A feeling of fullness in the bladder after visiting the toilet occurs when urine is not completely removed from the body. This symptom is characteristic of many diseases. It has a true or false character. The first option is characterized by the impossibility of emptying the bladder, the second by the appearance of unpleasant sensations not associated with the presence of liquid in it.
A feeling of fullness in the bladder after visiting the toilet occurs when urine is not completely removed from the body.
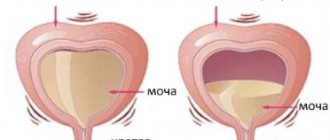
Normal process of deurination
Normally, many different processes occur in the genitourinary system, which complement each other and form the correct flow of urine. When the bladder is full, a signal is sent to the central nervous system that it needs to be emptied. Further, during urination, the brain sends a signal to relax the sphincter and contract the muscles, while urine exits through the ureter and the bladder is emptied.
Causes of pathology
The feeling of an incompletely emptied bladder in women and men can occur for many reasons. The most common of them are the following:
- chronic and acute forms of cystitis;
- stones and any formations in the organ;
- phimosis in males, as well as prostate adenoma;
- benign and malignant formations in the bladder, cancer metastases;
- inflammatory processes in any organs of the pelvic area, in which the bladder reflexes are excited;
- abnormally small bladder size;
- hyperactivity of the excretory system;
- damage to the innervation of the urinary system due to tumor or injury;
- infections introduced into the body that damage the kidneys;
- myelitis and other injuries of the spinal cord and brain, other pathologies of the nervous system;
- intoxication with drugs in case of their long-term use or excess dosage;
- for women – the state of pregnancy or the postpartum period;
- infection with herpes viruses;
- emerging urethral stricture;
- in elderly people - due to a natural decrease in the muscular functionality of the organ.
It should be noted that such symptoms can occur due to the consumption of alcoholic beverages, prolonged exposure to low temperatures in a damp room, as well as disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and digestion. In women, the feeling of incomplete emptying occurs most often during inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system.
More on the topic: How to rinse the bladder with Furacilin solution?
Treatment
Medicines
To eliminate urinary problems use:
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpu). Relieves sphincter spasm, relieving pain and restoring urination.
- Antibiotics (Monural, Nolitsin). Prescribed for cystitis and other inflammatory processes in the urinary system.
- Uroseptics (Canephron, Cyston). When used regularly, herbal medicines dissolve and remove stones.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin). Quickly eliminate swelling of the mucous membranes of the bladder and urethra, normalizing the outflow of urine.
Physiotherapy
In case of urination problems, the following procedures are prescribed:
- Electrophoresis of anticholinergics (Eufillin, Atropine). The effect of electric currents ensures the delivery of the drug to the affected areas.
- Ultrasound therapy. Restores innervation of muscle tissue, destroys pathogenic microorganisms. To get rid of the feeling of fullness of the bladder, 10-12 sessions are required.
- Paraffin applications. Warm up the muscles, promoting their relaxation. Paraffin heated to 45°C is applied to the lower abdomen. The procedures last 45 minutes and are performed every day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
For problems with urination, use a decoction of celandine.
ethnoscience
For problems with urination, the following folk recipes are used:
- Infusion of horsetail, cinquefoil and plantain. Herbs are mixed in a ratio of 3:3:4, 1 tbsp. l. collection, pour 1 liter of boiling water and leave for 2 hours. Drink 100 ml of infusion 3 times a day. Treatment is continued until urination is restored.
- Lingonberry leaves. 1 tbsp. l. The herbs are brewed in 200 ml of hot water and left for 40 minutes. The infusion is taken 2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day after meals.
- Celandine. For diseases of the prostate gland 1 tbsp. l. dry grass pour 0.5 liters of water. Drink the drug 1 tbsp. l. 3 times a day. The course of treatment is a month.
