You should not worry ahead of time. Quite often, excess urination in women is a consequence of drinking drinks such as coffee, alcohol, and weight loss drinks. Frequent urination can also be caused by the use of medications, hypothermia, stress, hormonal imbalances, or pregnancy. During pregnancy, women often experience discomfort due to an enlarged uterus, which puts pressure on the bladder. As a result, women urinate at night is inevitable.
The reasons listed above cannot be considered a pathology, but it is still better to consult a doctor if such a problem arises, since frequent urination is a consequence of many diseases.
Reasons and why it can be dangerous
You can talk about pathology if there is pain or burning sensation when going to the toilet, frequent urge to urinate (more than 3 urges in the dark) with a small amount of urine, that is, not too much urine is released when going to the toilet. Excessive urination at night often has a number of causes:
- diabetes;
- overactive bladder;
- increased calcium concentration in blood plasma;
- wasting of the pelvic floor muscles.
Excessive urination is a possible indication of the progression of kidney disease, edema of venous stasis, prostate adenoma, heart failure, and obstructive apnea. If the urge to go to the toilet at night brings discomfort and negatively affects the quality of life, you should seek the services of a doctor.
Causes of frequent night urination
The main causes of nocturia are problems with the bladder and prostate itself, as well as hormonal imbalance. In the first case, nocturia is provoked by infections, mechanical damage due to surgical interventions, and tumors. In the second, night urination becomes more frequent due to a lack of a hormone that inhibits urine production.
Without pain
Frequent, painless urination is usually not alarming until it becomes exhausting. The reason for frequent rises at night may be the development of diabetes insipidus, in which the body's water balance is disturbed (the kidneys are not able to properly concentrate urine). Two hormones are responsible for its maintenance: antidiuretic AVP (vasopressin), synthesized by the hypothalamus of the brain, and diuretic ANG, released by muscle cells in response to increased blood volume. Impaired production of AVP or its insensitivity by the kidneys leads to an increase in urine volume and sleep disturbances.
Additional symptoms:
- Increased thirst;
- Dry mouth;
- Decreased appetite;
- Almost colorless urine.
Increased levels of diuretic hormone are recorded in men suffering from sleep apnea (short-term stops in breathing).
Painless night urination can be caused by neurological disorders, including those arising from parkinsonism, tumors and injuries of the brain and spinal cord, and damage to the pelvic nerves during surgical interventions. The bladder begins to periodically contract involuntarily, causing an inappropriate urge to urinate (OAB syndrome). Bladder dysfunction often occurs in people who are alcoholics or drug users (toxic nerve damage).
With OAB syndrome, uncontrolled contractions of the muscle that pushes urine out, the detrusor, occur.
Frequent urination at night can be caused by heart failure. During the day, the heart works worse than at night at rest. As a result, during sleep, metabolic processes accelerate, the kidneys begin to excrete urine more actively, thus compensating for daytime delays. Additional signs:
- Swelling, which is especially noticeable in the legs in the evening.
- Periodic shortness of breath.
- Tachycardia.
In men over 50 years of age, frequent small amounts of urination at night may be associated with a decrease in bladder capacity. This occurs against the background of prostate growth (hyperplasia), when the gland begins to put pressure on the bladder in a lying position. There may be no pain.
Urologist-andrologist Nikolai Konstantinovich Soloviev talks about the causes and symptoms of frequent night urination in men.
The natural increase in urination at night in men after 60 may be caused by age-related androgen deficiency. The reason is a disruption in the production of nitric oxide, as a result of which the contractility of blood vessels decreases and blood circulation in the muscles of the bladder is disrupted. Against this background, OAB syndrome often develops.
Nocturnal polyuria in the elderly may develop due to a disruption in the circadian rhythm of vasopressin production. Normally, by night its level should increase; if there is a failure, this does not happen.
With pain
Frequent night urination with pain, as a rule, is provoked by infections of the genitourinary tract, which cause cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, urethritis. Additional symptoms may include pain in the groin and lower abdomen. With prostatitis, it radiates to the rectum, and with renal pathologies - to the lower back. Urethritis and acute prostatitis are accompanied by discharge from the urethra; blood may be visible in urine and semen.
