13.08.2017
Many people do not know what peritoneal dialysis or lavage is; it is one of the methods of blood purification; it is used when a patient has problems with their kidneys.
Doctors consider it twofold: firstly, peritoneal dialysis is the beginning of replacement treatment for kidney pathologies, after which they use hemodialysis or, in severe cases, organ transplantation.
Secondly, this is an indispensable procedure for the patient, because sometimes hemodialysis is strictly prohibited for a person.
What does this type of dialysis mean?
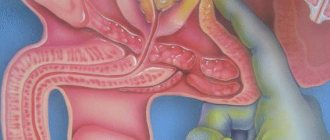
In peritoneal dialysis, blood is purified using the peritoneum as a membrane filter. That is, the solution for peritoneal dialysis is poured into the middle of the abdomen, and the cleansing process takes place there. If this method is compared with hemodialysis, then its advantage is that it is indicated for young children.
The positive effect is that the peritoneum has natural filtration properties. In this process, the main role is played by a thin membrane that covers all organs located in the abdominal cavity.
This membrane has strong blood flow. It can pass through the following substances:
- Water.
- Substances that are easily soluble in water and have a small molecular weight.
- Compounds with high molecular weight.
The peculiarity of this method over others is that it is convenient for the patient. There are two types of such cleansing, and each of them gives a person the opportunity to lead a full life and not deny himself anything. He can travel, study or work freely.
The main thing is to follow a diet and get tested and examined at the center from time to time. If they indicate that perinatal dialysis is necessary, it can be done at home.
Who is prescribed dialysis?
If chronic renal failure has reached the terminal stage and it is not possible to restore the functioning of the organ, the only way to continue living is to use peritoneal lavage.
The method can be prescribed if:
- serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system, if serious consequences are possible due to hemodialysis;
- problems with blood clotting, when the administration of anticoagulants is prohibited;
- intolerance to membrane filters that are installed for hemodialysis.
The technique also helps if it is not possible to create adequate and long-term vascular access, which is especially important for people with severe hypotension and children under 5 years of age. In addition, in the absence of contraindications, the procedure can be used at your personal request.
Peritoneal dialysis is contraindicated for some.
We are talking about patients with:
- excessive exhaustion of the body;
- diseases accompanied by the formation of adhesions in the abdominal cavity;
- severe heart failure;
- enlargement and traumatization of organs located in the abdominal area;
- infectious skin lesions in the area of the anterior abdominal wall;
- mental disorders;
- installed drainages;
- extreme obesity.
Indications for the procedure
First of all, this is done for people with chronic kidney disease. Dialysis will help people whose disease has become severe and the full functioning of the organ can no longer be restored. In this situation, only an injected peritoneal dialysis solution will help. Patients with severe pathologies can still be helped by conducting several sessions of such treatment.
There are special indications for which such procedures need to be carried out, so the doctor prescribes them to the patient:
- If access to vessels is impossible. This occurs in young children and people with high blood pressure.
- Severe diseases of the heart and blood vessels, if hemodialysis is performed, serious complications can arise.
- Poor blood clotting, in which medications that prevent blood clots are contraindicated.
- Allergic reaction to artificial filters for hemodialysis.
- Patient's refusal to undergo hemodialysis.
For young children, an injected solution for peritoneal dialysis will help if acute renal failure is diagnosed, or with other pathologies associated with urea.
How long have they lived with him?
The first mention of replacing renal function with this method was in 1923. Years have passed and scientists from all countries dealing with kidney problems have studied and improved methods of blood purification. This dialysis option has taken pride of place among them. It uses the natural properties of the body, is not difficult to carry out and does not entail irreversible processes.
Peritoneal dialysis can be used at home, and the machine is easy to transport when traveling. The cycler is also inexpensive and available for purchase by any, even the smallest medical offices.
The only obstacle is that peritoneal dialysis is not able to completely restore kidney function!
With severe kidney damage, people live as long as they can often resort to dialysis.
Types of procedure
Today, medicine has mastered two methods of dialysis: manual and automated. The choice of one method or another will depend on the following indicators: the patient’s lifestyle, indications for the procedure and the patient’s personal preferences.
