The color of urine is affected by the coloring pigments present in it - bilirubin, urochrome and urobilin. This indicator is also affected by protein impurities, as well as inclusions of blood. With healthy physiology, urine has the appearance of a transparent liquid with shades of yellow of varying intensity - from light straw to the color of an orange peel. If the color of urine becomes significantly different from the norm described above, then you should pay close attention to this, since this may be evidence of serious problems with the renal system of the body.
The causes of such symptoms may vary. Some appear only in women, others exclusively in men, and others are present in both sexes. More on this below.
Blood in urine. How to find out about this?
The results of a urine test are the most reliable source of information about all changes in the urinary system. Any malfunction in the functioning of the organs of this system is easily detected by primary diagnostics. It is necessary for a timely and correct diagnosis, since as a result of changes in the cellular composition of urine, symptoms may not occur for a long period. The absence of pain or other complaints can lead to the fact that a woman for a long time will not even realize that there is some kind of disease in her body. Below we will discuss the causes of urine with blood in women and the treatment of diseases associated with this.
Main reasons
Infections
There are many types of infections of the genitourinary system, and all of them, with varying probability, can lead to the appearance of blood in the urine. The most common types are cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), kidney tuberculosis, and various types of nephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), such as pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. It is possible to discharge urine with blood clots in case of various sexually transmitted diseases in both men and women.
It must be said that infection is the most common cause of this symptom. All infections can be of varying severity and only a specialist can prescribe the correct treatment. Cystitis most often occurs in women (in some cases after sex) - the design of their bladder is conducive to the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms.
Injuries
Due to traumatic damage to the kidneys or bladder, bloody urine is also often produced. Trauma can be penetrating (eg, wound, cut, wound) or blunt (severe bruising from a blow or fall). Many people do not know that long runs with an empty bladder can be dangerous - in this case, its walls rub against each other and the athlete is also likely to see blood in the urine. In case of injury, the urinary organs can rupture, which is a serious complication and requires immediate surgical intervention.
Presence of stones in the bladder or kidneys
Stones form when salt crystals are deposited in one of these organs, attracting more and more deposits. Such stones most often have a rough, uneven surface and can severely injure the internal surface of the organ, especially the urinary canal (when the stone passes along it, it can simply get stuck). Unfortunately, stones also create a favorable background for the development of infection, which can further complicate the course of the disease. Pain when urinating, bleeding, and other symptoms mean that the stones are already a serious threat. Urography will help to identify them in the early stages.
Neoplasms
If blood with clots comes out when urinating, and there are no other symptoms (pain, discomfort), and the patient has crossed the age limit of forty years, there is a possibility of bladder cancer. There are several types of such tumors and they have different causes: transitional cell carcinoma develops in the epithelium of the mucous membrane and can occur after injury; adenocarcinoma appears a little less often. The reason for the appearance of this neoplasm is parasitism of the schistosome worm. If cancer has developed in the urethra, then blood flows not only during, but also between urinations. It may not be much - two or three drops, but this is definitely an alarming symptom.
If blood is released in the urine in clots that resemble worms, this most likely indicates kidney cancer. However, urine with blood comes not only with malignant formations, but also with some benign ones. Particularly noteworthy is angiomyolipoma - a fatty formation riddled with blood vessels that can often burst. Treatment in these cases can vary from chemical irradiation to surgery.
Rare causes
Urine with blood always comes with congenital anomalies of the kidneys - cyst or polycystic disease. If a person takes drugs that reduce blood clotting or has certain bleeding disorders (leukemia, hemophilia), this can also be a cause. Vascular diseases, renal vein thrombosis, papillary necrosis in diabetes are other possible harbingers of the disease.
What is hematuria?
The presence of blood clots in the urine of women is called hematuria in medical terminology. The very fact of the presence of blood in urine should cause every woman great concern, since this can be a symptom of various, sometimes very serious, diseases.
It all depends on the number of blood cells in the urine. Obviously, if the urine changes color (becomes pinkish or darker), then there is a lot of blood in it, and this is a serious reason to consult a doctor. However, there are standards for the permissible number of blood cells in urine. If, during a general analysis of urinary sediment, single red blood cells are detected, then this is not a reason to panic. The structure of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys allows a few blood cells to pass through, which subsequently end up in the urine.
