The role of laboratory tests
Disturbances in the production of hormones lead to the development of a number of diseases, which often pose, in the absence of timely and adequate treatment, a threat to the health and life of the patient.
Diagnostics makes it possible to identify the disease in the early stages, when the pathological process can still be controlled without compromising the patient’s quality of life. Tests for the adrenal glands are prescribed by an endocrinologist. You can also get a referral for a study of the hormonal system from a therapist or specialized specialists - a gastroenterologist, a pulmonologist. The names of adrenal hormone tests for women are indicated by the gynecologist with whom the patient is treating an existing pathology or is registered for pregnancy. Research is carried out in the following cases:
- if a pathological process in the body is suspected, causing a decrease or increase in hormone production;
- when diagnosing diseases of the urinary, cardiovascular, respiratory and other systems;
- in obstetric and gynecological practice to monitor the process of fetal development and the course of pregnancy;
- to identify endocrine diseases.
Also, regular monitoring of hormonal levels allows you to determine the effectiveness of the therapy and, if necessary, make timely adjustments.
To check the adrenal glands, you should donate venous blood, daily urine or saliva to the laboratory. The test is called an analysis of the hormones dehydroepiandrosterone, cortisol, aldosterone and catecholamines.
How to examine the adrenal glands using instrumental methods
Standard clinical instrumental methods for examining the adrenal glands are indicated for suspected tumors, hyperplasia and other structural changes in gland tissue.
Ultrasound
No special preparation is required to perform an ultrasound examination. The method is informative, with the exception of patients with severe obesity.
The monitor clearly visualizes the inflammatory process with changes in the contours and boundaries of the organ, benign and malignant tumors. The doctor determines the structure of the glandular tissue, the degree of its echogenicity, and abnormalities in the development of the organ.
Scintigraphy
Scintigraphy is a hardware method for examining the body from the field of nuclear medicine. Substances (radioactive isotopes) capable of emitting light are injected into the patient's body. The monitor displays a color two-dimensional image of the internal organs. The radiopharmaceutical is eliminated from the body naturally. Absorption of the radioactive substance by the adrenal glands occurs within 3-5 days. Therefore, diagnosis is not carried out immediately after administration of the substance.
During the scan, the structure is checked for hyperplasia (overgrowth of glandular tissue). Tumors are also detected.
CT scan
CT allows you to visualize the size and examine the structure of organs. From the image you can find out about the presence of diffuse hyperplasia, neoplasms, and involvement of nearby lymph nodes in the pathological process.
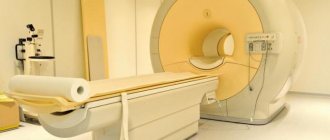
Magnetic resonance imaging
To achieve accurate examination results and make an accurate diagnosis, patients are prescribed MRI with contrast. This makes it possible to visualize clear contours, topography, and dimensions. A three-dimensional image allows you to see pathology at the initial stage of development.
Positron emission tomography
PET-CT is prescribed for suspected adrenal cancer. The technique accurately shows a detailed map of malignant formation in both adults and children. Allows you to draw up a scheme for surgical removal of the tumor. PET-CT shows the smallest structural changes, the presence and spread of metastases.
Procedure for collecting urine for research
To properly prepare the material, you need to perform the following steps step by step:
- Two days before the test, take a special preservative from the laboratory.
- Buy a sterile container for urine at the pharmacy.
- Wash thoroughly and scald with boiling water a large glass jar with a volume of at least 2.5 liters, closed with a tight lid.
- Place the preservative obtained in the laboratory into the jar.
- The next morning, release the first portion of urine into the toilet.
- Starting from the next desire to visit the toilet, during the day all biological fluid must be collected in a prepared jar, closing it each time.
- The container with the material should be kept in a cool, dark place.
- Mix all the material and pour approximately 50 ml into a container.
- Deliver the test to the laboratory no later than 1.5 hours after collection.
If you suspect a pathology in the adrenal glands, you need to take a test for the hormone dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), which is a male hormone and is responsible for the normal ratio of male and female sexually active compounds in the body. It requires venous blood. This analysis of the adrenal glands is especially important in women. If the production of this substance is disrupted, the menstrual cycle fails and secondary sexual characteristics begin to appear.
In order for the results to be reliable, you must prepare for the procedure in advance. Before collecting material, the patient must fulfill the following requirements:
- within 2 days stop taking hormonal medications;
- the day before visiting the laboratory, avoid physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- Avoid eating fatty foods 12 hours before and do not eat for at least 6 hours before blood sampling. The analysis is taken on an empty stomach;
- stop using cigarettes within 3 hours before the test;
- For women, it is more advisable to determine the level of DHEA from the 8th to the 10th day of the menstrual cycle.
Normal levels of the hormone in the blood depend on the gender and age of the patient:
| Age (years) | Men (µg/dL) | Women (µg/dL) |
| 10-15 | 24–248 | 33–280 |
| 15-20 | 70–490 | 65–368 |
| 20-25 | 210–490 | 148–406 |
| 25-35 | 160–450 | 99–340 |
| 35-45 | 89–427 | 60–335 |
| 45-55 | 44–331 | 35–255 |
| 55-65 | 51–295 | 19–205 |
| 65-75 | 33–250 | 9,5–246 |
| Over 75 | 16–123 | 12–155 |
An increase in the content of DHEA in the blood most often does not indicate a specific pathological process and in this case further more detailed studies are carried out. But sometimes an increase in indicators is observed with a tumor or proliferation of adrenal tissue.
A decrease in the amount of dehydroepiandrosterone in the blood indicates changes in the formation of biologically active compounds in the pituitary gland.
How to test urine for catecholamines
The functioning of the adrenal glands in women is checked by testing urine. It is collected three times. The starting point is the release of urine after waking up (it is not taken for analysis). The liquid resulting from urination is placed in a pre-treated container after 3, 6, 12 hours. This must be done within 24 hours.
Before donating urine, for three days it is forbidden to drink medications that contain:
- Rauwolfia;
- Ethanol;
- Theophylline;
- Caffeine;
- Nitroglycerine.
You will also have to give up chocolate, alcohol, bananas, and dairy products.
Cortisol test
Cortisol is produced in the adrenal cortex and therefore belongs to the group of corticosteroids. It is intensely produced during a stressful situation. Blood pressure, insulin production, electrolyte metabolism, and lipid metabolism depend on the level of cortisol in the body. Under the influence of the hormone, inflammatory processes decrease and the blood formula changes.
