What does a kidney lump look like on an ultrasound?
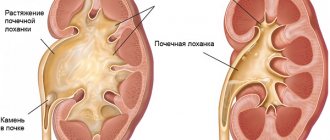
Kidney compaction is a symptom indicating changes in the epithelium that lines the inner surface of the pyelocaliceal system (PCS).
It is a reservoir for collecting urine, which is discharged into the ureter through a large pelvis in the region of the renal sinus. If you complain of dull pain in the lower back, urinary disorders (dysuria), a urologist or nephrologist prescribes an ultrasound examination of the urinary system. A change in the echogenicity of the joints indicates their compaction. If the walls of the collecting system thicken, the intensity of the reflection of the ultrasonic wave from their surface increases. During the examination, the ultrasound specialist will definitely notice:
- change in organ size;
- uneven edges;
- heterogeneity of tissues of the jaw;
- compaction of the pelvis;
- deformation of the cups.
The kidney is covered with parenchymal tissue, which has low echogenicity. But with tumors or inflammation, echogenicity increases significantly.
The conclusion of an ultrasound specialist cannot be considered a diagnosis. Consolidation of the jaw is a sign of pathological changes in the kidney, which are caused by many reasons.
Causes of seals
Various diseases are considered to be the main cause of renal lumps. In 60% of cases, pyelonephritis is considered the root cause. During an ultrasound, the doctor pays attention to the uneven edges of the organ and its decrease in size. In addition, an expansion of the heart rate may also be observed.
The main reasons for the appearance of seals:
- Pyelonephritis is a disease in which a person experiences inflammation of the renal pelvis. The cause is various bacteria and pathogens. The disease can develop when the outflow of urine from the body is impaired.
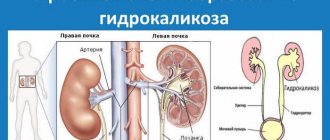
- Hydronephrosis is a disease in which the renal pelvis gradually expands, and the tissue of the organ atrophies, gradually becoming thinner and thicker. Hydronephrosis occurs due to urolithiasis, as well as damage to the urinary system. Kidney stones occur due to poor diet, excess weight, the use of certain medications, and poor drinking habits. With hydronephrosis, the patient may experience strictures. Stricture is a disease in which narrowing of tubular organs occurs. Symptoms in the first stage of hydronephrosis occur unnoticed and are usually accompanied by renal colic.
- Doubling the heart rate does not pose any threat to the patient’s health. Occurs due to the use of certain medications, alcohol and tobacco products. A doubling of the heart rate can also be observed with a lack of certain vitamins in the body. The disease can be congenital; the patient can live his entire life without even knowing about the presence of this anomaly.
In addition to the kidneys, lumps can form in the lungs and liver. Consolidations in the parenchyma and CL may indicate a tumor. Often the right organ is affected by the tumor. A tumor can be recognized by the following symptoms: blood in the urine, impaired urine flow, prolonged nagging pain in the lumbar region, nausea, vomiting, as well as loss of appetite and sudden weight loss. This occurs due to intoxication of the body, since the kidneys cannot cope with their main function - filtering fluids from harmful toxins.
To accurately diagnose a growth on the kidney , it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination, as well as deep palpation. The tumor is quite often confused with a humpbacked kidney. Humpbacked kidney is a disease in which the contours of the organ protrude. A humpback kidney occurs when the development of the urinary system is impaired or is a congenital defect. At the moment, the exact cause of the anomaly has not yet been clarified.
If there is blood in the urine or if there is prolonged pain in the lower back, you should consult your doctor. Don't delay kidney treatment. The sooner a pathology is detected, the easier it is to treat it.
Functions of the renal sinus
This part of the organ performs several functions:
- regulates the outflow of urine into the pelvicaliceal part;
- normalizes blood flow to organ tissues.
Since the area has a connection with large vessels, the sinus regulates the inflow and outflow of venous blood and the process of urine discharge.
If the functional capacity of the organs is impaired, various changes occur in the sinus area. They affect not only this part of the kidney. But when conducting examinations, it is possible to diagnose the appearance of characteristic compactions in the sinus area.
There is also general swelling of the kidney and a significant increase in size. But in order to diagnose the pathology, it is necessary to conduct a series of examinations.
When there are abnormalities of the renal sinus:
- the outflow of urine is disrupted, it accumulates in the body;
- The blood filtration process becomes difficult, and signs of intoxication appear.
In some cases, blood flow to the organ is disrupted, which leads to necrotic changes. In others, there is partial blockage of the main artery. But much depends on the cause of the pathological processes.
Kidney diseases with compaction of the collecting system
Congenital pathologies that manifest themselves over time as thickening of the pelvis include incomplete doubling of the kidney. It is manifested by the formation of a separate branch of the calyces and pelvis within the body of the kidney. In rare cases, the duplication has a separate membrane and forms a second bud. The pathology is not considered a disease and when inflammation occurs, it is treated therapeutically.
The bifurcation inside the kidney may have a separate branch with 2 - 3 cups, or several small pelvises approach one pyramid, which then connect into one large one.
When a person has pain in the lower back or the process of urination is disrupted, this indicates a problem with the kidneys.
The abnormal structure leads to incomplete urine output and its accumulation, stagnation. Symptoms occur:
- swelling;
- weakness;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- weak urination;
- increase in pressure.
