A healthy bladder does not cause any unpleasant symptoms in humans. But if there is a feeling of a full bladder, this is a sign of serious pathologies of the urinary system. Such sensations interfere with the normal flow of a person’s life, because they can be accompanied by more unpleasant manifestations, such as incontinence or acute pain. Therefore, it is important to know what the feeling of a full bladder indicates.
The feeling of bladder discomfort, such as false filling, should not be left without due attention.
The process of urination
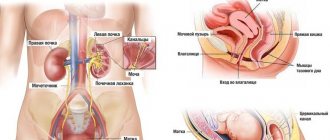
The human bladder is capable of holding 300 ml of urine for 5 hours. The walls of the organ are covered with receptors, from which signals are sent to the center, which is responsible for urination. It is located in the sacral region of the spinal cord. This area controls bladder activity through stimulation through parasympathetic nerve fibers. Under the influence of signals from the nerves, the walls gradually tense up, and the sphincters of the organ, on the contrary, relax, this is how the bladder is emptied, that is, at this moment urine comes out of the bladder.
How to get rid of an unpleasant symptom
To minimize discomfort during and after urination, you can use the following techniques:
- You need to take a comfortable position on the toilet and try to completely relax, especially for the pelvic floor muscles. Sit in this state for about 5 minutes. This exercise will help you remove as much urine as possible.
- To force the bladder to contract better and remove urine more actively, you need to press slightly above the pubis with your hand while urinating.
- You can open the water tap. The murmuring sound reflexively relaxes the muscles and stimulates emptying.
- You can also urinate in a bucket of hot water that produces steam. But you need to be careful not to burn the mucous membrane of the genital organs.
In addition, doctors recommend drinking diuretics, and traditional medicine uses various herbs that promote urine excretion. You can make various tinctures, decoctions, etc. from medicinal plants. But such treatment usually lasts a long time, and it is advisable to combine it with traditional methods.
Reasons why you feel like your bladder is full
As noted above, the bladder can normally hold 300 ml of urine. If such an amount accumulates in it, a person has a feeling of a full bladder, as the pressure on the walls increases. At the same time, you will really want to relieve yourself. But there are a number of factors that interfere with the normal excretion of urine, and, accordingly, cause discomfort in the bladder:
- diseases associated with inflammatory processes in the tissues of the urinary system: cystitis, urethritis;
- diseases associated with inflammatory processes of neighboring organs that spread to the bladder (there may not be urine in it, but it feels like this is not the case): pyelonephritis, enterocolitis, pelvioperitonitis, inflammation of the appendix;
- prostatitis and prostate adenoma (in this condition it puts pressure on the urethra);
- diseases of the genitourinary system in women: adnexitis, fibroids, endometritis, ovarian tumors;
- urolithiasis, due to which the walls of the bladder are affected - the presence of stones does not allow it to completely empty;
- neoplasms of any nature;
- problems with the spinal cord: multiple sclerosis, radiculitis, spina bifida;
- congenital impaired conduction of the nerves of the bladder, causing increased urinary function;
- excessive reduction in the lumen of the urethra;
- decreased contractile function of the walls and muscles of the bladder, which makes it impossible to fully contract it during urination;
- problems with stool, constipation, during which an overcrowded intestine puts unnecessary pressure on the bladder.
What is the name of the condition in which urine output is less than normal?
The norm for an adult is 6-7 small visits to the toilet per day with urine output of up to 1.5 liters.
At the first stage, a decrease in the amount of urine excreted does not cause any inconvenience. They think about visiting a urologist when it hurts to go to the toilet, urine comes out only if you take a certain position, the stream is “sluggish” or the liquid is already released in drops.
If not, then they begin to guess about the disease by a deterioration in general health, which can be expressed in periodic nausea not related to the process of eating, weakness and dizziness.
Infrequent urination may be associated with problems such as:
- inflammatory diseases;
- disruption of the excretory system;
- failure in the endocrine system;
- neurological pathology.
If a urological problem is not identified, then with the complaint: “I don’t go to the toilet a lot,” the doctor will refer you to the necessary specialists: a neurologist, an endocrinologist, or, in some cases, a cardiologist.
The general name for a condition in which urination is infrequent is called oliguria in medicine.
Before you start worrying about a sharp increase in the number of urges, during which a small amount of urine is released, you need to understand what exactly the urination process should be like in a healthy person.
Our kidneys work without interruption. Every second, millions of nephrons process blood plasma, releasing primary urine from it, and then secondary urine, which is sent through the ureters to the bladder. The body excretes about one and a half liters of urine per day. This volume is usually expelled with 5-9 urges to urinate. This is exactly what a healthy person experiences throughout the day.
