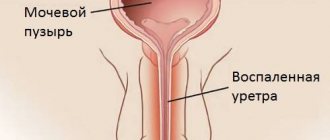
The urinary system is closely related to the reproductive system; it is not for nothing that they are combined into a single genitourinary system, which is why infections in these areas are common. But nevertheless, with an infection of the genital organs, the kidneys are not always affected. Even with cystitis, the kidneys may not hurt.
What infections cause inflammatory kidney diseases and under what conditions do they occur?
Indeed, in most cases, the main cause of urinary tract inflammation is infection.
Infection in the kidneys can be specific or nonspecific.
A specific infection is represented by sexually transmitted diseases (gonococcus, trichomonas, ureaplasma). Here the reason speaks for itself - unprotected sexual contact. In men, the urethra becomes infected directly during sexual intercourse, and subsequently the overlying parts of the urinary system become infected. In women, the infection enters the urethra from the vagina. These infections require special treatment under mandatory medical supervision, as they can cause serious complications.
Nonspecific pathogens of inflammatory diseases are numerous and often cause the disease. These are staphylococcus, streptococcus, E. coli, enterococcus, Proteus, and candidal fungus.
The spread of infection through the urinary system is possible in several ways:
• ascending - from the urethra, where the infection penetrates during sexual intercourse, from the vagina, rectum;
• descending - from the renal pelvis down through the ureters;
• hematogenous - with blood flow from foci in other anatomical areas.
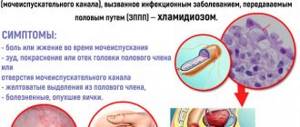
Nowadays there is also a group of hidden sexually transmitted infections - sexually transmitted, but diagnosed only through special studies.
Not all pathogens in this group cause diseases of the urinary system, but representatives such as ureaplasma, trichomonas and chlamydia often cause difficult-to-treat urinary diseases. These are the most stubborn diseases, but there are folk remedies for them too, which we will also talk about.
The most common inflammatory kidney diseases are pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis in acute and chronic forms, and urinary tract diseases are cystitis and urethritis.
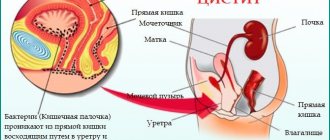
Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of one or both kidneys and occurs as a result of microorganisms entering the kidneys. Usually we are talking about the so-called ascending infection, spreading through the ureters from the bladder. Sometimes microorganisms enter the kidneys along with the filtrate from the blood.
But infection alone is not enough for pyelonephritis to develop. Typically, the disease occurs against the background of the following factors: stagnation of urine due to urolithiasis, in men - due to prostate adenoma, decreased immunity, exacerbation of concomitant diseases of other organs, hypothermia.
Glomerulonephritis is a bilateral diffuse inflammation of the renal glomeruli, which is based on an infectious allergy. But there is also autoimmune gpomerulonephritis. In this case, damage to the kidney tissue occurs due to the production of antibodies to the cells of the own organ. Children and young people usually get sick.
The most common causes of glomerulonephritis are bacterial agents (staphylococci, group A β-hemolytic streptococcus, pneumococci), parasites, and viruses. The triggering factor for development is often hypothermia.
www.vashmedsovetnik.com
Types of infections
The resulting kidney infection can be specific or nonspecific:
- A specific infection in the kidneys is associated with pathogens that are sexually transmitted (gonococcus, trichomonas, ureaplasma). The cause of the disease is clear. This is unprotected sex. In men, the infection immediately enters the urethra, and from there to the overlying areas of the genitourinary system. In women, the infection from the vagina enters the urethra and then moves along the same path of the genitourinary system. Infections must be treated, as quite dangerous complications are possible.
- Nonspecific. Such infections include staphylococcus, E. coli, streptococcus, enterococcus, candidal fungus and others.
A kidney infection can spread in several ways:
- The ascending route is from the urethra and rectum during sexual intercourse.
- Descending - passes from the renal pelvis down the ureters.
- Hematogenous route - brought by blood flow from other areas.
Blood in urine
Most kidney infections follow the same pattern: bacteria that enter the urinary tract move deeper into the body and easily reach the bladder. And since women have a shorter urethra than men, women are more likely to develop the disease. Frequent sexual intercourse, new partners and unprotected sex also increase risks. When the body fights an infection on its own, red blood cells can leak into the urine. Do not ignore this sign if the discharge has nothing to do with the beginning of a new menstrual cycle.
Causes
When an infection enters the human body, the kidneys are the first to suffer as they try to expel it.
A weakened body cannot always cope with such a problem, so the kidneys become infected and require adequate treatment.
