Category: Men's health
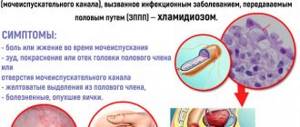
Painful urination and pathological discharge from the urethra in most cases indicate the development of urethritis in a man. Most often, such symptoms are caused by infection with pathogenic microorganisms from a sexual partner.
However, sometimes the disease is not associated with sexual activity, but is the result of primary inflammation of other parts of the genitourinary system.
Self-administration of antibiotics for urethritis is not advisable: for a specific infection, certain types of antibacterial agents are prescribed, and in some cases, self-medication can lead to chronicity of the process and quite serious complications.
Causes of urethritis in men
Pathogens enter the urethra from the skin, from the intestines, and also during sexual intercourse (anal and vaginal).
As long as the body’s immune system in general and the walls of the urethra in particular cope with this, everything is fine. But as soon as a decrease in the protective functions of the body occurs, urethritis will immediately make itself felt with its first manifestations.
Here are the main factors that can provoke the disease.
- medical manipulations. This could be surgery, bladder catheterization, smear collection, etc.;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- small amount of water in the diet. The fact is that regular urination helps wash away bacteria. If the break reaches several hours, then the risk of inflammation of the urethra increases significantly.
- Eating spicy, pickled, salty, sour foods, as well as alcohol. In large quantities, these products cause substances that irritate the walls of the canal and bladder to penetrate into the urine. This will not only cause the progression of existing urethritis, but also its emergence “from scratch.”
- irregular sex;
- a large number of partners;
- hard physical labor;
- urolithiasis disease. Stones passing through the urethra can also injure the walls;
- mechanical damage to the penis;
- hypothermia (one-time, and especially systematic).
It is better for every man to prevent prostatitis so that one day he does not encounter this problem.
Weak potency, what to do? How to fight? The answers are here: man-up.ru/zdorove/povyshenie-potentsii/pochemu-slabaya-potentsiya-osnovnye-prichiny.html.
No man is immune from the effects of these factors. Therefore, it is important to know how urethritis begins, so as not to delay its treatment.
How to cure urethritis?
Treatment of the disease mainly depends on the specific cause that provoked it:
- Bacterial, gonorrheal. A positive result is achieved when using antibacterial agents of the cephalosporin group. In addition, it is possible to use Tetracycline, Kanamycin, Erythromycin. Long-acting medications (Bicillin) are prescribed in short courses. In case of complications of gonorrheal pathology with other infections, several antibiotics can be used at once (Gentamicin, Azithromycin). Vitamins and immunomodulating agents are also prescribed.
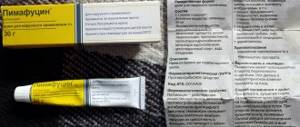
- Candida. The main means for eliminating candida are systemic antifungal drugs (Nystatin, Fluconazole, Pimafucin, etc.).
- Mycoplasma. Inflammation of the urethra is treated with tetracyclines, fluoroquinones, and macrolides. Doxycycline (tetracycline group), Clarithromycin (macrolides) give good results. In this case, immunostimulating agents are also used.
- Trichomonas. Male diseases are treated with Metrogyl, Metronidazole, Trichopolum. For Trichomonas chronic urethritis, antibiotics are added.
- Viral. In the case of this form of urology urethritis, therapy is carried out with antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Famciclovir, Riboverine, Gerpevir). The sooner treatment is started, the faster the recovery will occur. It makes no sense to use antibiotics, because... They have no effect on viruses.
- Chlamydia - the main antibiotic in the treatment of this form is Azithromycin. If the wrong choice of medication is made, chlamydia urethritis causes dangerous complications (infertility, epididymitis, inflammatory pathologies, Reiter's syndrome). If Azithromycin is individually intolerable, Doxycycline, Erythromycin, Clarithromycin, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin, etc. are used. Immunostimulants and vitamins are also used.
