Frequent urination in a child is scientifically called pollakiuria and always contributes to the anxiety of mothers and fathers. Why is this happening? How to find out the cause of this condition and correctly prescribe treatment?
The number of urinations per day has a direct correlation with the age aspect:
- from birth to six months, the frequency of urination per day is 15-20;
- from five months to a year - they urinate 9-14;
- up to three years – approximately 10;
- from 3 to seven years – about 8;
- up to 11 years – no more than 8;
- 11 years and more – about 6 times a day.
When the frequency of urination in children exceeds age norms, then this is a case to consult a specialist.
Why does a child have frequent urination?
The need for frequent bladder emptying can be caused by 2 reasons:
- influence of physiological factors;
- the presence of pathological disorders in the body.
If your baby doesn't get a lot of fluids before going to bed, he'll sleep well at night.
In the first case, the release of urine does not cause pain to the child. If his body doesn't get a lot of fluids before going to bed, he sleeps well at night and has a normal temperature. Sometimes frequent urination is a consequence of severe overstimulation. As soon as the provoking factors cease to affect children, the number of visits to the toilet becomes normal.
Often there is a painful, frequent urge to empty the bladder, which turns out to be false.
Repeated daytime urination without pain, false urges and other signs of pathology can occur under the influence of the following factors:
- excess amount of water or other liquids entering the body;
- severe hypothermia;
- emotional stress;
- increased physical activity;
- treatment of the child with diuretics.
Small deviations from normal diuresis parameters associated with physiological processes are acceptable. For example, if yesterday a 7-year-old child urinated 5 times a day, and today – 8-9 times. It is necessary to check whether external factors or diet have changed. Daytime urination also progresses to nighttime urination, when the child drinks a lot of liquid before bed.
- lingonberries;
- cranberries;
- cherries;
- watermelon;
- melon;
- bananas;
- carrot;
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes, etc.
Parents should consult a doctor if frequent urination in a child aged 4 or 5 years is accompanied by alarming symptoms.
If your child's urination is accompanied by alarming symptoms, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Pathological signs in older children, 7 or 8 years old, should be of even greater concern:
- pain in the lower abdomen or lumbar region, pain, false urges, which is a sign of cystitis;
- small portions of urine, typical for colds and neuroses;
- chills, high temperature, sweating, characteristic of kidney disease;
- swelling or bags under the eyes that appear with pyelonephritis;
- severe thirst or frequent urination at night, which occurs with diabetes mellitus and diabetes insipidus;
- a strong odor of urine, cloudiness, and the appearance of traces of blood, which may indicate the presence of tumors.
In some pathologies, urine leakage is not accompanied by pain or stinging. Among them:
- ARVI;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia, neuroses;
- brain injury or tumor;
- small bladder volume, etc.
With a brain injury, urine leakage is not accompanied by pain or stinging.
Prevention measures
Of course, it is impossible to insure a child against diseases of the urinary system. However, a number of preventive measures make it possible to timely identify pathology and prevent the occurrence of unpleasant complications.
- Be extremely attentive to the child’s condition and possible manifestations of the disease.
- Do not neglect scheduled visits to the doctor. Children under six months old should be examined by a pediatrician every month, up to three years old - every three months, after four years old - once every six months.
- Make sure that your child does not catch a cold; forbid him to sit on cold benches or damp ground.
- Pediatricians recommend feeding your baby breast milk for as long as possible. The urine of such children contains large quantities of immunoglobulin A, which protects against various infections.
- Do not try to find out on your own what may be causing frequent urination in children. Treatment and comprehensive examination can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Parents should constantly monitor how often their child goes to the toilet. For any deviations from the norm, you should contact your pediatrician. It is better to consult a doctor once again and protect the child’s body from possible complications.
What is physiological pollakiuria?
The causes of frequent urination may be harmless and not related to illness. In this case, physiological pollakiuria is usually meant. Its development is due to the following factors.
- Drinking large amounts of liquid. When a child drinks a lot, the urge to go to the toilet becomes more frequent. Parents should pay attention to the reasons for increased fluid intake. It’s one thing if a child in the family is accustomed to drinking mineral water every day or feels thirsty in hot weather, or after physical activity. If your baby constantly asks for water and pees a lot for no reason, this may indicate a disease such as diabetes.
