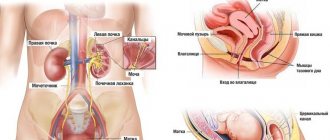
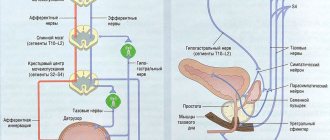
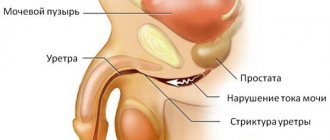
Difficulty urinating is observed in men of different age categories. The reasons for this may be different. For timely treatment, it is very important to identify the problem in time. At the first manifestations, you should immediately go to a doctor - a urologist. Only he will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Self-medication is prohibited.
Urinary standards
The rate of daily urination is determined by the person’s gender, age and body characteristics. Small deviations up or down are not considered pathology. Also, the number may fluctuate due to the liquid you drink, a heavy lunch and heredity.
Frequent and painful urination is a reason to consult a doctor. A specialist will help identify the cause and prescribe appropriate treatment. The number of urinations per day is different for each age. It changes under different environmental temperature conditions and depends on many external indicators.
| Age | Number of trips to the toilet per day | |
| Adults | Men | 4-6 |
| Women | 4-8 | |
| Children under 1 month | 20-30 | |
| Children under 1 year | 10-15 | |
| Children from 3 to 5 years old | 6-8 | |
| Children from 5 to 10 years old | 5-7 | |
| Senior students | 4-6 | |
For any illness, including ARVI and colds, the number of trips to the toilet may vary. When the body is intoxicated, metabolic processes slow down and dehydration occurs.
You can estimate the number of trips to the toilet only if:
- body temperature does not exceed 37 degrees;
- the person is healthy, there are no colds or viral diseases;
- a sufficient amount of water has been consumed;
- did not take diuretics or diuretics;
- there was no increased physical activity.
At night, a healthy person can get up no more than once from the urge to go to the toilet.
Treatment of a weak stream of urine with folk remedies
Of course, the problem of a weak urine stream is not new. In this regard, in folk medicine there are ways to treat this phenomenon. However, it will be effective only after consultation with a doctor and his approval, and also if it is used in combination with conservative treatment. Otherwise, the idea of being treated only with infusions and herbs may end in the development of complications leading to infertility, impotence or cancer.
Here are some of the most popular treatments:
- You can drink a decoction of medicinal plants, such as rosehip; not only its berries are brewed, but also the root, chopped into small pieces. Rowan tea helps well, that is, the same decoction, only from rowan berries and leaves. You can also brew chicory, lily of the valley and celery. The decoction is prepared in the same way as regular tea, that is, 3 liters. dry plant, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and let it brew for at least 5 hours.
- You can apply half a raw onion to the lower abdomen with the cut on the skin. To avoid holding it, you can wrap it with a bandage or stick it with a band-aid. It is best to do this before bed so that the compress lasts until the morning.
- For kidney diseases, the use of a warm belt knitted from dog hair is indicated.
Whatever treatment is used, if it does not help for more than 2 weeks, you should consult a doctor for a re-examination. Be healthy!
What are the violations?
Difficulty urinating in men can indicate a number of diseases of the genitourinary system. Sometimes such a sign can even indicate problems with the digestive system. All types of urinary disorders are combined into a general category of diseases called dysuria.
Main violations:
- frequent urination;
- difficulty excreting urine;
- urinary retention;
- incontinence (including nocturnal enuresis);
- complete impossibility of urine outflow.
Most often, in men, the symptom indicates inflammation of the prostate gland; in women, it signals an attack of cystitis. The causative agents are usually bacteria: ureaplasma, chlamydia, mycoplasma - and even some types of fungi.
Problems with urination in men and women can be caused by the following reasons:
- Pollakiuria . Usually this disease signals damage to the urinary tract, but it may also indicate kidney disease. It can also develop against the background of other diseases that provoke excessive urine production. This could be nephrosclerosis, convergence of edema. It is provoked by prostatitis, urolithiasis or other disorders.
- Urinary incontinence . In this case, the patient loses control over the self-management of physiological needs. Deviation can occur due to stress, psychological trauma, an overfull bladder, or all of the above.
