Rare urination in a child is a consequence of kidney disease or has an extrarenal origin.
Rare urination in infants is especially dangerous. A child with such problems should be examined.
Rare urination in a child is a symptom that is often underestimated by parents, as a result of which the diagnosis and initiation of treatment for diseases that can lead to disability in the child are delayed.
The causes of rare urine loss may be extrarenal pathologies, kidney and urinary tract diseases. A healthy child, on average, urinates about 20 times a day if he is not yet 6 months old, about 16 times - from six months to 12 months. From one to three years of age, children pee 10 to 12 times a day, with normal drinking regimen. After three years to nine - 7 times, and daytime diuresis predominates. From nine to fourteen children urinate 6 times a day.
Changes in the drinking regime, loss of water and sodium during diarrhea and vomiting, disturbance of water-salt balance during burns, and a drop in circulating blood volume during blood loss are extrarenal causes of rare urination in children. Renal factors include kidney diseases: glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis, chronic renal failure, tuberculosis and kidney tumors.
What kind of urination in children is considered rare?
When looking for the reasons for rare urination in a child, you should start with an understanding of the process itself and its norms.
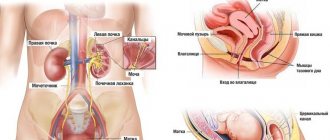
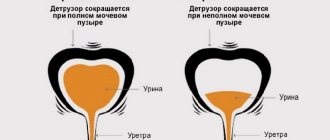
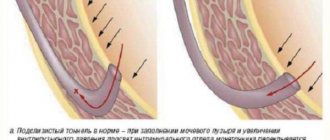
Urination is the process of filtering and removing urine from the body through voluntary muscle contraction and emptying the bladder. There are two important processes in urination - filtration and absorption (suction). The quality of urination depends on the activity and coherence of these processes.
The frequency of urination varies among different age groups. Human kidneys are one of the few organs that can develop outside the womb. The renal cortex and medulla can develop over several years, and the above-mentioned processes of absorption and filtration occur with their own characteristics in each age period.
To understand the facets of pathology, you need to understand what is considered normal. According to data adopted by the WHO (World Health Organization), the norms for urination in children are as follows.
| 1 - 5 days of life | 4 — 6 |
| Up to 6 months | 20 — 25 |
| 6 -12 months | 15 — 16 |
| 1 -3 years | 10 — 12 |
| 35 years | 7 — 10 |
| 5 -7 years | 7 — 10 |
| 7 - 9 years | 7 — 9 |
| 9 – 11 years | 5 -7 |
| 11 – 13 years | 5 — 7 |
Accordingly, a decrease in the frequency of urination compared to the lower limit of the age norm can be considered rare urination.
Why might urinary frequency change?
When considering this issue, it is necessary to highlight two main criteria - the child’s age and physiology. If everything is relatively clear with the first, then the second may raise questions.
The physiological nature of the problem of rare urination is caused by reasons not related to the child’s illnesses. Pathological is the opposite of physiological, indicating the presence of a disease.
Further, the causes of rare urination in children will be considered from the point of view of both criteria.
Physiological reasons.
- During the neonatal period and infancy, when the child is fed with single-component feeding (milk or formula), the reason for rare urination may be the increased fat content of the mother's milk. High-fat milk can also cause infrequent bowel movements in babies. The only effective way to avoid such problems is to regularly change the nursing breast. Primary milk, that is, milk from the “new” breast, is the least fatty. Additional soldering is also acceptable.
- In the period from 6 months and beyond, the cause may be either a physiological change in the rhythm of urination in a child or a violation of the diet. In the latter case, you need to adjust the calorie intake and the amount of fluid consumed.
Pathological reasons.
- Kidney diseases, both congenital and acquired. Parents, as a rule, learn about congenital pathologies in the first months. And acquired diseases include infectious diseases. In addition to rare urination, pain, burning, itching, and pain in the lower abdomen may be observed. These diseases are treated according to the cause that causes them.
- Infectious diseases of the urinary tract or mechanical blockage of the ureters (presence of stones in the kidneys and urinary tract). They are characterized by intermittent rather than rare urination in the child. Additional symptoms are the same as for inflammatory processes in the kidneys.
- Long forced abstinence from urination. After it, a reflex spasm of the bladder and urinary canal occurs, which causes urinary retention in children. Often this condition goes away on its own, but if it lasts a long time and causes severe pain, catheterization of the bladder is resorted to. In this case, painful urges and tension in the walls of the bladder, felt as a spasm, may occur.
- Neurological and mental disorders. Thus, hysterical seizures can cause both urinary incontinence and acute retention. Elimination of the seizure or neurological syndrome resumes spontaneous urination. In this case, symptoms characteristic of neurological pathologies will be observed - tics, paralysis and paresis. With mental disorders, disturbances of consciousness and behavior immediately catch the eye.
