Hello dear readers of my blog!
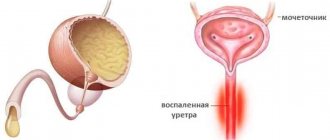
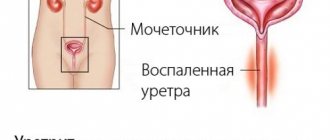
In the last article I told you about chlamydia in general. In this article I will tell you about the most common manifestation of chlamydial infection in men and women - chlamydial urethritis.
You can read in detail about what urethritis is and what they are like in my article “Urethritis. What you definitely need to know!” and watch a video about it.
Often when talking about chlamydial urethritis, they use the name urogenital chlamydia or chlamydial infection of the lower genitourinary tract.
In adults, chlamydia infection occurs in almost 100% of cases through sexual contact, and with any form of sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal).
The incubation period (the time elapsed from the moment of infection until the appearance of the first clinical signs of the disease) for chlamydial urethritis is on average 2-3 weeks.
With chlamydial urethritis, its latent course is possible - carriage or an asymptomatic form, when infection has occurred, chlamydia is present in the urethra, but the person does not have any signs of the disease, he does not feel anything, although at the same time, as you might guess, he is sexually contagious. It is believed that more than 70% of women have an asymptomatic course of the disease.
Therefore, my advice to you! If one of your partners is diagnosed with chlamydial urethritis, you should not immediately blame the other for the cause of the infection. We still need to figure it out, what if you had a hidden form and you are the source of infection for your other half!
If we talk about the classic course of chlamydial urethritis, then at the end of the incubation period, a person may experience the following symptoms with varying degrees of severity.
General information
The main method of infection is sexual intercourse without protection, during which chlamydia multiplies and passes from one organism to another. Often the disease occurs simultaneously with other infections caused by gonococci, Trichomonas or fungi.
After several infections are identified, the symptoms increase and the treatment course becomes more complex. The incubation period depends on the level of infection and can take from one to four weeks. If you do not start timely therapy, the disease will go into the chronic stage, which will be preceded by two of its forms - acute and subacute.
Treatment
Treatment of chronic and acute chlamydial urethritis should be comprehensive. Only in this case will it be possible to cope with the infection and prevent possible complications. It is necessary to treat a sexually transmitted disease using the following:
- antibacterial drugs (the type of antibiotics is selected during diagnosis);
- immunotherapy;
- local therapy;
- special nutrition (refusal of fried, spicy, salty, fatty, alcoholic products);
- refusal of sexual intimacy during treatment;
- abundant drinking regime.
The treatment regimen is selected by a specialist personally for each patient. The treatment method depends on the individual characteristics of the person, the severity of the disease, and the location of the lesion.
Treatment regimen
The standard treatment regimens for chlamydial urethritis are:
- Josamycin (Vilprafen Solutab) 500 mg twice a day;
- Doxycycline (Unidox Solutab) 100 mg twice a day;
- Levofloxacin (Levoflox) 500 mg once a day;
- Ofloxacin (Tarivid) 300 mg three times a day.
In the acute form of the pathological condition, the course of taking antibiotics is one week.
In the acute form of the pathological condition, the course of taking antibiotics is one week. For a chronic course of the disease with complications, at least three weeks. If there is a high resistance of pathogenic microorganisms to the anti-infective substances of various antibacterial drugs, several types of medications are prescribed at once. To strengthen the immune system, Leukinterferon, Interlock, Reaferon are prescribed. Moreover, both sexual partners must undergo treatment at once. Otherwise, the infection will continue to spread from one to another. We should also not forget about a balanced diet and giving up addictions (alcohol, cigarettes, drugs).
Types of chlamydial urethritis
Different species differ in their clinical signs. The acute pathological form is similar to infection with gonococci. In the chronic form, symptoms may not appear at all, or they may be of a different nature, changing periodically.
Different types of chlamydial urethritis differ in their symptoms in men and women and are sometimes diagnosed with other diseases. This happens because there are many signs, and all resemble manifestations of other diseases. Each type has its own detection methods and medications.
Chlamydia has a large number of types, depending on the location and level of damage. It is customary to distinguish:
- torpid – located in front;
- total – happens with complications in the prostate.
The first type is total and can acquire chronic forms. In particularly severe situations, it may be accompanied by prostatitis.
What is it and ways of transmission
Chlamydial urethritis in women and men is a venereal disease, predominantly sexually transmitted. The causative agent of the disease is chlamydia. International classification code (ICD 10) A 56.0.
An infection of the urinary system, as mentioned earlier, is transmitted through sexual intercourse without barrier contraception. Moreover, infection can occur during anal, vaginal, or oral sex. The risk group includes people 20-40 years old who lead an active intimate life.