- Nocturia . The volume of urine increases at night and decreases during the day. As a result, patients practically do not feel the need to urinate during the day, and at night they can get up to go to the toilet quite often. The reasons may be a number of pathologies of the body that provoke this condition. Among them, a violation of the ligamentous apparatus of the bladder, a decrease in its plasticity, cellular atrophy and dysfunction of the epithelium, a decrease in hormone levels, the acquisition of somatic diseases, and vascular atherosclerosis are noted.
- Polyuria . This is the body's excretion of excess urine per day. With polyuria, the number of visits to the toilet may remain the same (5-6 times a day). But the volume of urine produced is higher with each urination. The causes may be diabetes, hormonal problems, or urolithiasis.
- Oliguria . A disease in which the amount of urine produced is less than normal. Oliguria is usually diagnosed when urine output is less than 500 ml per day. The reasons may be dehydration, severe illnesses (acute gastroenteritis, esophageal cancer, liver damage), impaired blood supply to the kidneys, glomerulonephritis.
- Anuria . Complete cessation of urine excretion from the body. Usually it is evidence of critical conditions of the body. There are three types of anuria: prerenal, renal and postrenal. This is indicated by the localization of the pathology. The deviation is provoked by the presence of kidney stones, cancerous lesions of internal organs, cardiovascular abnormalities and other pathologies of the urinary system.
Such signs can appear not only in men, but also in women. Elderly patients suffer more often, but children are not immune from the occurrence of nocturnal enuresis due to emotional overload or health problems.
The mechanism of development of strangury
Urination is difficult and becomes so due to spasm of the muscular layer of the bladder wall in the area of its neck. This condition is called severe dysuria. It is not a separate nosology, but only a symptom that occurs in various pathologies. Strangury is not considered normal.
With strangury, the time for emptying the bladder is prolonged and multiple acts of urination occur, sluggish urine flow with interruptions and changes in direction. In addition, strangury is accompanied by some discomfort.
Diagnosed at any age, but more often after 50 years. Urological problems occur in 20% of men. In addition to stranguria, dysuria includes another type of disorder - ischuria.
Here, with a full bladder, urine cannot come out naturally. The cause of this phenomenon is most often prostate adenoma, urethral stricture (urethra) and stones in the bladder. Urination is more common in men than in women, which is facilitated to a certain extent by the anatomical structure of the male urethra.
Normal urination is a free stream of urine under pressure of about 1.5 liters per day. The ideal frequency is about 5 times a day during the day and 1 time at night.
Problems with urination
A normal adult male bladder holds about 300 ml of urine. The urge to urinate is controlled by the central nervous system and, if necessary, can be restrained for a certain time.
Causes of difficulty urinating
A weak urinary stream in men may have other causes than problems in women. Such differences lie in the anatomical features of the structure.
In men
The most popular cause of delicate problems is inflammatory diseases of the prostate gland. Due to the fact that the prostate increases in size, it puts pressure on the urinary canal, and a narrowing of the lumen of the urethra may occur.
Poor urine pressure in men occurs for a number of reasons:
- infectious processes in the prostate gland;
- urinary tract diseases;
- allergic reactions to cosmetics;
- diabetes;
- multiple sclerosis;
- syphilis;
- prostate diseases (prostatitis, adenoma, cancer);
- metabolic diseases;
- pathologies of the central nervous system;
- severe injuries of the musculoskeletal system.
Infection is the second most common cause of urinary dysfunction. Sexually transmitted diseases or contact with the mucous membrane of the genital organs of bacteria, fungi or viruses can make urination difficult. Even harsh chemicals can cause itching and burning in the urethra.
Among women
Representatives of the fair sex are less likely to suffer from this problem. The most common cause of toilet problems is cystitis and urethritis, which develops against the background of hypothermia or infection.
Problems with urination in women occur due to:
- mechanical damage to the urinary canal (narrowing of the lumen, presence of foreign bodies);
- chronic cervical cystitis;
- urolithiasis;
- chemical exposure to cosmetics and certain medications;
- presence of blood clots or mucus;
- pinching;
- tumor processes in the genitourinary system;
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- urethral stenosis;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- alcoholism;
- diabetes mellitus and metabolic diseases;
- misuse of contraceptives;
- injuries
There are many similarities with men's reasons. However, women more often experience false urges to go to the toilet against the background of the development of psychosomatic diseases. Also, vaginal contraceptives and their improper use can have similar side effects.
Symptoms
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to tell your doctor about the accompanying symptoms. Women and men may experience pain in the lower abdomen and discharge from the urethra. Most often, unpleasant symptoms appear in the morning.