- High body temperature, leading to dehydration, and as a result, rare urination. Insufficient fluid replacement when it is lost will not allow the body to get rid of toxins.
- Problems with urination in children can also arise due to injuries to the spinal cord and brain (concussion, fracture). In such cases, the child is given a bladder catheter for the entire period of recovery and treatment of the injury.
What tests are prescribed for children with rare urination?
For urinary disorders in children, a pediatrician, nephrologist or urologist should order examinations to determine the causes and make a diagnosis.
The following tests are prescribed:
- a general urinalysis determines the amount of fluid, its acidity, the presence of sediment, salts, glucose, leukocytes and erythrocytes, which allows us to judge the probable nature of the pathology;
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko allows you to identify the source and localization of the infectious process in 1 ml of urine;
- A general blood test helps determine the state of the immune system in general terms, as well as the presence of inflammatory processes in the body;
- Bacteriological culture of urine if a bacterial infection is suspected allows one to identify the pathogen in order to prescribe the necessary treatment.
In addition, research is being conducted:
- measuring the number of urination acts per day. This is the first thing parents or the child himself pays attention to;
- measuring the volume of a single portion of urine, which allows you to determine the deviation from the age norm;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs and ultrasound of the kidneys, which helps to see structural changes in the kidneys, bladder and urinary tract;
- voiding cystourethrography - this innovative method allows you to visualize congenital malformations of the bladder, kidneys, and ureters;
- scintigraphy to detect tumors in the kidneys and urinary tract.
Features in pregnant women
Rare urination during pregnancy is a very alarming symptom.
The physiology of pregnancy involves a significant increase in the load on the kidneys and a number of other organs, so as the duration of pregnancy increases, the disorder will worsen.
A dangerous consequence of infrequent urination during pregnancy is the accumulation of decay products and toxins in the body, an imbalance of water and salt balance - this is detrimental to both the mother and especially the child. Ignoring the problem can lead to the most tragic consequences, so in this case the help of a qualified doctor is necessary.
What can parents do?
If urinary retention is not painful, you can try to provoke it with warm sitz baths and the sounds of flowing water.
If urination does not occur, you should call an ambulance to have the bladder catheterized.
If a child has urinary disorders, the first thing you need to pay attention to is nutrition and water consumption. Not every liquid is equal to water, so it is worth teaching your child to drink regular clean water regularly. Fatty and spicy foods, as well as fast carbohydrates and coffee, which tend to retain fluid in the body, should be excluded from the diet.
Urinary problems in children are not a cause for panic, but a cause for concern. Therefore, timely contact with a specialist is the main and first thing parents should do when such problems arise.
Author: Sukhorukova Anastasia Andreevna, pediatrician
Frequency of stool and urination in newborns
We recommend reading: What to do if your child feels pain, stinging and burning when urinating
source: mama66.ru
At different ages, children may experience rare urination, and parents begin to sound the alarm: what’s wrong with the baby? Most often, panic turns out to be completely in vain: a small organism can simply adapt to a new age regime, because it grows, its food becomes more solid - accordingly, the number of urinations per day becomes less.
But sometimes there are cases when the cause of this phenomenon is a serious pathology of the urinary system, which requires long-term treatment. Therefore, first of all, you need to find out what factor caused the decrease in urine output per day.
Prevention of urinary retention
There are no targeted measures to prevent pathology.
A healthy and active lifestyle, proper nutrition, and avoidance of injuries will help you avoid the disorder. Monitor your body's water balance; in case of a cold or other illness accompanied by fever, drink more fluids.
If a symptom first appears, contact a specialist, do not self-medicate! Call the phone number listed on our website and make an appointment. Our urologists will definitely help you!
Causes of rare urination in children
The reasons for this phenomenon can be very different. Often, infrequent urination in an infant occurs due to the high fat content of the mother's milk. In such cases, the nurse must follow a certain diet in order to dilute the natural food for the baby. The second most common reason for this phenomenon is a decrease in urine output per day in accordance with age standards that every mother should know:
The third common cause of rare urination is improper drinking regimen. It often happens that a small body does not give signals that it needs liquid: the child does not ask to drink at all. In this case, it is necessary to regularly remind him that he needs to do this and even force him. If there is neither the fat content of breast milk, nor the age limits indicated in the table, nor the drinking regime, rare urination may be dictated by more serious reasons:
- pathology of the kidneys, which partially lose the ability to produce the required amount of urine;
- diseases of the ureters, their partial blockage;
- damage to the bladder (often occurs when abstaining from emptying it for too long);
- uncontrolled, improper use of diuretics;
- hysteria, hypochondria, nervous fever;
- excessive distension of the bladder;
- back or brain injuries;
- stones, sand in the kidneys or bladder;
- urethral pinching;
- new formation of blood vessels;
- urinary tract infections.