- Taking medications with a pronounced diuretic effect. These include diuretics, antiemetics and antihistamines.
- Hypothermia. Frequent urination in a child without pain is accompanied by a reflex spasm of the kidney vessels. After warming, pollakiuria stops.
- Eating foods that have a diuretic effect (lingonberries, watermelon, cucumbers, green tea). Most of them contain a large amount of water, so the number of trips to the toilet increases.
- Frequent urination in a 4-year-old child is possible due to stress and overexcitement. Against their background, adrenaline is released in the body, which affects the excitability of the bladder and the excretion of the fluid itself. Therefore, the child often visits the toilet, but urinates in small portions. This is a temporary condition that goes away on its own.
Physiological pollakiuria is completely safe and does not require specific treatment. Urination returns to normal after the provoking factor is eliminated.
Parents are not always able to independently determine the cause of such a disorder. In some cases, frequent urination in a child without pain is a symptom of a serious illness. These may be psychosomatic disorders, pathologies of the endocrine and nervous systems. The disorder is usually accompanied by fever, excessive sweating and refusal to eat. Let's look at the main diseases that cause frequent urination in more detail.
- Your child suddenly begins to urinate every 10 to 30 minutes, and the total frequency of urination per day reaches 30 to 40 micturitions per day.
- Your child produces very little urine per urination.
- The child's urination is painless.
- Your child does not wet his panties or pee in his pants during the day.
- Your child does not drink excessive amounts of liquid.
- Your child was already toilet trained and tidy when the illness began.
- Frequent urination does not bother the child during sleep (an important distinguishing feature)
Causes of pollakiuria
Frequent urination sometimes accompanies emotional stress. This means that your child is under psychological pressure. Symptoms are involuntary, not intentional. Frequent urination may begin 1 or 2 days after a stressful event or change in the child's daily routine. You can make the problem worse by worrying too much about your baby. Punishments, reproaches, ridicule also aggravate symptoms.
Although this condition rarely hides an organic pathology, your child should still be examined by a doctor. The only study that is required is a general urine test to rule out cystitis. Need for
x-ray examination
No.
How to help your child
1. Convince your child that he is physically healthy. Tell your child that his body, kidneys, bladder... everything he worries about is fine. Because family members may convey their anxiety to him, and he may be afraid that there is something wrong with his body, that he is in danger. Convince him as many times as you deem necessary - that he is healthy, that soon everything will pass without a trace.
Cystitis. Symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention
Information for patients. What is cystitis? Symptoms, clinics...
2. Explain to your child that if he wants, he can learn to wait longer periods of time between
urination
. Convince him that he most likely will not wet himself, because this is what the child is afraid of. If he does get exhausted, don’t hesitate to talk to him about it, explain that this sometimes happens to children, there’s nothing wrong with it. Tell him that the return to normal frequency of urination will happen gradually. If frequent urination bothers him while shopping or walking, try not to take him far from the house during this period.
3. Help your child relax. Frequency of urination can be an indicator of internal tension. Make sure your child has free time and positive emotions and favorite activities every day. If he has obligatory tasks that he does according to a schedule, relax the discipline, step back a little from the regime. Relaxation exercises may help your child if they are over 8 years old.
4. Happiness and harmony in the home usually helps restore a child's sense of security. Ask the staff of the school or kindergarten that the child attends to ease the child’s discipline as much as possible and in no case limit the frequency or duration of visits to the toilet.
5. Try to find out what is bothering your child. Talk to other family members and think through all the possible stressful moments that could have happened 1 or 2 days before the onset of the disease. Ask school and kindergarten staff about this topic. Discuss your thoughts with your child, try to identify and resolve the stressful situation, but remember that you should not be overzealous in this - your anxiety and excessive fussiness can aggravate the symptoms. Frequent stressful events that trigger this disease:
Acute pyelonephritis in questions and answers
Information for patients. What is pyelonephritis? Symptoms and...
central nervous system
Frequent urination in children without pain is often a physiological sign. But what to do if none of the diseases of the genitourinary system are diagnosed, and there are no physiological explanations for this?
In this case, we can assume that the chain of nerve endings from the center of perception to the organ has broken somewhere, and now the latter is left to its own devices.
It is logical that the baby wants to urinate as soon as the bladder is full, since nothing is stopping him from doing so. Here it will be important to immediately tell the child that he should not constantly endure.