Diet
If urination is impaired, flour and confectionery products, canned food, strong tea and coffee, salty and spicy foods, sorrel, and spinach are excluded from the diet. Lean meats, milk jelly, fresh and boiled vegetables, neutral-tasting fruits, and berry fruit drinks are allowed. Food is steamed, boiled or baked. Fried foods are completely avoided.
Development of the disease
In most cases, the development of the disease with characteristic symptoms of incomplete emptying is associated with residual urine in the organ. Typically, this occurs when there are stones in the urethral canal or a fusion of the urethra that prevents the normal movement of urine out of the body.
Pathogenetic factors also include hypotension or atony of the bladder, in which its walls cannot contract properly. One way or another, this is due to disruptions in the innervation of organs. There may be cases when the impossibility of completely emptying and getting rid of urine is caused by psychological problems of a person.
Infections of various etiologies introduced into the body can cause excessive stretching of the walls of the organ, and the frame is also susceptible to increase in case of fluid retention inside. In this case, the patient feels fullness in the pubic area and acute pain. With such problems, the bladder cannot contract normally.
The reasons include organ hyperactivity, as a condition opposite to atony. At the same time, the muscles of the bladder are in constant tone, which determines the person’s desire to urinate frequently. Since there is little liquid in the reservoir, it comes out in insufficient quantities and is accompanied by a feeling of incomplete emptying.
In pregnant women, the functioning of the organ is impaired due to the growth of the fetus, which puts pressure on all neighboring organs and systems. Also, in the body of the expectant mother, the genitourinary system does not have time to adapt to new conditions, due to which the bladder is constantly activated. In older people, problems with bladder tone occur after 60 years of age.
Folk recipes
To alleviate the general condition, traditional medicines are often used. Very often herbal infusions, teas and tinctures come to the rescue. Thus, to eliminate the symptoms of cystitis, decoctions containing horsetail, plantain and cinquefoil are suitable.
Herbal products such as bearberry, licorice, wheatgrass root, and corn silk have an active diuretic effect. It is customary to brew them and consume several glasses per day. However, diuretics should not be abused and the course should not be delayed for more than two weeks.
Because this creates a risk of leaching of nutrients from the body. Lingonberry leaves help with inflammation. They are brewed like tea and drunk throughout the day. This plant has an antiseptic effect and helps with incompletely emptied urine.
For male diseases, products based on celandine, garlic, lemon, and parsley are more useful. You can also make decoctions or mixtures from them, infuse them and use them morning and evening. Chestnut peel is useful in eliminating problems with urination; it is steamed in a water bath or in a thermal container.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of a full bladder are the frequent urge to deurinate, which occurs immediately after completion of the act of urination. The process itself is very painful, accompanied by discomfort and burning, as well as heaviness in the area above the pubis.
More on the topic: How is bladder cystalgia treated?
This occurs due to the stretching of the walls of the organs by a significant volume of fluid inside it. The psychological component is equally important, since the patient worries that he cannot leave the toilet and do normal activities. Fatigue, aggressiveness and irritability accumulate and only make the situation worse.
Men have special signs of pathology, which include potency, periodic involuntary leakage of urine, and an intermittent stream during urination. If the patient experiences general weight loss and lack of appetite, this indicates malignant formations in the prostate gland.
Cramping pain occurs with urolithiasis, especially if one of the stones or its fragments moves along the urinary tract. Sediment appears in the urine, bleeding and hematuria are possible.
Pain in the lower back, altered urine composition, and elevated body temperature are symptoms of developing pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. With a frequent desire to empty the bladder, accompanied by burning and pain when urinating, there is a suspicion of the development of urethritis and cystitis.
Diagnostic features
If the patient continues to feel the sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder, it is very important to correctly diagnose the disease that caused it and begin appropriate treatment. To do this, the doctor initially interviews the patient and examines him.
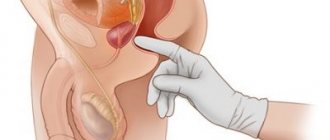
By palpating the anterior abdominal wall, a specialist can determine an enlarged bladder. This is observed if a large amount of residual urine remains in it. You can also suspect this reason for the persistence of discomfort even after urination by the appearance of pain and a feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen.