- Manual. With this method, the solution for peritoneal dialysis is poured in and drained throughout the day; this procedure should be done in an outpatient setting. This should be done five times, although the number of procedures can only be determined by the attending physician. The time of the procedure is selected depending on the patient’s employment. At home, “exchange” is carried out only in certain cases.
- Automated. This method is used only at night, its duration is twelve hours. In this case, a cycler is used, a special device for peritoneal dialysis, which completely controls the “exchange” process. In the morning, this device simply needs to be turned off.
Mechanism and types of dialysis
Under anesthesia, a catheter about 30 cm long, having a branch at its outer end, is fixed in the subcutaneous fat layer. Catheters will be connected to this branching area to introduce and remove fluids. The reliability of its fixation is controlled by a Dacron cuff.
Glucose solution is most often used as a dialysate. The injection time is up to 15 minutes, the stay inside is up to 6 hours, the removal time is up to 25 minutes. The patient's blood and fluid from the abdominal cavity are regularly checked to adjust the frequency of procedures and analyze the effectiveness of treatment.
There are the following types of peritoneal dialysis:
- manual or manual dialysis;
- automated, which is performed by a cycler apparatus.
To carry out the manual method, medical personnel themselves alternate the work of catheters. The procedure begins with the introduction of up to two liters of warm dialysate into the abdominal cavity, and the catheter is clamped, temporarily disconnected, and closed with a protective cap to maintain sterility. The solution remains in the stomach for 4 to 6 hours, “taking” toxins from the abdominal cavity. Then an excretory catheter works, which drains the fluid from the abdomen into a container. The peritoneum independently filters it, releasing toxins out. This catheter is closed, the first one is connected again, and the dialysate is reintroduced. Depending on the patient’s condition, the procedure is repeated 3–5 times a day.
The automated method has several advantages.
The cycler apparatus for peritoneal dialysis is compact and mobile, connected to the outer wall of the peritoneum with a main catheter punctured into the pelvis, as with the manual method. The cycler takes upon itself the determination of the time of draining and filling of solutions, controls the duration of the dialysate being inside, and maintains the required temperature of the incoming liquid. The doctor assigns this program to him, the device displays all the parameters on the screen and writes it to the memory card. This is how dynamics are observed even over a long period of time.
The cycler works at night, and after cleaning, it turns off in the morning. This is its main advantage - the entire process takes place while the patient is lying down. This significantly reduces pressure in the abdominal cavity, high levels of which provoke complications.
How is this procedure carried out?
The process of conducting a manual and automated “exchange” is very different, but the preparation is exactly the same. Preparation is the installation of a catheter, which is the same in both cases. It looks like a silicone tube, thirty centimeters long, with a diameter no larger than a pencil.
It is attached to the subcutaneous layer of fat and secured with a Dacron cuff; it is better if there are two of them. The installation is carried out under anesthesia, local or general, as chosen by the patient.
Twenty-one days must pass from the moment the catheter is installed until the first “exchange”. This is necessary so that the cuff grows into the body and is better attached.
Manual
No equipment is needed to perform the manual procedure. This operation is carried out using two containers, one containing saline solution, and the second empty. The recycled liquid will be drained into it. In addition to containers, straws are needed.
The main component of the dialysis solution can be called glucose; in addition to it, the solution also includes other components, for example: calcium, amino acid and much more. The main manufacturers of the solution are Germany and Ireland.
The cleansing process itself occurs in the middle of the abdominal cavity. First, the patient is injected with a solution through a catheter over a period of fifteen minutes, then it is closed with a special cap.
Six hours later, the patient comes back for the procedure. The recycled solution is drained and fresh solution is added. This happens over the course of forty minutes. This is done to the patient five times a day. In his free time, he can do whatever he wants.
Automated
As mentioned earlier, in order to carry out automated dialysis, you need a special device for peritoneal dialysis, which is called a “cycler”. It should be connected at night. The size of such a device does not exceed the size of a regular suitcase with wheels. Due to the fact that its dimensions are small, it can be taken with you if the patient is going on a trip.