To test the ability of the adrenal glands to produce this substance, it is necessary to take a test for the quantitative determination of cortisol. Considering that its indicators increase with increased psycho-emotional stress, the material for the study must be taken at rest. To do this, during the day you need:
- cancel any physical stress;
- neutralize the effects of irritating factors;
- stop smoking;
- stop taking contraceptive and hormonal medications.
Hormone levels in the blood, saliva and urine are of diagnostic importance.
Blood analysis
To check the adrenal glands for cortisol levels, you need to take a blood test from a vein on an empty stomach. To obtain reliable data, sometimes the doctor may order a control study.
If the material is taken in the first half of the day, normal levels of cortisol in the blood range from 140 nmol/l to 585 nmol/l.
When taking the test in the afternoon, normal values range from 65 nmol/l to 327 nmol/l.
Saliva analysis
Before collecting biological material for research, you must stop brushing your teeth, reduce physical and nervous stress, and stop smoking one day before. Saliva can be donated at any time of the day, but not earlier than 30 minutes after eating.
Normal indicators depend on the time of collection of the material:
| Times of Day | Norm |
| Morning | 0–6.9 ng/ml |
| Day | 0–4.5 ng/ml |
| Night | 1.8–3.5 ng/ml |
Analysis of urine
You can also take a urine test for adrenal hormones. To determine cortisol levels, it is necessary to collect biological fluid throughout the day.
Acceptable levels of the hormone in urine range from 57 to 400 mcg/day.
A decrease in cortisol content in the body indicates acute or chronic adrenal insufficiency, damage to the liver, thyroid gland, and adrenogenital syndrome.
Decreased production of the hormone indicates a malfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system, stress or depression, obesity, pregnancy, dysfunction of the secretory function of the thyroid or pancreas.
Symptoms of malfunction
When there is an imbalance of any hormone produced by the adrenal glands, a number of disorders occur in the human body that provoke the development of diseases. Based on some symptoms, you can understand which hormone dysfunction is observed:
- Aldosterone deficiency is accompanied by increased urinary sodium excretion. As a result, the patient suffers from hypotension (low blood pressure) and high levels of potassium in the blood.
- Impaired cortisol production provokes acute adrenal insufficiency, which in most cases is life-threatening. Symptoms of this malfunction include low blood pressure, decreased functioning of internal organs, and tachycardia.
- Impaired androgen production leads to delayed sexual development. A deficiency of these hormones during the intrauterine development of boys is considered especially dangerous, as this leads to further abnormalities of the baby’s genital organs. For girls, the production of androgens is no less important. When they are deficient, puberty is impaired and the menstrual cycle is delayed or completely absent.
The following manifestations are considered to be the main first symptoms of adrenal gland diseases:
- persistent low blood pressure;
- nervous excitability;
- increased fatigue;
- muscle weakness
- skin hyperpigmentation;
- frequent nausea and vomiting;
- lack of appetite, up to anorexia;
- darkening of the mucous membranes;
- bad dream.
In most cases, the patient does not immediately suspect a malfunction of the adrenal glands, but attributes his condition to ordinary fatigue. If any of the listed signs appear, you must immediately consult a doctor, otherwise the person risks acquiring more severe diseases that threaten his life.
Aldosterone test
To check the formation of the hormone in the adrenal glands in women and men, it is necessary to take a test for the hormone aldosterone. The content of the substance is determined in venous blood or daily urine.
Aldosterone is an active biological substance that regulates electrolyte metabolism in the body. A number of important functions depend on this compound, such as maintaining blood pressure, rhythm of heart contractions, and excretion of fluid by the kidneys.
To submit the material, preliminary preparation is required. To do this you need:
- 10-14 days before the test, limit the consumption of salt and carbohydrates;
- at the same time, stop taking all hypertensive, diuretic and contraceptive drugs;
- for three days, eliminate physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- 3 hours before the test, quit cigarettes.
Blood analysis
Laboratory material is collected in the morning on an empty stomach. There must be at least 8 hours between eating and donating blood.
Tests to determine the functioning of the adrenal glands begin by allowing the patient to rest, sitting in a relaxed position for about 2 hours. After this, you need to sit quietly for another 5 minutes in the manipulation room. Blood sampling is carried out only in a sitting or standing position.
The normal level of aldosterone in the blood is 30-350 pg/ml.
An increase in indicators indicates primary or secondary hyperaldosteronism, liver cirrhosis, heart failure, and renal pathology. This value also increases in pregnant women.
A decrease in hormone levels can occur with hypoaldosteronism, adrenal insufficiency, monosomy on the X chromosome, diabetes mellitus, and also in the elderly.
Analysis of urine
Urine tests for aldosterone will also help check the functioning of the adrenal glands. Normal values are in the range from 1.5 to 20 mg/day.
Basic adrenal hormones: norms, their significance and rules for preparing for analysis
The adrenal glands produce several hormones, but only 3 of them are considered the most important:
- aldosterone,
- DEA-SO4,
- cortisol
Aldosterone
For a more accurate diagnosis, an aldosterone test is prescribed together with a renin test. Their ratio allows us to determine the degree and form of adrenal dysfunction.
Aldosterone is responsible for the volume of fluid excreted from the body, the level of potassium and sodium in the blood and, as a result, maintaining normal blood pressure levels
Testing serum aldosterone levels is recommended in the following cases:
- the patient has a persistent increase in blood pressure of unknown etiology that is difficult to treat;
- manifestations of insufficiency of the adrenal cortex are observed (apathy, fatigue, muscle weakness, etc.);
- a low potassium level was detected in the blood;
- There were suspicions of the presence of an adrenal tumor.
The normal level of aldosterone levels directly depends on the patient’s age and is:
- for children from 3 to 16 years –12-340 pg/ml;
- for adults in a sitting position – 30-270 pg/ml;
- for adults in the supine position – 15-143 pg/ml.
Detection of elevated levels may indicate a hormone-producing tumor of the adrenal gland, kidney disease, cirrhosis of the liver, pathological narrowing of the renal artery, and can also be observed when taking estrogen-containing drugs.
A reduced level of this hormone can be observed with congenital or acquired insufficiency of the adrenal cortex, alcohol poisoning, in the postoperative period (after removal of an adrenal tumor), with infectious diseases and diabetes mellitus.
To conduct the study, venous blood is used, which is collected in the morning.
Before taking the analysis, quite a lot of preparation is required:
What are the adrenal glands responsible for in women?