Attention! Stagnation of urine is fraught with the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in it and their penetration through the ureters into the kidneys. Therefore, diseases of the lower urinary tract are often complicated by ascending pyelonephritis.
Clinical picture assessment
An important stage in diagnosing the cause of the sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder is the assessment of the symptoms from which the patient still suffers. Thus, inflammatory diseases of the urinary system, in particular urethritis, pyelonephritis, and cystitis, are characterized by:
- pain in the suprapubic region;
- burning and stinging when urinating;
- temperature increase;
- pain in the lower back, and more often they are observed only on one side of the body;
- change in the transparency, color and smell of urine, etc.
Features of the structure of the urinary organs in men
If such pathologies are more common among the fairer sex, then prostate diseases, which are also accompanied by stagnation of urine, are the scourge exclusively of men. They show themselves:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- weak pressure or even interruption of the urine stream when urinating;
- problems with potency;
- weight loss, which is more typical for the formation of malignant tumors in the tissues of the gland;
- slight increase in temperature;
- the presence of blood in the urine, etc.
Urolithiasis also often causes discomfort after and during urination.
But since it is almost impossible to confuse attacks of renal colic with anything, usually there are no problems with diagnosing the reason for the persistence of the desire to urinate. The greatest difficulties await doctors in the presence of an overactive bladder, since to a large extent this diagnosis is made by excluding other pathologies. This disease is characterized by frequent (more than 8 times a day) urination, and the urge usually occurs quite suddenly and is immediately so strong that patients do not always manage to get to the restroom on time.
Attention! Having episodes of urinary incontinence is an important diagnostic sign, so don't be shy about talking about them.
Laboratory and instrumental methods
To confirm or refute his assumptions, the doctor prescribes:
- bacteriological examination of urine;
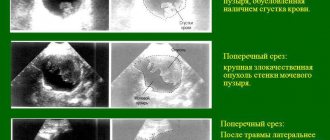
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and pelvic organs;
- radiography, including contrast urography;
- cystoscopy.
Ultrasound is a highly informative method for diagnosing most diseases of the genitourinary system.
Important: in particularly difficult cases, the patient is recommended to undergo an MRI or CT scan in order to finally establish the reason for the persistence of the urge after urination.
Thus, the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder can accompany quite serious diseases. Therefore, if it occurs, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Neurogenic bladder is a dysfunction of urination caused by damage to the nervous system. Neurogenic bladder dysfunction cannot be considered as an independent disease. This is a collective syndrome that combines conditions that arise in connection with congenital or acquired lesions at various levels of the nerve pathways and centers that innervate the bladder and provide the function of voluntary urination.
Causes of neurogenic bladder:
· Inflammatory-degenerative diseases and tumors of the brain and spinal cord (encephalitis; diabetic, alcoholic and post-vaccination neuropathies, cholesteatoma, tuberculoma, multiple sclerosis, etc.).
· Traumatic injuries to the brain and spinal cord (stroke, ruptures, compression, destruction, surgical interventions on the pelvic organs).
· Congenital defects of the terminal spine, spinal cord, and nervous system of the bladder.
Clinic
Disturbances with a neurogenic bladder occur either in the form of pathological urinary retention or in the form of incontinence. True urinary incontinence is accompanied by a lack of sensation of bladder filling. The patient cannot hold urine; it does not accumulate in the bladder and is continuously released drop by drop as it enters it.
With paradoxical urinary incontinence (sluggish bladder), reflex emptying of the bladder is impaired. The detrusor does not contract and the internal sphincter is closed. The bladder fills, but the reflex does not work. When the bladder is full, urine flows out in small portions due to mechanical stretching of the internal sphincter. In this case, a large amount of urine remains in the bladder (residual urine).