Therapeutic treatment and salt-free diet.
Dilatation of the ventral joints of both kidneys is rare. Typically, enlargement of the pelvicalyceal nodes is formed in one organ. There is a congenital pathology in infants - primary hydronephrosis. Basically, the disease is acquired in nature - secondary. As a result of inflammation or injury, strictures occur - severe narrowing and even complete closure of the ureter. The patient is diagnosed with hydronephrosis.
At the initial stage of hydronephrosis, the renal vascular system is expanded. Unable to exit normally, urine accumulates and a progressive expansion of the pelvis and cups occurs, followed by their atrophy. Based on the nature of the pathology, the causes of hydronephrosis are distinguished:
- internal;
- external;
- functional.
Hydronephrosis of the kidney - expansion of the collecting system caused by fluid pressure on the kidney from the inside
Internal pathologies occur at the level of the ureter. Narrowing and blocking of the outflow of urine occurs due to the formation of:
- fungal infections of the urethra;
- stones;
- tuberculosis;
- blood clots;
- endometriosis;
- polyps;
- ureterocele;
- tumors.
The development of mycetoma and aspergilema fungi in the ureter gradually overgrow the lumen and completely block it, preventing urine from flowing into the bladder.
Stones are formed due to poor nutrition, a predominance of acidic or alkaline minerals in food, and an imbalance in drinking balance. The accumulation of salts, the lack of sufficient clean water to dissolve them, leads to the formation of sand, then stones.
Blood clots occur due to destruction of tissue integrity. Most often this is the result of injuries to the lumbar region during accidents, lifting very heavy weights and hypothermia of the kidneys and severe inflammation with hematuria - bleeding inside the organ.
Endometriosis occurs mainly in women. During hormonal changes, endometrial cells grow through the mucous membranes and close the lumen.
Ureterocele is a cystic formation, a defect of the ureter in men. Formed as a result of prostatitis, physical activity, and injuries. Urethrocele is a protrusion of the urethra in women through the vaginal wall that appears as a consequence of pathological or frequent childbirth.
Hydronephrosis of the kidney during pregnancy is a very common, almost standard phenomenon.
External causes of the formation of hydronephrosis are characterized by the impact on the ureter by expansion or displacement of neighboring organs:
- pregnancy;
- sarcoma;
- cystosis;
- cervical cancer;
- BPH;
- lymphocele;
- aortic anephrism;
- idle;
- prolapse of the kidney - dystrophy.
When the uterus enlarges, especially in late pregnancy, many organs are pressed, including the urinary canals. After childbirth, the process of urine outflow normalizes.
Tumors and cysts press on the outside of the canals, disrupting the passage of urine. As a result of adenoma, the prostate compresses the lower part of the bladder and the canal emerging from it. Inflammation – prostatitis – acts similarly. Most female gynecological diseases block the outflow of urine. Unable to flow out, urine accumulates in the renal pelvis and calyces, stretching them.
When the smooth muscles that support the kidneys in their normal position weaken, the organ begins to sag. As a result of stretching of the vessels, their cross-section decreases and the blood supply to the kidney is disrupted. The urinary tract bends, breaking the lumen.
Symptoms manifest themselves when the chest extends: aching pain in the lower back and groin, swelling and increased pressure
Functional - internal causes of hydronephrosis can be congenital pathologies in the structure of the kidneys or caused by internal diseases:
- inflammation of the kidneys and bladder;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- spinal cord injury.
Symptoms appear when the maxillary joint expands: aching pain in the lower back and groin, swelling and increased pressure. If the cause is stones, the walls are damaged and blood appears in the urine - hematuria.
Types, stages and localization of compactions
If the doctor finds a lump on the kidneys on an ultrasound, he will prescribe additional examinations to determine the causes of the disorders. Depending on the origin, there are 2 forms of pathology:
- Congenital. Changes in the collecting system of the kidney occur in the embryonic period at the stage of formation of the urinary system of the unborn child. Provoking factors include intrauterine infections, maternal use of nephrotoxic drugs, late toxicosis, and radiation exposure.
- Acquired. Secondary compaction is caused by underlying diseases, the negative influence of internal or external factors.
In 78% of patients, secondary changes caused by inflammation or trauma to the maxillary joint are detected. They are conventionally divided into 3 stages:
- Enlargement of the right kidney, what is it?
- Alteration. Pathogenic agents penetrate inside the kidney - bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, which cause inflammation of the internal structures. It is provoked by urolithiasis (urolithiasis), immunodeficiencies, and chronic infections.
- Infiltration. Defender cells - macrophages and leukocytes - are sent to the lesions. As a result, the epithelium of the renal collecting system swells.
- Proliferation. Damaged areas of the organ are regenerated, destroyed nephrons are replaced by connective tissue. It has a high density, so changes are easily detected during ultrasound.
Depending on the cause, the compactions are localized in different parts of the joint:
- small and large cups;
- the junction of the cups;
- renal sinus;
- pelvis.
The greatest danger is posed by deformations and compactions of the pelvis - a funnel-shaped cavity that connects to the ureter. As its lumen decreases, the outflow of urine into the bladder slows down, which leads to an increase in pressure in the organ.
Causes
As practice shows, damage to the structures of the pyelocaliceal system in 85% of cases is associated with an inflammatory reaction occurring in the urinary system, which means that the disease must be treated with antibacterial drugs.