Various specific urethritis require joint treatment of two sexual partners.
Discharge
Normally, a man experiences the following discharge from the penis: urine, semen, lubricant (during sexual arousal).
Here's what you should be wary of:
- blood is a signal of mechanical damage (urgent medical attention is required);
- prostate secretion (can be released in men with chronic prostatitis after sexual intercourse or during bowel movements);
- mucus (discharge caused by urethritis).
Sometimes it is difficult to identify inflammation of the urethra without special examination and testing, since it can be asymptomatic. But this is extremely rare.
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. If this is not urethritis, then it is clearly a violation of some other nature.
Main signs of male urethritis
The first manifestations of urethral inflammation are detected 2-3 days after infection. Often the clinical picture develops over several months.
The main manifestations of urethral inflammation include:
- frequent, painful urination;
- the appearance of pathological impurities in the ejaculate or urine;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- increased sensitivity of the penis;
- itching, burning in intimate places, which intensifies with urination;
- pathological discharge from the urinary canal of purulent or mucous consistency (does not always occur);
- painful sexual intercourse.
Manifestations of male urethritis are not always pronounced and obvious. Considering the nature of the pathogen that caused urethritis, the course of the pathology can vary from asymptomatic development of the disease to severe manifestation of symptoms.
How to treat urethritis?
The first thing the doctor will do is refer you for an examination. Before treatment, you need to determine the causative agent of urethritis . Therefore, the patient will be tested for the presence of sexually transmitted infections, as well as opportunistic ones. In addition, it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the bladder, scrotum, and prostate gland for complications.
Then direct treatment is prescribed, which should solve 2 problems:
- elimination of infection;
- restoration of the walls of the urethra.
To solve the first problem, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. They are taken together with vitamins, enzymes and immunomodulators to minimize the side effects of the medication.
for administering medication into the urethra are also prescribed . With this method, up to 80% of pathogens die. In addition, the active ingredients in such drugs for urethritis in men are also aimed at restoring damaged walls.
We deliberately do not give the names of the main drugs for urethritis in men, since ONLY the attending physician should prescribe them based on the data of a diagnostic study.
Diagnostics
With signs of urethritis, contact a urologist or andrologist. First, the doctor conducts an external examination of the penis, assesses the condition of the sponges and the nature of the discharge, then palpates the urethra. By palpation, you can detect soft areas of inflammation, painful compactions, and protrusions.
The main material for laboratory research is scraping from the urethra. It is taken after 4 hours of abstaining from urination. To diagnose chlamydia, it is recommended to use two methods: PCR and PIF.
What tests should be taken if you suspect urethritis, says urologist, dermatovenerologist Sergey Gennadievich Lenkin
After taking a smear, the patient gives a two-glass urine sample according to Thompson. If threads of pus and cloudy flakes are present only in the first glass, then the inflammation is localized in the anterior urethra. If red blood cells are detected, an endoscopic examination (urethroscopy) is prescribed.
Other diagnostic methods: palpation and ultrasound of the prostate, secretion analysis, general analysis of urine and blood, uroflowmetry, urethrocystoscopy. Chronic inflammation of the urethra is often accompanied by sluggish pyelonephritis, prostatitis, diabetes mellitus, and paraurethral fibrosis. These pathologies are in most cases discovered during diagnosis.
Complications
Don't delay visiting a urologist . Otherwise, the situation may worsen and the inflammatory process may further spread to the scrotum, bladder, and prostate gland.
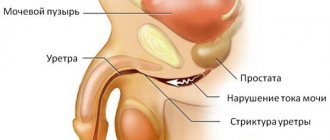
Chronic urethritis in men without appropriate treatment will lead to narrowing of the urethra , and as a result, to a decrease in urine pressure and the further impossibility of draining it. Severe cases will require surgery.
Another trouble that you may encounter is inflammation of the seminal tubercle. It represents the point of the canal at which the opening of the ejaculatory ducts of the seminal vesicles occurs. And this disease is accompanied by very severe pain, spreading to the abdomen, thighs, scrotum, and perineum.