It is easy to use, you should learn it in the hospital, it takes about ten days. The patient simply connects his catheter to the device and selects the optimal portion of the solution for himself. Fluids are exchanged throughout the night and the device is turned off in the morning.
However, before this, a daily dose of liquid is infused. Sometimes during the day the “cycler” needs to be connected to drain the processed solution.
Dialysis peritonitis as a special form of postoperative peritonitis
Peritonitis, occurring in patients with end-stage chronic renal failure receiving renal replacement therapy in the form of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, is the most serious complication of this type of treatment.
As shown above, in the modern international classification of peritonitis, dialysis peritonitis is identified as a separate nosological form.
In patients receiving peritoneal dialysis, the development of dialysis peritonitis is associated not only with a threat to life, but also with the risk of loss of functional properties of the peritoneum and the need to terminate the peritoneal dialysis program.
Dialysis peritonitis is divided into bacterial, fungal and aseptic.
The occurrence of aseptic peritonitis is explained by chemical irritation of the peritoneum by the dialysate solution, the influence of the low pH of the dialysate solution, the presence of pyrogens, high glucose concentrations, or the presence of foreign particles in the solution.
Currently, with a highly developed industry producing systems and solutions for continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis, the influence of pyrogens and foreign particles in the solution is excluded. In this section we will focus on the most common dialysis peritonitis caused by bacteria and fungi.
Clinical symptoms of peritonitis traditionally include cloudiness of dialysate flowing from the abdominal cavity, abdominal pain, symptoms of peritoneal irritation and fever.
We have experience using continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis in 174 patients suffering from end-stage chronic renal failure.
Peritonitis developed in 21.6% of patients. In 7 (9.45%) patients, peritonitis complicated the program of continuous outpatient peritoneal dialysis 2 times or more. The average incidence of peritonitis was one case per 31±1.6 dialysis sessions per month.
In almost all patients, peritonitis manifested itself in diffuse cloudiness of the dialysate solution, combined with acute abdominal pain.
In a significant number of cases, fever, chills, gteHOTa and vomiting, difficulty in the outflow of dialysate fluid and a decrease in the amount of ultrafiltrate were noted.
We analyzed the results of continuous outpatient peritoneal dialysis in 124 patients, including 23 patients with urological diseases.
In our observations, the frequency of clinical manifestations of dialysis peritonitis was as follows: cloudiness of the solution - 91% of patients, abdominal pain -78%, fever (body temperature 37.5 °C and above) - 54%, nausea - 30% and diarrhea - 8% sick.
It is known that the content of leukocytes in the dialysate solution is no more than 8 per 1 mm3. With the development of peritonitis, their number, as a rule, exceeds 100 per 1 mm. For early diagnosis of dialysis peritonitis, we used test kits, which, using the method of color test strips, allow laboratory confirmation of the development of dialysis peritonitis in the preclinical stage.
At the same time, a reliable diagnosis of dialysis peritonitis and the choice of adequate etiotropic antibiotic therapy are possible only after obtaining the results of cultures of the dialysate solution.
We studied the sensitivity of the dialysate microflora to antibiotics in two groups: urological patients and patients with end-stage chronic renal failure caused by other diseases (Table 6.1).
It can be seen that resistant strains are more common in urological patients.
In our opinion, this is due to the fact that urological patients with a chronic focus of infection, even in the pre-dialysis stage, as a rule, received massive antibiotic therapy.
That is why the treatment of dialysis peritonitis in urological patients presents significant difficulties, and the complex of therapeutic measures cannot be limited to generally accepted measures.