Treatment
Hematuria is not a disease, but a symptom indicating the presence of pathologies of the kidneys, bladder, and genital organs. This requires mandatory consultation with a doctor for timely treatment.
Therapy depends entirely on the diagnosis.
Which specialist should I contact?
Blood in the urine is one of the reasons for a visit to a specialist and examination using ultrasound, x-ray or pelvic tomography . Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The presence of chronic diseases - cystitis, urethritis, prostatitis - requires complex treatment in full.
A specialist who deals with problems of the genitourinary system is a urologist . It is necessary to contact him for any troubling conditions related to the functioning of the kidneys.
Preventing blood in urine
The main methods of preventing blood in urine are maintaining personal and intimate hygiene and strengthening the immune system .
Complications of hematuria
In order to completely cure infections of the urinary tract and kidneys, it is necessary to complete a course of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs .
Otherwise, the disease becomes chronic with exacerbations and relapses.
Symptoms of the presence of blood clots in urine in women
It happens that besides blood in the urine, a woman has no other symptoms. This indicates that there are very few blood cells in the urine and they can only be detected during examination under a microscope. In this case, the color of the urine changes to darker. We are talking about such a medical concept as microhematuria.
Severe hematuria is the presence of red blood cells in the urine, which is visible even without a microscope. During severe hematuria, the urine becomes red and streaks and clots are visible in it.
In addition to the fact that with hematuria the urinary sediment changes color, there are other symptoms that can be combined in various ways. These are like:
- Increased uncontrollable urge to urinate.
- During the process of emptying, severe pain is felt (from aching to cutting), which can be accompanied by bloating of the lower abdomen and discomfort in the perineum.
- There may be pain in the lumbar region that lasts for a long time.
- Hematuria can be combined with severe pain of a spastic nature (colic).
- Pathological discharge may appear - mucous or purulent. They cause discomfort, burning and itching occurs.
- The temperature rises and other symptoms appear that indicate intoxication of the body: performance decreases, severe headaches periodically occur, the woman feels unwell and apathetic.
- Complaints of profuse night sweats appear and body weight decreases.
- During sexual intercourse, discomfort occurs and pain is felt.
Thrush
One of the most common reasons for the appearance of such cervical mucus is the appearance of a fungus. In this case, the fairer sex has discharge in the form of white clots and itching. A woman may also feel a burning sensation in the vagina, which simply prevents her from living normally. Among other things, a lady can detect a white coating between the labia. A distinctive feature of thrush is the appearance of a peculiar odor. Discharge in the form of white clots smells like bread or dairy products.
If such a pathology is detected, you must definitely see a gynecologist. After conducting a series of tests, the specialist will prescribe the necessary antifungal drugs that will help eliminate discharge in the form of white clots, itching, burning and discomfort. Treatment does not take much time; in some cases, taking one tablet is enough.
Inflammatory process
When infections enter the organs of the urinary system, inflammatory processes occur. Depending on which organ is affected by the infectious agent, the patient’s diagnosis is determined. So, if inflammation develops in the kidney tissues, pyelonephritis occurs, cystitis occurs in the bladder, and urethritis occurs in the urethra.
Typical complaints with pyelonephritis are pain in the area of the inflamed kidney, increased body temperature, and changes in the color of urine. In addition, symptoms occur that indicate intoxication.
Frequent urge to go to the toilet, cramps and pain when urinating, as well as the release of a small volume of urine when emptying the bladder indicate that a woman has a disease such as cystitis.
Urethritis causes mucous or purulent discharge and dysuric disorders, which are expressed to varying degrees.
White urine - what is the reason?
The appearance of such a shade may indicate a large amount of foreign impurities in the urine. These can be lipids, leukocytes, protein clots or phosphoric acid. But there are quite a few reasons for the appearance of such impurities. Most often, this effect is caused by pathologies of the following nature:
- Diseases or inflammatory processes of the urinary and reproductive systems,
- Exorbitant physical activity,
- Psycho-emotional stress - stress,
- Frequent hypothermia,
- Fevers of different etymologies.
Injured urinary system
Another possible cause of blood clots in the urine may be various manipulations in the organs of the urinary system. These include cystoscopy, urethroscopy, catheterization. They can lead to injury to the tissues that line the walls of the urethra and bladder. The occurrence of such hematuria is temporary, and the woman does not experience severe discomfort.