Seal of the sinuses in both kidneys is a sure sign of problems with the urinary system. The epidemiology of the pathology is based on congenital and acquired causes of sinus compaction.
The first category includes anomalies of the intrauterine period:
- heredity;
- internal infections of the mother;
- bad ecology;
- smoking or drinking alcohol by a pregnant woman;
- long-term use of medications.
Acquired causes include pathologies that manifest themselves during life. With an acquired anomaly, two paired organs are damaged. The following diseases and conditions can provoke this condition:
The trigger mechanism is also other diseases of the urinary system, which can cause inflammation or put pressure on the parenchyma of the organs.
Possible complications
Complications vary. Much depends on the cause of changes in the functioning of the urinary system. The pathological process can lead to:
- to tissue necrosis;
- renal failure;
- development of a state of shock;
- tumor degeneration (cancer development).
If the outflow of urine is blocked, the fluid enters other parts of the body, leading to the development of pulmonary or cerebral edema. A tumor can change from benign to malignant.
It is difficult to say what complications should be expected; it all depends on the patient’s condition and the reason that led to the development of an anomaly in the sinus.
Kinds
Compaction of the sinuses of the kidneys or enlargement (thickening) of the organ is often provoked by rapidly developing urolithiasis or inflammation of the fatty “cushion”. Pathological changes may manifest themselves as changes in the size or structure of the entire organ.
If there is thickening of the renal sinus, it can be assumed that there is fluid in the pelvis. The cause may also be metabolic disorders, thrombosis, varicose veins, etc. Based on the type of damage, pathological changes in the kidneys can be divided into several types:
- an increase in the size of the kidney, which often occurs due to inflammation;
- reduction in volume, which is caused by congenital pathology;
- thickening of the kidney walls.
During an ultrasound examination, a specialist distinguishes between several types of visualization of diffuse changes:
- clear and fuzzy;
- weak or moderate;
- expressed.
Additional examinations
If compactions are detected in the pyelocaliceal complex, additional tests and studies are necessarily prescribed. To determine the causes of pathological changes, perform:
- general and biochemical urine analysis;
- clinical blood test;
- test according to Nechiporenko and Zimnitsky;
- excretory urography;
- radioisotope renography;
- kidney biopsy.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor determines the optimal treatment strategy. If tumors are detected, kidney surgery is recommended. In case of infectious inflammation, conservative therapy is limited.
Diagnostics
If there is a suspicion of compaction of the renal sinuses or a history of renal pathologies, the doctor will prescribe a number of laboratory and instrumental studies, including:
- Ultrasound;
- CT scan;
- blood and urine tests;
- intravenous urography.
The diagnostic results will help to identify disturbances in the functioning of the kidneys and determine the pathology of the structures of the pelvic system. Based on the examination results, the doctor makes a final diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Conservative therapy
There is no specific drug treatment. Conservative therapy is carried out before or after surgery.
If the problem lies in atherosclerosis or thrombosis, then therapy involves eliminating the root cause of the pathological processes. It is aimed at correcting the patient's condition.
If the problem is stones, then they are removed by any available method. For tumors, excision of the organ is permissible, but if the formation is not large, it is removed laparoscopically or by puncture.
In rare cases, amputation of the kidney is required; it is performed only if long-term disorders have led to the development of necrotic changes, and they are local in nature.
Space-occupying formations on the kidneys: types and diagnosis
Have you been trying to cure your KIDNEYS for many years?
Head of the Institute of Nephrology: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your kidneys just by taking it every day...
Read more "
Tumor-like neoplasms rarely occur in both kidneys at once: either a mass formation is detected in the left kidney, or the problem occurs in the right. In each specific case, the doctor conducts a full examination to identify the cause and choose a treatment method. Typically, for formations on the kidneys, radical therapy is used - surgery.
What are the variants of pathologies?
Treatment tactics and prognosis for recovery depend on the type of renal tumors. All formations in the kidneys can be divided into the following types:
- single-chamber or multi-chamber cyst containing fluid;
- renal polycystic disease, when many small formations form on the kidney;
- inflammatory tumor (abscess, carbuncle);
- benign neoplasm;
- malignant tumor;
- damage to renal tissue by metastases.
What are the features of the location of the tumor in the kidneys?
Depending on the symptoms, the doctor may suspect the occurrence of a tumor formation on one side. When the tumor is localized in the right kidney, when there is a high risk of impaired blood flow through the inferior vena cava, the following manifestations will occur:
- pain in the right side;
- swelling of the legs;
- pronounced changes in tests (appearance of protein in the urine with a decrease in the blood, metabolic disorders);
- serious liver and heart problems with an increased risk of pulmonary thromboembolism.
All these clinical and laboratory symptoms are much more serious and prognostically more important than when identifying a left-sided renal tumor, which is characterized by:
- pain in the left side;
- expansion of veins in the groin area due to compression.
If a doctor suspects a tumor-like neoplasm in any of the kidneys, he will definitely prescribe an additional examination.
What diagnostic options are optimal?
You should start with simple and minimally invasive techniques.
Ultrasonography
Echography allows you to quickly, painlessly, without trauma to tissues and with high reliability detect any of the tumor-like neoplasms. Main criteria for ultrasound diagnostics:
- organ size;
- echogenicity (structures reflect the ultrasound signal differently);
- condition of renal tissues and changes in blood flow.