The most common causes of kidney infections are:
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Anemia.
- Penetration through the circulatory system.
- Diabetes.
- Low immunity.
- Inflammatory processes in other organs.
Also, kidney damage may be associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and uterus. Even dental caries can cause infection. This also includes hypothermia of the body and incorrect treatment of colds.
Problems emptying the bladder
In rare cases, problems emptying the bladder may be the cause of an infection rather than a consequence of it. For example, men with an enlarged prostate also experience a frequent urge to urinate due to increased pressure from the inflamed organ on the bladder. Women, on the other hand, have the problem of urinary incontinence during menopause. Any of these conditions leads to partial emptying of the bladder, and the remaining fluid is a favorable environment for the development of bacteria. In the chronic course of the concomitant disease, recurrent infections are most likely to occur.
Symptoms of a kidney infection
The presence of infectious inflammation in the kidneys can be determined by the following signs:
- General malaise.
- Pain in the lower back, abdomen and groin.
- Temperature increase.
- Frequent urination.
- Little urine is excreted, it does not come out completely.
- Nausea.
- Loss of appetite.
- Itchy and sometimes sharp pain when urinating.
- Swelling of the face.
- The color and smell of urine changes.
- Presence of blood when urinating.
The most common diseases:
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the kidneys as a result of the penetration of microorganisms. In addition, other pathologies are associated (for example, reduced immunity, kidney stones, hypothermia, inflammation in the adrenal glands and other ailments).
- Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory process of the renal glomeruli, which develops against the background of an infectious allergy or due to the production of antibodies to its own organ. The spread is most often observed in children and young adults (under 30 years of age).
During pregnancy, kidney and urinary tract infections are quite common. Since the enlarged uterus compresses the organs of the genitourinary system, thereby creating good conditions for the occurrence of pyelonephritis. Its signs are more pronounced in a pregnant woman, and complications are observed more often. Therefore, in order to avoid infection of the fetus and premature birth, the woman is placed in a hospital where she undergoes a course of treatment.
Symptoms of a kidney infection
Increased body temperature and fever are possible symptoms of infection.
Among the most characteristic signs of the appearance of an inflammatory process in the kidneys are the following symptoms:
- a sharp increase in body temperature, fever;
- nagging pain in the side or back;
- painful and frequent urges;
- changes in the color and odor of urine, sometimes mixed with blood or pus;
- weakness, increased fatigue, apathy;
- dizziness, nausea;
- increased blood pressure.
Return to contents
Diagnostics
First of all, the patient’s medical history is collected, an examination is performed, and a urine test is taken to find out whether there is a bacterial infection.
In case of complications of pyelonephritis, the patient is placed for inpatient treatment. It is also necessary to draw blood for a general analysis. The kidneys are checked for the presence of stones using an ultrasound or x-ray.
If the infection is protracted, complications such as an abscess, kidney swelling, and blood poisoning may occur (the infection enters the blood). The symptoms of the complication are clearly pronounced and cannot be ignored. People who have concomitant diseases are more susceptible to the occurrence of acute pathologies.
There are also several categories of people who are at risk of complications:
- Pregnant women.
- Elderly people.
- With diabetes.
- With the presence of chronic kidney disease.
- With weak immunity.
Treatment
For all infectious diseases associated with the kidneys, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. The following medications are prescribed:
- Antibiotics - first, broad-spectrum drugs are prescribed, and when the causative agent of the disease is identified, an individually selected drug is prescribed.
- Disinfection solutions intravenously - cleanse the body and blood.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs - to eliminate inflammatory processes. This allows the patient’s condition to improve in a short period of time.
- Diuretics – to improve kidney function and prevent urinary stagnation. For this, diuretics are prescribed.
- Antihypertensive drugs - to normalize blood pressure, as a rule, they lower it.
- Antispasmodics – relieve spasms and improve urine flow during genitourinary tract infections.
- Painkillers – relieve pain.
- Antipyretics – to lower body temperature.
In the presence of chronic forms of pyelonephritis, constant relapses are observed, so it is necessary to remove the primary focus of the disease. For this, either surgical or complex therapy is used.
Urgent surgical intervention is performed in the presence of purulent processes in the kidneys.
During the operation, the entire kidney or part of it is removed, then a drainage is installed to ensure the release of pus.
ethnoscience
Milder forms of pyelonephritis can be treated at home. Also, during treatment, you need to follow a diet that includes low salt intake, and it is also necessary to exclude protein foods.
Traditional medicine recipes are often used as an additional measure:
- It is necessary to drink at least two liters of water per day, which will increase the amount of urine output, which removes bacteria from the body.