The role of the kidneys in the body
Naturally, these indicators are relevant for normal drinking conditions, as well as standard climatic conditions.
A person feels the urge to urinate when the bladder is about a quarter full. The greater the volume of urine entering the organ, the more its walls stretch. The tissue contains a large number of nerve receptors. When stretched, they are irritated, sending a corresponding signal to the urination center located in the spinal cord. Strong stretching provokes strong irritation, therefore, the more urine in the bladder, the stronger the urge.
Sometimes the urge may be false; when visiting the toilet, very little or no urine is released
But this is all normal. Sometimes the urge may be false, that is, when visiting the toilet, very little urine is released, or there is none at all. This situation should be considered more carefully, since it is obvious that during a normal physiological process it should not exist. This is especially true if you want to go to the restroom about 15 times a day.
Feelings of incomplete emptying of the bladder and associated symptoms
Attention to uncomfortable symptoms when urinating is the key to timely treatment of emerging diseases.
The feeling of a full bladder after urinating is complemented by other unpleasant sensations:
- constant pain that intensifies when palpating the abdomen, active movements, or lifting something heavy;
- attacks of acute pain in the lumbar region, characteristic of urolithiasis;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the lower abdomen;
- pain during the emission of urine;
- elevated temperature, fever;
- changed composition of urine;
- involuntary frequent urination or trouble urinating;
- the appearance of blood in urine.
Diseases of the urinary system
Pathology of any part of the urinary system is always accompanied by frequent urges. In this case, the following symptoms arise:
- urethritis - burning sensation when urinating, feeling of bladder fullness;
- cystitis - painful, frequent passage of small amounts of urine, pain in the lower abdomen;
- pyelonephritis - nagging pain in the lower back, temperature and intoxication (weakness, pale skin, etc.);
- urolithiasis - the movement of even the smallest stones (sand) causes pain in the back and lower abdomen, burning (when sand passes through the urethra), and blood is often detected in the urine;
- urinary incontinence - caused by weak muscle tone of the urethral sphincter, often observed in old age;
- Bladder overactivity - congenital or acquired muscle hypertonicity provokes a frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- Prolapse of the bladder - often diagnosed in older women; frequent urges result in the passage of a small amount of urine.
Possible complications due to incomplete emptying
When the bladder is not completely emptied, stagnation of urine forms in its cavity. Very often this residue provokes a constant pressing sensation and the feeling that the bladder is full. In addition, the development of bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms that affect the bladder and urethra begins in stagnant urine. This means that cystitis occurs as a result. If the inflammation rises along the urinary tract and reaches the kidneys, the person will also develop pyelonephritis. No matter what sensations a person has, it is important to seek medical help in a timely manner, otherwise there is a chance of starting an already progressive disease.
What are the characteristic signs to use to diagnose the disease?
Since a large number of diseases can provoke a feeling as if the organ is full, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis before prescribing treatment. When making a diagnosis, not only the patient’s symptoms are taken into account, but also diseases of any nature that he had previously suffered from, gender and age. According to statistics, women are more often susceptible to diseases of the genitourinary system.
Inflammation of the urinary system
With the development of the inflammatory process in the organs of the genitourinary system, the most common diseases are cystitis and urethritis. If you do not pay attention to the felt filling of the bladder and other manifestations, the disease will develop into pyelonephritis. Most often it is women who get sick due to physiological characteristics. Characteristic manifestations of the inflammatory process: In men, sensations of incomplete emptying may occur due to problems with the prostate
outward and there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The main signs indicating prostatitis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- a weak, intermittent stream when a man relieves himself;
- involuntary leakage of a certain amount of urine.
Also, swelling and similar symptoms are characteristic of the development of impotence. If the patient has prostate adenoma, in addition to the previously listed signs, weight loss and prolonged elevated temperature will be added. In addition to prostate tumors, neoplasms can also occur in other organs of the genitourinary system. The appearance of blood in urine is a signal of the onset of bladder cancer.
Any person experiences the feeling of a full bladder several times a day. To get rid of it, a healthy person just needs to go to the toilet.
However, urination does not always lead to the desired result - a feeling of fullness may remain. Such a violation is a signal of a problem in the urinary system or, less commonly, a sign of a malfunction of other systems.
The structure of the bladder is a reservoir where urine accumulates, with locking sphincters. There are two sphincters, one of which a person controls consciously. They are located at the junction of the bladder and the urinary canal - the urethra.