If an ultrasound scan reveals an isoechoic structure of the tumor, then it may be a benign neoplasm, which is almost no different from normal renal tissue. If the doctor identifies a hypoechoic formation, then the presence of a cyst can be assumed. Hyperechogenicity is characteristic of solid tumors without fluid inclusions. In addition to the hypoechoic option, cysts and tumors with cavities may have an anechoic appearance on ultrasound scanning.
X-ray examination
The most informative are x-ray techniques, in which a special contrast agent is injected into the urinary tract and subsequent images are taken. These include:
- excretory urography;
- retrograde pyelography;
- nephrotomography;
- renal arteriography and venocavography.
As additional methods, according to indications, the doctor may prescribe endoscopic and radioisotope examination options.
If a hypoechoic renal formation is detected on ultrasound, the diagnosis must be continued: a safe and non-traumatic method of echography reveals a tumor, but does not allow making a correct diagnosis. X-ray techniques help confirm the assumption, clarify the location of the large tumor in the right or left kidney and make a decision on treatment tactics.
Induration of the kidneys - what is it? Quite often, such a term appears in medical reports, which leads people to panic, as they think that it is something oncological. In fact, not everything is as scary as it seems at first glance. Consolidation of the joints of both kidneys or one kidney is simply a sound criterion, which lets you know that the tissue density is increased and because of this, therefore, sound waves will flow worse.
Causes of compactions and stages of inflammation of the collecting system
The density of the pyelocaliceal system of the walls can increase for various reasons, but chronic pyelonephritis has always been and remains one of the most common diseases. During this process, a doctor studying ultrasound will, in addition to compaction, also note an expected reduction in the damaged organ or both organs, uneven edges of the kidney, and also dilatation with deformation of the pelvis and calyces. In case of urine backflow, any urolithiasis and other pathologies, this diagnostic criterion can also be manifested. This means that the picture that the doctor saw is not a sign of a specific disease in any particular organ.
The compaction can manifest itself not only in both kidneys, but also in the lungs, and in the liver, and in other parenchymal organs. Consolidation in the kidney is primarily a sign of some kind of inflammation, that is, complex vascular changes, namely capillaries and veins, and it is also a tissue connection that is formed in response to local exposure to a pathogenic irritant.
As an inflammation of a certain system in the body, the deformation of the CLS is divided into three main stages:
- The first is called alteration. It is formed when, when microbes enter, the body is no longer able to resist them, that is, when the epithelium dies at the time of the formation of certain defects on it.
- The second stage is called exudation. During exudation, leukocytes and immunocomplexes rush to the affected areas, which, in turn, fight the negative effects of microbes. For this reason, blood flow to the damaged area increases and the walls of the joint swell very much.
- The third stage is proliferation. Already at this stage, tissue density increases due to the fact that the epithelium begins to divide quite quickly and grows in the inflamed area, while separating the diseased area from the healthy one.
Diseases associated with hardening of the jaw
Like any other organ, CLS and all diseases associated with it can be not only acquired, but also congenital. Hydronephrosis, strictures and doubling of the heart rate are congenital pathologies.
Hydronephrosis is a certain expansion of the pelvis and calyces with atrophy of the parenchyma of two kidneys at once. Often this defect is secondary, which developed with narrowing of the ureter. Sometimes it can be caused by congenital vesicoureteral reflux (returning of urine).
Stricture is a narrowing and complete fusion, which is accompanied by hydronephrosis.
Doubling the heart rate does not really affect human health; it is possible to live your whole life without even realizing the existence of this defect.
ChLS is a very important component of the kidney, which is why if dull pain begins to appear or blood is observed in the urine, then you must immediately contact a specialist in order to get rid of this ailment.
Be healthy!
The folk way to cleanse the kidneys! Our grandmothers were treated using this recipe...
Cleaning your kidneys is easy! You need to add it during meals...
General concepts
What are the compactions of the pharyngeal joints of both kidneys and what does this pathology indicate?
- What is doubling of the left kidney?
First of all, you should decipher the abbreviation itself. The PLS is the pyelocaliceal system, which forms the anatomical structure of the organ. And the tissue density of the paired organ, which is determined by this system, indicates the degree of echogenicity during ultrasound.
Therefore, this conclusion cannot be called a diagnosis. Consolidation of the jaw suggests the presence of some disease, and therefore is a sign of it.
Treatment options
Seals in the parenchyma (kidney tissue) or CLS in medical practice are not an independent disease. This is a symptom of an inflammatory process in the body. Therefore, in order to cure seals, it is necessary to eliminate the root cause of their appearance.
In 50% of cases, the cause of the formation of compactions is pyelonephritis . That is why the most effective treatment method is antibacterial therapy. If the diagnosis reveals a hardening of the joints of both kidneys, intensive treatment will be required.
Seals also indicate improper functioning of the urinary system. In such a situation, treatment is prescribed, which is aimed at eliminating obstacles that interfere with the normal functioning of the organ.
Clinical picture of the pathology
The diagnosis is based not only on the results of an ultrasound scan, which showed the presence of thickening of the kidney sinuses, but also on a number of the patient’s sensations. There are no distinctive signs of such anomalies in the pelvis areas. However, there is a general list of symptoms:
- pain in the lumbar region;
- frequent urge to urinate (they can often be false);
- presence of bloody discharge in the urine;
- bloating;
- elevated body temperature.