- Drink a glass of water with a spoonful of soda dissolved in it 2-3 times a day, this will make it possible to cleanse the body of toxins.
- Eating blueberry mousse will help remove pathogenic bacteria from the body.
- Add a spoonful of vinegar to a glass of water and drink it in the morning on an empty stomach. This recipe helps stop the inflammatory process and improve digestion.
Infectious processes in the kidneys must be treated in order to avoid chronic forms of the disease, which often lead to kidney failure and can sometimes cause human disability.
2pochki.com
Knowing how to recognize the symptoms of a kidney infection is very important as this can help to treat the disease early and thus reduce the risk of any kidney damage.
If not treated promptly, a urethral or bladder infection can travel up the body and affect one or both kidneys, causing a full-blown kidney infection (also called pyelonephritis).
Women are more prone to kidney infections than men.
There may be two reasons for this: a shorter urethra (3.8-5 cm) in women; and its close location to the anus. These two factors allow bacteria to easily enter the bladder and cause an infection that can spread to the kidneys. Below is a list of common symptoms of a kidney infection in women, as well as some information on treating the infection.
What indicates a kidney infection?
Symptoms of a kidney infection are usually immediate. For most people, they tend to appear several hours or days after the infection begins.
So, the following symptoms may indicate a kidney infection:
- Pain in the back, sides and area around the genitals
- High temperature (39 °C)
- Chills
- Feeling tired and weak
- General malaise
- Nausea, vomiting
- Poor appetite
- Abdominal pain/cramps
If your back pain is persistent and your temperature is accompanied by one or more severe symptoms, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Severe symptoms may include:
- Painful urination
- Blood in the urine or cloudy urine
- Urine with a strong odor
- A persistent or frequent urge to urinate
- Burning feeling when urinating
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed depending on the pathogen, determined using a urine test, as well as the patient’s condition. First-line treatment is usually the use of antibiotics to kill the pathogen causing the infection. Most people experience improvement in symptoms within a few days of starting treatment, and recovery in about 2 weeks. However, it is often necessary to take antibiotics for a week or even longer. This ensures complete destruction of the infection. If the infection is severe, hospitalization may be required.
Home Remedies
Drinking large amounts of liquids, including water. Drinking plenty of fluids helps maintain fluid balance and helps flush bacteria out of the body. Avoid drinking alcoholic or caffeinated drinks as they irritate the bladder
Peace. Staying at rest helps the body fight infection and shortens the recovery period. Use painkillers if necessary. Before taking such drugs, it is recommended to consult a doctor. Applying a heating pad to painful areas. This helps relieve pain.
Prevention measures
An important factor in preventing urinary tract infections (UTIs), and thus kidney infections, is completely emptying your bladder. Women are not recommended to “hang” over the toilet seat (that is, not be in a sitting position) while urinating, as this, according to doctors, can lead to incomplete emptying of the bladder, which, in turn, promotes bacterial growth.
You should not tolerate the urge to urinate. Urinary retention increases the risk of UTI. You need to go to the toilet as soon as the need arises; It's even better to simply empty your bladder often.
Doctors also emphasize the importance of emptying your bladder soon after sex.
This practice helps to get rid of any bacteria in the urinary tract and thus reduce the risk of infection. It is important for women to wipe themselves after using the toilet from front to back. Clinical studies suggest that drinking cranberry juice can also help prevent bacteria from growing in the urinary tract and preventing the spread of infection.
Kidney infection can be easily treated with antibiotics. However, timely medical attention is necessary to prevent serious complications such as kidney damage. For example, knowing the common symptoms of a kidney infection and recognizing them when they appear can help you avoid making the disease worse.
Disclaimer: The information contained in this article is for educational purposes only and should not substitute for advice from a healthcare professional.
Video
Related link: Hiccups in the womb
Source: buzzle.com Photo: medicalnewstoday.com
www.vitaminov.net
Signs
When a kidney infection occurs, the following symptoms develop:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- burning, pain and stinging when emptying the bladder;
- pain in the lower back or suprapubic region;
- temperature, febrile state;
- general weakness, drowsiness, fatigue;
- cloudiness of urine, presence of blood streaks in it;
- in severe cases, the infection causes confusion, delirium, nausea and vomiting.
Types and causes of infectious kidney diseases
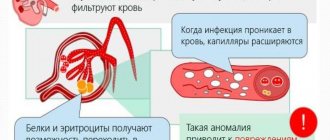
During the day, about 200 liters of blood pass through the kidneys, which they cleanse of waste, toxins and decay products. The causes of infection are simple: pathogenic microbes enter the organ through the blood or lymph. At first, the kidneys, performing their main function as a filtrate, try to independently cleanse the blood of harmful bacteria. But when their number becomes too large, inflammatory processes occur. In medicine, kidney infections are divided into two types: ascending and descending. With the ascending type, the infection enters the kidneys from the urethra and bladder. When descending - from the oral cavity or respiratory tract.