Symptoms of acute and chronic urethritis
Acute urethral inflammation appears several days after infection and is characterized by pronounced symptoms. In this case, pain during urination, itching, burning of intimate places and pathological discharge are observed.
Chronic urethritis is characterized by less pronounced signs of inflammation. The chronic form of urethral inflammation is characterized by the following pathological disorders and abnormalities:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- scanty or absent urethral discharge;
- discomfort during urination and ejaculation;
- constant itching in the area of the urinary opening.
Exacerbation of chronic urethritis occurs against the background of decreased immunity, with excessive consumption of spicy foods and alcoholic beverages, as well as insufficient fluid intake.
Diagnosis
In order to diagnose the disease, it is necessary to conduct a urine test. This is done using the three-glass test method. Morning urine is collected in turn into 3 sterile containers. It is important to remember that the presence of a disease such as urethritis is determined by 1 portion of urine.
Typically, the following result is achieved:
- The first portion of urine has a cloudy structure. It contains a large number of leukocytes, since there is an inflammatory process in the cavity of the urethra.
- The second portion contains much fewer leukocytes.
- In the third portion they are completely absent.
The material obtained from the urethra for research is analyzed by bacterial culture, and the degree of sensitivity of the flora to antibiotics is also determined. If the case is complex, then specialists use polymerase chain reaction (PCR). With its help, it is possible to determine the type of pathogen by DNA, even with a latent course of the disease. For analysis, a tissue sample is taken from the wall of the urinary canal using a probe. This is a very difficult procedure, since the female urethra is very small. This method is necessary in order to detect herpetic or chlamydial urethritis.
To perform ureteroscopy, local anesthesia is used.
Often, specialists will prescribe antibiotics a week before the procedure to prevent further spread of the infection.
Using ultrasound, you can determine cystitis and identify disease in the pelvic organs.
There is also a radiopaque examination using voiding cystourethrography. The introduction of a contrast agent into the cavity of the bladder makes it possible to take photographs. Using these images, you can detect poor patency, neoplasms, adhesions and similar defects. Women must undergo examination by a gynecologist. This is necessary to exclude inflammatory diseases of the cervix and genital organs.
Why does urethral disease occur?
Urethritis is divided into 2 main types:
- non-infectious origin;
- caused by infectious agents.
Diseases of non-infectious origin occur:
- in case of mechanical damage to the integrity of the mucous membrane by stones, the movement of which is characterized by urolithiasis;
- injury from a cystoscope, catheter, etc.;
- allergies;
- malignant tumors;
- diseases of the genital organs;
- venous stagnation in the pelvic organs.
Infectious diseases arise as a result of pathogens entering the body through sexual contact:
- gonococci;
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasmas;
- herpes viruses.
Treatment used
Despite the fact that it brings a woman very uncomfortable and painful sensations, there is no need for treatment in a hospital setting. The mild form of the disease is treated on an outpatient basis.
Initially, you should undergo an examination prescribed by a specialist. During the examination, you can determine the cause of the disease, the type of pathogen, and select the most suitable, effective anti-inflammatory drug. When infection occurs through sexual contact, not only the woman, but also her sexual partner should be treated.
- it is important to avoid intimacy until complete recovery;
- limit physical activity as much as possible;
- prevent hypothermia of the feet;
- eat right, or rather: exclude salty, spicy, smoked foods and, of course, alcoholic drinks from the diet;
- regulate the amount of fluid consumed: throughout the day you need to drink about two liters of water in the absence of diseases associated with fluid retention in the body;
- Eat fermented milk and more fruits and vegetables every day.
As for drug treatment, doctors prescribe the use of a wide variety of drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect, prescribe injections, tablets, vaginal suppositories, douching, etc.
The antibiotic must be taken for 5 to 10 days. The exact dosage is determined by the doctor, taking into account the degree of the inflammatory process, body weight, and age of the patient.
Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. It is especially contraindicated to use antibiotics longer than prescribed, since microorganisms develop resistance to the drug, and then the medicine does not have the desired effect.
Treatment tactics are determined by the type of pathogen:
- for a disease caused by a fungus, antifungal drugs are prescribed;
- if the disease appears due to mycoplasmas, use drugs of the imidazole group.
To enhance the effect of medications, experts recommend using them in the form of suppositories. Due to the fact that the suppositories are injected directly into the area of inflammation, their composition is completely absorbed by the pelvic vessels. Thus, there is an anti-inflammatory effect on nearby organs.
In addition to potassium permanganate, you can use a decoction of herbs that have an anti-inflammatory effect. Douching with antiseptic agents is recommended.
Urethral dystopia in women and its treatment
One of the most common diseases affecting the fair sex is cystitis, an inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
It is associated both with the negative influence of external factors, for example, prolonged exposure to low temperatures, and is caused by internal problems. A common cause of a chronic recurrent process is urethral dystopia in women.
This is a disorder that is an incorrect location of the urethral outlet on the anterior wall of the vagina.
This pathology is an anomaly of intrauterine development. The exact reasons for its occurrence are currently unclear. Women whose urethra opens into the vagina constantly suffer from cystitis after coitus, as the urinary tract becomes infected.
In addition, the inflammatory process also affects the reproductive system. Conservative methods in the treatment of urethral dystopia in women do not give the desired result, since they do not eliminate the main cause of the symptoms of the lesion.
The most effective are radical surgical techniques that allow you to restore the natural location of the external opening of the urethra.
Causes of pathology
This problem relates to congenital anomalies and is formed in utero. To date, the factors causing the occurrence of this disease are unknown.
In many cases, dystopia of the external urethral opening remains undiagnosed until adulthood or before the onset of active sexual life, since it is intimate intimacy that most often provokes the appearance of the clinical picture.
There is an assumption about the genetic component of the disease, but there is no evidence for this hypothesis yet.
Main features
In many cases, only one symptom of abnormal urethral location is detected - cystitis.
Inflammatory damage to the mucous membrane of the bladder is often initiated by sexual intercourse.
During sex, the incorrectly located end of the urethra is mechanically injured, which leads to the development of an ascending infection. The most characteristic clinical signs of this lesion are:
- Frequent urination, which causes significant discomfort to the woman. In this case, the bubble does not fill properly. The urge to go to the toilet occurs due to irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Painful urination is a key symptom with which representatives of the fair sex consult a doctor.
- In some cases, general weakness and a rise in body temperature are noted.
Along with cystitis, urethritis often occurs, as well as inflammatory lesions of the vulva and vagina. Urine is an excellent nutrient substrate for bacteria that normally inhabit a woman's genitals. Taken together, these symptoms significantly reduce the patient’s quality of life.
Diagnostics
Determining the presence of urethral dystopia using modern visual methods is not difficult. The process of confirming the disease begins with collecting an anamnesis, which contains complaints characteristic of the disease. To make a diagnosis, they also resort to a special O'Donnell-Hirschhorn palpation technique. It allows you to determine the exact location of the external urethral opening.
To exclude other concomitant ailments, blood tests and bacteriological tests are used. X-rays with contrast are also indicative.
It is carried out using special agents introduced into the bladder through the urethra. With its help, unique photos are obtained, which also help in determining localization.
In some cases, an endoscopic examination of the vagina is required, and a computed tomography scan is also performed.
Treatment
Conservative methods of combating urethral dystopia in women do not give lasting results. Even while taking anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs, cystitis and vulvovaginitis recur, especially if the patient has an active sex life.
The most effective treatment is surgery. It allows you to completely get rid of the problem and prevent the constant occurrence of post-coital inflammation of the bladder mucosa.
There are a number of contraindications to the procedure, but it is actively used to combat dystopia.