Signs of pathology:
- decreased libido (erectile dysfunction in men);
- state of weakness and malaise;
- discharge from the penis or vagina.
Itching and burning in the urethra may also occur. It is worth paying attention to the speed of urine outflow, strength and even the feeling of complete or incomplete emptying of the bladder.
Additional symptoms of the problem:
- prolonged urination;
- a thin, poor stream directed downward;
- urinary retention even with a strong desire to urinate;
- splashing and splitting of the jet;
- reduction in speed.
Urethral diverticulum
A depression in the wall of the urethra. Appears after surgery or other medical procedures. It can also be a consequence of an infectious disease. Urine, passing through the urethra, is retained in the cavity. Therefore, the exit jet becomes weak. Over time, the liquid flows out drop by drop. There is pain in the urethra, which gets worse during sex and urination. There may be bleeding from the head. To get rid of the pathology, diverticula are removed surgically.
Diagnostics
The first step is to consult a doctor. Both men and women can visit a urologist. The examination is aimed at identifying the cause of difficulty urinating, determining the condition of the muscular wall of the bladder, the presence or absence of residual urine and other complications.
Diagnostics includes:
- Palpation. This is palpation of the bladder and other organs. A man needs a rectal examination of the prostate to detect an inflammatory process.
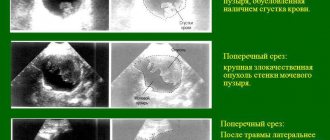
- Ultrasound. An examination of the conditions of the bladder, kidneys and prostate gland is carried out.
- Urethrocystoscopy. It will help to most accurately assess the location of the problematic emission.
- X-ray and other studies. Prescribed if the cause of the symptoms has not been found.
Standard examinations
Urologists examine patients with complaints of urinary disorders. Since it is very likely that the “root of evil” lies in pathologies of the male reproductive system, an additional consultation with an andrologist is required.
The best option would be to find a urologist-andrologist, since we are talking about an interdisciplinary problem. At the initial appointment, the specialist interviews the patient, asks questions regarding the patient’s condition, his well-being and complaints. An anamnesis is collected (the doctor finds out what diseases the person has suffered during his life).
The complex of pathological manifestations prompts the specialist to think about the probable cause. At the initial consultation, the doctor performs a digital rectal examination of the prostate gland. It allows you to assess the size of the glandular organ, its structure, and identify all nodular formations.
Using similar methods, the attending physician puts together an approximate clinical picture in his head. The next step is verification (confirmation) of the diagnosis. For these purposes, the following studies are prescribed:
- Analysis of prostate secretions. Based on the volume, density, and nature of the fluid, one can accurately diagnose prostatitis at any stage of the process. The fact of the presence/absence of infectious agents in the structure of the secretion is also of great importance;
- Ultrasound examination of the prostate gland. The most informative study that allows you to identify pathologies of the glandular organ. Visually presents information about the state of the male reproductive system;
- Ultrasound examination of the bladder. Necessary for determining the amount of residual urine. Significant urinary disturbances are not typical for prostatitis. The sign is pathognomonic for hyperplasia;
- Additionally, a general blood test is prescribed in combination with a general urine test;
Such a small list of studies makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis even at the early stages of pathology formation.
[adsp-pro-6]
Treatment in men
Drug therapy is prescribed only by a doctor. Self-medication can only make the situation worse. Usually, medication and lifestyle modification are indicated. The patient can also use additional conservative treatment methods, such as folk remedies or physical therapy.
Drugs
There are many pills for treating male problems. The goal of therapy is to eliminate the cause, not to overcome the main symptom.
The most popular medicines:
- Phytocaps Adeno-Complex. Prescribed for prostate diseases.
- Oxybutynin. Eliminates frequent urges.
- Sonizin. Indicated for adenoma.
- Spasmex. Has an anticholinergic effect (against enuresis and frequent urge).
- Duloxetine. Eliminates pain and pain when emptying the bladder.
- Imipramine. Helps control urination and relieve enuresis.
For diabetes, you will need insulin-based medications that can lower blood sugar levels. Treatment prescribed by a specialist may vary depending on the cause of the disease and the patient's medical history.
Folk remedies
Grandmother's recipes also have medicinal properties, but are used only as additional treatment. Alternative therapy must be agreed with your doctor. Even herbal remedies can cause allergic reactions.