Much more dangerous are situations in which the urinary organs are ruptured, crushed, etc. Such patients, as a rule, are in serious condition, and they need urgent help from surgeons. In this case, blood clots in the urine of women can be seen with the naked eye. This is evidence that severe bleeding begins in the organs of the urinary system.
Diagnostic methods
When collecting an anamnesis of the disease, the doctor finds out in detail all the complaints and the time of their occurrence, the factors that could have preceded this, etc.
Laboratory and instrumental examination includes the following methods:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine (allows you to assess the presence of the inflammatory component and its severity, as well as other cellular changes); biochemical blood test (determine indicators such as total protein and its fractions, creatinine, urea, fibrinogen and others);
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko (if indicated);
- inoculation of urinary sediment on nutrient media and determination of antibacterial sensitivity of detected infectious agents;
- bacterial examination of vaginal and urethral discharge (if any);
- general x-ray of the urinary tract and excretory urography;
- Ultrasound of the genitourinary system (a method that allows you to detect inflammatory changes, the presence of stones, space-occupying formations, etc.);
- CT and MRI (methods that have the greatest information content and diagnostic value are indispensable in complex clinical cases).
Growing a culture of a pathogenic microorganism is an important and mandatory diagnostic step
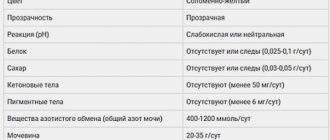
What tests you need to do depends on your symptoms and treatment prescribed. Normally, urine looks like this: a transparent liquid of a yellowish color or slightly darker, without sediment, fibers or flakes, with a slight specific odor.
- A general urine test determines whether the following indicators are normal: protein, glucose, hemoglobin, leukocytes, red blood cells, epithelium and others. The presence of bacteria and fungi that can provoke infectious inflammation is checked.
- A biochemical urine test is carried out to check the condition of internal organs and metabolism according to the following indicators: total protein, glucose, amylase, potassium, magnesium, sodium, phosphorus, creatinine, microalbumin, uric acid.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko is carried out in this way: a middle portion of urine is collected, in which the level of leukocytes, erythrocytes, and cylindrical formations is checked. High rates indicate diseases such as cystitis, prostatitis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis and others.
In order to check for abnormalities in the anatomical structure of the genitourinary system and to identify the presence of stones, a diagnostic method such as ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder is used.
Ultrasound reveals various anomalies, tumors and inflammatory processes that provoke the appearance of protein in the urine, white flakes and mucus.
A darker color of urine in the morning due to increased concentration and stagnation is considered an acceptable deviation. The appearance and smell of urine may change after consuming certain foods or medications.
In order to avoid distorting the results of urine tests in women, it is necessary to first carry out thorough hygiene procedures to prevent vaginal secretions from getting into the urine. To collect samples, special containers are used (sold in pharmacy chains); the collected biomaterial cannot be stored, especially in the refrigerator.
The most obvious and effective means of diagnosis is a general urine test. Not in all cases, the detection of white discharge in urine indicates the development of a similar disease, and the real causes most often do not pose any danger. Sometimes this is due to the fact that people refuse to observe basic hygiene rules, which is why foreign elements (grains of sand, grains, pieces of skin) get into the container during urine collection.
During laboratory tests, the doctor determines the nature and origin of the detected discharge. This will help determine the type of disease and the features of its development. Only after this is it possible to draw up any recommendations or strategies for treating the disease. Sometimes additional examination (ultrasound or CT) of the abdominal organs is necessary.
Before collecting urine, in order to exclude an erroneous diagnosis, the following procedures must be performed:
- limit the intake of foods that change the color of urine (carrots, beets),
- take a bath and thoroughly wash the perineum without using household chemicals,
- when collecting samples, use the fluid released in the middle of urination,
- the collected material must be immediately delivered to a medical institution for analysis.
- limit the intake of foods that change the color of urine (carrots, beets);
- take a bath and carefully wash the perineum without using household chemicals;
- when collecting samples, use the fluid released in the middle of urination;
- the collected material must be immediately delivered to a medical institution for analysis.