When the bladder is full, its walls stretch, an urge arises, but one of the sphincters holds back urine as long as the person wants it. When urinating, it relaxes the sphincter, urine comes out through the urethra. Normally, up to 20 ml of urine can remain in the cavity.
After urination, some of the fluid may be retained, causing a true feeling of fullness. Urine is either not excreted at all, then up to one liter of liquid can accumulate in a full bladder, or not all of it is evacuated. Pathology is considered to be an accumulation of more than 50 ml of fluid. Urine cannot be removed for two reasons:
- there is a mechanical barrier to its outflow;
- the muscles involved in the process of urination are weakened.
Features of different types of pathology
A true sensation of bladder distension is more common in men.
Tumors, stones, and anatomical abnormalities of the urinary tract can act as mechanical obstacles.
A false feeling of fullness is said to exist if there is no urine in the bladder, but the urge remains. This condition occurs due to signals generated in:
- brain or spinal cord;
- the organ itself;
- surrounding tissues.
Most often, a false sensation of incomplete emptying is recorded in women with bladder dysfunction.
In recent years, doctors have noted an increase in the number of patients with this pathology, which occurs without changes in the qualitative composition of urine. This proves that neuroendocrine pathologies and mental changes more often become a source of dysuria.
In pregnant women, the growing fetus puts pressure on the bladder, causing an unpleasant feeling that it is full, even with little urine.
Drinking diuretic drinks, such as those containing alcohol, caffeine or aspartame, causes a false urge.
Any feeling of fullness, if it occurs constantly, requires contacting a urologist.
Painful manifestations
When a person constantly wants to go to the toilet in a small way, he tries to understand whether this is normal, and if not, then what disease does it indicate and what the threat is. Some factors will help you understand the severity of the symptoms:
- Frequency of urination - the situation is abnormal if you want to urinate more than eight times a day and wake up more than once at night to run to the toilet.
- Difficulty passing urine - the stream is weak and intermittent, it feels like the bladder is about to burst, but in fact very little urine comes out.
- Inability to hold back urine - with some diseases, you suddenly want to go to the toilet in a small way, and you cannot stand it for a minute, rushing headlong to find the restroom.
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder is the main reason that not even ten minutes have passed since you left the toilet, and you already need to urinate again.
- Pain, burning, feeling.
- Detection of traces of blood in the urine.
If in a young person this condition continues for a long time and is not provoked by the consumption of large amounts of liquid, diuretic products or medications, the reason clearly lies in health problems. First of all, these are inflammatory processes of the kidneys and urinary tract of various natures, inflammation, adenoma or malignant neoplasm of the prostate.
The need to frequently visit the toilet not only interferes with normal life, making full-fledged work and rest impossible. This may indicate a serious illness, which means you should not put the matter off, but urgently consult a doctor, find out the causes of this condition and make every effort to restore health.
Let's take a closer look at those cases when you often want to write due to diseases of the genitourinary system.
Causes of feeling a full bladder
The sensation of a full bladder after urinating may occur periodically or be constant. It occurs due to pathology or the influence of physiological factors.
Bladder overflow can be caused by:
- drinking plenty of fluids (more than 2.2 liters per day),
- taking substances that stimulate the urinary system.
In these cases, discomfort does not indicate illness; it can be eliminated by reducing the amount of fluid consumed or replacing medications.
A separate group of causes of the feeling of fullness of the bladder includes neuroendocrine, iatrogenic (spinal cord injuries due to operations, manipulations) factors and mental disorders.
A constant feeling of a full bladder is possible with diseases of neighboring organs - the small intestine, appendix, ovaries.
Main Factors
Why doesn't my bladder empty completely? Urine retention occurs if its outflow is obstructed. Possible reasons for this:
- Mechanical compression of the urinary canal:
- full intestines with constipation;
- enlarged uterus;
- tumors, neoplasms;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- enlarged prostate gland.
- Urethral obstruction due to:
- blockage with stones, blood clot, pus, foreign bodies;
- urethral strictures;
- neoplasms.
- Detrusor weakness.
Features in men and women
In a man, the feeling of a full bladder most often occurs when the urinary tract is obstructed due to prostate pathologies (adenoma, prostatitis). Hyperplasia of the central lobe of the prostate leads to compression of the urethra. It becomes difficult to pass urine through the narrowed channel. For this reason, the bladder begins to fill with remaining urine.
A common cause of urinary stagnation is urethral pathology. A narrowing of the urethra (stricture) is more often observed in men due to its large length. Stricture is caused by injuries to the urethra (most often), infectious diseases (gonorrhea), and chemical burns during self-medication.