Folk remedies for treating weak urination in men:
- Celery juice. Every morning you need to consume about 2 teaspoons of fresh stem extract. After a month, the patient will notice relief.
- Walnut shell. It is ground in a coffee grinder and consumed 5-10 g daily with water. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks.
- Hop cones. The raw materials need to be ground into powder and brewed like tea. You need to drink 200 ml during the day. The course of treatment is 3 weeks.
Such recipes will also help restore libido. Do not drink traditional tinctures and powders for less than 3 weeks. Herbal recipes have a cumulative effect.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of prostatitis and prostate adenoma is complex. In the early stages - medication. The following groups of medications are indicated:
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin. Allows you to relieve inflammation and swelling of the prostate gland;
- Antispasmodics. Relieves spasm of the glandular organ;
- Alpha adrenergic blockers. Relieves pathological tension in the tissues of the gland and urinary tract. More often, such drugs are prescribed for the treatment of adenomatosis;
- 5 alpha reductase inhibitors. Stabilizes the size of adenomatous prostate nodes;
Pharmaceuticals can be effective only in the initial period of the disease, when the size of the hyperplasia does not reach 50 mm in diameter or when the prostate has not yet lost its functions.
In the later stages of hyperplasia, surgery cannot be avoided. It is carried out using two methods:
- Transurethral access (transurethral resection or TUR). It is prescribed only for small tumor-like structures (up to 80 mm). It is characterized by comparative low-impactness and high efficiency. However, relapses of the disease are possible.
- Open access (traumatic). Abdominal surgery during which tissue of the anterior abdominal wall and bladder is excised. But such a technique has one undoubted advantage: radicalism. Relapses are excluded. Open adenomectomy is indicated for large tumor sizes.
Prostatitis is rarely treated surgically. The most common indication is the calculous form of the disease. This is the process during which calculi (stones) develop in the ducts of the prostate gland.
It is not the sluggish flow that needs to be treated, but the root cause of the condition. The condition itself is relieved with adrenergic blocking drugs.
[adsp-pro-5]
Treatment in women
It is important for women to determine the cause of the problem. In case of inflammation of the bladder, you need to take a course of antibacterial drugs, uroseptics and auxiliary medications. Such therapy will help improve the condition of the organ tissues, improve its functioning, and speed up recovery.
If a tumor process is detected, radiation therapy is prescribed. For urolithiasis, drug therapy or surgery can be used. If an STD is detected, antibiotics are prescribed and you will need to visit an additional gynecologist and venereologist.
Therapy
A set of therapeutic measures is carried out after the root cause of the disease has been established. Conservative treatment with anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents is indicated for infectious processes, surgical treatment is indicated when progressive tumors, adhesions or scar changes are detected in the sphincter of the bladder.
For chronic prostatitis, urologists can prescribe a course of physiotherapy: ultrasound, massage, electrophoresis. If urine stagnates and is poorly excreted due to narrowing of the urethra, doctors perform bougienage (stretching it with air using a special instrument). In case of hormonal disorders, replacement therapy, dietary nutrition and moderate physical activity will help restore the previous urine pressure.
By treating the underlying disease, patients can restore normal functions of the genitourinary system.
Complications
Those patients who do not take any measures to treat difficult urination are at risk. Chronic pain may appear and infection may spread to other organs.
Possible complications:
- constant discomfort;
- decreased libido;
- infection of other organs;
- urinary retention;
- intoxication of the body;
- decreased fertility;
- infertility.
Timely treatment is the key to a full recovery.
Prevention
To avoid long-term drug therapy, you should start taking care of your health right now.
Preventive measures:
- sports moderate loads;
- rejection of bad habits;
- balanced diet;
- regular sex life without frequent changes of partner;
- temperature regime of the genital organs;
- stable emotional state;
- preventive examinations by doctors.
Don’t put off going to the urologist; tell us about the problem now to prevent complications from developing.
Preventive measures
To avoid such an unpleasant illness. Like sluggish and difficult urination, you need to follow fairly simple rules. Lead a healthy lifestyle. Maintain personal hygiene to avoid the development of inflammatory diseases of the external genitalia. Protect yourself when having sex, especially if you are unsure of your partner, since strangury is often caused by sexually transmitted diseases.
It is very important not to sit at home and try to deal with the symptom on your own, but to immediately consult a specialist for advice, since strangury is just a symptom that can indicate a serious illness, and the sooner you are examined, the more effective the treatment will be. Take good care of your body and be healthy!