Table b. 1
Sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics (in%) in urological (1) and nephrological (2) patients
| Selected microflora | Sensitivity of strains ( conditional % ) | |||||||||
| Ampicillin | Cipro – floxacin | Ofloxacin | Imipinem | Vancomycin | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| Staph, epidermidis | 6,3 | 6,8 | 96 | 100 | 94,1 | 100 | 99,8 | 100 | 94,2 | 100 |
| Staph, aureus | 1,1 | 12,4 | 86,1 | 92,6 | 93,6 | 100 | 50,9 | 51,7 | 98,1 | 100 |
| Strept. viridans | 50,3 | 54,3 | 40,3 | 44,5 | 70,8 | 75,1 | 81,6 | 86,3 | ||
| Strept. faecalis | 1,2 | 3,1 29,7 | 59,8 | 61,8 | 57,1 | 58,6 | 80,6 | 87,7 | 80,7 | 85,3 |
| Escherichia coli | 28,7 | 90,6 | 93,5 | 89,3 | 91,4 | 93,1 | 98,9 | 91,2 | 99,4 | |
| Klebsiella species | 81,2 | 86,3 | 80,6 | 84,2 | 89,9 | _90,4 | 94,5 | 99,8 | ||
| 10,7 | 86,3 | 87,3 | 81,3 | 81,9 | 84,4 | 82,1 | 95,2 | 100 | ||
| Pseudomonas species | 90,7 | 93,4 | 89,2 | 91,3 | 91,4 | 92,6 | — | ———- |
Share the link:
Source: https://med-slovar.ru/khirurgiya/posleoperatsionnyj-peritonit-khirurgicheskoe-lechenie/2258-dializnyj-peritonit-kak-osobaya-forma-posleoperatsionnogo-peritonita
How does dialysis work in children?
Babies have their own dosage of dialysis solution and duration of the cleansing cycle.
Filling or draining the solution should only take five minutes, sometimes the time can increase to ten minutes. The duration of the entire cycle is only three hours, and not six as in adult patients. The duration of the exchange is considered to be two hours.
When infusing the solution into young children, you should constantly monitor the child’s weight, breathing, pulse and blood pressure.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that dialysis is done to almost everyone for whom it is indicated, unlike hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis still has its contraindications.
Most contraindications relate to chronic pathologies of the abdominal cavity, but there are also general contraindications related to the dialysis procedure:
- Intestinal adhesions.
- Traumatic injuries or changes in the size of organs in the area of the solution infusion.
- With reduced ability of the peritoneum to filter.
- With installed abdominal drains.
- Purulent erosions of the skin in the abdominal cavity.
- The patient is overweight.
- Pathologies of a mental nature due to which the procedure cannot be performed.
- Heart diseases.
Diet for peritoneal dialysis
Nutrition during dialysis has a number of features. The diet maintains a stable condition of patients:
- Restriction of liquid and table salt intake is required.
- Since glucose is present in the dialysate, it is necessary to reduce the amount of it in food consumed.
During hemodialysis, trace elements are lost: iron, calcium and phosphorus. It is worth restoring them from products:
- Iron is found in liver, eggs, red vegetables and fruits.
- Calcium - in dairy products.
- Cheese and seafood are rich in phosphorus.
Thus, if you comply with all the requirements, you can live a long life with this disease.
Possible complications
All complications of this procedure can be divided into types, namely, infectious and non-infectious.
Infectious ones are:
- Peritonitis, that is, an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity.
- Infection of the catheter insertion area.
Such complications arise because hygiene rules were not followed during the “exchange” of fluids. This complication is easy to treat. You should take antibiotics, wash the peritoneum, and stop the dialysis procedure indefinitely. Sometimes you need to remove the catheter.
Peritonitis is considered a dangerous disease, so patients should clearly know all its symptoms. If treatment is not started in time, the inflammatory process can become sepsis, which can be fatal.
Non-infectious include:
- Incorrect operation of the catheter, when it becomes impossible to infuse and drain fluid. The reasons for this may be different, for example: a change in the location of the catheter, its bending, blocking it with the intestines and much more. The therapy is as follows: it is necessary to rinse the tube, replace the catheter itself, or operate on the patient.
- The appearance of an umbilical or inguinal hernia can occur if pressure increases inside the peritoneum.
- If the solution leaks under the skin, the silicone tube must be replaced.
- Right-sided pleurisy. Appears if the solution penetrates into the pleural cavity. If this problem occurs, it is necessary to reduce the volume of injected solution.