- for 10 days the usual regimen of salt intake should not be disturbed, while the amount of carbohydrates consumed must be reduced;
- for the same period of time, in agreement with the doctor, you must stop taking diuretics and hormonal drugs, as well as drugs that affect changes in blood pressure;
- active physical or psycho-emotional stress can give a falsely increased result;
- It is not recommended to take the test if the patient has symptoms of viral or infectious diseases.
But any deviations of indicators from the norm cannot be assessed unambiguously. In such cases, a repeat examination using additional diagnostic methods is prescribed.
DEA-SO4 or dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate
This protein substance is produced by the adrenal glands under the influence of the pituitary gland (one of the segments of the brain). Therefore, its level in the blood can be affected not only by changes in the structure and functioning of the adrenal glands, but also by tumors and dysfunction of the pituitary gland.
DEA-SO4 is the “raw material” for its processing into sex hormones (testosterone, estradiol and estrogen).
Measuring the level of this hormone is necessary for:
- assessment of adrenal gland function;
- diagnostics of tumor formations;
- clarifying the causes of disturbances in the functioning of the reproductive system in both women and men (early or delayed puberty, absence of menstruation, excessive or insufficient hair growth in some areas of the body, infertility, frigidity, etc.).
Excessive production of DEA-SO4 manifests itself with quite pronounced symptoms in the form of increased hair growth, especially in women
Standard indicators differ for men and women. They depend on the age of the patient:
- children from 1 to 9 years old – 5-85 mcg/dl;
- adolescents from 11 to 15 years old – 20-263 mcg/dl;
- adult women from 18 to 49 years old – 30-335 mcg/dl;
- adult men – 135-440 mcg/dl;
- women during menopause – 30-200 mcg/dl.
Women of childbearing age are recommended to take a test to detect the DHEA-SO4 indicator immediately after the end of menstruation, that is, on days 5-8 of the menstrual cycle.
A difference in the patient’s blood levels from the norm is a sign of disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands and an indication for more in-depth diagnosis.
There are certain rules of behavior before taking the test, compliance with which will increase the accuracy of the study and eliminate the detection of false indicators. The main ones are:
- refusal to eat 4-5 hours before blood sampling;
- exclusion of stress factors before the study (depression, quarrels);
- You should not drink alcohol at least 24 hours before the test;
- It is necessary to avoid taking most medications (including oral contraceptives) for 24-72 hours. If this is not possible, the attending physician must be notified;
- Smoking is not allowed 2-3 hours before taking blood.
The analysis is carried out in the morning, mainly on an empty stomach. Blood is taken from a vein.
Cortisol
This hormone is also produced by one of the layers of the adrenal cortex. Its content in the blood regulates almost all metabolic processes, blood pressure levels and the ratio of muscle mass to fat mass.
The adrenal glands produce cortisol in response to the production of a special protein by the pituitary gland. Therefore, deviations from the norm may be associated not only with pathology of the adrenal glands, but also with diseases of the brain (mainly tumor formations of the hypothalamus and pituitary gland).
If increased secretion of cortisol is detected, it may be necessary to diagnose the work of not only the adrenal glands, but also the brain
A study of cortisol levels in the blood should be prescribed in the following cases:
- the patient has symptoms of excessive or insufficient activity of the adrenal cortex (rapid weight loss or gain, muscle weakness, thinning of the skin, difficult to regulate blood pressure, the appearance of maroon or purple stripes on the skin);
- there are suspicions of the presence of tumor formations.
Cortisol levels do not depend on the age or gender of the patient, but they vary significantly throughout the day, reaching a maximum in the morning and a minimum at night. Therefore, it is considered advisable to order several blood tests at different intervals of the same day. This allows you to check whether the cyclical changes in indicators correspond to the norm.
The standard values of cortisol in the blood are:
- before 12 noon – 170-540 nmol/l;
- after 12 noon – 65-330 nmol/l;
- during pregnancy, indicators can exceed the values by 4-5 times, while being the norm.
Excessive production of the hormone may indicate pathological growth of the adrenal cortex, hormone-producing tumors of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, kidneys or testicles, excess body weight, stress or pregnancy.
Catecholamine analysis
Sometimes, in cases of persistent hypertension, suspected myocardial infarction, or tumor processes in the adrenal glands, the doctor recommends determining the level of a special group of biological active substances - catecholamines.
To check the production of this group of hormones by the adrenal glands, it is necessary to take a catecholamine test. Their content is determined in venous blood and daily urine.
Blood analysis
When preparing for the study, you must follow the following rules:
- two days before the start of material collection, all diuretics are canceled, and medications are canceled one day before;
- the day before the analysis, you must give up smoking, nervous and physical stress.
Attention is also paid to the daily diet. For two days before the test, you should not drink tea, coffee, alcoholic beverages, or eat bananas, cheeses, or avocados. The last meal should be 12 hours before visiting the laboratory.
Analysis of urine
Urine can be collected for 3, 6, 12 hours and a full day. The longer the biological fluid is collected, the more reliable the research results will be.
Normal catecholamine levels:
| Hormone | Amount in urine | Amount in blood |
| Adrenalin | up to 21 mcg/day | up to 110 pg/ml |
| Norepinephrine | 15–80 mcg/day | from 70 to 750 pg/ml |
| Dopamine | 60–400 mcg/day | up to 87 pg/ml |
Serotonindo 200 mcg/day 50 to 220 pg/ml
Also, to control the production of hormones by the adrenal glands, in addition to the listed names of tests, the content of a number of electrolytes is determined.
Determining adrenal hormones will help not only in diagnosing the disease, but also in choosing the most effective treatment. To early detect pathology in the body and prevent the development of severe forms of disease, such tests should be carried out every few years.
Author: Irina Ramazanova, doctor, especially for Nefrologiya.pro
What hardware research shows
Ultrasound, MRI, and computed tomography are needed to diagnose the cause of the disease. Ultrasound examination determines the size of the organ being examined, foreign formations, and determines the transverse dimensions of the organ. However, not everything is visible on an ultrasound; small neoplasms may not be diagnosed; the cortex and medulla of the endocrine glands are not clearly visible.
Magnetic resonance imaging does a more thorough analysis of the adrenal glands, but it is not indicated for everyone. It is contraindicated in patients suffering from claustrophobia.
The most popular method is computed tomography. It helps to identify the presence of a tumor and monitor it during treatment. CT scans quite effectively examine blood vessels and determine the presence of pathology. CT allows not only to detect the smallest tumors, but also to determine their nature. Each image taken with a CT scan can actually be viewed on a computer and printed out for detailed study.