In women, the feeling of fullness often turns out to be false, its sources:
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- bladder stones;
- fibroids, endometriosis.
The cause is irritating signals coming from the bladder or other organs, most often when they are inflamed. Painful impulses in women provoke contraction of the bladder, intravesical pressure increases, which causes a feeling of fullness. Similar inflammations can occur in men, but in women they are recorded more often. The female urethra is wider and shorter, which facilitates rapid upward penetration of microorganisms. Sexual intercourse causes the transfer of bacteria from the vulva to neighboring organs.
The urinary and genital organs of women have a close anatomical location, common blood supply and innervation. This creates the prerequisites for the mutual involvement of the urogenital organs in pathological processes.
Stones can also block the urinary tract, causing fluid to accumulate. The calculus can close the entrance to the urethra only at the moment of urination, then the process suddenly stops. When changing body position, urine output is restored. In addition, stones injure the mucous membrane of the bladder, causing pain impulses.
Bladder dysfunction with endometriosis or fibroids is caused by two factors: tissue compression and hormonal imbalance affecting the organ's receptor apparatus. In women, a feeling of a full bladder without pain occurs when:
- menses,
- pregnancy.
What to do?
There is hardly a person who would argue with the fact that a condition that interferes with life needs to be corrected somehow. Moreover, in the literature or on the Internet, you will find a lot of detailed information about the risks of the health disorders listed above.
And the need to frequently visit the toilet is far from the worst thing that can happen. And if you think that all this is only in books and smart articles, and will never happen to you, you are deeply mistaken: such a result is inevitable, the only question is how quickly complications will develop.
And there is only one way to solve the problem - do not turn a blind eye to your condition, do not justify inaction by lack of time, a good specialist and similar, excuse me, nonsense, do not try to cope with the disease with all sorts of drugs and other useless means, but immediately go to the doctor and do everything recommendations.
Do you often need to go to the toilet a little? What's wrong with that? You may have drunk more fluids than usual. Or the frequent need to urinate is caused by external factors (stress, excitement, cold). In general, what is the normal urination rate for an adult? Let's try to figure it out.
What is normal urinary frequency?
During the day, each healthy person excretes, on average, 1.5-2.0 liters of urine. This usually amounts to about 75 percent of the liquid taken per day. The remaining fluid is excreted in sweat and feces. Typically, the normal frequency of urination varies from 4 to 10 times a day.
Naturally, frequent urination may occur more frequently if you drink frequently or take in more fluids. If frequent urination does not depend on fluid intake, then this fact may indicate the presence of some disease in the body.
Why might you constantly want to go to the toilet for a little while?
The list of diseases of the genitourinary system with similar symptoms is quite extensive. Frequent urination in men can be caused by diseases such as:
Frequent urination in women
Women may experience increased urination during pregnancy. This happens because the uterus and fetus, as they develop, begin to put pressure on the bladder, creating a feeling of fullness. At this time, it is important not to reduce fluid intake to prevent dehydration, otherwise serious problems with the urinary system may occur.
Also, frequent trips to the small can be due to the woman’s age. With the onset of menopause, the body reduces estrogen production, which leads to some changes in the functioning of the genitourinary system. In this case, there is a frequent urge to go to the toilet, especially at night.
Reader Questions
18 October 2013, 17:25 During defecation, urination is not possible, why and is this normal? Immediately after defecation, urination is excellent, but during defecation it is not. I assume the following, immediately before defecation and during this process, feces accumulate at the exit from the rectum, the rectum enlarges and this puts pressure on either the prostate or the urinary tract and generally blocks it, but these are my assumptions. Thank you in advance!
Ask a Question
The cause of problems with urination may be disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, which is especially typical for older women.
Frequent urination in women is a symptom of diseases such as:
Acute cystitis, acute urethritis, pyelonephritis;
Urinary tract infections and sexually transmitted diseases;
Diseases of the urinary system: the presence of stones in the kidneys and urinary tract, chronic renal failure;
Diseases of the reproductive system: uterine fibroids, uterine prolapse, endometriosis.
Hormonal imbalance is one of the most common causes of increased frequency of urination. The fact is that some hormones affect the ability of the bladder to stretch. A woman's hormone levels can change during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause.
As you can see, the range of diseases and conditions that make you run to the toilet is quite wide. In any case, it is important not to hold back your urine. The bladder should be emptied when there is an urge to do so. To avoid nighttime urination, try to drink less before bed.
If the urge to go to the toilet has become more frequent than your average norm, you should not delay your visit to the urologist.
Take care of yourself and be healthy!