Preparation and performance of the operation
Before surgery, preliminary antibiotic therapy will be required. It allows you to reduce the possible risk of complications associated with infection of the urogenital tract.
An important condition for a successful operation is the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
They help combat swelling of the external opening of the urethra and vagina, which greatly facilitates the surgeon’s work.
Preparation also depends on the presence of other concomitant diseases in the patient. Since various anesthesia protocols are used to carry out the manipulation, from local to general, it will be necessary to undergo a number of examinations, as well as correct the violations identified during the diagnosis.
Surgical treatment of dystopia is reduced to raising the external opening of the urethra. To do this, the patient is placed on her back. The bladder is pre-catheterized, which greatly facilitates the surgeon’s further work. The operation is called transposition of the distal urethra.
A small incision is made 1 cm above the existing urethra, after which it is transferred to a physiological position. The remaining wound is closed with stitches.
If there are urethrogeminal adhesions, they are dissected during the operation, since they cause significant discomfort to the woman during intimacy and contribute to the development of vaginitis.
Indications and contraindications for surgery
The operation is performed in the presence of dystopia, accompanied by recurrent postcoital inflammation of the mucous membrane of the bladder. This type of treatment is the most effective.
Like any other surgical intervention, manipulation has contraindications. They are associated with exacerbation of chronic processes in the body and the presence of significant infection of the genitourinary tract. In such cases, preoperative examination is required, as well as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Transposition of the distal urethra is not recommended for nulliparous women. This is due to the characteristics of the reproductive system and its proximity to the urethra. As a result of surgical treatment, the elasticity of adjacent tissues decreases.
Such changes increase the risk of developing pathology during childbirth, as the mobility of the urethra decreases and the likelihood of injury increases.
There are even newer methods of treating dystopia of the external opening of the urethra. They allow not only to give the structure a physiological position, but also to cope with associated defects.
For example, with hypermobility of the urethra, which causes injury, and in some cases even partial obstruction, the structure is sutured to the pubic bone. For this purpose, a special technique of applying a ligature is used.
This procedure is not used very often, although it has obvious advantages.
When serious contraindications to full-fledged surgery are identified, injections of a biodegradable gel are practiced. The use of preparations based on hyaluronic acid is widespread.
The substance is used in cosmetology and minimally invasive surgery because it is well tolerated by patients. By introducing the gel into certain points, a kind of plastic surgery of the urethral outlet is performed, due to which it rises.
This manipulation is carried out under local anesthesia, and the drugs used for the procedure also include an anesthetic component.
The disadvantages of the technique include a temporary effect, and its duration varies due to the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. In some cases, hyaluronic acid injections are used as a “trial” treatment.
Reviews
Margarita, 26 years old, Astrakhan
She suffered from constant chronic cystitis, which worsened every time after sex, which made sexual life significantly more difficult. I went to see a doctor who diagnosed urethral dystopia. The decision was made to carry out the operation. After a comprehensive examination, surgery was performed and the symptoms disappeared.
Anastasia, 22 years old, St. Petersburg
Since the beginning of sexual activity, cases of cystitis have become more frequent. It was difficult to go to the toilet, and there was nothing to say about intimacy. I decided to see a doctor. I was diagnosed with urethral dystopia. The doctor prescribed antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and hyaluronic acid injections. Transposition surgery was recommended to be performed after the birth of the child.
Loading…
Source: https://ProSindrom.ru/urinariorum/distopiya-uretry.html
Structure of the urinary canal
The second name for the urethra (Latin) is urethra. The duct responsible for releasing urine into the external environment is located inside and looks like an elastic, soft tube. The walls of the tube consist of three layers:
- connecting outer layer;
- the middle layer is muscle;
- mucous membrane.