Computed tomography can be done in 2 ways: contrast and without contrast. There are no specific recommendations for CT with contrast. If a CT scan without contrast is prescribed, then you should not eat anything 4 hours before the procedure. The general rule is no metal objects or jewelry on the patient.
Modern medicine has everything necessary to identify problems with the adrenal glands in their buds. Checking the functioning of the adrenal glands is not difficult. Tests, instrumental studies, and doctor’s recommendations will help you return to a full, healthy life.
Useful video about adrenal hormones
List of sources:
- Melnichenko G.A., Fadeev V.V. Fundamentals of laboratory diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency (lecture) // Clinical laboratory diagnostics. 1997. No. 8.
- Lelevich V.V. Biological chemistry. Grodno: GrGIU, 2009.
- Melnichenko G.A., Fadeev V.V. Laboratory diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency // Problems of endocrinology. 1997. No. 5.
source
How else can you check the adrenal glands in women and men?
In their work, diagnostic doctors use various methods for identifying pathologies of the endocrine glands - histology, cytology, endoscopy.
Needle biopsy
Biopsy is the name of a test that involves taking a tissue sample by inserting a long needle into the pathological area. In the laboratory, the biomaterial is studied under a microscope and a conclusion is drawn on whether atypical cells and their types were detected. The analysis reveals diseases such as cancer, adrenal adenoma, and other benign tumors.
What are the blood tests for adrenal hormones and help in deciphering them?
The adrenal glands, being part of the endocrine system, produce such important hormones as aldosterone and cortisol. As a rule, an analysis of adrenal hormones is prescribed by a general practitioner if there are characteristic complaints.
Blood tests for adrenal hormones can be compared with diagnostic testing of the condition of the human body. For example, elevated levels indicate constant stress, severe fatigue, and can also be the cause of insomnia, etc. Hormones of the pituitary-adrenal system are represented by:
- cortisol;
- aldosterone;
- dehydroepiandrosterone.
How the research is carried out
An analysis of adrenal hormones allows you to evaluate the functioning of these important glands. The main biological material for such a study is blood serum.
Its collection is usually carried out in the morning (from 8 to 11 o’clock), on an empty stomach. Since the concentration of each hormone can be influenced by various factors, it is important to prepare properly for laboratory tests.
- For 10 days, do not break your usual salt intake and try to eat less carbohydrates.
- 2-3 days before the analysis, avoid physical and emotional stress, give up intense sports.
- Avoid stressful situations.
- For smokers, try to reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke per day.
- After consulting with your doctor, stop taking the following medications - combined oral contraceptives (COCs), estrogens, diuretics, antihypertensive drugs, Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone, Diprospan.
- It is better for women to donate blood on days 5-8 of the menstrual cycle.
Standard medical procedure
Important! It is better to stop the hormone test if the patient suffers from an acute infectious or viral disease, or has recently undergone surgery, radiotherapy or chemotherapy.
After blood collection, the test tubes with biological material are sent to the laboratory, where they are carefully studied. Typically, test results are ready within 1-2 days.
Dehydroepiandrosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone is an androgenic steroid hormone produced by cells of the adrenal cortex. It is the prohormone, which, due to complex processes, is transformed into the main male hormone - testosterone and the female hormone - estrogen.
Norm of indicators
The indicators have a fairly wide range and depend on age. The test systems used and the blood analyzers themselves may cause some errors. The following are considered the norm:
- in women – 810-8991 nmol/l;
- in men – 3591-11907 nmol/l.
When are they appointed?
A blood test for this hormone of the pituitary-adrenal system is prescribed for:
- suspicion of existing disturbances in the production of their own corticosteroids by the adrenal glands;
- tumors of the adrenal cortex;
- miscarriage;
- fetal malnutrition;
- existing symptoms of delayed sexual development;
- suspected excess levels of hormones of the pituitary-adrenal system in a pregnant woman.
How to prepare for the test
Before donating blood for adrenal hormones, you must stop taking the following medications:
Advice! To make the result more accurate, you need to inform the nurse about the medications you are taking that can affect the biochemical composition of the blood.
Types of hormones
The adrenal glands are real record holders for the amount of hormones produced.
They synthesize biologically active substances of three different groups:
- mineralocorticoids;
- glucocorticoids;
- female and male sex hormones.
Adrenal hormones
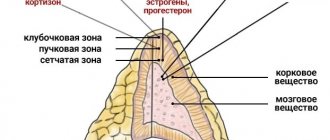
The main representative of mineralocorticoids is aldosterone. Its production occurs in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal glands.
It is primarily responsible for water and electrolyte balance: under its action, sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion in the kidneys are increased. Due to this, the hormone controls blood pressure.
Mechanism of action of aldosterone
The most well-known glucocorticosteroid hormone is called cortisol. It is produced in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex.
Its main function is considered to maintain metabolism. In addition, it controls the activity of the cardiovascular, immune and central nervous systems under stress.
Operating principle of GKS
The main sex hormone produced by the adrenal cortex is dehydroepiandrosterone. It is a prohormone that can be transformed into both testosterone and estrogen. Therefore, when answering the question of what tests are taken for adrenal disease, the doctor usually identifies three laboratory tests.
The names of the studies for women and men are the same:
- dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DEA-s, DEA-SO4);
- general cortisol;
- aldosterone.
Cortisol (K)
Cells of the adrenal cortex take part in the production of the hormone. It belongs to the category of glucocorticoids. It is cortisol that is responsible for controlling the production of ACTH and corticoliberin.
Cortisol is characterized by strong daily fluctuations:
- the maximum is observed from four o'clock to eight in the morning;
- minimum - from nine in the evening to three in the morning.
When is the test taken?
Blood donation for cortisol is prescribed:
- with hirsutism;
- to confirm Itsenko-Kuchinga syndrome and Addison's disease;
- with oligomenorrhea;
- with accelerated puberty;
- for osteoporosis;
- with increased skin pigmentation;
- with unexplained muscle weakness.
How to donate blood for cortisol
What conditions must be met? The day before the test, you should stop (if possible) taking the following medications:
- estrogens;
- drugs from the category of opiates;
- contraceptives.
Also, on the eve of visiting the laboratory, you should avoid active sports and smoking.
Advice! It is the measurement of the daily amount of cortisol in the blood that is a mandatory blood test if Cushing's syndrome is suspected. An increased level of this hormone of the pituitary-adrenal system is characteristic of this pathology.
