes a person attributes thirst to the onset of diabetes and makes an appointment with an endocrinologist. After testing, it turns out that his phosphate levels are too high and he needs to consult a nephrologist.
Types of urinary formations and risk factors for their development
The most common stones found in animals of this species are divided according to their chemical origin into phosphoric acid salts (struvite or phosphates), oxalic acid salts (oxalates) and uric acid salts (urates).
Struvite.
These are the most common salts found in cat urine sediment. This is the basis for the formation of stones of a phosphate nature and the main factor here is an excess of phosphorus in the food consumed by the animal, firstly, and food that gives an acidic urine reaction, secondly. Struvite is an alkaline salt, so it is highly soluble in an alkaline medium. When the urine reaction changes to acidic, these salts lose solubility, precipitate and become the basis for stone formation. Thus, the decisive factor in the occurrence of urolithiasis with phosphate stones is food with a high phosphorus content - fish. Of course, there are other foods rich in phosphorus, but cats, as a rule, do not eat them. For cats, the actual cause of phosphate stone formation is precisely the consumption of fish - raw or boiled.
In addition, there are conditions conducive to the formation of phosphate stones. By themselves, they cannot cause the onset of a pathological process, but if there is a cause, they contribute and accelerate its development. Such risk factors include hereditary predisposition, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and previous diseases.
The hereditary predisposition is that cats have a developed ability to retain water in the body. Cats received this phylogenetic inheritance from their ancestors, who existed in conditions of water scarcity. Cat urine is naturally highly concentrated. However, in modern home conditions, this ability changes its absolutely positive significance in the opposite direction. With ill-conceived, random, uncontrolled nutrition, the process of phosphate stone formation can begin. Therefore, your cat should always have access to clean and fresh drinking water.
Oxalates.
These are salts of oxalic acid, which are formed when animals consume feed containing an excess amount of this substance - nuts, seeds and others. However, cats consume this type of food extremely rarely. It is possible, of course, that there is an individual taste preference, but oxalate urolithiasis is still a rarity.
Urats.
Uric acid salts. They are formed in all situations that are accompanied by the disintegration of cell nuclei with the release of nucleic acids and their further degradation into uric acid. This is possible in conditions of recovery due to
Struvite from a cat's bladder.
past infectious and inflammatory diseases, as well as with a feeding regime overloaded with meat. There are other reasons, for example, keeping the animal in an area with high radioactivity.
Diagnosis
The initial examination consists of palpating the abdominal area and assessing the general state of health. It is obligatory to submit biochemical tests of urine and urine:
- An increase in the content of leukocytes and protein metabolism products indicates an inflammatory process, presumably in one of the parts of the urinary system.
- A low platelet count in blood samples indicates a weakened immune system.
To identify the causative agent of an infectious disease, the main cause of increased crystallization of tripelphosphates, a urine sample is cultured. Also important indicators are:
- Concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen and magnesium ions.
- Quantitative content of stone formation inhibitors.
- An indicator of urine acidity.
If pathogenic microorganisms are detected, the following examinations of the pelvic organs are carried out:
- Ultrasonography.
- CT scan.
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
To determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of stones, X-ray defractometry and infrared spectrophotometry are performed. Analysis of the composition of tripel phosphate is mandatory when diagnosing urolithiasis, since the quantitative content of phosphorus allows us to establish the cause of the development of the pathology and its pathogenesis. Knowledge of the pathology of a metabolic disorder will help when prescribing drug or surgical therapy.
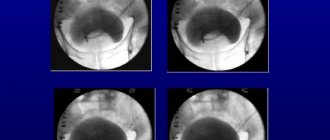
If urolithiasis is suspected, it is mandatory to obtain a survey x-ray of the abdomen in the area of the kidneys, bladder and ureters. Thus, X-ray positive stones are diagnosed. This technique allows you to visualize stones and determine the area of their localization.
To make treatment more effective, consultations with an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist and nutritionist will be required.
Cystine stones
A rather rare type of stones, the formation of which is caused by a genetic pathology - cystinuria.
Children and young people are most susceptible to the development of cystine stones.
The main component of the stone is amino acid.
Doctors call the main feature of the symptoms of the disease constant pain, even after taking painkillers.
Treatment of the pathology is as follows:
changing the acidity of urine with citrates; special diet; drug treatment; crushing stones; surgery if conservative therapy is ineffective.
In some cases, the only way to cure the patient is a kidney transplant.