In the case when tissue density is observed on both sides, the pain is distributed evenly. With unilateral compaction, the sensations are concentrated in one kidney, and therefore will be more obvious.
The presence and type of changes in tissues, as well as the reasons for their appearance, are determined by ultrasound.
How does the anomaly develop?
The inflammatory reaction, during its development, can create different degrees of compaction of the kidney tissue.
The inflammatory reaction, during its development, can create different degrees of compaction of the kidney tissue. There is a classification according to the phases of development of this anomaly:
- Stage of damage (alteration). At this stage, settled pathogenic microorganisms settle on the mucous membrane of organs, and the process of releasing their waste products and toxins begins. This can happen in one kidney or in both at the same time. In most cases, this indicates the inability of the immune system to cope with an infectious lesion, which leads to massive death of epithelial cells (as shown by urine tests);
- Exudation stage. At this stage, the body sends leukocytes and immune complexes to the affected area, which begin the process of suppressing pathogens. In this area, blood flow increases, tissues swell and thicken, which is diagnosed by ultrasound;
- Stage of structural changes at the cellular level (proliferation). Epithelial cells divide rapidly, and inflammation progresses. The parenchyma becomes significantly denser with a tendency to increase the degree of damage; a clear outline of the compaction is visible on ultrasound. In the parenchyma, the replacement of cells with connective tissue begins, due to the sclerotic process (similar to the formation of scars on the surface of the skin after a violation of its integrity).
Manifestation of symptoms
It is noteworthy that pathological processes over a long period of time can occur without specific symptoms. Signs occur periodically and intensify over time.
It is nominally believed that if there are disturbances in the functioning of the sinus, then the person is bothered by typical signs of diseases of the urinary system. It can be:
- pain in the lumbar spine;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- disturbance of the urination process;
- decrease in total daily diuresis (due to fluid accumulation);
- change in urine color (hematuria).
The patient may not complain at all, and this is considered quite normal. Because if only 1 organ is affected, the other takes on more work. This compensates for the condition; there are no characteristic signs.
The only specific symptom is an increase in blood pressure. If the blood pressure is consistently high, then it is worth checking not only the heart, but also the kidneys. Because the cause of everything may be fluid retention in the body.
- Is it possible to eat before an ultrasound of the kidneys: diet before ultrasound diagnostics
Treatment options
Only after a complete diagnosis can treatment begin. If the compaction in the kidneys was caused by inflammation and bacterial infection, then it is necessary to undergo a full course of antibacterial and auxiliary therapy. The process of suppressing pathogens occurs using the following drugs:
If everything was prescribed correctly, then at the next ultrasound examination the doctor will not find any signs of compactions.
If a cyst or stone is found in the kidney, surgical intervention is required. During the operation, all salt formations are removed, and the person can safely return to their normal lifestyle.
If a paired organ is affected by tumors, the patient must undergo a course of chemotherapy or radiation simultaneously with therapy.
The duration of therapy depends entirely on the cause of the disease and its stage. This may take from two weeks to several months.
Important! The occurrence of lumps in the kidneys can be prevented. To do this, it is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle and adhere to proper nutrition.
Pregnant women should be especially careful about their health. If you still feel pain in the kidney area, your doctor will prescribe an ultrasound.
This is the only effective method of examination during pregnancy. With its help, you can easily identify the cause of pain. However, the results of an ultrasound examination are not a final diagnosis!
Remember that hardening of the kidneys is not an independent disease.
Hardening of the kidneys indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body. In order to understand what stage it is in, you need to pay attention to the symptoms: pain in the lumbar region, heaviness in the kidneys, problems with urination, etc. After identifying dangerous signals, you must urgently consult a specialist.
Modern medicine can quickly save a person from this problem. Only a doctor can prescribe treatment!
Kidneys are one of the most important organs in the human body; they maintain water-salt balance and cleanse the blood of toxins. Impaired kidney function can lead to serious consequences. If a patient is found to have lumps, he should begin treatment immediately.
Stages of inflammation
Any inflammatory process has three stages. When a bacterium enters the mucous membrane of the urinary system, it begins to secrete toxins, as well as products of its vital activity. It happens that the local immunity of the ChLS itself solves the problem. The person does not feel anything, his condition does not change.
If the immune response is weak, then the first stage of inflammation occurs. It's called alteration. As a result, the mucosal epithelium dies and defects appear.
Then the second stage begins. It was given the name exudation. Leukocytes and other active cells “come” to the affected area to fight pathogenic microorganisms. And then the damaged area looks swollen because blood has rushed to it. And at such a moment, an ultrasound scan will show a thickening of the joints of both kidneys.
The third stage is called proliferation. The tissue becomes even denser because the epithelium begins to grow to protect healthy areas from damaged ones.
Cells that have died are replaced by areas of connective tissue. They become sclerotic. For a more complete understanding, you need to imagine the scar left on the skin after wounds and scratches.
Compaction stages
The compaction of both kidneys can be divided into several stages.
- The initial stage is called alteration. The seal appears after the penetration of various harmful bacteria into the body, which provoke the onset of the inflammatory process. Their development has a detrimental effect on the condition of the kidneys. First, the inner shell begins to collapse, and over time it may even die. If a person has a strong immune system, then the alteration stage can be asymptomatic. In this case, time will be lost, and various complications may arise.