What are the normal levels of cortisone in the blood?
The norm of indicators depends on the age of the person:
- under 16 years old - 83...580 nmol/l;
- over 16 years old - 138...635 nmol/l.
Deviations from the norm
Elevated numbers may indicate the presence of:
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- adrenal cortex carcinoma;
- blood sugar levels drop below acceptable levels;
- adrenal tumors;
- decreased kidney function;
- virilizing hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex;
- hyperthyroidism.
Increased cortisone levels are observed:
- during pregnancy;
- while taking oral contraception;
- for stress and depression;
- if you are overweight;
- with alcoholism.
A decrease in indicators may confirm:
- adrenogenital syndrome;
- disruption of the synthesis of corticosteroids by the adrenal glands;
- insufficient production of hormones by the adrenal glands (Addison's disease);
- panhypopituitarism;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- hypothyroidism.
A reduced rate during pregnancy may indicate the development of early toxicosis.
Indications for research
Main indications for examination of the adrenal glands:
- identifying the causes of electrolyte imbalance in the body (potassium, chlorine, sodium);
- detection and differential diagnosis of hyperfunction of the adrenal cortex (Itsenko-Cushing syndrome - severe neuroendocrine pathology);
- suspicion of a malignant tumor of internal organs;
- monitoring the effectiveness of surgical treatment of malignant, hormone-synthesizing neoplasms;
- screening of primary, secondary Conn's syndrome (excessive production of cortical hormone in the zona glomerulosa of the gland);
- as part of a comprehensive diagnosis of hypertension in young patients;
- assumption of acidosis (blood oxidation).
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is a hormone synthesized by the adrenal cortex. It is responsible for regulating electrolyte balance, as well as adjusting the total volume of fluid in the body and blood pressure indicators.
What is the hormone responsible for?
By influencing the renal tubules, the hormone delays the removal of sodium and chlorine from the body. This causes a much smaller amount of fluid to be excreted from the body along with saliva, urine and sweat. But at the same time, potassium excretion increases.
Aldosterone helps maintain normal blood pressure levels. With an increase in the amount of the hormone in the blood, the formation of edema, an increase in blood pressure, a decrease in muscle tone, convulsions and disturbances in heart rate are observed.
When is it appointed?
The study is prescribed to clarify the following pathologies:
- adrenal insufficiency;
- orthostatic hypotension;
- accelerated growth of adrenal cortex cells (hyperplasia);
- tumors of glandular tissue (adenomas) of the adrenal cortex;
- increased production of the hormone aldosterone.
Blood tests for adrenal hormones are also necessary in case of uncontrollable arterial hypertension.
Norm
In this case, the norm is the same for men and women: 35-350 pg/ml.
Deviations from the standard
Elevated aldosterone levels may indicate:
- Conn's syndrome (with primary aldosteronism);
- adrenal hyperplasia, occurring bilaterally (with pseudoprimary aldosteronism);
- heart failure;
- nephrotic syndrome (complex pathology, accompanied by the appearance of severe edema, as well as changes in some biochemical parameters);
- Bartter's syndrome;
- hypovolemia caused by bleeding;
- cirrhosis of the liver, accompanied by the formation of ascites;
- renal hemangiopericytoma.
Exceeding the norm of the hormone of the pituitary-adrenal system can occur in the following conditions:
- during pregnancy;
- after a long fast;
- under thermal stress.
A decrease in hormone concentration below the permissible level:
- Addison's disease (if there is no diagnosed hypertension);
- with existing hypertension - increased production of corticosterone, Turner's disease, diabetes mellitus, alcohol poisoning;
- excessive consumption of table salt;
- adrenogenital syndrome;
- arterial hypertension that occurs during pregnancy.
How to prepare for the test
In order for a test for the hormone of the pituitary-adrenal system to give the correct result, the following conditions must be met:
- maintaining the usual rhythm of salt intake for two weeks;
- blood cannot be donated during illness (indicators may be artificially low);
- before visiting the laboratory, it is necessary to avoid increased physical and psycho-emotional overload;
- discontinue medications that may affect the test results (this should be discussed with your doctor).
To donate blood for hormones of the pituitary-adrenal system, it is recommended to choose specialized laboratories. This is explained by the presence in such institutions of all the necessary equipment, as well as trained personnel.
source
What symptoms indicate that your adrenal glands need to be checked?
Indications for complex diagnostics:
- the appearance of goosebumps in the arms and legs,
- numbness, coldness of the extremities,
- the appearance of stretch marks not related to pregnancy on the thighs, abdomen,
- amyotrophy,
- infertility,
- sexual development begins prematurely,
- in women, male characteristics are formed, virilization of the body develops,
- problems with blood pressure appear for no apparent reason,
- bothered by cramps,
- morbid obesity develops
- acne spots form on the body,
- libido decreases,
- hair fall out,
- a severe form of hypertension develops in combination with tachycardia,
- during an increase in blood pressure, patients experience a panic attack, the skin turns pale, urination increases, hands tremble,
- excess hair appears on the face, chest, back, arms,
- the usual glucose levels change, diabetes mellitus develops,
- adipose tissue accumulates in the abdomen, face,
- tests show a violation of the water-electrolyte balance: high levels of sodium combined with a low concentration of potassium.
Which doctor should I contact? Diseases of the adrenal glands require the help of a qualified endocrinologist.
What is FAM of the mammary gland and how to get rid of the formation?
Read useful information. Find out about the causes of increased gastrin hormone and how to bring the indicators back to normal from this article.
Important details:
- for disorders that negatively affect the functioning of the reproductive system, women additionally visit a gynecologist, men a urologist,
- when a malignant tumor process is detected, therapy is carried out under the guidance of an oncologist,
- improper functioning of the adrenal glands negatively affects the state of the central nervous system and peripheral nerves: signs of neuropathy, paresthesia, convulsions, and muscle weakness appear. The patient should consult a neurologist,
- If hypertension develops, you need the help of a cardiologist.
Against the background of pathological changes in the adrenal glands, the production of hormones is disrupted:
- steroids,
- catecholamines,
- mineralocorticoids,
- glucocorticoids.
With adrenal insufficiency, the secretion of regulators sharply decreases. In case of tissue hyperplasia or the presence of hormonally inactive tumors, tests do not show hormonal imbalance. With congenital anomalies of the structure and functions of the adrenal cortex, the endocrine glands increase the production of some types of regulators and decrease the level of other bioactive components. The development of active tumors (they release substances into the blood) - carcinoma, sarcoma, pheochromocytoma, adenoma - is always combined with increased secretion of adrenal hormones.