The most common inflammatory diseases are pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. They occur when a viral infection enters the kidneys. With glomerulonephritis, infection occurs only in the renal glomeruli - glomeruli. And with pyelonephritis it covers the entire organ as a whole. Nephrites are divided into primary and secondary. Primary develops against the background of any pathologies of internal organs. Secondary - occurs as a cause of complications of diseases such as syphilis, thrombosis, lupus erythematosus, tuberculosis. They occur in acute, chronic and latent forms.
In cases where the infection has entered the renal pelvis, pyelitis occurs. The renal pelvis is a small cavity that is funnel-shaped and is used as a reservoir for urine. As the disease develops, its outflow is disrupted and inflammation of the mucous membranes occurs. Pyelitis is caused by harmful bacteria - staphylococci and streptococci. Complications after tonsillitis, intestinal infections, and scarlet fever also contribute to the development of the disease. In most cases, pyelitis occurs in children under 5 years of age, more often in girls due to the structural features of the genitourinary apparatus. The disease often affects women during pregnancy due to the fact that the fetus puts pressure on the bladder during development.
Possible complications
Complications usually occur with poor quality treatment or its complete absence and even lead to death. It is possible to develop renal failure, in which partial tissue sclerosis occurs. The active part of the kidney has to work twice as hard. Over time, sclerosis progresses to healthy areas of the organ, which leads to its death. This disease develops gradually and sometimes appears even several years after the infection.
If kidney infections are not treated, bacteria will begin to actively multiply and their number will increase. The infection will enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Purulent inflammation will appear, affecting healthy tissue. Urosepsis will occur, which greatly worsens a person’s condition and often leads to his death.
Groin pain
Men often feel a kidney infection through pain in the groin area. This is directly related to human anatomy. When the embryo is in the womb, its kidneys are still too small in relation to the total mass. As the fetus develops, this organ begins to grow and acquires many nerve endings. This is the classic case when one organ hurts, but the pain radiates elsewhere. This is why some men experience pain in the groin when they have a kidney infection, an area that also contains many nerve endings. This gives reason to mistakenly believe that painful sensations can cause inflammation of the genital organs.
At-risk groups
Anyone can develop kidney infections, but there are certain groups of people who are more susceptible to them:
- Due to physiological characteristics, women get sick more often than men. A viral infection can more easily enter the female body through a short urethra.
- During pregnancy, when a woman's body undergoes physiological changes in the urinary system and kidneys. The growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder, making it difficult for urine to flow out and increasing the likelihood of developing germs.
- Due to low immunity, infectious diseases often develop in children, especially under the age of 3 years. According to statistics, an average of 3% of girls and 1% of boys suffer from pyelonephritis.
- As you age, the risk of developing diseases increases. Especially in people over 65 years of age, due to the development of immunodeficiency.
- The presence of chronic diseases that lead to a decrease in the body's resistance. For example, diabetes and AIDS.
- Urolithiasis, during which stones obstruct the outflow of urine, which leads to its stagnation and the development of bacteria in it.
- Congenital pathologies in the kidneys or bladder often lead to the development of nephritis and, as a consequence, renal failure.
- Infection often occurs during treatment, which requires the use of a catheter to remove urine. The closed drainage system of the catheter creates ideal conditions for the growth of bacteria.
Prevention
Often, a kidney infection occurs as a result of a pre-existing urinary tract infection. The best way to prevent developing a kidney infection is to keep your urethra or bladder free of bacteria.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids.
- Urination: Urinate whenever you feel like it. Do not wait.
- Sexual contact: Urinate after intercourse. Wash your genitals before and after sexual intercourse.
- Toilet hygiene: After passing the chair, wipe the anus from the front and back. This reduces the risk of spreading bacteria to the genitals.
- Fiber: Eat plenty of fiber to help your stool pass easily without causing irritation or damage to your skin. Constipation increases the risk of developing a kidney infection.
Diagnostic measures
To make an accurate diagnosis, the following research methods are usually used:
- Ultrasound examination. The most popular diagnostic method that identifies signs of inflammatory processes and their causes. Using ultrasound, you can determine whether the liver has increased in size, which is typical for pyelonephritis.
- Blood and urine analysis. In infectious diseases, a blood test shows a high number of white blood cells. The patient's urine contains a large number of bacteria, and its specific gravity decreases.