Drug and surgical treatment
A dangerous complication of urolithiasis is renal colic, accompanied by sharp, unbearable pain. To relieve it, injections of atropine and antispasmodics are used. Doctors also prescribe:
Treatment begins with eliminating the cause of the formation of tripelphosphates - an infectious disease of the urinary system. Antibiotic therapy is carried out for 10-14 days using:
- Clarithromycin.
- Amoxiclava.
- Antibiotics of the cephalosporin series.
In case of extensive inflammation, Metronidazole is additionally prescribed, and sometimes antifungal treatment is required. To prevent the development of dysbiosis, doctors recommend taking probiotics (Acipol, Linex, Bifiform), immunomodulators (Amiksin, Immunal, Cycloferon), vitamin complexes (Selmevit, Vitrum). To prevent relapses of infection, anti-inflammatory herbal drugs (Cyston, Canephron), as well as antimicrobial drugs (Nolitsin, Norfloxacin) are used.
If drug treatment is ineffective or tripelphosphates have grown excessively, then surgical operations are performed to remove the stones. These include:
- Abdominal operations. During the operation, the abdominal cavity is opened and the surgeon removes tripelphosphates.
- Laparoscopy. The operation is characterized by minimal mechanical damage to tissue: the surgeon makes small punctures through which stones are removed using special instruments. This technique is characterized by rapid recovery of patients.
- Lithotripsy. Triple phosphates are destroyed remotely using a shock wave. Under X-ray control, a directed electromagnetic wave crushes the stones into small pieces, which are then passed out of the body during urination.
- Transurethral method. A thin metal tube with a built-in video camera is inserted through the ureter to the area where the stone is located. The stone is then broken down by laser, ultrasound or pneumatic tools.
- Percutaneous nephrolitholapaxy. The most suitable option for removing tripelphosphates that have already taken on the appearance of branched corals. A puncture with a diameter of 10 mm is made in the lumbar region, through which stones are removed.
After surgery to remove tripelphosphates, the patient should regularly donate blood and urine to evaluate the effectiveness of the surgical intervention and prevent relapses.
Cholesterol and protein
Very rare types of kidney stones include protein stones - white formations, small in size, flat in shape and soft in consistency. Such pebbles are formed from fibrin (a protein formed during blood clotting and which is, in fact, the basis of a blood clot). Cholesterol stones are also soft in consistency, but their color is black. Cholesterol formations are formed entirely from cholesterol and are characterized by increased fragility.
The chemical composition of kidney stones does not affect the symptoms of the disease, but this information is extremely important in choosing the treatment of urolithiasis and its prevention. To avoid the development of urolithiasis, you need to drink more fluids (3-3.5 l), eat right and lead an active life.
Tweet
Prevention
Regardless of the treatment method, patients are recommended a special diet during the recovery period:
- Increasing the daily volume of clean water consumed.
- Limit salt and spices.
- Increasing the amount of fiber consumed.
Since tripelphosphates crystallize only in the presence of breakdown products of pathogenic microorganisms in the urine, personal hygiene should be observed to prevent bacterial infections. A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle are an excellent prevention of tripelphosphate crystallization.
Tripelphosphates (struvite) are a dangerous type of kidney stones. Such stones have a smooth surface, so they do not damage the mucous membranes, but they can become huge, which is why over time the kidney has to be removed.
Classification of kidney stones
International mineralogy classifies kidney stones into 4 main types:
Compounds of inorganic calcium salts - phosphates oxalates - these types of stones are found in 7 out of 10 patients with urolithiasis; About 15-19% of patients carry struvite and magnesium phosphate stones in the kidneys; Uric acid stones, called urates, occur in approximately every 10 patients; Cystines and xanthines account for only 1-3% of all cases of urolithiasis and are formed as a result of a malfunction in amino acid metabolic processes; There are also carbonates, protein and cholesterol stones, but they are practically never found in their pure form.
Urats
Urates are formed when there is an excess of uric acid salts. Their color is similar to brick, with a hard texture and smooth surface. Kidney stones of urate origin are quite difficult to notice on an x-ray, but they are easily detected by ultrasound. Urate stones dissolve without problems under medicinal influence.
The formation of urate formations is promoted by digestive pathologies and renal tubular disorders. If you have urate kidney stones, it is recommended to completely exclude highly acidic foods from the menu and drink more fluid (about 3 liters a day) in order to reduce the acid concentration in urine. It is advisable to eat more vegetable stews and salads, fruits.