Dmitry Belov
For a healthy person, the normal frequency of urination is one to eight times a day. If you feel the need to do this more often, or wake up in the middle of the night to relieve yourself, you need to think about problems with urination.
An exception can be made for elderly people. For them this is considered the norm.
This article describes the causes of frequent urination, as well as the treatment and prevention of various diseases associated with it.
If you constantly want to write, the reasons for this feeling are quite extensive. Often these sensations indicate the onset of a disease. Moreover, such symptoms can appear in men and women. They can suffer from the same or completely different diseases.
You can get rid of this unpleasant condition. To do this, you need to determine the reasons for its occurrence. Only a doctor can do this. He will prescribe special studies that will allow you to choose the right treatment. You can, of course, try to treat yourself, but you don’t know what this will lead to.
Let's list the main reasons why you constantly want to write:
- taking diuretics;
- eating foods that contain substances that promote urination. Such products include some fruits, vegetables and berries;
- infection of the urinary organs;
- development of diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal disorders;
- which is associated with damage to the nervous system;
- inflammation of the prostate gland (occurs only in men);
- inflammation of the reproductive organs in women;
- benign or malignant neoplasms in the bladder can act as irritants on its walls;
- urolithiasis disease. also act irritatingly on its walls;
- overactive bladder syndrome (often abbreviated).
All inflammatory diseases are caused by opportunistic microflora of the reproductive system or pathogenic microorganisms. Under the influence of certain factors, their number increases, which causes health problems.
Smoking and other bad habits are common causes of bladder inflammation.
Factors leading to the development of the inflammatory process are:
- bad habits;
- hypothermia;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- decreased immunity;
- chronic diseases.
In men
The phenomenon that a man constantly wants to write is quite common.
The feeling that you constantly want to write may arise for the following reasons:
- the presence of infections (you want to pee often, even after the bladder has completely emptied);
- diabetes;
- chronic renal failure;
- urolithiasis disease.
Only a qualified specialist can diagnose such diseases. Since the symptoms of all diseases are similar, a full medical examination is required to determine the exact cause. It is necessary to take blood and urine tests.
As men age, they visit the toilet more often for minor needs. They have night urges. The male body begins to work differently in old age. It processes fluid in its sleep. However, if a man wants to pee more than twice during the night, he should think about it and pay close attention to this problem.
Among women
Women are just as susceptible to urinary problems as men. If there is a feeling that you constantly want to pee, in women without pain or with it, the cause is often all kinds of infectious diseases of the reproductive system.
In urology, there are a number of reasons why women constantly want to write:
- bladder prolapse;
- reactive arthritis;
- presence or ;
- neoplasms in the urinary tract or bladder.
You should immediately consult a doctor if problems with frequent visits to the toilet worsen during menstruation.
During pregnancy
The female body has several features that are directly related to the possibility of having children.
During pregnancy, changes occur that affect all internal organs, including the urinary system.
If you constantly want to pee during pregnancy, this is considered a normal condition for a pregnant woman.
Although if they are accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms, this may indicate some violations. After childbirth, all processes return to normal and urination is restored.
Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder and associated symptoms
Regardless of the etiology, an overfilled bladder itself becomes the cause of the development of diseases and the appearance of some associated symptoms.
- With prolonged overfilling of the bladder, the muscle wall stretches, atony of the organ muscles and stretching of the sphincters develops. Weakness of the sphincters that hold urine allows it to come out in separate drops or leak.
- Accumulated urine is a good environment for the rapid development of microorganisms. Therefore, constant stagnation of urine and a feeling of fullness of the bladder are often accompanied by a complication in the form of infectious inflammation.
- One of the signs of acute inflammation is pain. Therefore, the feeling of incomplete emptying in women is often accompanied by pain during urination.
- Trying to get rid of the feeling of a full bladder, men and women often go to the toilet and strain hard and for a long time when urinating. This increased work of the detrusor leads to hypertrophy, which deforms the ureter and interferes with the movement of urine from the kidneys. Stagnation of urine in the upper urinary tract triggers pathological mechanisms in the kidneys.
- Concentrated urine in the bladder and kidneys is a good environment for the formation of stones.
Related pathological conditions
Some symptoms are not associated with bladder fullness, but accompany this feeling in women and men:
- Pain syndrome outside of urination. The intensity and localization are determined by the organ in which the pathological focus is located. Severe pain is typical for acute conditions, mild pain is typical for indolent inflammation and slow onset of urine passage.
- Disorders of the urination process. They may be a manifestation of irritation:
- frequent and painful urination;
- imperative urges;
- increased urge at night;
or obstruction:
- difficulty urinating;
- thinned stream;
- increased duration of urination.