- CT scan. The most accurate method. Mainly used to identify complications of pyelonephritis and abscesses.
- Angiography. A method that is used specifically for diagnosing kidney pathologies. A small number of radioactive isotopes are injected into the patient's body, which help monitor abnormalities in the functioning of the organ.
How to treat a kidney infection?
Treatment depends on the exact diagnosis and is selected individually. For mild forms of nephritis, treatment is carried out at home, and for severe forms - in a hospital. The patient is prescribed bed rest, plenty of fluids and a special diet that excludes the consumption of salt and protein foods. A whole range of medications is prescribed, which includes the following drugs:
- Antibiotics. After an accurate diagnosis and identification of the pathogen, antimicrobial treatment is prescribed, aimed at suppressing the growth and reproduction of bacteria.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Used to lower body temperature and eliminate pain symptoms. Prevents the development of complications, especially renal failure. Contribute to rapid improvement of the patient's condition.
- Diuretics. To increase the amount of urine excreted, along with which pathogenic bacteria and waste are removed from the body.
- Medicines to lower blood pressure. Prescribed in cases where an infectious disease is accompanied by hypertension.
- Painkillers and antispasmodics. To eliminate pain, relieve spasms and improve urine flow.
During pregnancy?
During pregnancy, timely treatment of an infectious disease is mandatory. This will help avoid complications such as premature birth, hypertension or toxicosis. An antibiotic is prescribed by a doctor taking into account the assessment of the possible risk to the fetus and individual characteristics - the level of severity of the disease and the duration of pregnancy. In addition, in case of fever, antipyretic medicine and uroseptics based on herbal components are prescribed.
How to treat children?
Mild forms of kidney inflammation in children are treated at home; in any other cases, treatment is carried out, under the constant supervision of a doctor, in a hospital. Depending on the type of causative bacteria, antibiotics are prescribed. Particular attention is paid to general strengthening therapy, therefore the main treatment complex includes drugs aimed at increasing immunity. When treating glomerulonephritis, diuretic, anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic drugs are prescribed. Chemicals have a negative impact on children. To avoid this, herbal medicine and drugs containing natural ingredients are often prescribed.
ethnoscience
Home remedies help relieve unpleasant symptoms, improve kidney function and speed up recovery. In addition, they have a general strengthening effect, cleanse the body and remove toxins. It is impossible to cure the disease only with the help of folk recipes, but in combination with medications, they have a positive effect on the body.
- Baking soda will help relieve pain. Add one teaspoon of soda to a glass of water. Drink once a day after the main meal.
- Cranberry juice helps to quickly remove pathogenic bacteria from the body. It is better to prepare the juice yourself, then it will retain all the beneficial substances.
- Apple cider vinegar is often used for kidney infections. It helps relieve inflammation and also improves metabolism. It should be taken diluted and always after meals.
- Asparagus cleanses the kidneys and is essential for urinary tract infections. It is usually added to salads, vegetable soups and stews.
- Coconut water has antibacterial properties and helps fight E. coli.
- Rosehip decoction is an effective diuretic and strengthens the body's defenses. You need to drink at least 2 glasses of decoction per day.
- For inflammation, marshmallow root, birch leaves, horsetail and St. John's wort are also used. Decoctions and infusions are prepared from herbs.
Pyelonephritis in men: symptoms and treatment
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Problems of the genitourinary system in men are an unpleasant pathology that affects reproductive function. Such manifestations should be taken seriously. This article will discuss the causes and symptoms of pyelonephritis in men, and methods of treating the disease.
What is pathology
Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the area of the renal pelvis and calyces. As a rule, women are more often affected by this disease, but they are also characteristic of the male body.
Pyelonephritis in men is infectious in nature, can be caused by streptococci, staphylococci, E. coli, mycoplasma, and other opportunistic microorganisms and is accompanied by impaired urine output.
The infection enters the kidneys in the following ways:
- Through the blood stream - hematogenous;
- through the lymphatic system (nodes) – lymphogenous;
- Through the urinary tract, the infection enters the kidneys - an ascending method.
There are primary and secondary forms of pyelonephritis. The first is typical for children 7–8 years old and people with weakened immune systems. In older men, renal pathology is secondary, occurring against the background of inflammatory processes.
What provokes the development of pyelonephritis
The 7 main causes of primary kidney inflammation in men are:
- Hypothermia;
- vitamin deficiency, which causes a weakening of the immune system;
- elevated blood sugar levels;
- numerous stressful situations;
- excessive physical activity;
- bad habits;
- active proliferation of harmful bacteria.