With prostatitis at night, the volume of the prostate gland increases due to deterioration in the outflow of blood and lymph, and pressure on the urethra and bladder neck increases. As a result of tissue compression, the concentration of receptors increases, and the urge to urinate intensifies. There may be no pain.
Painful, frequent urination (and even incontinence) day and night is common after prostatectomy (removal of the prostate). The symptom is caused by a violation of the nervous regulation of the bladder neck and urethral tissue. In the first weeks, blood periodically appears in the urine. Urination is completely normalized after six months. For some men, this process drags on for a year.
Symptoms and types of nocturia
This ailment can be temporary, that is, it can occur as one of a number of symptoms signaling the occurrence of a problem in the body, or permanent, when it indicates damage to internal organs. Nocturia can be true and intermittent. The first type is expressed in a decrease in the amount of urine excreted by the kidneys during the daytime. The second type does not affect the amount of urine produced during the day and indicates the possible occurrence of a number of the above diseases.
Symptoms include excessive urine production at night, insomnia, which is provoked by the need to get up to go to the toilet several times a night, as well as a small bladder capacity, depression, too light sleep, irritability, the volume of night urine exceeds that of the day, increased daytime fatigue, forgetfulness.
Symptoms of nocturia
Symptoms of the disease are characterized as the excretion of 2/3 of urine at night, and only 1/3 occurs during the daytime and before bedtime. Urination occurs at night both without pain in men and without pain in women, also in children over two years of age. Concomitant pain with frequent urges is provoked by another disease. Nocturia is not an independent symptom if a person cannot cope with the discomfort on his own. It implies the presence of health problems, and treatment should begin immediately.
Diagnostics
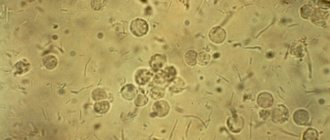
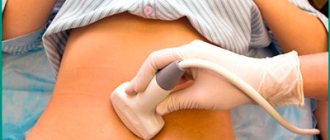
An increased number of trips to the toilet at night requires consultation with a doctor. The specialist will conduct an initial examination and collect information about your medical history, symptoms, living conditions, past illnesses, and also prescribe tests to identify what causes urination at night. To identify possible ailments, bacteriological culture of urine is carried out, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, bladder, kidneys is performed, as well as a general analysis of urine. Sometimes the Zimnitsky test is used to determine the water excretion and concentration capabilities of the kidneys and the dilution function. After receiving the results, the doctor prescribes the optimal course of therapy.
In older people, the level of antidiuretic hormone is additionally examined. Under normal conditions, this hormone responds to regulating the volume of urine produced per day. In old age, the level of this substance in the body may decrease, as a result of which nocturia may occur.
Diabetes mellitus and nocturia
Diabetes mellitus is a disease associated with insufficient functioning of the pancreas, which synthesizes insulin. This disease is associated with increased water consumption, which leads to nocturia. Urine is excreted both at night and during the day in large volumes. If symptoms such as severe constant thirst, dry mucous membranes in the mouth, or a large amount of fluid drunk and excreted per day appear, you should immediately consult a doctor and be tested for diabetes.
All patients with frequent night urination must have their blood checked for sugar.
What to do if you urinate frequently at night without pain?
The problem of urinating at night with pain should be subjected to complex therapy, not limited to drug treatment alone. If you urinate frequently at night, a special role should be given to diet. A similar recommendation also applies to those who do not have discomfort during urination, but frequent urination at night causes inconvenience. Problems of this kind are dealt with by gynecologists, urologists, nephrologists, neurologists and endocrinologists.
Weakness of the bladder wall provokes an increased level of urine excretion (sometimes without pain), but the process of excretion occurs very often and the patient does not produce much urine; the situation is often aggravated in older people. This way of functioning of the bladder is due to the fact that the rather weak wall of this organ of the excretory system is not able to withstand the pressure exerted by its own contents. As a result, the desire to empty the bladder comes quite quickly, although a small amount of urine comes out. A situation of this kind is solved with the help of specially selected exercises, medicines, and folk recipes. In some cases, the traditional approach to therapy does not give the desired results (more often in older people) and operations are performed to restore normal functioning of the body.