Rare urination in a child caused by these diseases and pathologies will require long-term drug treatment, including surgical intervention. Therefore, it is so important to carefully monitor the condition of a small organism and recognize trouble in time.
Features of pathology in women
When the normal daily volume of urinary fluid decreases by 30% or more from the norm, doctors diagnose oliguria in women.
Rare urination in women (oliguria) may be due to the development of pathologies specific to the female body.
Among the relevant disorders are oncological formations in the female genitourinary organs (uterus, ovaries), the presence of hormonal imbalance during menopause, uterine bleeding, nervous disorders and other pathologies.
If female oliguria is physiological in nature, it is potentially not dangerous and can be eliminated by correcting the drinking regime and special therapy.
The pathological type of oliguria should cause serious concern. It is a symptom of many serious diseases that require long-term treatment, sometimes surgery.
In any case, a visit to a specialist is important.
In Moscow, experienced urologists work in our center. They will conduct a diagnosis and determine the most effective way to combat the disease.
| Code | Name | Price |
| 03.00 | Initial appointment with a urologist (candidate of medical sciences) | 2,000 rub. |
| 03.04 | Repeated appointment with a urologist (candidate of medical sciences) | 1,200 rub. |
| 03.60 | Initial appointment with a urologist (MD) | 5,000 rub. |
| 03.61 | Repeated appointment with a urologist (MD) | 3,000 rub. |
| All prices of the men's and women's health clinic | ||
Symptoms of problematic urination
A serious illness can be suspected if the following symptoms are present, which usually accompany infrequent urination in such cases:
- the urine stream is thin and has low pressure;
- urine is released in drops;
- this process becomes possible only with some specific, specific position of the body;
- burning, soreness;
- The urge to empty the bladder is felt, but is accompanied by pain and a feeling of strong pressure.
If such problems arise, it is recommended to immediately contact a pediatrician, who will be able to redirect parents to a more specialized specialist or independently identify and treat the underlying disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you experience abnormalities in the process of urination (little urine and rare urination), even if this situation is not accompanied by additional alarming symptoms, you should still contact a urologist and undergo a diagnostic procedure.
The examination will determine the cause and nature of the pathology related to the problem, explain why infrequent urination occurred, and the doctor will be able to determine the optimal treatment path.
Diagnosis in our women's and men's health clinic is carried out comprehensively.
The first and mandatory stage of diagnosis is a medical appointment, which involves a conversation with the patient and a physical examination. During communication with the patient, the doctor finds out how long the symptom has been onset, the presence of additional pathologies, in particular, chronic diseases of the genitourinary organs, what operations the patient has undergone and what medications he has taken recently.
The further diagnostic process includes a number of laboratory and instrumental methods for examining the patient:
- conducting a general clinical analysis of urine and blood;
- bacteriological examination of smears from the genitourinary system;
- ultrasound examination of the genitourinary system;
- X-ray of the pelvic and abdominal organs (general and excretory contrast urography).
If necessary, additional methods can also be used in the form of biochemical and hormonal analyzes of relevant biological media, as well as instrumental research methods (tomography, urocystoscopy, MRI and others).
In our center, diagnostics are performed using the latest generation equipment, and the examination results are guaranteed to be accurate.
All doctors undergo strict selection. They are professionals, polite and attentive to their patients.
The results of the treatment are felt after the first visit. We guarantee you a solution to any problems
We carry out diagnostics using modern European devices. Diagnostic reliability - 99%
Our doctors treat everyone with care and understanding. Appointment with a doctor is completely confidential
Treatment
The main therapy is to eliminate the factors that provoked the disease. An individual approach is applied to each little patient. The main methods of treating bladder pathologies that result in rare urination are:
- 1. Sitz bath
At the very beginning of treatment, the water temperature of such a bath is 26 °C, but gradually it is increased to 30 °C. For inflammatory processes, sitz baths are prescribed once a day for 15 minutes.
- 2. Compresses
Compresses may be prescribed to the location of the bladder. Sometimes more extensive compresses may be prescribed for the entire body. If there is an inflammatory process in the body, soothing compresses are applied to the baby’s lower abdomen.
- 3. Therapeutic diet
This condition in children may also depend on their diet, so with this pathology it is recommended to follow a certain diet. Firstly, food should not irritate the walls of the stomach. Secondly, you need to let your child drink as much liquid as possible.
- 4. Douching
Douching is prescribed to a child only by a doctor only if rare emptying of the bladder is accompanied by pain and discomfort. If the disorder is severe, this procedure is performed using a catheter in a hospital.