Phosphates
Phosphate types of kidney stones are formations based on phosphoric acid salts. They can be completely smooth or slightly rough to the touch. The formation of stones with a similar chemical composition is facilitated by a violation of material metabolism, coupled with the abuse of products of dairy and plant origin. Phosphate kidney stones are predominantly milky white or light gray in color and grow rapidly. The texture of such pebbles is soft, so they can easily be crushed with mineral water with an alkaline base. Acidic juices (lingonberries, cranberries) help in crushing such stones, which help remove salt deposits. The formation of phosphate stones is indicated by the presence of white flakes in the urine.
Attention! Phosphaturia develops as a result of abuse of calcium-rich foods, so patients are recommended to eat a diet that excludes dairy and fermented milk products.
Most often, such stones are produced using the Pechenevsky method, which consists of using infusions of rosehip, barberry and grapes. Regular use of these products helps to quickly dissolve phosphate stones. A special diet involves excluding fermented milk products from the daily menu and limiting the consumption of vegetable dishes and fruits. Therapeutic nutrition is based on flour products, fish and meat with the addition of vegetable oil.
Oxalates
Oxalate formations are distinguished by a dense consistency, uneven surface, often having sharp and even spiky edges. When moving such a calculus, injuries are caused to the mucous membranes, internal bleeding appears, causing the color of the urine to acquire a reddish tint. These stones are usually gray or black in color and can be easily detected by x-ray examination. The formation of oxalate kidney stones is facilitated by excessive saturation of the body with oxalic or ascorbic acid, so it is recommended to avoid citrus fruits and sorrel, coffee and chocolate, tea and ascorbic acid.
The formation of oxalate stones can develop as a result of vitamin B6 deficiency or against the background of certain intestinal pathologies.
Oxalate stones, unfortunately, do not dissolve, so treatment with magnesium drugs and diet therapy is resorted to as a preventive anti-relapse measure. Patients are advised to limit their consumption of carbohydrate and overly salty foods to ensure alkalization of urine. Doctors consider oxalate stones to be the most dangerous for the patient. They often do not respond to lithotripsy and must be removed by open surgery.
Carbonates
Carbonate kidney stones are formed from carbonic acid salts. They are usually white, with a smooth surface and varied shapes.
Struvite
Struvite refers to fast-growing soft formations of white and light gray shades, having a rough or smooth texture. Struvite formations can form renal coral stones; they are practically insoluble in dissolution, so they are treated with lithotripsy.
Lithotripsy is a method of destroying kidney stones using shock waves. Lithotripsy can be electromagnetic, electrohydraulic or piezoelectric. The technique is characterized by low trauma, non-invasiveness and high efficiency.
The formation of kidney corals is promoted by stagnation of urine in the kidneys, as a result of which a bacterial infection develops. In a relatively short period of several weeks, struvite fills the entire renal cavity. The result is a cast that resembles the renal pelvis. The formation of struvite can also be facilitated by various paralysis and paresis that develop as a result of injuries or diseases of a neurological nature. This type of kidney stones occurs predominantly in female patients and is characterized by asymptomatic development.
Tripelphosphates - what is it?
The formation of tripel phosphates is caused by chemical reactions, the main reason for which is metabolic failure. This creates:
- blood composition changes;
- the percentage of salts increases;
- the volume of fluid circulating throughout the body decreases.
Due to the increase in salts in urine, their inability to dissolve with water, crystallization occurs. And this is fraught with urolithiasis. The calculus is formed from various chemical elements, taking into account the pH of urine. For example, the alkaline composition of urine leads to the formation of stones and sulfur-containing amino acids, urea, and their compounds. Triple phosphates form when the pH of urine becomes more alkaline.
For struvite formation, an increase in the percentage of ammonium anions is necessary. This condition is provoked by protein breakdown products when an infectious pathogen enters the body. When struvite is detected, doctors suspect pyelonephritis and cystitis.
If a person is healthy, his urine contains substances and salts that prevent the crystals from sticking together, forming large stones. Such substances include pyrophosphates, magnesium cathodes, and citrates. When reacting with small crystals, these substances destroy them or prevent them from settling on the walls of the kidneys. If the percentage of crystallization inhibitors falls, stone formation accelerates.
Typically, tripel phosphates form in areas of the upper parts of the urinary system, especially inside the calyces, renal pelvis. For their formation, an alkaline composition of urine, magnesium ions, as well as phosphorus and ammonium are needed. Doctors call such stones infectious, since the conditions for their growth occur during inflammatory conditions inside the body.