The pathogen can enter the body through contact and household contact. This happens quite rarely. Infection can occur through bath accessories or when wearing someone else's underwear.
Infection is possible vertically (from mother to child). This can happen during intrauterine development or when a baby is born. Although the risk of such infection is small, women need to be careful during pregnancy. After all, not only her health, but also the life of the baby depends on this.
Causes of the disease
Promiscuous sexual relations and the lack of protective equipment are the most common reasons for the development of pathology.
Bacteria are able to pass from both the male and female bodies. Chlamydia in male patients remains on the mucous membrane of the penis and sometimes penetrates the rectum. After this, they begin to multiply and infect the body.
If the immune system is weakened, then damage to the genitourinary system occurs. Bacteria multiply, provoking an inflammatory process. Chlamydia releases toxins that negatively affect the structure of the ureteric passage.
Preventive measures
Prevention of urethritis, which is caused by chlamydia, involves preventing pathogenic bacteria from entering the mucous membrane of the genitourinary system. First of all, this is the use of a condom during intimate relationships. It is important to have an orderly sex life. Casual relationships very often lead to the occurrence of sexually transmitted diseases.
It is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene. You should wash your hands after using the toilet. Showering and changing underwear should occur twice a day.
Manifestation of pathology
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- during the process of urinating, pain and itching are felt in the urethra;
- droplets of blood may appear in the urine;
- purulent accumulations are released from the urethra.
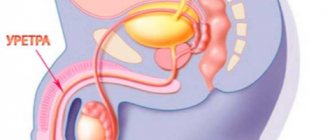
Symptoms in men
Quite often, the disease does not manifest itself in any way in the male half of the population. Only after a few weeks do not very pleasant sensations appear. It all starts with problems associated with urination, which indicates an inflammatory process.
The head of the penis swells and turns red, and a yellowish discharge appears from the penis. Urination becomes difficult, urine is released in small portions. The same signs can be observed in patients with gonorrhea. It happens that both pathologies occur simultaneously. Medicines for chlamydia and gonorrhea may be prescribed, since it is quite difficult to distinguish between the diseases.
Symptoms in women
At first, the disease does not show itself in any way. The patient begins to experience discomfort in the genitals, and mucous discharge appears from the urethra. This is the first and main sign of the disease.
In addition, women may experience not very pleasant sensations during sexual intercourse; pain, burning and itching appear when urinating. An unpleasant odor emanates from the genitals, and discharge with pus and blood may be observed.
If you do not start a timely course of therapy, the disease can affect the uterine cervix.
During an exacerbation of the disease, symptoms resembling infection with gonococci occur. To begin with, the first wall of the urethra is affected, then the signs of the disease disappear, but return stronger, confirming the spread of the infection.
Diagnostic methods depending on gender
When a patient consults a doctor, an anamnesis is taken. The patient is examined, existing complaints are studied. For women, a gynecological examination is required. A man should definitely visit a urologist.
The following examinations will help identify the pathogen:
- general urine analysis;
- smear of urethral discharge;
- urethroscopy;
- bacteriological culture;
- culture for sensitivity to antibiotics;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- PCR diagnostics.
In women, to make a diagnosis and determine the stage of development of the disease, discharge is taken for analysis not only from the urethra, but also from the cervical canal, since chlamydia initially enters the vaginal mucosa, and later they penetrate the urethra.
Diagnostics
The doctor begins the examination by interviewing the visitor to identify complaints and clarify the time when the first signs of a problem appeared. Then an examination is scheduled, during which smears are taken from the urethra, which help determine the type of urethritis disease. If the form is chronic, then urethrography and urethroscopy will be prescribed.
Urine is submitted for analysis, which may contain pathogenic bacteria. Bacterial culture of urine is performed to determine the degree of resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics.
As a supplement, an ultrasound examination of the genitourinary organs is performed.
Comprehensive diagnostics makes it possible not only to determine the disease. With its help, causes and pathogenesis are identified. This allows you to choose the most effective treatment methods.
Traditional Treatments
The disease can be cured with antibiotics. Since the problem is caused by harmful microorganisms, it is necessary to take antibacterial drugs - Rulid, Dixicycline, Ofloxacin.
Women during pregnancy are not recommended to use them, or should exercise extreme caution so as not to cause side effects.
The therapeutic course can be performed orally, or medications are injected into the urethra. For chronic diseases, physiotherapy may be prescribed.
During the entire treatment course, you should abstain from sexual relations. If there is a regular partner for sex, then therapeutic therapy must be performed by everyone to avoid re-infection.
If the disease is identified correctly and therapy is started in a timely manner, the treatment course will be as effective as possible, helping to quickly get rid of the problem. Remember that during the treatment period you will have to give up spicy foods and completely avoid drinking alcohol.