In the absence of cortical regulation of urination (in case of damage to the spinal cord above the centers of segmental innervation of the bladder), the bladder is emptied reflexively - automaticity of the bladder is formed: as it stretches with accumulated urine, corresponding irritations of stretch (pressure) receptors occur and reflex emptying occurs. Urine is released involuntarily. The feeling of bladder filling and the urge to urinate are most often absent. In this case, there is periodic urinary incontinence with constant residual urine in the bladder (spastic bladder).
Another disturbance in the sensitivity of the bladder may be a lack of feeling of fullness and the urge to urinate. With this disorder, a person does not feel his bladder and has to constantly remember the need to urinate. This disorder, especially in combination with sphincter spasm, can lead to pathological expansion of the bladder, reflux of urine into the ureters and kidneys with the development of inflammation in them.
Along with the inability to control urination, pathological sensations in the bladder may occur, such as a feeling of excessive fullness with the so-called false urge to urinate. False urges can occur very often, depriving a person of the opportunity to work and communicate normally.
Due to the fact that denervation of the bladder leads to pronounced trophic disorders, the course of the disease is often complicated by interstitial cystitis, which causes sclerosis and shrinkage of the bladder. This severe complication increases the risk to the kidneys and in some cases requires special surgical interventions to increase bladder capacity.
Diagnostics
In addition to examination, great importance is attached to laboratory and instrumental studies in the diagnosis of a neurogenic bladder. Laboratory diagnostics includes a general urine test, a Zimnitsky test, a general blood test, and a biochemical blood test. Radiological studies include survey radiography, urethrocystography (regular and voiding), excretory urography, and ascending pyelography. Significant methods of instrumental diagnostics are ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder, radioisotope renography, cystoscopy, urodynamic study and video-urodynamic study (uroflowmetry, cystometry, sphincterometry).
Treatment
Treatment of neurogenic bladder directly depends on the cause of nerve damage and requires, first of all, treatment of the primary disease. There are three main areas of treatment: medication, electrical stimulation and surgery.
The main type of treatment is the use of pharmacological agents. If urinary retention occurs, adequate drainage of the bladder using an indwelling catheter is also necessary; prevention of urinary tract infection or treatment of urological infection if it develops with antiseptics and/or antibiotics. In patients with urinary incontinence, measures are taken to resume reflex emptying of the bladder. For this purpose, regular clamping of the permanent catheter every 2-3 hours and other methods are used.
You can undergo diagnosis and treatment of the disease in the neurology department of the Spinal Cord Pathology Center of our clinic.
Incomplete emptying of the bladder is often perceived as a subjective sensation. But this may be one of the symptoms of diseases of the urinary system.
There are two options for developing this process. In the first case, it is truly a subjective sensation and the bladder is empty. In the second, the so-called true incomplete emptying of the bladder is observed. This is due to the fact that the exit of urine from the urinary canal is difficult. In men, the second variant of pathology is most common.
Establishing diagnosis
In order to make a diagnosis of incomplete bladder emptying, several stages must be followed. The attending physician finds out the patient's medical history, asks him about the symptoms experienced and the condition before them. The presence of chronic diseases and previous surgical interventions is also important.
The woman needs to be told about her menstrual cycle and her last birth. The specialist palpates the area of the bladder and when it is full, it is felt under the fingers. You can also visually observe its bulging.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor assumes that the bladder is full and prescribes additional examination. Laboratory tests are required for blood and urine, and blood is also tested for biochemistry and bacteriological culture.
Urine is examined for microflora balance. Additionally, a urographic examination, cystoscopy, and pelvic ultrasound are required. If all these methods are ineffective, isotope techniques and MRI and CT scanning will be required.
Prevention
Urologists advise:
- urinate regularly at the first urge;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- minimize alcohol intake;
- stop smoking;
- avoid severe stress and depression;
- avoid chronic lack of sleep.
Strong physical activity on all muscle groups is beneficial. Exercises that strengthen the abdominal and pelvic muscles are especially effective. Just 10-15 minutes of training a day, and the bladder will be reliably protected from incomplete emptying and urinary incontinence.