- The next stage is exudation. The presence of congenital diseases of the urinary system can greatly complicate the situation. The fact is that at this stage swelling of the jaw may appear. With a weak urinary system it is more pronounced. Blood flow to the affected area begins to increase. It is at this stage that you can notice the appearance of the first compacted areas of tissue.
- Proliferation. At this stage, the process of rapid compaction of the kidney tissue begins. This occurs due to the proliferation of epithelial tissue that separates the diseased tissue from the healthy tissue. The consequence of such changes may be nephrosclerosis. This means that the kidney tissue will be replaced by connective tissue. We can often observe this process on our skin when new scars form.
Important! The compaction can spread to either one kidney or two.
What is a lump in the kidney?
Structural abnormalities of these organs, such as hardening of the kidneys, are detected by ultrasound.
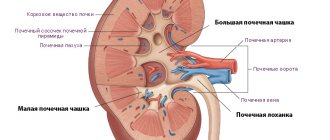
The kidneys are a unique filtering paired organ of the human body, capable of completely passing through the entire volume of human blood in five minutes. The structure of the kidney is represented by the pyelocaliceal system (PSS), in which the process of accumulation of urine occurs, which is then sent to the lower urinary parts of the system. The renal sinus is the “gate” in the process of urine formation. The medulla and cortex of the kidney make up the renal parenchyma; these layers are penetrated by vessels and nephrons. The complex structure of these organs, and in particular the CLS of both kidneys, forms and removes urine further into the ureters.
Structural abnormalities of these organs, such as hardening of the kidneys, are detected by ultrasound. Densification of the kidneys is a change, most often, of the inflammatory nature of the parenchymal structure, affecting the connective tissue or causing disturbances in the blood flow of the vascular system of the kidneys.
Compaction is a natural reaction to inflammation. The compaction appears during ultrasound diagnostics as an area with increased echogenicity, which differs from the wave characteristics of other parts of the kidney. The collecting system is the area where abnormal compaction is most often diagnosed; the renal sinus is less often affected. Ultrasound also determines the area, localization, degree of tissue heterogeneity and compaction contours, as well as other possible deformation changes.
Recommended reading:
How to find a kidney recipient and who can become a donor?
Note! Ultrasound establishes the fact of compaction in the kidney and its localization, however, additional research is needed to differentiate and make an accurate diagnosis.
Kidney seals: causes, symptoms, treatment
Kidneys are one of the most important organs in the human body; they maintain water-salt balance and cleanse the blood of toxins. Impaired kidney function can lead to serious consequences. If a patient is found to have lumps, he should begin treatment immediately.
Lumps in the kidneys
A diagnosis such as “lumps in the kidneys” may sound quite serious, since the word “lumps” is associated in many patients with cancer. However, this is not quite true. That is why additional research should be carried out, and, if necessary, appropriate treatment should be prescribed.
Kidney hardening can be detected using ultrasound. Often, renal compactions are just an ultrasound criterion that characterizes increased tissue density and is in no way associated with serious diseases, however, a mandatory examination is necessary.
The kidneys have a rather complex structure. The pyelocaliceal system is located inside the paired organ. It consists of several cups, which gradually turn into the pelvis.
The pelvis resembles reservoirs. Urine accumulates in them before going into the ureters and exiting naturally.
If there is a focus of inflammation in the body, then more and more fluid accumulates in these reservoirs.
The walls of the organ stretch and at a certain period may rupture, and urine will spill into the peritoneum.
In a healthy person, the CLS works smoothly. However, minor disruptions in their work can lead to the development of serious complications. Due to the inflammatory process, hardening of the jaw and kidneys may appear. There is also impaired blood microcirculation in the vessels and connective tissue.
Compaction stages:
- The first stage of compaction is alteration. It occurs when all sorts of pathogenic and inflammatory microorganisms enter the body. They have a detrimental effect on the paired organ: the inner membrane dies and defects begin to form on it. With normal functioning of the immune system, inflammation can be asymptomatic.
- The second stage is exudation. During exudation, severe swelling of the jaw is observed. Gradually, blood flow to the deformed area begins to increase. At this stage, you can notice the appearance of the first seals in the area of the paired organ during an ultrasound scan.
- The third stage is proliferation. At this stage, the density of the organ tissue increases. This occurs due to the proliferation of epithelial tissue, which separates the healthy area of the organ from the affected one. As a result of this deformation, sclerosis may develop. Sclerosis is a disease in which the tissue of a certain organ begins to thicken and degenerate into hard connective tissue. Quite often, this deformation can be noticed on the skin: small scars form on the skin.
Causes of compaction of the maxillary sinus, parenchyma, structures of the renal sinuses
The main causes of these pathologies are divided into 2 groups: congenital and acquired.
- Congenital - doubling of the urinary tract, compression of the canal, sinus and urinary duct, scarring of ureteral tissue due to its intersection with vessels, atrophy of kidney tissue (in the form of dilation of the pelvis and calyces);
- Acquired - pyelonephritis (a contagious disease that causes inflammation of a paired organ), elevation of a cyst on the kidney tissue.
Important: the pathology should be treated on time, otherwise it can lead to death due to the development of renal failure.