Test for chlamydia
To test for chlamydia in urethritis, a smear is often taken - a scraping from the urethra. Moreover, to obtain reliable results, it is recommended not to urinate for at least 3 hours before taking the test. This is very important to obtain reliable survey results.
I would like to draw your attention to the fact that nowadays, with modern diagnostic methods, there is no need to drink any beer before taking the test, although such advice can be found on the Internet!
Diagnosis usually occurs using molecular biological methods of laboratory research, for example PCR (polymerase chain reaction), when specific fragments of DNA and/or RNA of chlamydia trachomatis are detected.
Important! If a person’s test for chlamydia is positive, but there are no subjective and objective signs of an infectious-inflammatory disease and risk factors for getting this infection, additional research must be done using a different method to confirm the diagnosis!
Application of traditional medicine
Alternative methods of treatment should be used as adjuncts. As an independent therapeutic course, they do not bring the expected result; they affect the source of the disease, but do not eliminate it.
It is best to drink cranberry juice, which is excellent in getting rid of the infection. Tinctures and decoctions of black currant reduce the inflammatory process. A parsley decoction prepared with milk is an excellent remedy for inflammation of the genitourinary system.
They use marshmallow roots, blue cornflower flowers, and hemp seed. Before using traditional methods, you should consult a specialist so as not to harm your health or worsen the situation.
Sexual infection chlamydia: features
Genital chlamydia appears as a result of damage to the body by chlamydia. This disease is considered one of the most common.
Chlamydia causes inflammation in the genitourinary organs.
Damage to the genital organs may occur in association with other species. There are several types of infections:
- Trichomoniasis;
- Ureaplasmosis;
- Gardnerellosis;
- Mycoplasmosis.
The appearance of at least one of the listed infections is a reason to perform tests for chlamydia.
Chlamydia can have different localizations, and it leads to damage to various organs and systems.
Damage not only to the genital organs is noted, but also to diseases of the eyes and respiratory system. Infection of the conjunctiva and respiratory tract leads to chlamydial conjunctivitis and pneumonia. Joints may be affected, and chlamydia can cause arthritis. In severe cases, the cardiovascular system may be affected.
The location of the causative agent of chlamydia is the mucous membrane of organs. Penetrating inside the genital organs, the microorganism begins to parasitize, causing inflammatory processes.
Latent sexual chlamydia is detected quite often. For this reason, the disease is quite difficult to diagnose.
As a result, there is no treatment, and various complications appear. Chlamydia can take a chronic course.
How often does infection occur?
Chlamydia is transmitted through sexual contact. But there is also a contact and household route of infection. In this case, infection occurs through personal items (towel, washcloth).
It is possible for a child to become infected while passing through the birth canal. In such cases, infection of the organ of vision or breathing occurs.
Complications and consequences
Chlamydia urethritis entails diseases of the genitourinary organs. In advanced situations, hemorrhagic cystitis and epididymitis may develop. Doctors determine urethral stricture and damage to the seminal vesicles. If the pathology is not treated in a timely manner or with violations, then difficulties may arise that are quite difficult to get rid of.
Men with advanced chlamydia disease suffer from chronic prostatitis, and impotence often appears. In women, cervical erosion occurs, and ectopic pregnancy may occur. Difficulties arise with conceiving and carrying a baby, and miscarriages often occur.
Negative consequences of urethritis
Not everyone is aware of the possible complications of this disease. If chlamydia is left untreated, it can lead to the spread of germs. The following consequences are possible:
inflammation of the prostate gland;- disturbance of spermatogenesis;
- inflammation of the bladder mucosa;
- orchitis;
- epididymitis;
- vesiculitis;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- obstruction of the fallopian tubes;
- infertility;
- cervicitis;
- proctitis;
- pharyngitis;
- violation of potency;
- urethral stricture;
- swelling of the scrotum;
- acute urinary retention;
- erasure of orgasms;
- decreased libido;
- chronic pelvic pain.
In the presence of Reiter's syndrome, balanitis, balanoposthitis, stomatitis, as well as damage to vital organs (lungs, heart, kidneys) are possible. A common complication of chlamydia in women is the formation of adhesions in the pelvic area. When the rectum is involved in the process, the process of defecation becomes difficult. Another complication of chlamydia is inflammation of the gallbladder.
Preventive measures
To prevent the formation of chlamydial disease, which can cause significant harm to health, you should take sexual relations seriously and use protective equipment. Using contraceptives can reduce the likelihood of becoming infected with chlamydia. You should not ignore periodic examinations with a doctor in order to have confidence in your own health.
Women are advised to carefully comply with all personal hygiene requirements. Timely detection of pathology will increase the chances of prompt and successful treatment. You should not ignore preventive measures to avoid serious health problems.