Tripelphosphates grow quickly - after 2-3 months, a large calculus is detected inside the kidney. Another name for tripel phosphate is coral stone, due to its ability to branch, filling space. After some time without treatment, such a stone clogs small vessels, reducing the filtration of the kidneys, and then stopping its functions. With this development of events, dissection of the kidney parenchyma and removal of the stone are required. If there are irreversible changes, the kidney is removed.
Xanthines and cystines
Such formations usually appear in patients with severe hereditary characteristics. If a patient develops hereditary xanthine oxidase enzyme deficiency, then he is at risk for the formation of xanthine stones in the liver. In such patients, xanthine (a purine base) is not processed by the kidneys into uric acid and is excreted in its pure form. The xanthine substance is poorly soluble, and in the urine it turns into crystals. Xanthines cannot be dissolved, so they are treated surgically. Such stones are detected mainly in childhood, are easily detected by ultrasound, but are invisible on X-ray images.
Impaired absorption of the cystine amino acid leads to the formation of cystine stones, which are usually round, with a yellowish tint, soft and smooth structure. Cystines can be dissolved, for which patients are advised to use citrates and alkaline drinks. Since the formation of such stones is caused by hereditary diseases, they are usually detected at an early age in children and adolescents.
Symptoms of education
As a rule, large phosphate stones are not discovered by chance - they are always accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. The formation of tripelphosphate stones is fraught with deformation of the inner surface of the ureters. You can find out about such damage by drops or blood clots that appear in urine from time to time. With infectious diseases of the ureters and kidney pathologies, urination becomes difficult, accompanied by pain, and the urine thickens. One of the signs of struvite formation is a stagnant odor from urine.
Small crystals stick together, forming phosphorus stones against the background of the participation of harmful microorganisms and infectious agents, so the condition is usually accompanied by the following clinical picture:
- hyperthermia, fever, chills, perspiration;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - vomiting, nausea, poor appetite;
- apathy, fatigue, weakness;
- dull, nagging pain.
One of the frequently occurring symptoms accompanying the formation of tripelphosphates is excessive fluid intake. Such obvious thirst often leads the patient to an endocrinologist due to fears of developing diabetes mellitus. However, test results show an increase in the number of phosphates, and the specialist refers the patient to a nephrologist.
Problems with urination also become a sign of tripelphosphates - usually urination is difficult and infrequent. If the stones are large, the renal pelvis and calyces expand, and urine output decreases. Due to stagnation of urine, the functions of the kidney parenchyma are lost. Hydronephrosis leads to dangerous conditions, so urgent consultation with a doctor and measures to eliminate the problem are necessary.
How to treat
Only a doctor can determine a treatment regimen, because no two dogs are the same, there is no universal method. Drugs are prescribed individually, depending on the stage of the disease, research results, and the type of stones that complicated the pathology.
It is important not to stop treatment when the dog’s condition improves and until the doctor stops the medication.
What are the main therapeutic measures aimed at:
- Maintaining heart function;
- Restoring the outflow of urine by installing a catheter or washing the urethra;
- Relieving spasms;
- Anesthesia;
- Stop bleeding;
- Antibiotic therapy to kill the infection;
- Restoration of the body, removal of toxins in conditions of stagnant urine;
- Complex therapy to eliminate general inflammation in urolithiasis.
- Diet - depending on the detected stones, with a reduced content of protein, calcium, phosphorus.
Diagnostics
If a urine test reveals the presence of tripelphosphates, this is a signal that urolithiasis needs to be treated. An urgent response is associated not so much with the potential development of inflammatory processes, but with the rapid crystallization of phosphates. In just 1 month, a phosphate stone can fill the space of the kidney and suppress its functionality.
During the initial examination, the nephrologist palpates the abdomen and assesses the general condition of the patient. A referral for biochemical testing of urine and blood is required. If an increased level of leukocytes, products of protein breakdown, is detected, an inflammatory process in any part of the urinary system can be suspected. A decrease in the number of platelets in a blood test indicates a decrease in the patient’s body’s defenses.
To determine which infectious pathogen provoked increased crystallization of tripelphosphates, a urine test and culture are prescribed. Other important parameters that can characterize the condition of the urinary organs are:
- level of nitrogen, phosphorus, magnesium ions;
- acidity of urine;
- number of stone formation inhibitors.