As for the secondary form of pyelonephritis, it can occur as a result of damage to the bladder area, after which the impact of harmful bacteria passes to the kidneys. The main causes of the disease include:
- Inflammation of the prostate gland;
- prostate adenoma (impaired urine outflow due to compression of the prostate on the urinary canal);
- urolithiasis (has the ability to provoke the formation of stagnation);
- less often as a complication after urine excretion using a catheter.
Another predisposing factor for kidney inflammation is the patient’s advanced age and infection of the body with sexually transmitted diseases. In this case, pyelonephritis in men develops against the background of existing ailments, as the protective functions of the body as a whole decrease.
How does pathology manifest itself?
The initial stage of pyelonephritis in men is often characterized by constant aching pain in the lower back. The pain intensifies with heavy physical activity. In acute kidney disease, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- High body temperature, and it may decrease after each bladder emptying;
- disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, often accompanied by increased sweating, chills, dehydration or headaches;
- blood clots may be found in urine that becomes cloudy;
- swelling of the body (especially under the eyes and lower extremities);
- constant painful manifestations in the kidney area;
- fatigue and weakness;
- sudden changes in blood pressure;
- increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, detected by a blood test;
- at the moment of urine excretion, the patient often experiences unpleasant sensations that develop into sharp pain.
At the moment when chronic pyelonephritis develops, some signs begin to weaken significantly or have a hidden course. At the same time, even the results of laboratory tests record normal values. However, the emergence of new and more dangerous signs of pyelonephritis cannot be ruled out. These include:
- Pain in the lower back increases noticeably and becomes relatively frequent;
- as a result of decreased appetite, the patient begins to lose weight and experience severe weakness, and headaches develop into migraines;
- constant urge to urinate, even when the bladder is empty;
- the appearance of blood in urine and an unpleasant odor, change in urine color;
- purulent inflammation at an advanced stage.
It should be noted that the symptoms of chronic pyelonephritis are in many ways similar to those of other genitourinary diseases. That is why it is important to correctly diagnose kidney disease in a hospital setting in order to further exclude the presence of other diseases and plan further treatment of the disease.
Diagnosis of pyelonephritis
The manifestation of the first signs of the inflammatory process implies immediate seeking medical help. The main task is to establish the cause of the development of kidney inflammation.
For pyelonephritis in men, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are used. After a visual examination of the patient by palpation, the doctor prescribes clinical tests, among which urine analysis is of paramount importance.
To examine the patient, the following types of tests are prescribed:
- A general urine test reveals an increased content of leukocytes;
- urine analysis according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky;
- culture of urine on a nutrient medium;
- general and biochemical blood tests.
In some cases, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys;
- cystourography;
- excretory urography;
- radioisotope research.
The above methods for examining the kidneys will show the complete picture of the disease.
How to treat kidney pathology in men
If initial symptoms of pyelonephritis occur, it is recommended to visit a urologist or nephrologist, who, after an examination, will prescribe a course of therapy.
In general, the general method of treating the disease comes down to the following:
- Removing stones from the ureter that have caused a kidney infection.
- Eliminate pain and relieve inflammation.
- Reducing the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
Depending on the severity of the disease, both outpatient and inpatient treatment is practiced. The patient must remain in bed and take the following medications:
- The use of drugs that stabilize blood pressure and reduce temperature.
- Taking analgesic medications to relieve attacks of pain.
- Relieving inflammation with medications, for example, diclofenac or metamizole.
- Normalization of kidney function with the help of furadonin.
- Use of antibacterial drugs for 7 – 14 days. More often, fluoroquinol or cephalsporin medications are prescribed, for example, ampicillin, ceftriaxone.
- Prescribing a course of immunostimulants (amixin, echinacea, betaferon).
- In some cases, they resort to taking muscle relaxants (no-spa, papaverine) and diuretics (veroshpiron, indapamine).
During illness, you should drink plenty of fluids, stay in a warm room, and avoid hypothermia.
For purulent abscess, surgical treatment is used. Acute pyelonephritis in men is often treated with intravenous infusions.
In general, the main thing is to eliminate the symptoms of acute and chronic pyelonephritis and avoid complications. Chronic pyelonephritis subsequently requires long-term therapy (2-3 months) with the help of herbal uroseptics, registration at a dispensary and an annual examination of the body.
A prerequisite for pyelonephritis in men is compliance with a special diet, including:
- Limited consumption of salty, smoked and fatty foods;
- constantly drinking plenty of herbal infusions;
- refusal of hot sauce, spices, strong tea and coffee, alcoholic beverages and tobacco.
The basic diet during illness should include:
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
- water-based cereals;
- dairy products;
- vegetable puree;
- steamed meat and fish;
- baked vegetables.