Possible complications of urethritis due to Chlamydia trachomatis
Complications of chlamydial urethritis can be various diseases of the genitourinary system, often this occurs in the absence of timely treatment.
In advanced cases, the patient may experience the following consequences:
Salpingitis
Salpingitis is inflammation in one or both fallopian tubes.
Symptoms usually appear after menstruation.
Most often this is abdominal pain, unpleasant odor and abnormal color of vaginal discharge.
Also bloating, fever, lower back pain, nausea, pain during ovulation/menstruation, painful intercourse, vomiting.
Among women with tubal factor infertility, 50% have no history of pelvic pathology, but have scarring on the fallopian tubes and antibodies to C. Trachomatis.
Cervicitis
Cervicitis refers to inflammation in the cervix.
Sexually transmitted diseases are the most common cause of cervicitis.
Typical symptoms include grayish or yellowish vaginal discharge and vaginal bleeding.
After sexual intercourse or between menstrual periods, spotting is observed.
Worries include pain during sexual intercourse, problems with urination and, less commonly, abdominal pain or fever.
Left untreated, a cervical infection can cause problems with fertility (ability to become pregnant).
The infection can spread from the cervix to the uterus and surrounding organs, causing life-threatening conditions.
However, such a complication is rare.
Epididymitis
Epididymitis is an infection of the epididymis.
In the absence of adequate treatment, acute epididymitis can progress, becoming chronic and causing numerous complications.
For example, the formation of an epididymal or testicular abscess; testicular ischemia can cause testicular infarction, necrosis, or atrophy; infertility and scars/cysts in the epididymis.
Orchitis
Testicular inflammation is a fairly rare disease that can affect one or, rarely, both testicles.
Typical signs of pathology are painful and swollen testicles.
A complication of testicular inflammation can be an abscess (encapsulated formation of pus as a result of tissue fusion).
In such cases, only surgical intervention can help.
Vesiculitis
Vesiculitis is an inflammation that is localized in the seminal vesicles.
The symptoms of vesiculitis are similar to the symptoms of prostatitis.
The patient may complain of dull, aching pain in the abdomen, discomfort in the urethra, pain after intercourse, the presence of blood in the seminal fluid, premature or painful ejaculation and impotence.
Treatment usually involves taking antibiotics after determining the exact cause of the inflammatory process.
If treatment is inadequate, there is a risk that seminal vesiculitis will transform into a seminal vesicle abscess.
Cystitis
It is an inflammation of the bladder, namely the tissue of the inner wall of the organ.
Cystitis is mainly caused by the following symptoms: pain when urinating (dysuria), frequent urination (pollakiuria), a feeling of inability to hold urine.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis
It is a relatively rare condition that is usually accompanied by intermittent symptoms of urinary tract infections.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is difficult to diagnose because symptoms may come and go.
A blurred clinical picture may be observed, making it difficult to detect bacteria causing inflammation.
Chronic prostatitis can develop into follicular and parenchymal.
Clinical manifestation of prostatitis in the chronic stage:
- Recurrent infectious processes of the urinary system.
- Sharp and strong desire for deurination.
- Urination is accompanied by pain and a feeling of pain in the urethra.
- Burning, itching in the urinary tract.
- Hematuria (appearance of drops of blood in urine).
- Nagging pain in the anogenital area, radiating to the lower back.
- Painful ejaculation.
- Flu symptoms such as chills and fever.
- Weak urine flow, inability to redirect the stream.
Another dangerous complication is the development of urethral stricture.
The process is accompanied by narrowing of the urethral canal and obstruction of the passage of urine.
Terminal hematuria, hemospermia, deferentitis, cooperitis may be observed.
Prolonged lack of treatment can provoke Reiter's syndrome and concomitant circinar balanoposthitis.
What you need to know about chlamydia
This disease is transmitted mainly through sexual contact, during unprotected intercourse. At this time, bacteria actively multiply on the mucous membrane and transfer to a new “host” without any problems.
Most often, chlamydia appears together with other microorganisms, for example, gonococci, trichomonas and various fungi.
If infection with several infections is detected at once, the symptoms become several times brighter. The period during which the infection can manifest itself ranges from seven to thirty days.
In the case when the disease is diagnosed at the wrong time, it begins to take on a chronic form, which in turn is divided into two subtypes: acute and subacute forms.
How to prevent infection with chlamydia and other harmful bacteria
To protect yourself from negative consequences and unpleasant symptoms, you should approach sexual intercourse responsibly and always use protective equipment.
Contraceptives significantly reduce the risk of infection with such bacteria! It is also recommended to be examined by a doctor at least once a year.
Women need to constantly maintain hygiene. Remember that it is important to detect the infection in time. This is the only way to effectively get rid of bacteria and prevent the development of pathology.