Patients are prescribed ultrasound, CT, MRI as needed, if the doctor considers a detailed examination of the tissues of the urinary organs and kidneys necessary.
To determine the qualitative and quantitative composition of stones, X-ray defractometry and infrared spectrophotometry are prescribed. Such a diagnosis is mandatory when signs of urolithiasis are identified, since the amount of phosphorus will indicate the cause of the pathology, the nature of its development, and will allow making a prognosis. Accurate detection of pathology will allow you to adequately select treatment - medicinal or surgical.
If urolithiasis is suspected, a survey x-ray of the peritoneum in the area of the kidneys, ureters and bladder will be taken. Such a study is indicated for X-ray positive stones; it helps to determine the size of the stones and their exact location.
For the effectiveness of the upcoming treatment, it is necessary to consult an endocrinologist, nutritionist, or gastroenterologist.
Find the answer
The onset of KSD in dogs is asymptomatic and easy to miss. Urolithiasis does not occur immediately. If the owner is attentive to the pet, he will see changes in his mood and behavior. In addition, you need to regularly take a routine urine test so as not to miss the disease.
The main symptom - frequent painful urination - becomes noticeable when the ICD has already gained strength.
To a greater extent, the disease affects dogs of small breeds: Pekingese, Yorkies, schnauzers, dachshunds and others.
For the treatment to be effective, the doctor determines the composition of the stones or sand. In addition to a detailed urine test, x-rays, clinical and biochemical blood tests and ultrasound examination are prescribed.
Older dogs and males are more often affected because they have a long urinary tract. Stones or sand have more chances to clog it.
Drug treatment
The most dangerous complication of ICD is renal colic. The condition causes severe pain that cannot be tolerated. To reduce pain, an antispasmodic, atropine, is used. In addition, the doctor prescribes: Ortofen, Ketoral, Indometacion, Diclofenac. Therapy begins with eliminating the cause that provoked the formation of tripelphosphates; we are talking about an infectious lesion of the genitourinary system. Antibacterial agents are prescribed for 2 weeks. This could be Amosxiclav, Clarithromycin, drugs of the cephalosporin group.
If inflammation has affected a large area, Metronidazole and antifungal drugs are prescribed. To avoid dysbiosis, probiotics are prescribed - Linex, Acipol, Bifiform. Taking immunomodulators (Vitrum, Selmevit) is also indicated. To avoid recurrence of the infectious process, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed - Canephron, Cyston, and at the same time - antimicrobial drugs - Norfloxacin, Nolitsin.
Disease prevention
Like other diseases, it is easier and cheaper to prevent pathology than to treat it. Preventive measures regarding the appearance of tripelphosphates in the urine are quite simple:
- If possible, reduce the consumption of spicy, sour, smoked and salty foods. If phosphorus salts are already detected in the urine, then the listed products should be completely abandoned until the test results return to normal;
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day, unless there are contraindications. In hot climates, increase the volume of liquid further;
- from time to time use a kidney mixture from a pharmacy, diuretic herbs;
- eliminate the possibility of hypothermia (dress appropriately for the weather, use transport in winter);
- undergo regular examinations and urine tests at the frequency recommended by your doctor;
- If you have lumbar pain, try not to delay visiting a nephrologist.
It is important to take into account that phosphates in urine are not yet a disease, but a very clear signal that undesirable processes are occurring in the body. It is important at the initial stage to correct the functioning of organs and systems, and to pay more attention not to pills, but to correcting the diet. A nephrologist and nutritionist will give you the necessary recommendations. Self-medication is unacceptable, it will lead to dangerous complications.
Rules for collecting urine from cats
The main way to detect tripelphosphates is urine analysis, but the reliability of its results depends on the correctness of the analysis, storage conditions and time of delivery of the sample to the veterinary laboratory.
Rules for collecting urine from cats:
- For analysis, it is necessary to bring an average portion of morning urine collected immediately after a night's sleep.
- The external genitalia of your pet must be thoroughly washed with boiled water and laundry soap and dried well with a towel.
- The tray should also be treated with laundry soap and boiling water; it is not recommended to use chemicals to disinfect it, as they can negatively affect the results of laboratory tests.
- A special non-absorbent filler or plastic bag must be placed in the tray, from which urine must be collected with a sterile syringe.
- The volume of collected urine should be at least 10 ml.
- After collection, it is recommended to submit a urine sample to a veterinary laboratory within 2 hours.