Etiological factors
The etiological factors of such an unpleasant symptom as frequent urination can be different. They are somewhat different for both women and men.
Causes of nocturia
The physiological etiological factors of nocturia in women include the following:
- menopause;
- premenstrual period;
- pregnancy.
Pathological causes of nocturia in women:
- hormonal imbalance due to the progression of certain pathologies, such as diabetes, menopausal syndrome, etc.;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- pathologies of the genitourinary system, such as cystitis, adnexitis, etc.;
- ailments of vital organs and systems.
Reasons for the manifestation of nocturia in representatives of the stronger half of humanity:
- pathologies of the bladder and urinary canal, such as urethritis, cystitis, etc.;
- impaired renal function;
- damage to the intestines and prostate;
- diseases of the central nervous system.
Drug treatment
Treatment of frequent urge to go to the toilet at night is aimed at eliminating the root cause of such a disorder. Therefore, diagnosis consists of searching for a disease that gives such a symptom, since only after the root cause is cured does urination return to normal. The complex of drug treatment may include alpha-adrenergic receptor blockers (Tamsulosin, Terazosin), 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Dutasteride). Depending on the disease that caused nocturia, the doctor selects other drugs that are suitable for the patient in each individual case. For example, for cystitis, Zenix, Monural, and Espa-Focin are prescribed. During treatment, it is recommended to take vitamins and mineral complexes that increase the overall well-being and tone of the whole body.
During the treatment period, it is worth minimizing the amount of liquid you drink before bed, limiting the consumption of coffee (especially black), alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks. You should adhere to a diet, minimize spicy foods, fried, fatty, too salty, confectionery products. Physical activity should be light and not overload the body.
Recommendations for treatment
Treatment for nocturia depends on the causes that caused it. Treatment is aimed at normalizing kidney function, as well as the ratio of urine output.
However, there are several rules that absolutely everyone should follow. First of all, it is necessary to normalize fluid intake. On average, an adult should drink about 2 liters of water per day. You should not abuse liquids and fruits, which contain a lot of water, several hours before going to bed. It is also not recommended to eat 2.5 hours before bedtime.
To normalize sleep, you can take mild sedatives. However, you should not abuse sleeping pills, since their frequent use can be addictive.
Urologists recommend that people suffering from nocturia perform special exercises. They will help strengthen the pelvic muscles. Such exercises are especially effective for older people.
Thus, nocturia may indicate the presence of serious pathological changes. A timely visit to a doctor will help identify the causes of nocturia and normalize the body’s functioning through complex therapy.
Folk remedies
At the moment, increased urination at night is treated with the use of folk remedies that regulate the functioning of the kidneys. One of the main points that traditional treatment includes is nuts (walnuts or pine nuts are most often used). These fruits increase tone and reduce the volume of urine produced at night. Eating dried fruits or berries (in their natural form) forces the body to expend a large amount of fluid for processing and absorption, which has a positive effect on the daily volume of urine in case of a similar problem. It is optimal to consume these products before bed (100-200 grams), having previously cleaned them of dirt with boiling water. Folk remedies include cheese, which has a positive effect on the adrenal glands, since these paired organs are responsible for the production of hormones and partly influence the formation of urine. You should eat cheese a couple of hours before bed.
Diagnosis of nocturia
To differentiate nocturia, the patient is prescribed the following studies:
- kidney test according to Zimnitsky;
- blood chemistry;
- blood sugar test;
- Ultrasound or x-ray of the kidneys (if urolithiasis is suspected).
Urinalysis is a mandatory diagnostic method for frequent urination
The most informative study is the Zimnitsky test. It consists of collecting daily urine every three hours. At the end of the collection, daytime and nighttime urine output is calculated. If nocturnal diuresis predominates, then the question arises of further examination of the patient in order to identify the causes of nocturia.
Symptoms
To get a clearer picture, symptoms that often accompany frequent urination can help make a diagnosis. Among them are:
- bleeding of the uterus;
- diarrhea;
- elevated temperature;
- malaise;
- chills;
- pain or discomfort in the pelvic area.