- Sudden irresistible urges that do not end with urine output.
- Urinary incontinence. Dripping urine without urge occurs due to weakness of the sphincters and pelvic floor muscles. A sharp contraction of the sphincter and detrusor leads to an acute urge, accompanied by rapid uncontrolled release of urine - the person does not have time to get to the toilet. This type of involuntary urination is observed with cystitis, neoplasms, and urolithiasis.
Practice shows that up to 70% of women over 40 years of age lose control of urinary continence and only 3-20% express a desire for treatment.
- Body temperature rises to subfebrile levels, higher only with inflammation of the kidneys.
- Bladder swelling occurs gradually, which is why painful sensations are not always present.
- Blood and discharge in the urine. Fresh blood in the urine appears with tumors of the urethra and bladder, stones or hemorrhagic cystitis. White flakes in the urine are clots of mucus that appear when the organs of the urinary system become inflamed. Yellow or green discharge and an unpleasant odor indicate purulent inflammation. Brown flakes are a sign of glomerulonephritis.
- Sexual disorders. An increase in symptoms leads to a weakening of sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, disappearance of nocturnal erections, and a decrease in the frequency of intercourse.
If any of these symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor, despite the sensitivity of the problem. Even a combination of several symptoms will not allow the urologist to make an accurate diagnosis - additional research will be necessary.
Individual causes of oliguria in men and women
Most diseases associated with work disorders occur in the same way in men and women. But due to the difference in the structure of the genitourinary organs, the appearance of oliguria can be caused by various reasons.
For men, a decrease in the amount of fluid secreted is often associated with inflammatory diseases of the prostate, its enlargement, and the appearance of tumors in it.
Urination in such pathologies is painful, and men rarely delay visiting a urologist.
In women, a decrease in the amount of urine excreted may be due to:
- atony of the bladder, which occurs due to inflammation or against the background of stressful situations;
- with age-related changes;
- due to hormonal imbalance.
Diagnostics
The examination of the patient is aimed at identifying the cause of the pathology in order to prescribe the correct therapy. It is quite difficult to establish the cause of violations. After reviewing your medical history and taking into account your symptoms, your general practitioner will order general tests.
Women may be referred for additional examination of the genital organs to a gynecologist; in men, the prostate gland is examined. It is possible to prescribe an ultrasound, CT with contrast (urography) or MRI. Informative methods are cystoscopy and cystography.
Treatment
If you constantly feel like your bladder is full, you need professional medical help. Self-treatment results in unpleasant consequences: injury to the urethra when trying to insert a catheter, infection, and possible rupture of the organ in the absence of therapy.
Treatment is carried out after the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis. In an emergency, the patient is given a urethral catheter to remove fluid. Depending on the type of disease, treatment with medications or surgery is prescribed. For spasms, antispasmodics are prescribed, pain is relieved with analgesics. Cystitis and other pathologies of inflammatory etiology are treated with antibiotics. Tumors, strictures, and blood clots are removed surgically.
Prostate adenoma is treated depending on the stage of development - conservatively or surgically. Small stones are dissolved with drugs, the choice of which is determined by the origin of the formations; large ones, in case of difficulty in the outflow of urine, are removed surgically. Treatment of neurogenic excessive contractions of muscles and sphincters is carried out with anticholinergic blockers. When muscles weaken, exercises are prescribed to restore their tone and diet.
Prevention
If discomfort appears in the bladder, this, in combination with pain and other accompanying symptoms, indicates the development of pathology. A timely visit to a qualified urologist will allow for correct treatment and prevent possible complications.
For prevention, it is necessary to undergo routine examinations with a therapist. A healthy lifestyle (walking in the fresh air, proper nutrition, good hygiene) will help avoid many diseases and promote longevity.
If the pain is constant, then it is necessary to establish its cause. This also applies to the unpleasant sensations that disturb a woman after urinating.
Etiology
Urine leakage after urination is caused by insufficiency of the bulbocavernosus muscle, which surrounds the middle and proximal parts of the urethra (urethra). Normally, after urination, the m.bulbocavernosus reflexively contracts and promotes the “evacuation” of urine from the urethra. Urine leakage is associated with retention of urine in the bulbar urethra with subsequent release of the latter during movement or under the influence of gravity.
A healthy bladder does not cause any unpleasant symptoms in humans. But if there is a feeling of a full bladder, this is a sign of serious pathologies of the urinary system. Such sensations interfere with the normal flow of a person’s life, because they can be accompanied by more unpleasant manifestations, such as incontinence or acute pain. Therefore, it is important to know what the feeling of a full bladder indicates.