On a note! Violation of the functionality of the adrenal glands is more common in women, especially during critical periods of life associated with hormonal changes. Congenital anomalies often develop not only due to genetic predisposition, but also under the influence of carcinogens and high doses of radiation.
How are adrenal hormones checked, what tests need to be taken?
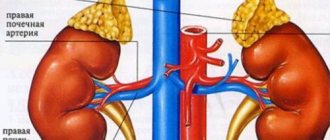
How to test your adrenal glands? This question was asked by every person who encountered symptoms of a deficiency or excess of hormones secreted by this element of the endocrine system. The adrenal glands are paired endocrine glands that are shaped like triangles and are located directly above the kidneys. Their main function is the regulation of the stable course of metabolic processes in the body, as well as participation in the synthesis of sex hormones in men and women (progesterone, estrogen, testosterone). In this article we will take a closer look at what tests check the adrenal glands?
Importance of the Adrenal Glands
The adrenal glands in a woman’s body work in an enhanced mode at certain moments in life. Therefore, it is in the weaker sex that diseases of these glands are especially dangerous, and disturbances in their functioning can lead to the most serious consequences.
One of the most important periods of a woman’s life, in which the role of the adrenal glands is more important than ever, is pregnancy. In the early stages during the formation of the fetus, if the adrenal glands are not working at full capacity, the expectant mother periodically experiences malaise. In the last trimester, the function of the adrenal glands is performed by the baby’s endocrine system, as a result of which the newborn child has problems with the functioning of these glands.
The next high-risk age period is premenopause and menopause. If in men the production of testosterone decreases gradually and the adrenal glands are able to maintain the acceptable level of this hormone without problems, then in women the decline of sexual functions occurs rapidly. At the same time, the adrenal glands may not be able to cope with the need to completely take over the work of producing estrogen in a short time.
Even healthy endocrine glands, which also need to produce other equally important hormones, are difficult to cope with such a load. As a result, in addition to menopause, which is quite a serious stress for a woman, other malfunctions may begin in the body.
To prevent possible problems with the adrenal glands, it is necessary to undergo timely examinations and diagnosis of these glands, which are important for a woman’s health.
Clinical diagnosis
The main form of examination is to take tests for adrenal hormones. This diagnostic method is preceded by a clinical method of studying the patient’s health status based on external signs indicating dysfunction of the adrenal glands, as endocrine glands that take part in most vital processes of the human body. It is indicated for both women and representatives of the male half of the population.
A clinical examination to check the health of the adrenal glands consists of an external examination of a patient who has suspicions of their pathological condition. Diagnosis can be carried out by the attending physician, or a person can independently examine his body.
Particular attention is paid to the following symptoms, indicating a high likelihood of adrenal gland disease in women and men:
- rapid growth of skin hair in various areas of the epithelium where hair follicles were previously absent, or their growth is an anomaly (this sign of the disease especially concerns women who may develop a mustache, grow a beard, hair on the chest, back or stomach);
- changes in pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes, when dark or light spots of a bronze hue appear on the body with increased localization in the palms and neck, and the palate, gums, tongue, and inside of the cheeks become bluish;
- behavioral disorders in the form of constant depression, feelings of inexplicable fear, anticipation of the imminent onset of catastrophic events, apathy towards life, or vice versa, increased agitation, aggressiveness towards others, mood swings.
Diagnosis of the primary manifestations of the pathological condition of the adrenal glands is the initial stage of a comprehensive examination of the endocrine and excretory systems. It is important to remember that the kidneys and adrenal glands are located in close proximity to each other. Therefore, it is necessary to check the performance of kidney tissue. Is the filtration function fully preserved, are there any tumor formations or inflammatory processes that can negatively affect the health of the adrenal glands.
Signs of poor adrenal gland function in the female body
Disease of the adrenal glands can occur latently, or may manifest itself with a number of characteristic symptoms. Who needs to be wary? If you have the following symptoms:
- You are losing weight due to indigestion.
- Painful premenstrual syndrome.
- The raging menopause throws you into a fever, then into a cold sweat, and your blood pressure jumps.
- I have many years of experience taking hormonal contraceptives.
They will 100% indicate a problem with the adrenal glands:
- hair growth on the face and body;
- voice mutation;
- hyperpigmentation;
- vitiligo.
Blood test
Tests for adrenal hormones are carried out in a laboratory, whose specialists determine the concentration in the blood of the following biochemical indicators:
- DHEA-SO4 (this is a hormone of the androgen group, the level of which allows doctors to make a differential diagnosis and distinguish between signs of hormonal imbalance caused by improper functioning of the ovaries in women, tumor processes, or indeed the pathology is associated with adrenal dysfunction);
- cortisol (one of three hormonal substances that are produced by the tissues of the adrenal glands and are involved in most metabolic processes associated with the breakdown of proteins into amino acids, the conversion of carbohydrates and fats into food, and then into vital energy);
- aldosterone (controls the balance of male and female sex hormones, ensures the stability of the electrolyte composition of the blood, maintains the optimal ratio of platelets, erythrocytes and leukocytes);
- adrenocorticotrope (a hormone responsible for excitation of the central nervous system in a stressful situation, increases heart rate, stimulates liver tissue to release glycogen reserves in order to increase blood glucose levels, giving a person additional vitality and energy).
An analysis of adrenal hormones is carried out in an inpatient endocrinology department, or in a clinic after an appointment with a doctor. In order to obtain the results of the examination, the patient must donate blood for hormones from a vein. 20 ml is enough to obtain comprehensive information about the patient’s hormonal background, the concentration of these hormonal substances and the health of the adrenal glands. Men can undergo this type of examination on any day of the week, and women no earlier than 6-7 days after the end of menstruation.
Normal functioning of the adrenal glands
The paired organs are located on top of the kidneys and are shaped like triangles. The adrenal glands are responsible for the production of vital hormones involved in fat metabolism, sexual function, and also in the psycho-emotional state of a person. The organs consist of 2 parts, each of which is responsible for the production of specific hormones:
- The outer part or cortex of the adrenal glands produces cortisol (a substance involved in fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism), aldosterone (a hormone that regulates water-salt balance). In addition, the outer part of the adrenal glands produces androgens, hormones that are responsible for a person’s sexual characteristics and regulate his sexual activity.