You should adhere to proper nutrition throughout the general course of treatment.
Traditional methods of treatment
In combination with drug therapy, traditional medicine recipes are used, the main goal of which is to relieve the symptoms of acute inflammation and increase urination.
When treating pyelonephritis, the following are effective:
- lingonberry decoctions;
- infusions of dried nettle and black currant leaves;
- bearberry decoction;
- To enhance the diuretic effect, consume vegetables and berries (watermelon, pumpkin, fresh juice of young potatoes and carrots).
Under no circumstances should the patient self-medicate. Before using any product, you should consult your doctor to avoid side effects.
Prevention methods
Preventive measures will help reduce the risk of developing pyelonephritis, which include:
- Rejection of bad habits;
- annual preventive examinations;
- following the principles of proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle;
- preventing hypothermia of the body;
- carefully observe hygiene;
- avoid frequent changes of sexual partners and use contraception;
- harden the body;
- observe drinking regime;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes.
It is important to immediately begin treatment at the first signs of pyelonephritis, which will help quickly overcome the disease and avoid complications. Remember that the health of your kidneys is in your hands.
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is an acute infectious disease that selectively affects the blood vessels. The disease is accompanied by intoxication, fever and affects the kidneys. Representatives of different genders and ages suffer from the disease. The disease is quite rare, but serious.
Causes of the disease
The main carriers of the disease are rodents: field mouse, gray mouse, black rat. In animals, the disease occurs without symptoms. The main sources of transmission of the virus are urine, feces, and saliva. Infection is rare. Patients with fever are not contagious. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome can be transmitted from a carrier to a person in various ways:
- airborne dust;
- food;
- contact
The virus is transmitted between rodents during interbreeding or prolonged stay in the same room. Direct contact is required for transmission of the virus. For rodents, there is another way of transmitting the disease (aspiration). Infection occurs by inhaling dust and dry excrement. For humans, infection can mean eating the meat of an infected rodent, direct contact with animal excrement, a bite, or contact with saliva.
Most often, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome spreads in the summer. At this time, there is a high probability of contact with infected secretions. Even if you previously caught the animals, one of them turned out to be a carrier of infection, and after contact with it you did not wash your hands, then there is a high probability of infection. Getting rodent saliva into cuts and abrasions can transmit infection.
In winter, infection can occur through aspiration. Farm workers and owners of private houses may be at risk (if there is a possibility that mice or rats live in the house). Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome can be transmitted through ticks that are found on the body of rodents. But these ticks do not attack people.
Symptoms of the disease from 1 to 11 days
The development of the disease may take up to 1 month. In the first 2 weeks, the patient experiences the initial and oliguric stages of disease progression. Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome begins to appear from the 1st day of infection. The patient develops a very high temperature (up to 40°C), which is accompanied by chills. After this, symptoms appear:
- Weakness throughout the body.
- Extreme thirst and dry mouth.
- Headache.
- Swelling of the neck, face and chest.
A rash similar to an allergic one sometimes appears on the skin of patients. On day 2, the patient may experience swelling of the respiratory tract, severe malaise, and back pain. Typically, no change in the functioning of internal organs is noted at the initial stage of infection. Rarely, patients may have pain in the heart area and difficulty breathing.
The febrile period begins on the 4th day of the incubation period and lasts until the 11th day of illness. A person continues to have a high fever for 2-3 days, but usually it subsides on the 7th day. Following this, there are no significant changes in the patient’s condition. The main symptom that manifests itself most strongly is lower back pain.
If the painful sensations disappear on the 5-6th day of the incubation period, this may mean that the diagnosis was made incorrectly. On the 6th day, patients begin to experience prolonged, causeless vomiting, which can be repeated many times throughout the day. A person's stomach begins to swell and hurt. The swelling of the mucous membrane begins to increase, but no manifestations of the lesion are noted on the skin.
Symptoms of the disease from 12 to 26 days
On day 12, the patient's temperature may gradually decrease. But this is not at all a sign of improvement in his condition. During this period, internal inflammation of organs may develop. The patient develops irresistible thirst, dry skin, dry mouth, severe headaches and lethargy. The patient cannot sleep, and pain in the lumbar back begins to spread to the entire abdominal cavity.
The level of nitrogenous wastes in the patient’s blood begins to rise sharply. This occurs due to the breakdown of proteins and disruption of the amount of nitrogen excreted by the kidneys. The patient experiences a significant decrease in the amount of urine produced. The more severe the disease, the less urine the body produces per day.
Renal syndrome may be accompanied by isohyposthenuria. This disease develops in almost all patients due to fever and provokes a sharp decrease in urine density. A study of the blood of patients at this stage of the disease shows an increased content of leukocytes in the plasma.