Male urethra
The length of the male urethra is much larger than the female one, the average length is about 20-25 cm. It is hidden and is divided into posterior and anterior segments. The anterior one is located away from the center, and the posterior urethra runs from the hidden opening to the cavernous body. The urethra in men can be visually divided into 3 components, described in the table:
| The structure of the urethra in men | |||||
| Sections of the urethra | Components | Location | |||
| Prostatic part |
| Duration 3 cm. The internal opening near the bladder is the beginning, then passes the prostate. At this point, small prostatic glands open into the canal | |||
| Membranous part |
| Duration 1–2 cm. Narrow and short, passes through muscle strips (urogenital diaphragm), forming a voluntary sphincter | |||
| Spongy part |
| Duration 1–2 cm. Narrow and short, passes through muscle strips (urogenital diaphragm), forming a voluntary sphincter | |||
The stationary parts of the urethra in men are the prostatic and membranous sections, the spongy section is the moving segment.
Features of the structure of the organ in women
The female urethra is open, its length is about 3-5 cm, and its width is 1-1.5 cm. The initial segment is located above the pelvic floor. Rushing forward, the female urethra passes the anterior wall of the elastic canal of the reproductive system (vagina) and the upper pubic bones. At the end of the female urethra, below the clitoris, is the external urethral meatus. The wide and short female urethra is located close to the vagina and anus, which makes women susceptible to inflammatory and infectious pathologies.
The inside of the canal in women is covered with mucous, collected in longitudinal folds, which make the diameter of the lumen smaller. Connective tissue consists of many elastic threads and a vaginal collection of veins of various sizes. Together they form an obstructing pad that promotes closure of the duct.
Treatment of urethritis with traditional methods
Traditional methods are not as effective as they should be. That is why experts insist on drug therapy. Despite this, there are some herbs that complement the action of the drugs, and such complex treatment can achieve success. For this purpose, herbs and plants that have diuretic, antimicrobial, and antispasmodic effects are used.
The following should be consumed when eating:
- lingonberry, carrot or cranberry juice, free of sugar and preservatives;
- from fresh herbs - parsley, as well as beets;
- decoction of parsley, linden, cornflowers, black currants.
Microflora
The process of microflora development begins during human birth. Once on the skin, microbes penetrate inside and are distributed into the internal organs, their membrane. Microorganisms remain on the mucous membrane; urine and internal secretions do not allow them to move further. Additional protection is provided by the ciliated epithelium. It is those living microorganisms that attach to the mucous membrane that form the innate microflora.
Features of female microflora
The number of microorganisms in a woman is greater than in the body of the stronger sex. This difference is influenced by the structure of the urethra, gender characteristics and location. 90% of a healthy woman's microorganisms secrete acid. This is necessary to maintain an acidic environment, since as a result of the development of an alkaline environment, there is a risk of developing inflammatory processes. From birth, bifidobacteria and lactobacilli predominate. As the girl grows, the microorganisms change and coccal flora appears.
Features of male microflora
The microflora includes staphylococcus, streptococcus, and corynebacteria. From the moment of its inception throughout its existence, it does not change. The urethral urethra is characterized by a neutral alkaline environment, favorable for the life and development of staphylococci. This is the environment needed for sperm maturation. The set of microorganisms does not perform important tasks, but can change, which affects the development of pathological complications.
The normal microflora of the urethra includes commensal bacteria (staphylococcus), rod-shaped bacteria, ureaplasma, and neisseria. Candida, chlamydia, and ureaplasma fungi are much less common. Microorganisms transmitted through sexual contact are considered particularly dangerous.
Routes of infection
There are 3 ways by which infectious pathogens enter the urethra:
- contact, which occurs during the body’s transportation of urine from the kidney, where the epicenter of the infection is located, to the bladder;
- sexual – in the process of intimacy with a sick partner;
- hematogenous - the infection enters from inflammatory foci of chronic diseases through the blood circulation.
Urethritis is classified according to the nature of its distribution:
- primary - develops if an infectious bacterium enters the urethra;
- secondary - pathogenic microbes enter during the blood circulation from the pelvic organs, intestines or other location of the chronic focus.