- The inner part , also called the medulla, produces hormones that prevent the body from becoming exhausted during nervous overload and stressful situations. These substances are called adrenaline and norepinephrine.
In males and females, the adrenal glands produce different hormones:
- The paired organ of the weaker sex produces estrogens - female hormones that promote the proper development of the genital organs and are responsible for the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics in women. Every month, thanks to the production of estrogen, the female body is ready for procreation. In addition to estrogen, women's adrenal glands produce another sex hormone - progesterone, which is simply necessary for the weaker sex for normal pregnancy and preparation of the mammary glands for breastfeeding the baby.
- Male sex hormones, androgens (dehydroepiandrosterone), are involved in spermatogenesis and are responsible for the quality of the seminal fluid produced. In addition to the function of reproduction, androgens are responsible for the development of the skeleton, muscles, as well as the growth of hair on the body and face in men.
Biochemical composition of saliva
A blood test for adrenal hormones is one of the most effective and reliable examination methods, the results of which can confirm or refute a diagnosis indicating pathology of the adrenal cortex. Despite this, a test for cortisol levels is actively used. This diagnosis is distinguished by its simplicity, accessibility and efficiency in terms of personal time. To check the adrenal glands, you need to donate regular saliva, which is secreted by the glands of the oral cavity throughout the day.
Practicing endocrinologists involved in the treatment of adrenal diseases believe that this type of analysis shows a more accurate clinical picture of the functional activity of the glands. A similar effect is achieved due to the fact that the patient donates saliva several times a day. Doctors immediately conduct a biochemical study of the selected biological material and receive several results of rapid tests of cortisol levels in the human body. In this case, the hormone concentration is recorded at different time periods.
Ultimately, the doctor examining the patient has comprehensive information about how the adrenal glands work at different times of the day, what affects the decline in their dynamics, provokes increased synthesis of cortisol, or the production of the hormone stops under the influence of certain factors. This plays a key role in shaping the further course of treatment.
The norm of the adrenal glands according to saliva analysis is recorded only if the following results were obtained as a result of the diagnosis:
- in the morning from 06-00 to 10-00 the level of cortisol in saliva is the highest;
- from 10-00 to 14-00 the concentration of the hormone decreases sharply;
- from 14-00 to 17-00, the decline in cortisol levels continues, and the indicators of the biochemical composition of saliva do not differ significantly from those that were sampled at noon;
- from 17-00 to 21-00 hours is the period when the concentration of cortisol in saliva, and therefore in the patient’s entire body as a whole, is the lowest (the decrease in hormone levels continues throughout the night and increases only closer to the morning hours).
This is the normal dynamics of the production of adrenal hormones, which shows the functional state of the endocrine glands, as well as the concentration of the hormonal substance. In order to take tests, it is necessary to extract saliva into a sterile container, which is given to the patient in the department of laboratory testing of biological materials. As a rule, this is a plastic cup with measuring divisions.
Decoding indicators
Diagnosis and treatment of adrenal diseases in men and women necessarily include monitoring the levels of cortisol, adrenaline and aldosterone. The indicators are deciphered by an endocrinologist. Thanks to the tests, it is possible to identify Addison's disease, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, embolism and thrombosis of the adrenal veins.
But deviations are not the only evidence of the listed pathologies. The diagnosis is made based on a combination of clinical manifestations, laboratory test results and obvious evidence identified using instrumental methods. Often, disruptions in the functioning of the adrenal glands are caused by an incorrect lifestyle. Then getting rid of harmful addictions is the most effective treatment.
Instrumental diagnostics
After the patient has been tested for the adrenal glands, the next stage of the examination is to study the tissues of the organ using special medical equipment. It allows you to study the structure of the endocrine glands, the state of their cells, and the level of blood circulation. Instrumental examination of the adrenal glands is especially important if the patient has signs of a tumor process. To check the health status of the adrenal glands as thoroughly as possible, the following instrumental diagnostic methods are used:
- positron emission tomography (used only for complex pathologies of the endocrine system, when there is suspicion of concomitant diseases of the thyroid and pancreas);
- computed tomography of the pelvic organs (digital information is collected and analyzed about the state of the tissue of the adrenal glands, as well as organs located in the circle, on the stable operation of which the functionality of the patient’s endocrine system depends);
- magnetic resonance imaging (in this case, the structure of the tissues of the kidneys and adrenal glands is subject to detailed study in order to exclude possible damage to these organs by foreign neoplasms of malignant or benign origin);
- ultrasound examination (prescribed at the initial stage of instrumental examination, so that the attending physician receives basic information about the state of the adrenal glands, as well as their cortex, records possible deviations from the norm and, if necessary, selects further diagnostic methods).
It is believed that computed tomography is the most effective way to study the adrenal glands, which allows, in just one procedure, to obtain information about the quality of local blood circulation in the tissues of the organ and to determine vascular pathologies.
If a tumor has formed inside the adrenal glands or on the surface of their cortex, then a CT scan will also determine this. In case of mechanical damage to an organ, computed tomography will make it possible to determine the severity of tissue damage, areas with a necrotic process or areas of scarring.
How to check the functioning of the adrenal glands using the instrumental method? The patient will be required to make an appointment with a specialist who conducts these types of examinations. It is advisable that the doctor immediately decipher the diagnosis and issue a conclusion, which is transferred to the attending physician for study. If decoding is not carried out, then the results of the examination are analyzed by the doctor who is seeing the patient.
Instrumental research methods
The retroperitoneal location of the glands behind the thickness of the muscles and subcutaneous fat caused difficulties for diagnosticians: how to check the adrenal glands? However, modern equipment makes it possible to study any organ layer by layer in different planes, making visualization of the adrenal glands possible.
Methods used for research:
- Ultrasound - it is used only in cases where it is not possible to carry out more accurate imaging methods. The strength of the ultrasonic wave when passing through the skin, subcutaneous fat, and all organs of the abdominal cavity is so weakened that it does not allow obtaining a detailed picture of the structure of the adrenal glands. Ultrasound helps to quickly identify large space-occupying formations in the glands, changes in their size or structure.
- Computed tomography is the preferred method for examining the adrenal glands. The tomograph allows you to obtain a huge number of X-ray images in various planes, on the basis of which the processor builds a three-dimensional image of the glands. Depending on the pitch of the tomograph (the thickness of the layer being examined), tumors only a few mm in size can be visualized.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is a high-precision method for studying soft tissues, based on the interaction of atomic nuclei with a powerful magnetic field. The advantage of the method is the absence of radiation exposure, but it is contraindicated for people who have metal objects in their bodies (knitting needles, screws, heart rate drivers). The tomograph also takes a series of images of the organ at different depths, from which the processor builds a complete image.