Since the body does not understand this command, “trouble” can happen at any moment. And then it’s up to the doctor and a course of therapy to correct and normalize everything.
Neuroses can also cause the baby to go to the toilet more often. Stress plays a huge role here. In this case, the child will experience aggressiveness, mood swings, and uncontrollable emotions.
If problems in the central nervous system are suspected, consultation with a neurologist is mandatory.
Treatment
If urination is painless, it is enough to eliminate the physiological factors that caused it, and the unpleasant phenomenon will disappear without treatment. But if the child urinates with pain, complex therapy will be required. Only cystitis and urethritis can be treated on an outpatient basis without complications. For all other diseases, hospitalization is necessary.
Complex therapy uses:
- drug treatment;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- traditional medicine.
Frequent urination is treated conservatively with the use of drugs that relax the bladder muscles, antibiotics, and sedatives. Their choice is determined by the etiology (origin) of pathological disorders in the urinary system or kidneys.
Surgical interventions are performed in extreme cases if stones or tumors are detected in children.
Surgical interventions are performed in extreme cases if stones or tumors are detected in children. Urination of an inflammatory nature responds well to physiotherapeutic treatment. Procedures are prescribed when the acute stage of the disease has passed.
Speed up recovery:
- electrophoresis;
- amplipulse;
- diadynamic currents;
- ultrasonic influence;
- laser radiation;
- hyperbaric oxygenation (saturation of the body with oxygen).
Who to contact
If your child is urinating more frequently, you should first go for an initial examination with a pediatrician. He will make a preliminary diagnosis and refer you for consultation to a urologist, nephrologist, neurologist or endocrinologist. After examination and diagnosis, the child will be treated by the doctor whose specialization covers the identified disease.
The pediatrician will make a preliminary diagnosis and refer you for consultation to a urologist, nephrologist, neurologist or endocrinologist.
Drugs
Their purpose depends on what causes frequent urination. The following groups of medications are used:
- anticholinergic drugs (Oxybutynin, Vesicare, Urotol, etc.) - for an overactive bladder;
- antispasmodics (Driptan), m-anticholinergics (Atropine, Ubretide), nootropics (Picamilon) - for a lazy bladder;
- uroseptics (Canephron N), antibiotics (Amoxiclav, Sumamed, Monural) - if urination is caused by inflammatory processes;
- sedatives, nootropics, antidepressants (Pantogam, Picamilon, Melipramin) - for neuroses;
- hormonal drugs (Insulin, Minirin, Prednisolone), cytostatics (Chlorobutin, Leukeran, etc.) - for diabetes, glomerulonephritis, enuresis (urinary incontinence).
An experienced physician may prescribe anticholinergic medications for your child. For example, Vesicare.
Folk remedies
Popular recipes to help normalize urination:
- Pour 1 tsp with a glass of boiling water. birch buds, leave for 2-3 hours. Give your child half a glass 3 times a day before meals.
- Grind thin cherry stems, brew and drink as tea. Alternate with dried corn silk.
- Take 4-5 tbsp. l. dry crushed mint, pour 1.5 liters of boiling water, boil for 8-10 minutes. Drink a glass of decoction before meals 3 times a day.
If the child's frequent urination is short-term, painless and not accompanied by any health problems, treatment is not required. In this case, parents only need to carefully monitor the baby and, if necessary, eliminate factors that contribute to changes in the number of urges to defecate.
Frequent urination with pain and other symptoms of pathological processes in the body are a reason for mandatory consultation with a doctor and subsequent treatment. The treatment regimen will depend on what caused the disorder.
Frequent urination with pain and other symptoms of pathological processes in the body are a reason for mandatory consultation with a doctor and subsequent treatment.
Who to contact?
Before treating pollakiuria in a child, it is necessary to visit a pediatrician who will conduct an initial examination, prescribe a series of tests and recommend consultation with specialists. Additional examination is performed by pediatric specialists: urologist, nephrologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist.