The presence or absence of symptoms is very important. If you do not experience any of the above, then most likely frequent urination is of a physiological nature (drinking heavily, hypothermia, poor diet, etc.)
Therapeutic features
The problem of frequent urination at night in women is subjected to complex treatment based on various methods of influence. A patient with such a problem should reconsider her diet, physical activity, and, if possible, limit herself from stress.
Further therapeutic intervention is carried out in accordance with the cause of the disorder.
- Any microbial inflammatory lesions of the urinary tract are treated with antibiotics. They are prescribed based on the results of cultures from the urethra, which helps to achieve complete eradication of pathogenic microflora.
- Weakness of the pelvic floor muscles is treated conservatively with various strengthening exercises. If they are ineffective, surgical intervention is considered.
- For diabetes mellitus as the root cause of nocturnal diabetes, insulin therapy is established. The same is the case with cardiovascular pathology, which requires drug compensation. With the help of hormonal substitutes, the harmful effects of menopause are neutralized.
It is good to support any etiotropic treatment with vitamin-mineral complexes and a rational sleep and wakefulness regime. Fluid intake must be strictly controlled, alcohol and caffeine-containing drinks should be completely avoided.
Frequent urination at night in women should be a reason to seek medical help, even if it does not significantly bother the patient. This symptom may be an early warning sign of a serious illness that can cause damage to the entire body. We should not forget about the close connection of the urinary organs with the reproductive function, which is assigned to the fair sex. Paying close attention to your health will allow you to feel great, not get sick, and conceive a child without any problems.
Preventive measures
To prevent the development of nocturia, doctors recommend following simple rules. The first thing that is important is to systematically visit a gynecologist and urologist in order to diagnose problems related to the genitourinary system in a timely manner. In addition, it is important for males over 45 years of age to be examined for prostate adenoma every year. You should adhere to an active lifestyle, take a contrast shower, and spend more time outdoors. It would be useful to maintain a proper and balanced diet and avoid food that acts as an irritant to the mucous membrane of the bladder. Such foods include herbs, spices, fatty, spicy and sour foods. You will also need to give up the abuse of alcoholic beverages and smoking.
prourinu.ru
Causes of frequent urination in women at night associated with diseases of the endocrine system
Impaired metabolism is accompanied by diabetes mellitus, or diabetes mellitus. The disease is characterized by increased concentrations of glucose in the blood. One of the symptoms of the disease is polyuria, associated with increased urine output. The reason for this is the increased osmotic pressure of urine caused by dissolving glucose.
Other key signs of type 1 diabetes:
- Uncontrollable hunger (polyphagia). The inability to eat is associated with a metabolic failure: body cells stop absorbing and processing glucose.
- Sudden weight loss, sometimes reaching the point of exhaustion. Associated with the disappearance of glucose from the process of cellular metabolism, as well as with accelerated fat-protein catabolism.
Type I diabetes occurs due to excessive stress or as a result of a viral infection. The above symptoms always accompany the disease of this group; sometimes, but not always, they are also characteristic of type II diabetes. It develops due to a sedentary lifestyle and an unbalanced diet rich in sweets and baked goods. In adult women, it is the second type of diabetes mellitus that is most often observed.
Both types of the disease are also accompanied by headaches, decreased vision, itching, and dry mouth. Diabetes mellitus can be confirmed using a glucose tolerance test. If you have disturbing symptoms, you should go to an endocrinologist or therapist. Patients are recommended to have a special diet and, if necessary, antihyperglycemic drugs are prescribed.
Sometimes night urges are provoked in a small way by a form of the disease insipidus. In this case, a reduced level of the hormone vasopressin in the blood is observed and urine filtration by the kidneys fails. The main symptom of the disease is very strong thirst, which results in an increased desire to visit the toilet. As a rule, therapy involves taking hormones throughout life.
Alarming symptoms
Frequent urination in women can be associated with various diseases, which, if ignored, can lead to serious complications. The absence of pain or discomfort is not a reason to refuse to visit a doctor.
The occurrence of burning sensations and pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by frequent urination, serves as an alarming signal. Diseases that affect the genitourinary system are insidious and can affect reproductive function, so if you have the slightest suspicion of a disease, you should seek help from a specialist.