There are 3 main stages of development of inflammation in the CLS:
- alteration: the first level of inflammation in which defects occur in the epithelium of the mucous membrane. Due to the penetration of microbes into it and the inability of the body to protect itself from this environment;
- exudation: the second level of pathology development. The walls of the mandibular joint swell due to a rush of blood and the first compressions are visible;
- proliferation: third level. The compaction of the collecting system becomes stronger due to the replacement of dead cells.
Causes of seals
The main reason for thickening of the joints of both kidneys is congenital and acquired diseases of the organ. In 70%, the root cause is pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. During an ultrasound, the specialist looks at the uneven edges of the kidney and changes in its size. Diseases that can cause hardening of the renal sinus:
- pyelonephritis is a disease that is accompanied by severe inflammation of the pelvis. Its occurrence is provoked by various infections. Also, pyelonephritis can develop when the outflow of urine is impaired;
- hydronephrosis provokes dilation of the renal pelvis. In this case, the tissue is affected, which will become denser over time. This disease appears with urolithiasis, as well as with chronic diseases of the urinary tract. In turn, kidney stones appear due to an incorrect lifestyle, diet, etc. This disease can cause strictures in a person. This is another disease that causes narrowing of the tubular organs. Symptoms at the initial stage of the disease are mild, usually only renal colic appears;
- doubling the heart rate is absolutely safe for humans. Inflammation can develop after long-term use of medications, abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products. This problem can also appear due to a lack of vitamins and beneficial microelements in the body. A person can live his whole life with such a diagnosis, but never know about the presence of this anomaly.
Important! In addition to the kidneys, lumps can even appear in the lungs or liver.
Seals in a paired organ may indicate a neoplasm. Statistics show that the right organ is more likely to develop a tumor. The first symptoms that indicate the development of a neoplasm are:
- the appearance of blood in urine;
- constant pain in the lumbar region;
- nausea and vomiting;
- painful sensations when urinating.
Can bilateral compaction indicate the presence of a tumor?
If the CLS is compacted on both sides, then this question can be answered in the negative. The likelihood that malignant neoplasms will appear simultaneously in two kidneys is negligible.
An exception is nephroblastoma . This is a tumor that develops in young children (the peak of the disease occurs at 3 years) from embryonic organ tissue. In 5% of young patients it affects both kidneys at once.
Sources used:
- https://simptom.info/nefrologiya/uplotnenie-chls-pochek
- https://urohelp.guru/anatomy/sinus-pochki.html
- https://pocki.top/mochekamennaya-bolezn/uplotnenie-pochechnykh-sinusov/
- https://pochki.guru/bolezni/uplotnenie-chls-pochek.html
- https://uran.help/surveys/radiology/uzd/uplotnenie-chls-i-sinusov-pochek-na-uzi.html
- https://lecheniepochki.ru/patologii/uplotnenie-v-pochkax-chto-eto-takoe.html
- https://pochkam.ru/bolezni-pochek/uplotnenie-chls-obeih-pochek.html
- https://kardiobit.ru/pochki/lechenie/uplotnenie-chls-obeih-pochek-chto-eto-takoe-prichiny-i-posledstviya
Consolidation of the joints of both kidneys: what is it, causes and consequences
The term “consolidation of the renal joint” is quite often found in the reports of doctors performing ultrasound examinations of the kidneys. It means that the tissue density is higher than normal, and it transmits ultrasound less well. In itself, such a conclusion is not a diagnosis, but may indicate pathological processes occurring in the paired organ.
What is the calyx system?
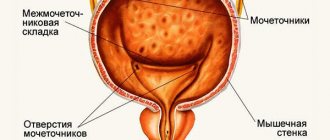
Each kidney has a special system through which the urine formed in it is discharged into the ureter. It can be imagined in the form of funnels inserted into each other. The smallest of them are located in the cortex of the kidney and are called small calyces. They receive filtered urine from the collecting ducts (they collect fluid formed in the medulla of the organ).
Small calyces - there are from 6 to 12 - are combined into 2-3 large calyces, and they form the pelvis. A continuation of the pelvis is the ureter . The place where it begins is called the neck. The neck is the narrowest part of the ureter.
All the calyces and the pelvis are the calyx system (abbreviated CLS) of the kidney. The inside is lined with mucous membrane. Underneath it is a muscle layer consisting of smooth muscle bundles. These bundles, contracting, ensure the forward movement of urine.
Mechanisms causing tissue compaction
Any tissue becomes denser if inflammation occurs in it. The inflammatory process has three stages:
- Alteration is damage to the mucous membrane by pathogenic agents.
- Exudation is swelling at the site of injury.
- Proliferation is increased cell division to delimit the diseased area.
- Acute and chronic pyelonephritis.
- Chronic glomerulonephritis.
- Initial stages of purulent processes (abscess, carbuncle).
- Infectious diseases (tuberculosis, hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome).
- Autoimmune kidney damage (with systemic lupus erythematosus, Wegener's granulomatosis, periarteritis nodosa, Goodpasture's syndrome, thrombocytopenic purpura, etc.).
- Formation of stones or deposition of salt crystals (gout, urolithiasis, hyperparathyroidism, primary hypercalciuria, Wilson's disease, etc.).
- Diabetic nephropathy.
- Amyloidosis of the kidneys.