Drugs
To treat pathological frequent urination in children, the doctor prescribes medications, taking into account the source of the disorder:
- for inflammatory diseases of the urinary system - uroseptics, antibiotics, NSAIDs, antispasmodics;
- for neurotic conditions - sedatives;
- for diabetes mellitus - Insulin injections;
- for vulvovaginitis - antimicrobial, hormonal, antifungal medications of general and local action;
- for balanoposthitis - anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antiseptic ointments;
- for glomerulonephritis - hormonal drugs, cytostatics;
- for a neurogenic bladder - nootropic drugs, m-anticholinergics.
To treat pathological frequent urination in children, the doctor prescribes medications, taking into account the source of the disorder.
Folk remedies
To eliminate inflammatory processes, normalize urination and strengthen the immune system, the following folk recipes are used:
- 1 tbsp. l. Brew mint in 250 ml of boiling water, leave for 1-2 hours, strain. Give the child 0.5-1 tbsp. l. 2-3 times a day. This drink is good for cystitis and type 2 diabetes.
- Wash 2 cups of fresh cranberries, squeeze with your hands or mash with a masher, strain the juice, set it aside. Pour the cake into 1 liter of water, bring to a boil over moderate heat, then combine with the juice obtained earlier and add 1-2 tbsp. l. honey The child should take 100-200 ml of fruit drink 1-2 times a day after meals. The product is indicated for use in cases of cystitis, urethritis, and pyelonephritis.
- For inflammatory diseases of the external genitalia, sitz baths are performed with herbal decoctions - calendula, chamomile, sage. To prepare the solution, you need to combine 90 g of plant material and 1 liter of hot water, place the mixture in a water bath for 10-15 minutes, then filter, cool slightly and pour into a basin. The child needs to be undressed from the waist down and placed in a container filled with liquid for 10 minutes, after making sure that the temperature of the broth has become comfortable.
Alternative medicine is an effective complement to drug therapy.
The exact dosage and duration of use of any folk medicine is calculated individually, depending on the age and health of the child. Before starting to take medications, you should consult your pediatrician.
Alternative medicine is an effective addition to drug therapy, but cannot be used as the only means of eliminating dysuric disorder in children.
What to do if your child starts writing frequently? Should we be alarmed or can we wait? First of all, you need to ask your doctor these questions to rule out urinary tract infections and any pathology.
Frequent urination in babies, accompanied by painful symptoms, requires immediate treatment. But first of all, the doctor analyzes the factors that could cause this. If this is a central nervous system disorder, sedatives are prescribed. If there is a tumor, surgery is required.
When inflammatory processes occur, uroseptics are prescribed, and in extreme cases, antibiotics. Frequent urination in adolescents often requires hormonal therapy and the prescription of cytotoxic drugs.
Based on the examination results, the doctor can determine what is causing frequent urination in children and the causes of the pathological disorder. After this, the pediatrician prescribes appropriate treatment.
For physiological pollakiuria, specific therapy is not used. All other causes require treatment in a hospital setting, where it is possible to fully diagnose diseases and monitor the child’s condition around the clock.
The course of therapy is prescribed in accordance with the diagnosis, since pathological pollakiuria cannot be overcome without affecting the underlying disease. The selection of specific drugs remains up to the doctor. The range of remedies used for frequent urination in children is very wide. For example, for neuroses, sedatives are prescribed; for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, insulin is required. In case of dysfunction of the central nervous system, surgical intervention may be required.
Parents should understand that pollakiuria is a fairly serious disorder that can be caused by dangerous diseases. If a child's fever and frequent urination persist for several hours, it is necessary to call a team of medical professionals. Self-treatment of this pathology is not recommended.
Diagnostics
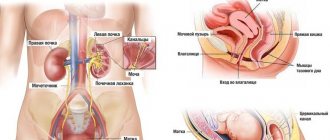
To find out whether organ diseases are “hiding” behind urination, the first thing you need to do is take your urine for a general analysis (a fresh morning portion in a glass container). Based on the results of this analysis, the doctor can refer you for examination to a specific specialist: urologist, neurologist, gynecologist, nephrologist or endocrinologist.
Further diagnostic methods may include:
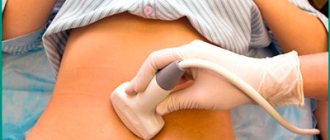
- Ultrasound of the urinary system;
- urine collection for Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky or Addis-Kakovsky samples;
- daily urine collection to analyze the amount of salts, glucose or protein;
- blood test to determine hormone and glucose levels;
- urography intravenously and voiding cystography using a contrast agent.