The feeling of bladder discomfort, such as false filling, should not be left without due attention.
Causes
Unpleasant sensations after urination often occur due to an inflammatory process in the urethra or bladder (urethritis, cystitis). The outflow of urine further irritates the already inflamed mucous membrane. Women suffer from cystitis more often than men due to the different structure of the genitourinary system.
Urolithiasis can also cause pain. After all, the stones that come out injure the mucous membrane, which causes pain. This is a serious problem that requires immediate treatment.
Genital infections sometimes provoke discomfort when urinating.
Other reasons:
- damage to the urethra after violent sexual intercourse;
- allergies to hygiene products (soap, sanitary pads);
- severe hypothermia of the body;
- urethral candidiasis;
- pyelonephritis (pain in the lower back occurs after visiting the toilet);
- tumor of the pelvic organs.
Pregnant women experience pain and burning after emptying their bladder due to the enlarged uterus pressing on the urinary tract.
Causes of discomfort during urination
Discomfort during urination can be expressed by the appearance of various types of pain, burning and itching. There are several reasons for discomfort during bladder emptying.
The most common factor determining the appearance of the above symptoms is an inflammatory process limited to the genitourinary system. Mostly, problems during urination appear due to urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) and cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). A characteristic sign of urethritis is the appearance of burning and stinging at the very beginning of the act of passing urine; in turn, with cystitis, discomfort in the urethra in women appears after urination.
A special place should be given to the so-called defloration cystitis. It is popularly known as “honeymoon cystitis.” Defloration is the rupture of the hymen as a result of sexual intercourse. As a result of such damage, a “portion” of bacteria enters the vagina, as well as nearby organs. Pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the ascending path into the bladder and cause inflammation. Also, the rupture of the hymen itself can cause bleeding in combination with the fact that it will be painful for a girl to pee on the first day after sexual contact.
If it is painful for a woman to go to the toilet, then this pathology can be caused by inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. Most often, the cause of this pathological condition is sexually transmitted infections. These include:
- trichomoniasis;
- gonorrhea;
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasmosis;
- mycoplasmosis;
- combined bacterial infection.
Vaginal candidiasis, better known as thrush, can also provoke the occurrence of unusual sensations during the act of urination. The disease is a fungal infection of the vagina and is considered the most common infectious disease of the reproductive system. Discomfort in the urethra in women associated with candidiasis may appear after treatment with antibiotics. In this case, the use of antibacterial agents becomes the cause of vaginal dysbiosis (disturbance of the normal microflora of the environment). This in turn is a favorable condition for the proliferation of fungal infections.
Urolithiasis can also cause severe pain during urination. Even with this pathology, an interruption of the urine stream may be observed, despite the fact that the bladder has not had time to completely empty. A similar symptom in clinical medicine is called “laying in” syndrome. When you change your body position, the process of urination immediately resumes. With this diagnosis, it is not only painful for the girl to write, but she may also notice blood in her urine.
Discomfort during urination in women may be due to the use of certain cosmetics designed to care for the intimate area. Certain types of shampoos, soaps, and even toilet paper can cause irritation of the mucous membrane of the external genitalia, including the external urethral sphincter. Also, failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene can cause discomfort during the passage of urine. When a woman toilets her genitals too often, the natural microflora and acid-base balance of the vagina are disrupted. Dysbacteriosis and vaginitis that appear against this background are manifested by a burning sensation during urination.
Another reason for the appearance of such delicate problems may be injuries to the urethra. They can be caused by some kind of mechanical force (for example, a fall or blow), medical intervention (it may be painful for a woman to pee after taking a smear from the urethra, undergoing an endoscopic examination of the bladder or inserting a catheter), as well as forced sexual intercourse. It can also be painful to go to the bathroom after a C-section or difficult vaginal birth.
In rare cases, itching and burning during urination occurs due to the consumption of certain foods. Because of this, the composition of urine may be disrupted, and it will irritate the walls of the urinary tract.
Discomfort in the urethra in women can be caused by pregnancy. During this period, pain when urinating most often indicates a progressive fungal infection of the vagina or increased pressure of the fetus on the fundus of the uterus. Thrush can occur at any stage of gestation, and excessive pressure of the child on the uterine wall can occur at the end of pregnancy. In the latter case, nausea, lower back pain, fluctuations in body temperature, and a feeling of increased pressure in the pubic area also appear. In addition, if it becomes painful for a woman to go to the toilet during pregnancy, then an exacerbation of a sexually transmitted disease can be suspected, this is especially typical for the postpartum period.