On ultrasound, signs of compaction can be seen starting from the second stage of inflammation, in the third they become even more pronounced.
Another reason for increased tissue density is sclerosis . At the same time, many connective tissue fibers appear in it. They replace the working cells of one or another organ, but do not take over their functions. Nephrosclerosis is a late stage of some chronic kidney diseases.
Reasons for tightness of the joints
Many kidney diseases at one stage or another can be the cause of hardening of the chest. This:
Some of them can affect only one kidney (abscess, carbuncle, urolithiasis), others - both. Bilateral damage is especially typical for chronic pyelonephritis, autoimmune diseases, amyloidosis and diabetic nephropathy.
When are changes on ultrasound not considered pathological?
The calyx system is surrounded by fibrous and adipose tissue, blood and lymphatic vessels. Together they form an anatomical structure called the renal sinus.
If an ultrasound is performed on an empty stomach, then normally the doctor can only see the entire renal sinus. It is impossible to separate the ChLS from it.
During a water-load study, the calyces and pelvis become visible and appear as a tree-like formation.
Normally, the calyx system is compacted in children under three years of age and people over 60 years of age. In children, all kidney structures, including the calyces and pelvis, are located more compactly than in adults. In older people, initial signs of sclerosis of the collecting system and blood vessels are observed, so the renal sinus appears denser.
Can bilateral compaction indicate the presence of a tumor?
If the CLS is compacted on both sides, then this question can be answered in the negative. The likelihood that malignant neoplasms will appear simultaneously in two kidneys is negligible.
An exception is nephroblastoma . This is a tumor that develops in young children (the peak of the disease occurs at 3 years) from embryonic organ tissue. In 5% of young patients it affects both kidneys at once.
Possible consequences of the problem
Consequences occur in diseases that lead to compaction of the calyx system. They can progress, causing corresponding symptoms and syndromes.
Thus, with systemic lupus erythematosus, fibrous tissue begins to grow in the organs, replacing normal cells. In this case, thickening of the pelvic region may signal an early stage of autoimmune kidney damage.
One more example. A patient with diabetes mellitus has become more severe. This may indicate that diabetes is complicated by nephropathy, which may result in chronic renal failure.
Tactics for dealing with increased density of the ChLS
Is it worth sounding the alarm if the conclusion issued by a functional diagnostician says that the CLS is compacted? This issue should be decided by the doctor who gave the referral for an ultrasound examination.
If the patient’s complaints, examination and test results coincide with the picture presented on the ultrasound, then making a diagnosis is not particularly difficult. But in some diseases, it is impossible to determine the cause of changes only from ultrasound data. In this case, the patient is prescribed additional examination methods - MRI, intravenous urography, radioisotope renography, etc.
Loading…
Source: https://KardioBit.ru/pochki/lechenie/uplotnenie-chls-obeih-pochek-chto-eto-takoe-prichiny-i-posledstviya
How to cure kidneys at home?
SWELLING of the face and legs, PAIN in the lower back, CONSTANT weakness and fatigue, painful urination? If you have these symptoms, there is a 95% chance of kidney disease.
If you care about your health, then read the opinion of a urologist with 24 years of experience. In his article he talks about RENON DUO capsules. This is a fast-acting German remedy for kidney restoration, which has been used all over the world for many years. The uniqueness of the drug lies in:
- Eliminates the cause of pain and brings the kidneys to their original state.
- German capsules eliminate pain already during the first course of use and help to completely cure the disease.
- There are no side effects and no allergic reactions.
Treatment of deviation
There is no such diagnosis - kidney compaction. What it really is and why it arose - the doctor will tell you when he conducts a series of additional studies. For the doctor, changes in thickness will be a signal of an inflammatory reaction. He will suspect pyelonephritis.
After confirmation, antibacterial therapy will be prescribed. Upon completion of treatment, a follow-up examination can be performed. As a result, there will be no trace left of the compaction. If changes were noticed in both kidneys, then therapy should be more powerful.
The density of the pelvic floor indicates that the outflow of urine is impaired, and the mucous membranes experience constant irritation.
On the monitor, the specialist sees why urine cannot easily leave the body. When the cause is eliminated, then the walls of the joint will return to normal. Recovery usually takes no more than two weeks.
Note that in newborns this picture is the norm. An experienced specialist must differentiate what he sees from inflammation. Seals in children disappear after a year.
Often, areas with reduced echogenicity are mistaken for compactions. This term is used by a sonologist to designate areas that transmit ultrasound waves less well. A similar picture is observed with swelling and inflammation. We must not lose sight of the fact that tumors also behave this way on ultrasound.
Based on all of the above, it should be concluded that if you have a lump in your kidney, you need to continue to be examined together with your doctor. Especially if, along with this symptom, the pelvis is dilated and deformed.
Diagnosis and treatment
The main diagnostic method is ultrasound examination of the kidneys. During an ultrasound, the doctor will assess the location of the organ, its size, see the compaction of the walls, deformation of the pelvis and cups, as well as the presence of sand and stones. A urine test is also required; if necessary, additional tests are prescribed to help clarify the diagnosis.
Treatment is selected depending on the identified problem. It is quite possible to cope with urolithiasis and pyelonephritis with the help of conservative measures. If there is significant damage to kidney tissue or congenital pathologies, treatment can only be symptomatic. In severe cases, hemodialysis or surgery is indicated.