If all of the above treatment methods turn out to be ineffective, and the baby’s condition does not change or improve, the only way out can only be surgical intervention (in case of serious pathology of the genitourinary system). But to confirm the diagnosis, numerous laboratory tests, tests, ultrasound and other diagnostic methods are first carried out. However, most often, rare urination in a child does not have such serious reasons and very soon goes away with the normalization of the drinking regime and proper nutrition.
Doctors' recommendation
There are a number of conclusions about the dangers of washing cosmetics. Unfortunately, not all new mothers listen to them. 97% of shampoos use the dangerous substance Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) or its analogues. Many articles have been written about the effects of this chemistry on the health of both children and adults. At the request of our readers, we tested the most popular brands.
The results were disappointing - the most advertised companies showed the presence of those very dangerous components in their composition. In order not to violate the legal rights of manufacturers, we cannot name specific brands. The Mulsan Cosmetics company, the only one that passed all the tests, successfully received 10 points out of 10 (check out). Each product is made from natural ingredients, completely safe and hypoallergenic.
If you doubt the naturalness of your cosmetics, check the expiration date; it should not exceed 10 months. Be careful when choosing cosmetics, this is important for you and your child.
source: www.vse-pro-detey.ru
Does your child rarely go to the toilet? This phenomenon occurs in children of all ages. Often the phenomenon can be eliminated after minor adjustments to lifestyle and nutrition. But it happens that rare urination becomes a sign of a serious illness. In what cases can a phenomenon be considered normal, and when does it indicate a pathology of the urinary system? What can parents do?
General principles of therapy
In cases where a child urinates little, treatment depends on the cause of the disorder. Therapy should be aimed at eliminating the factors that caused the pathology.
If the cause of rare urination is bladder disease, the following methods are used:
- sitz baths. Initially, the water temperature should be 26 degrees. It should be gradually increased to 30 degrees. A sitz bath can be done for 15 minutes once a day;
- often during inflammatory processes, soothing compresses are prescribed to the area where the bladder is located;
- for rare urination, a therapeutic diet is also important. It is necessary to feed the child food with a low salt content. You also need to give your baby plenty of fluids to drink;
- if rare urination is accompanied by pain and discomfort, the doctor may prescribe douching;
- in severe cases, a catheter is used to remove urine.
If these methods of therapy are ineffective, and the child’s well-being does not improve, then surgical intervention may be required.
To confirm the need for surgery, the patient needs to undergo an examination, namely, take all tests and have an ultrasound.
If no pathologies from the urinary system are detected, it is recommended to take the following measures:
- The baby should be allowed to drink as much as possible, especially in the hot season and during active physical activity;
- exclude salty foods from the diet;
Only a pediatric urologist should treat diseases of the urinary system. Timely contact with a specialist will prevent the development of complications and the transition of the disease to a chronic form.
Norms of urination in a child per day
Before panicking, parents should find out what can be considered the daily urine output rate for a child.
The authoritative pediatrician A. Papayan, back in Soviet times, compiled a table with the norms of urine output according to the age of the child. This table still serves as the main guideline for many pediatricians when examining a child for the presence (absence) of pathology.
| Child's age | Daily urine volume, ml | Daily number of urinations | Volume of urine per urination, ml |
| 0-6 months | 300-500 | 20-25 | 20-35 |
| 6-12 months | 300-600 | 15-16 | 25-45 |
| 1-3 years | 760-820 | 10-12 | 60-90 |
| 3-5 years | 900-1070 | 7-9 | 70-90 |
| 5-7 years | 1070-1300 | 7-9 | 100-150 |
| 7-9 years | 1240-1520 | 7-8 | 145-190 |
| 9-11 years | 1520-1670 | 6-7 | 220-260 |
| 11-14 years old | 1600-1900 | 6-7 | 250-270 |
You need to worry if a child goes to the toilet much less often than his peers, although in this case the reason may not be dangerous at all.
The daily amount of urine during pregnancy is normal
In order to draw conclusions about possible violations, you need to have a good idea of what is called normal, in this case, the standard volume of urination. Medical practice considers this standard to be 1500 ml of urine per day. This volume will depend on the amount of liquid you drink per day, as well as on a number of other factors. Approximately ¾ of what you drink can be excreted in the urine; if this ratio is significantly less, then we are talking about urinary retention during pregnancy.
If there is too much urine, more than two liters per day, this can also be caused by natural reasons: in the second half of pregnancy, the bladder feels the pressure of the growing uterus. The second probable cause is inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs. Finally, we can talk about polyuria - exceeding the daily norm, or even urinary incontinence during pregnancy. It is caused by a lack of protein foods, as well as diseases such as diabetes mellitus, nutritional dystrophy, renal failure, epilepsy, and a number of diagnoses associated with dysfunction of the nervous and cardiovascular systems.