Oncology
The most dangerous causes of blood clots in the urine in women include an oncological process in the organs of the urinary system. If blood is detected in the patient’s urinary sediment, the doctor must first check it for the presence of oncology.
It happens that, having discovered microhematuria, the doctor undertakes its local treatment. However, it often becomes the only sign that there are neoplasms in the organs of the MVS, the origin of which can be either benign or malignant.
Diagnosing an oncological process in the urinary tract is quite difficult, since the symptoms of this disease are often nonspecific and remain unattended. A woman may be bothered by profuse sweating, sudden weight loss, apathy and weakness.
Removal of the plug before childbirth
A woman may observe discharge in the form of white clots during pregnancy shortly before giving birth. This is the norm when the pregnancy is full-term and the baby is ready to meet the outside world.
During the removal of the plug, a representative of the fair sex may detect one large clot or several small ones. The plug can come out either at once or in parts over one or two weeks. The large volume of released substance should not be scary. Normally, you can detect up to two tablespoons of such discharge.
It is worth noting that cork is not always white. Sometimes there may be discharge in the form of white clots with blood. Also, the cork can be brownish, beige or completely transparent. All this is normal and does not require any treatment. However, it must be remembered that if the plug is bright red and bleeding occurs, then this is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Endometriosis
This disease is one of the most common in the medical practice of a gynecologist. At risk are women of reproductive age with a genetic predisposition. Endometriosis occurs against the background of decreased immunity.
The disease is caused by cells in the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium), which can spread outside the uterus. Tissue made up of these cells can move in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder and rectum. Moving on to other organs, the endometrium is able to grow through their tissues, which is why blood can appear in the urine and feces.
With endometriosis, women complain of menstrual irregularities, pain that practically does not stop, etc.
Female vaginal discharge
Changes occur in a woman's body throughout the menstrual cycle. Hormones play a major role in this. The sensitivity of the mammary glands and nipples, sexual desire and attraction, as well as the color of the cervical mucus that is secreted change.
Immediately after the end of menstruation, a woman may feel a dry vagina. Closer to the time the egg is released from the ovary, the lady notes that the discharge has become more mucous and abundant. After ovulation, hormones begin to actively work, under the influence of which cervical mucus resembles a thick cream. If pregnancy occurs, a representative of the fairer sex observes copious watery discharge.
Blood clots during pregnancy
During pregnancy, colossal hormonal and physiological changes occur in the female body. Each organ or organ system has a double burden. This also applies to the kidneys.
Causes of blood clots in a woman’s urine during pregnancy:
- If a woman had a disease of the urinary system before pregnancy, then there is a high probability of relapse. Or the occurrence of such a disease against the background of an interesting situation.
- The occurrence of hormonal imbalances (for example, imbalance in the first trimester).
- As the abdomen enlarges (due to the growth of the uterus), intra-abdominal pressure increases, which affects the kidneys, ureters or bladder.
In pregnant women
The phenomenon of white flakes and dense particles in the urine often occurs during pregnancy for several reasons:
- hormonal changes, disorders in the endocrine system,
- an increase in mucous secretions that protect the genital tract from infections, and the entry of a mucus plug from the vagina a few days before childbirth.
Urine tests in pregnant women require close attention from a doctor, since untimely treatment can lead to developmental disorders of the fetus.
After childbirth, the female body is weakened and susceptible to various inflammations, this is due to the fact that the genital and urinary organs are closely located. Therefore, in the postpartum period, vaginitis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, candidiasis, and endometriosis are more often diagnosed.
In children
Before the age of 6-7 years, white flakes in a child’s urine may appear due to anatomical features or the occurrence of “adult” infections. Inflammation in children (such as cystitis, pyelonephritis) can begin if they do not eat properly, are overcooled and dressed inappropriately for the weather, or have a weakened immune system.
In addition, the child’s body is still adapting to various foods, so flakes and sediment in the urine sometimes appear due to the consumption of unusual foods.
Some parents try to give more proteins necessary for a growing body, this also affects the tests. Nutrition should be balanced and rational so that renal dysfunction and digestive disorders do not occur.
When a girl is pregnant, her main task is to take care of her own health, which should have a beneficial effect on the condition of the unborn baby. To do this, she needs to constantly monitor changes in her body by undergoing various examinations. One of the most highly informative methods is a general urine test.
