Dependence of cystitis on ovulation
The menstrual cycle affects the functioning of all body systems.
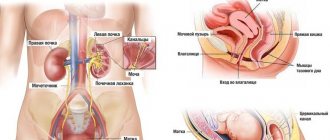
This is due to the fact that during the maturation of the egg, hormonal levels change several times. The main substances produced by the female reproductive system are estrogen and progesterone. Ovulation is the maturation of an egg. When the egg matures, it leaves the follicle and begins its movement towards the uterine cavity. Thanks to hormonal changes, the most optimal conditions are created for this.
Ovulation occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle. You can determine the exact date of egg maturation by measuring basal temperature. This method is the most effective. Each woman has a different duration of the menstrual cycle, so ovulation occurs purely individually for each female representative.
During the period of ovulation, the most important changes for the development of cystitis occur, which include:
- Increased blood supply to the uterus. Increased blood flow in the uterine area leads to minor ischemia of nearby organs. As a result of insufficient blood supply, local immunity in the bladder decreases. This situation is fraught with the fact that even a small amount of bacteria can lead to the development of the acute phase of the disease.
- Enlargement of the uterus. Due to the fact that under the influence of hormones the functional layer of endometrial cells can increase several times, the uterus enlarges. All this leads to the fact that it compresses the remaining pelvic organs. This phenomenon aggravates the ischemic condition in them.
- Local decrease in body temperature. With the onset of ovulation, there is a decrease in basal temperature. This is necessary so that the sperm reaches the egg and does not die, since low temperatures are comfortable for it.
Frequent urination before, during and during ovulation - causes and what to do
Inflammation of the bladder mucosa, or cystitis, is a common disease among women caused by pathogenic bacteria. The connection between ovulation and cystitis occurs against the background of a weakened immune system due to hormonal changes. Regardless of how ovulation ends, the processes occurring in the body affect the development of opportunistic flora of the vagina and intestines. If ovulation ends with fertilization, then the female body begins to rebuild its hormonal levels. During this period, the size of the uterus increases, resulting in greater pressure on the bladder, and the body's defenses are greatly reduced. All these processes can affect the occurrence of interstitial cystitis. The growth of microbes and their reproduction is enhanced by a decrease in the tone of the bladder and stagnation of urine in it, as the level of the hormone progesterone increases. When fertilization does not occur after ovulation, a subsequent transition of the cycle to another phase is observed. Basal body temperature increases.
This had never happened before; ovulation always occurred, although not often, but asymptomatically. And then in the third cycle I notice that just as ovulation occurs, on the same day I start running around and even get up at night.
What are the symptoms of cystitis?
Most often, this disease appears in spring, winter or autumn. The patient’s immune system at this moment is very weakened, the weather is quite unstable, and the activity of pathogenic microorganisms is always quite high. During ovulation, the female body is most vulnerable to bacterial activity, moreover, if fertilization has occurred, then this vulnerability increases significantly.
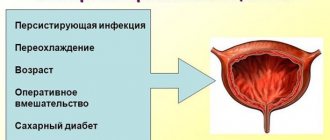
Cystitis occurs during ovulation and after its completion for the following reasons:
No. Useful information
| 1 | weak immunity |
| 2 | decrease and changes in the patient’s hormonal levels |
| 3 | insufficient personal hygiene of the external genitalia |
| 4 | the occurrence of allergies to components of intimate gels and care products |
| 5 | inflammation in the genitourinary area |
Cystitis that occurs during ovulation often resembles a non-infectious inflammatory process. In the bladder, the mucous membranes become severely irritated, pathogenic microorganisms enter them and the infectious process begins.
When urinating, a woman experiences severe pain, itching and unpleasant pain in the genitals. Long-term pain appears in the lower abdomen, which torments and exhausts the patient. Often, against this background, lower back pain and headaches occur, the woman loses her ability to work, and experiences general weakness. As a rule, the body temperature is slightly elevated.
The most obvious sign of cystitis is pain every time you urinate. In addition, the urge is felt too often, from 3 to 10 minutes, while only a few drops of fluid are released. The color during urination also changes, becoming cloudy and dark, and not a straw color, as in the normal state.
Hematuria may occur when drops of blood appear in the urine. When examining urine, a high level of leukocytes and mucus are detected. In advanced forms of cystitis, the menstrual cycle is disrupted and the disease becomes more complicated.