If it becomes painful to go to the toilet during menstruation, and the unpleasant sensations are quite mild, then the reason for such phenomena is the peculiarities of the menstrual cycle.
Overactive bladder should be included in a separate category of diseases, one of the manifestations of which is dysuria. This disease is a violation of the mechanism of urine storage and the appearance of a sudden uncontrollable desire to empty the bladder. This problem is most often acute in nature and is manifested by periodic unconscious passage of a certain amount of urine, in other words, incontinence. Urination becomes more frequent (more than 6 times during the day, 1–2 times at night). With this diagnosis, stress urination occurs or occurs when coughing, laughing and sneezing. This can become a serious problem for a woman socially and psychologically.
Associated symptoms
Unpleasant sensations after urination is a general term. But what exactly does a woman feel?
The inflammatory process provokes muscle spasm when emptying the bladder. The organ is not completely emptied. This causes a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen. At the same time, the woman experiences burning and itching. The urine that remains in the bladder can cause the development of a chronic disease.
Inflammation causes not only the above sensations, but also provokes a false urge to urinate. The woman visits the toilet more and more often, but does not feel relief.
Pain after emptying the bladder may be accompanied by other symptoms:
- the color of the urine is not the same as usual;
- body temperature is increased;
- nagging pain in the lower back is disturbing;
- general weakness of the body.
Physiological increase in urination
Frequent urge to go to the toilet, which does not require any treatment, can be caused by the use of:
- excessive amounts of liquid, watermelon;
- alcohol, especially beer;
- many cups of coffee;
- meat, pickles, spicy dishes;
- drugs with a diuretic effect - diuretics (Lasix, Furosemide), antihypertensives (Arifon, Acripamide, Lorista, Micardis plus).
Frequent urination is also possible when taking medicinal herbs: corn silk, kidney tea, lingonberry leaf. Even the usual chamomile, a decoction of which is taken for various inflammatory diseases of the throat, can provoke frequent urges. A frequent desire to write is common among pregnant women, especially in the first and last months of pregnancy. Physiologically, the increased urge to urinate during pregnancy, sometimes requiring immediate emptying, is explained by compression of the bladder by the uterus and movements of the growing fetus, as well as a weakening of the muscle tone of the pelvic day due to hormonal changes. Normally, for pregnant women, the frequency of urges increases by 2–3 times.
Survey
Unpleasant sensations after urination are a reason to consult a doctor. He will conduct a detailed survey. The woman should tell in detail about all the symptoms, the frequency of visits to the toilet, how long this problem has bothered her. Additionally you will need:
- submit urine for analysis;
- do an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and kidneys;
- undergo endoscopic examination;
- undergo screening for sexually transmitted infections.
The results of all tests enable the doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and begin adequate treatment that will relieve the woman of the problem.
How to treat?
Depending on the disease that provoked such sensations, certain treatment will be prescribed:
- Cystitis and urethritis require the use of drugs that will destroy infectious agents and relieve inflammation (antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Urolithiasis requires a more serious approach. The woman will have to undergo a stone crushing procedure. But this does not always solve the problem. Surgery may be required.
- For allergic reactions, antihistamines are prescribed.
- Antifungal agents are used in cases of candidiasis.
- Tumors (and sometimes injuries) require surgery.
For any problems with the bladder, a strict diet is needed. Smoked, spicy, pickled foods should be excluded. Avoid alcoholic beverages. You need to drink more fluids, which will help flush the infection out of the body faster.
All medications should be prescribed only by a doctor. Self-medication can aggravate the situation and lead to dangerous consequences.
Any changes in the body that cause constant discomfort require medical attention. If a woman experiences pain, itching, or burning after visiting the toilet “in a small way,” then she should consult a doctor as soon as possible to determine the cause and, if necessary, undergo a course of treatment.
Video on the topic
Causes of frequent urination in women:
It is important to remember that you can get rid of frequent urination only after eliminating the causes of the disease. As a result of self-treatment with folk remedies or inadequate therapy in the case of inflammatory diseases, urinary incontinence or persistent muscular hypotonicity of the bladder may develop.
People who rarely go to the toilet are sometimes said to have “an iron bladder,” and to some extent they are envied. Rarely visiting the toilet is a valuable quality for a diplomat and any employee who has to attend events from which it is difficult to leave even for a short time.
Therefore, with the complaint: “I don’t go to the toilet very often,” people go to the doctor only when urinating becomes painful or when you begin to notice swelling in yourself. That is, when the disease is already in an advanced form.
The disease in its initial stage, when the amount of urine gradually decreases, is rarely paid attention to.