During pregnancy, a urine test must be taken once a month until the 20th week, and after it and until the birth of the child, this procedure must be performed twice a month. By examining samples of this waste product, doctors can determine the presence or absence of diseases, and, if necessary, take treatment steps in a timely manner.
During the study of this physiological fluid, it is assessed by many parameters, such as: color, smell, density, presence of impurities (leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, sugar, bacteria). The analysis also makes it possible to determine the presence of intoxication in the body.
In a normal state, there should not be protein in the urine, but since the body of a pregnant woman experiences a double load, doctors allow its concentration to reach 14 grams per liter. The condition of the expectant mother requires careful monitoring. Problems do not arise if the increase in protein levels was a one-time increase.
In addition, the reasons for this behavior of the body are allergic reactions, disorders of the kidneys, urinary system, and so on. The most dangerous disease is considered gestosis, the characteristic signs of which are white flakes in the urine, the appearance of excess weight, swelling throughout the body and increased blood pressure. At the same time, the state of health remains normal, which can ultimately lead to convulsions.
Anticoagulants
Long-term use of drugs that thin the blood requires constant monitoring by a doctor, as there is a risk of significantly increasing bleeding. The result can be not only blood clots in the urine in women and men, but also much more serious diseases.
Basically, such problems arise due to excessive intake of these drugs or non-compliance with the prescribed dosages.
In patients taking anticoagulants, blood in the urine is visible to the naked eye, and this is the first sign of the onset of serious bleeding in the urinary organs. In addition, this is often accompanied by bleeding not related to the urinary system (nose, uterus, gastrointestinal tract, etc.). The appearance of hematomas on the skin and mucous membranes is often observed.
Features and types of hematuria
This condition can manifest itself in two varieties - the clearly visible presence of blood inclusions, called macrohematuria, and the invisible presence of the naked eye - microhematuria. The latter can only be detected with the help of laboratory tests, if the patient comes in because of symptoms that bother him or during a preventive examination.
Blood in the urine is a unique way of the body’s response to an irritant - physiological or pathological. Therefore, such a manifestation cannot be ignored, but it is necessary to conduct a full examination, understand the reasons for its appearance and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment. The most important thing is to seek help as soon as possible, especially if you have a fever, pain, or decreased urine output.
Classification
Normally, there are no red blood cells in the urine sediment or they are present, but not more than 2 cells. With erythrocyturia, the number of red blood cells exceeds the physiological norm. Depending on the severity of the symptom, the pathology is classified into:
- gross hematuria;
- micrognematuria.
In the first case, blood is visible to the naked eye. Urine takes on a pronounced red, dark brown or even black color, so the symptom can be identified without laboratory tests. The consistency of urine may be heterogeneous, and blood clots are possible.
In the second case, blood is not visually detected. It can only be detected through laboratory tests. Therefore, most men do not even realize that there is a problem and find out about it completely by accident as a result of undergoing a routine urine test.
According to ICD 10 there are 2 varieties:
- NO2 - stable and recurrent;
- R31 - nonspecific.
Hormonal disorders
As you know, in the second phase of the cycle, a woman may experience creamy white discharge. They are normal and do not require treatment. However, in some cases, such cervical mucus is not cyclical, but is constantly present. What could be causing this?
Most likely, the woman has a hormonal imbalance. In this case, such discharge is accompanied by an irregular cycle, fatigue, irritability, and poor health. In this case, it is necessary to visit a qualified specialist as soon as possible to carry out the appropriate correction.
Infections that affect the genitals
In some cases, a representative of the fairer sex may detect discharge in the form of white clots with impurities of a strange color and an unpleasant odor. In this case, a genital tract infection most likely develops. It can be obtained through sexual contact, as well as through ordinary personal hygiene items.
This condition must be corrected. Otherwise, you risk developing serious health problems in the future, which may lead to infertility.
Elimination of sexually acquired infections should be mandatory. Treatment must be carried out together with a partner. If you decide to carry out the course of correction alone, then at the very first sexual intercourse without protection you will again receive a portion of pathogenic bacteria. The only way to avoid this is to use a condom.
If you do not have a permanent partner, then you definitely need to protect yourself from unwanted conception and various infections that can be sexually transmitted.