Some statistics
Even more interesting:
Apple cider vinegar for warts
Ovaries during menstruation
p, blockquote 5,0,0,0,0 —>
After a girl’s menstruation has become stable, after a while she begins to notice changes in her condition that occur approximately in the middle of the cycle. Usually they only concern the mammary glands, mood changes or increased sexual desire, but 20-30% of women notice that their lower abdomen hurts during ovulation. This pain is nagging in nature, varies in intensity, and is usually noted on one side.
p, blockquote 6,0,0,0,0 —>
In 85% of women, pain during ovulation is associated with natural processes. In 14% of cases, such symptoms indicate a pathology of the reproductive system. Finally, there is a small, about less than 1% probability that just during the ovulatory phase of the cycle another pathology will develop, not related to the very release of the oocyte from the follicle.
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
Treatment
If a girl regularly experiences an increased urge to urinate during ovulation, it is imperative to determine what is causing the development of this condition. To do this, it is recommended to go to a gynecologist who will carry out the necessary diagnostic measures.
If a symptom develops under the influence of physiological factors, then after their elimination the condition stabilizes. So, for example, if a girl drinks a lot of liquid and loves watermelons or melons, then it is necessary to reduce their amount. It is very important to prevent hypothermia, as this is favorable conditions for the development of many gynecological diseases.
For some, frequent urination during and after ovulation is caused by the progression of urolithiasis. This pathological condition must be treated. It is very important to go to a urologist as soon as possible, who will issue a referral for a stone crushing procedure.
Subsequent therapy is carried out using medication. If the disease is not advanced, then sometimes it will be enough to take prescribed medications:
- Allopurinol;
- Etamide;
- Solimok.
In situations where an increased urge to urinate is associated with the development of gynecological diseases, the method of therapy should be determined only by a leading specialist, after a thorough diagnosis, as well as interpretation of test results. In most cases, treatment is carried out conservatively.
If cystitis appears after ovulation, then it is necessary to begin treatment for the disease as early as possible to prevent the spread of infection. Medicines from the following pharmacological groups are often prescribed:
- Antibiotics;
- Antispasmodics;
- Probiotics;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Herbal medicines.
It is not recommended to independently select medications, since there are a lot of them, and there is a high probability of incorrect treatment, which will blur the clinical picture, but will not contribute to recovery, and the development of serious side effects is also possible.
Does pain affect the likelihood of conception?
If the pain of ovulation is caused by natural causes, then this even increases the likelihood of conceiving a child. Since a woman knows the onset of “dangerous” days.
The article discusses the main causes of painful ovulation.
If the symptoms are caused by the presence of pathologies, then the likelihood of pregnancy depends on the type of disease (oncology, inflammation in the organs of the reproductive system or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract). It is important that before planning a conception, it is recommended to undergo a full examination so that the pregnancy proceeds without the development of complications due to the presence of hidden pathologies.
Prevention measures
According to statistics, cystitis occurs less often in men than in women. It is one of the most common urological diseases. It is impossible to completely protect yourself from cystitis, but you should take all available preventive measures to minimize the likelihood of being affected by the disease.
A woman must carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene (regular washing and changing underwear), use only high-quality intimate hygiene products that do not cause allergies. Such actions should be taken not only during menstruation, but throughout the rest of the time.
You should protect yourself as much as possible from stressful situations, eat right, avoid hypothermia and protect yourself during sexual relations with a new partner.
First of all, remember that you cannot skimp on personal hygiene products. Pads and tampons should only be from reliable and trusted manufacturers. Budget products can cause an allergic reaction, as well as create a “greenhouse effect”, so beloved by bacteria and microbes. Tampons and pads should be changed at least as often as indicated in the instructions on the package.
During menstruation, you should thoroughly wash your genitals 2-3 times a day, this is necessary in order to prevent the creation of favorable conditions for the proliferation of bacteria.
Take care of your health through proper nutrition, include fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins and beneficial microelements in your diet. This is especially important in the spring to avoid vitamin deficiency.
Be less nervous, stressful situations can reduce your immunity and make you a target for many different diseases.
Remember the importance of barrier methods of contraception. They will protect you from diseases that can become catalysts for cystitis.
Avoid hypothermia: dress appropriately for the weather, do not sit on cold surfaces and do not swim in cold water.