From the 13th day, the patient may stop vomiting and nausea, gain appetite and the ability to move normally. During this time, there may be a significant increase in the amount of daily urine; gradually it reaches a normal value. The person continues to have dry mouth, weakness throughout the body and malaise.
After this stage, slow recovery begins. The final recovery period can take a very long time. This usually takes from 4 to 12 months. Recovery is accompanied by kidney pathologies, dry mouth, and polyuria. If these symptoms continue for too long or are very severe, the patient may need to be readmitted to the hospital.
Often the disease contributes to disruption of the excretory-secretory function of the tubules and other less pronounced disorders. Such processes can continue in the human body for a very long time, and it may take up to 10 years to fully restore all body functions. However, during this time the disease will not develop into a chronic form of renal failure.
Complications and prevention
After illness, patients sometimes experience complications. They are expressed through:
- development of infectious-toxic shock;
- renal failure;
- swelling of the respiratory tract;
- internal hemorrhages;
- frequent seizures;
- loss of consciousness;
- dilated pupils;
- partial loss of pulse.
As the disease progresses, many patients may experience vomiting and nausea. Often the consequences are expressed through hiccups and increased fatigue and drowsiness. Patients often develop nervous tics and involuntary movements of the facial muscles. When examining a blood test in plasma, the content of urea and creatinine increases sharply. Complications may be accompanied by severe lower back pain and heavy bleeding.
Prevention of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome involves careful behavior of people in parks, forests, and plantings. It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene. On the territory of private sectors, preventive work should be carried out to eliminate rodents from the territory of the populated area. People need to be extremely careful when coming into contact with rodents.
Treatment of hemorrhagic fever
All patients with this disease are non-contagious. Therefore, they can be placed in any hospital that is equipped with equipment capable of monitoring kidney function. It is very important to take all precautions when transporting such patients, as there is a high risk of rupture of the renal capsule.
Patients are prescribed bed rest for several days. It is necessary to ensure compliance with hygiene and diet rules. The patient is prohibited from consuming salt and must drink plenty of water. If a person’s condition is critical, then any protein is completely excluded from the diet for a certain period.
Hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome is treated with etiotropic therapy and pathogenetic treatment. The doctor's prescription will depend on what stage of development the disease is at and how severe its symptoms are. First of all, drug treatment is aimed at eliminating the unpleasant manifestations of the disease and painful symptoms.
If the patient’s condition does not improve within 5 days, and the signs of renal failure become more pronounced, then he is prescribed stronger drugs aimed at reducing the level of urea in the blood. For treatment, special injections, tablets and mixtures are used that eliminate severe kidney pain and prevent the development of cardiovascular failure.
It is important to carry out prevention when treating fever. Typically, this stage of treatment begins after diuresis has been restored. When the patient begins to recover, drug treatment is gradually discontinued and only intravenous administration of an isotonic solution remains. The patient is discharged only after complete recovery.
The doctor must be sure that the virus is completely destroyed and will not begin to progress again after some time. Patients usually remain in bed after treatment for 4 months.
Any physical labor (in particular, sports) is strictly prohibited for 1 year.
The recovery period can last much less if the patient follows all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Prevention measures
To prevent a kidney infection from occurring, it is important to follow simple hygiene rules that will help prevent germs from entering the body. When washing, it is advisable not to use products that contain fragrances; this can negatively affect the microflora. It is not recommended to wear very tight or tight clothing. Underwear should be made only from natural, “breathable” materials. It is important to avoid hypothermia, do not sit in the cold, and try not to walk in wet shoes for a long time.
A sedentary lifestyle contributes to blood stagnation and the accumulation of extra pounds. This is a common cause of bladder stones, which in turn cause kidney infections. You need to try to move as much as possible, walk, play sports. You should not neglect the disease or self-medicate. Such actions can lead to the disease becoming chronic or relapses. At the first symptoms, you need to consult a doctor who can prescribe high-quality and effective treatment.
During the prevention and treatment of kidney infections, you need to drink as much fluid as possible. Drinking plenty of fluids flushes bacteria from the body. Fruit juice is especially useful, as it “oxidizes” urine and makes it unsuitable for the proliferation of microbes. The diet must include fresh fruits, vegetables and herbs, especially parsley. As well as dairy products, lean meats and fish, soups with vegetable broths. Garlic, ginger and cinnamon have an anti-inflammatory effect. Do not overuse fatty and fried foods; sweets; canned and smoked products. Too salty and sour foods are harmful to the kidneys.
kidney.propto.ru