Which doctor should I contact?
Which doctor examines the adrenal glands and what is the name of his specialty? In order to undergo a comprehensive examination of this organ of the endocrine system, you should visit an endocrinologist. A medical specialist of this profile performs all stages of diagnosis, starting from an initial examination with determination of current symptoms, ending with instrumental examination.
In addition, the endocrinologist establishes what tests need to be taken for a particular patient, explains what they are called, why they need to be taken, and how to donate blood or saliva without violating any rules for the selection of biological material. After the tests are completed and the examination results are received, the endocrinologist decides to make a diagnosis, or refutes suspicions that the patient has adrenal pathologies.
If the disease is confirmed, the patient receives detailed consultation with a specialist. He is prescribed a course of treatment, a prescription is issued for the purchase of medications, where their names, daily dosage and duration of use are indicated in detail. Most often, hormone replacement therapy is used to compensate for the deficiency of cortisol, as well as other secretions synthesized by adrenal tissue.
Which doctor prescribes the collection of tests?
Since the symptoms of adrenal gland disorders are very diverse, there is no clear answer to the question of which doctor checks the level of these hormones.
When checking the functioning of the adrenal glands, you may need to consult several specialists at once
But most often, tests for the level of adrenal hormones are prescribed on the recommendation of such specialists:
- urologist,
- cardiologist,
- oncologist,
- therapist,
- endocrinologist.
Any, even serious deviations from the norm cannot be interpreted as an unambiguous diagnosis. This only gives the doctor information about the presence and possible location of the pathological process. For a more accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to use hardware techniques and repeat tests.
Self-diagnosis
Medical statistics indicate that women, unlike men, are 2-3 times more likely to encounter various diseases of the adrenal glands. This is due to the fact that the hormonal balance of the female body depends not only on the endocrine glands, but also on the phases of the menstrual cycle and the functional activity of the internal genital organs.
Therefore, an independent examination of the health of the adrenal glands is especially suitable for women who experience extremely unsatisfactory health during menstruation, lose appetite, and are prone to severe depression, aggressiveness, outbursts of anger, mood swings or apathy. The following diagnostic methods do not require special medical equipment or professional skills.
Method No. 1
Based on fluctuations in blood pressure. It is necessary to take a horizontal position. It is best to lie on the floor or couch to ensure a perfectly flat surface. The muscles of the entire body should be completely relaxed for the next 5 minutes. After the specified time has passed, pressure readings are measured in the forearm area.
After this, the person takes a vertical position and uses a tonometer to record blood pressure again. If there are no significant disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands, then in a standing position the pressure will be 10 units higher.
To obtain more reliable information, it is recommended to perform this procedure 3-4 times a day. Stable blood pressure results are the key to adrenal health.
Method number 2
A kind of test for cortisol levels. You can also take it at home, without using complex diagnostic schemes. To do this, you will need to measure your body temperature daily for 7 days. Every 3 hours, a person takes a regular mercury or digital thermometer, inserts it into the armpit, and writes the measurement results in a separate notebook indicating the exact time.
The body temperature of a healthy person cannot be constant. It periodically rises and falls by several degrees throughout the day. For example, it is not a deviation from the norm if in the morning the body temperature is 36.6, and in the evening it rises by 0.3 degrees Celsius. If the indicators of this type of examination indicate constant maintenance of the same temperature without fluctuations, then this is an alarming sign indicating a possible imbalance of cortisol and problems in the functioning of the adrenal glands.
It is important to remember that even the most accurate and effective home method for testing the functioning of the adrenal glands will not replace a detailed consultation with an endocrinologist with further diagnostic examination. Therefore, if you suspect a deficiency or excess of adrenal hormones, it is recommended not to waste precious time and make an appointment with a specialized specialist.
source
Self-diagnosis methods
You can suspect pathological changes in tissues and functional failures of the adrenal glands independently by the development of certain symptoms.
The first signs of organ disease:
- moderate and severe obesity (symptoms of the disease in women);
- formation of specific stretch marks on the abdomen;
- increased blood pressure (BP), throbbing pain in the occipital region of the head;
- muscle tissue dystrophy, general weakness, chronic fatigue;
- skin pigmentation.
When the amount of sodium decreases, lethargy, weakness, and confusion are observed; when it increases, a decrease in the amount of daily urine, constant thirst, nervous excitement, and convulsions are observed.
When potassium levels decrease, malaise, sudden weight loss (anorexia), increased urine production, thirst, decreased blood pressure, inhibition of reflexes, and vomiting appear. An increased content of potassium in the body is manifested by diarrhea, cramps, arrhythmia, and ventricular fibrillation.
With acidosis, the general condition worsens, the person is disoriented in space, the heart rhythm and respiratory rate are disturbed.
The exact function of the adrenal glands that is impaired can be judged by the following symptoms:
- hypocortisolism (adrenal insufficiency) – characterized by weight loss, fatigue, hypotension, darkening of the skin, epigastric pain;
- hypercortisolism (increased cortisol concentration) - manifested by increased blood pressure, increased body weight, the appearance of purplish-red stretch marks on the skin, and excess hair growth;
- virilization (excessive production of androgens in women) – male pattern hair growth, acne, menstrual irregularities, infertility;
- feminization (production of excess amounts of female hormones in men) – lack of body hair, delayed development of secondary sexual characteristics;
- excessive synthesis of catecholamines - adrenaline crises that cannot be controlled by antihypertensive drugs during physical exertion, in stressful situations, with deep palpation of the peritoneum, headaches, panic attacks, rapid heartbeat;
- hyperaldosteronism (excessive synthesis of aldosterone) – high blood pressure, frequent urination, muscle weakness.
A functional method for testing the functioning of the adrenal glands is a physical test. To carry it out, you need to lie in a horizontal position for 5-10 minutes and measure your pressure. Then you should stand up sharply and measure your blood pressure with a tonometer again. If the discrepancy in numbers is more than 10-20 values, this is a signal of problems with the gland.
Due to the varied clinical symptoms of adrenal diseases, referrals for examination are given by therapists, pediatricians, cardiologists, nephrologists, andrologists, gynecologists, urologists, as well as psychiatrists (in case of outbursts of aggression, panic attacks, depression).