Troubleshooting methods
If during ovulation frequent emissions completely torment a woman, she must definitely consult a doctor. During the treatment period, it is important to follow these rules:
- Drink more fluids to be able to flush out pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, you should pay attention to the severity of edema.
- Eat foods that contain iron. They increase the amount of hemoglobin and also strengthen the immune system.
- Observe personal hygiene rules. You need to wash your genitals twice a day. It is advisable to do this also after visiting the toilet.
If frequent urination is caused by pathologies, the woman is prescribed drug therapy. It involves the use of such drugs:
MedicinesPeculiarities of administration
| Means for crushing stones with a diuretic effect | 1. "Allopurinol". It is prescribed by a doctor. The dosage can be increased if necessary. 2. "Solimok". 3. "Etamide". The medicine is taken for no more than 2 weeks. After the therapeutic course there is a 7-day break. |
| Antibiotics | They are necessary if the patient has a bacterial infection. The most commonly used are vaginal suppositories, as well as douching solutions. Tablet medications are also required. Typically, a woman is prescribed Sumamed, Monural, Tetracycline (usually in the form of an ointment), Azithromycin, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav. |
| NSAIDs | Required for fever and pain: Nurofen, Ibuklin, Ibuprofen. |
| Antispasmodics | They eliminate pain. Doctors prescribe No-shpa, Drotaverine, Spazmolgon. These medications relax muscle tissue. |
| Herbal remedies | Often prescribed to patients who are pregnant. They cause minimal side effects and contain natural ingredients. This group includes “Canephron”, “Urolesan”, “Cyston”. The main rule for taking them is timeliness and regularity. Otherwise, the positive effect will not be achieved. |
| Probiotics | Prescribed for violations of intestinal and vaginal microflora. “Hilak Forte” and “Rioflora” will help here. |
It is also important for the patient to eat properly. The consumption of watermelons, melons and other diuretic products should be limited. If there are no diseases, then the situation should soon return to normal on its own.
First signs of pregnancy after ovulation
First signs of pregnancy
Signs that a woman is pregnant are often visible to the naked eye shortly after ovulation. The first week can proceed similar to premenstrual syndrome, although it is more intense.
The most eloquent signs of conception may be pink vaginal discharge on the eve of the menstrual cycle. This phenomenon is associated with the process of implantation of the zygote into the uterus. The presence of white discharge after ovulation is also considered a hallmark of pregnancy.
If you want to get pregnant, it is important to know on what day the characteristic initial symptoms of conception appear. The first signs of pregnancy after ovulation are mainly observed in a certain sequence:
- 2-3 days – weakening of the immune system;
- 4th day after ovulation – pain in the lower abdomen and the likelihood of bleeding;
- 7th day after ovulation – the appearance of brown vaginal discharge
Pregnancy develops at a rapid pace, and every day gives the expectant mother new sensations. Her body adapts to the conditions that have arisen, and therefore the woman experiences general weakness and fatigue.
The fourth day after ovulation can become noticeably uncomfortable due to pain and the appearance of bloody discharge. Particularly noteworthy is the 6th day of pregnancy.
It is at this time that the basal temperature rises. Traditionally, its increase refers to the very first symptom of successful conception.
Basal temperature is measured by inserting a thermometer into the rectum in a lying position, immediately after waking up in the morning.
In normal conditions, a woman’s basal temperature ranges from 37-37.2°C. Its noticeable increase, up to 37.5°C, often indicates the attachment of the embryo to the walls of the uterus. At first, the zygote is in a floating state; seven days of pregnancy is the optimal period for its consolidation in the main reproductive organ of the female body.
Particular attention should be paid to a basal temperature of 38°C and above. Such a symptom may indicate pathology or the presence of inflammatory processes in the body.
Having decided to resort to the method of measuring basal temperature, it is important to remember that it will only be effective if there are previous regular measurements.
A week after conception, other symptoms become more and more apparent: toxicosis, engorgement of the female breast, diarrhea, increased nervous excitability and others.
When to see a doctor about ovulatory pain.
To rule out conditions such as appendicitis or ectopic pregnancy, see your doctor if you experience new or sudden, severe pain in your lower abdomen, or if the pain lasts more than two days.
Also see a doctor if your abdominal pain is accompanied by symptoms such as:
- Fever.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Early signs of pregnancy and/or a positive pregnancy test.
- Vaginal bleeding between periods.
- Foul-smelling or other unusual vaginal discharge.