Why does my kidney hurt?
There are many causes of kidney disease. These include inflammatory and tumor diseases, injuries to this area, and developmental anomalies of the urinary system, which “raise their heads” under the influence of provoking factors. Let's look at everything in order.
Glomerulonephritis
This is a disease when the kidney tissue suffers from an attack by its own immune cells, which, starting to fight the infection, mistake the kidney cells for microbes. The pathology most often develops after a streptococcal disease (for example, tonsillitis).
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis:
- lower back pain;
- blood visible to the eye in the urine;
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling on the eyelids, legs.
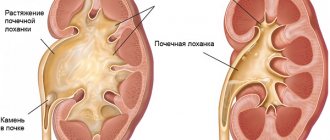
Kidney stone disease
If pain in the left side of the abdomen/back appears as a result of a pathological process, then there are several diseases that can provoke the appearance of such sensations.
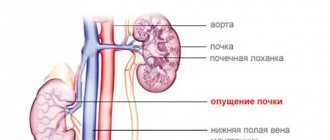
Why is nephroptosis dangerous?
There are several complications with the development of nephroptosis:
- Hydronephrotic transformation. When the ureter is twisted or bent, urine stagnates in the kidneys;
- Development of pyelonephritis. This is an inflammation of the kidneys, which is accompanied by renal colic and requires surgical treatment;
- Arterial hypertension, which develops secondary. It develops when renal blood flow is impaired, when the pressure cannot be reduced. This leads to hypertensive crises.
Causes
Let's look at the most common diseases with kidney pain syndrome, which people describe in a certain way.
Pain syndrome associated with alcoholism
Let's look at why your kidneys hurt after drinking beer:
- this drink “pulls” water from the tissues, which leads to increased load on the kidneys: first you need to remove the increased volume of urine, and then also the liquid that the person took due to thirst caused by beer;
- over time, the blood becomes thicker (most of the liquid has already left), and it is more difficult for the kidneys to filter it;
- As a result of this “dehydration assault,” the tissues lose the necessary electrolytes (potassium, calcium, phosphorus) and proteins, which gradually settle in the kidneys and form stones.
The following conditions can cause pain in the area of the right kidney:
- Inflammatory processes of the appendix, which often contribute to the appearance of pain in a different area where it usually occurs. Pain sensations are observed in the right organ and in the lumbar area.
- Nephroptosis, which is a displacement of an organ, is often diagnosed in women. Nephroptosis of the right side develops due to a decrease in the strength of the ligaments of the organ on the right and the pressure exerted on the organ by the liver located above.
- Right-sided pyelonephritis in pregnant women. It develops due to a physically caused enlargement of the reproductive organ, which often moves to the right side. With the disease, frequent urination and fever are observed.
- Urolithiasis, which, according to statistics, is diagnosed in the right kidney in 60% of cases.
- Hydronephrosis, which is a disease characterized by necrosis of kidney tissue.
- Neoplasms in the right kidney.
- Cystic formations.
- Inflammation and purulent process in the right organ.
- Organ injury.
- Diseases of a parasitic nature.
Pain in the kidney area is most often caused by direct damage to the organ or an inflammatory process (infection). Sometimes other types of pain: in the lower back or back are perceived as renal colic.
You need to know that independent pain in the kidney area during a pathological process is rare; it is usually accompanied by other accompanying symptoms: changes in urination, fever, swelling, and disturbances in general well-being.
You need to know that true pain or renal colic may indicate diseases directly related to the inflammatory process in the kidneys, so when the first symptoms appear, consult a urologist to determine the cause.
The main cause of lower back pain is inflammation of the kidneys (chronic pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis) or prolapse (nephroptosis), as well as the presence of stones in the kidney itself or the urethra (urolithiasis).
Additional symptoms that indicate kidney disease are: impaired urination (increased or decreased frequency), pain, burning during urination, change in the color of urine (cloudy, mixed with blood or pus), swelling on the face and legs (usually in the morning), and also weakness, malaise and fever (with infection).
Urostasis of the kidney: what is it, symptoms of stagnation of urine in the kidneys and bladder - About the Kidneys
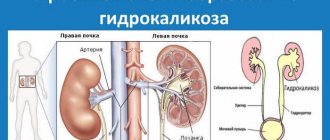
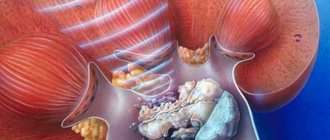
Hydronephrosis is stagnation of urine in the kidneys, enlargement of the renal system and its calyces. According to statistics, the disease affects women more often than men. The development of hydronephrosis in men most often ends with prostate cancer, urethral stricture, and in young people the disease is caused by urolithiasis.
Congestion in the kidneys is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the renal cups, as a result of which the functionality of the renal system is disrupted and a pyelocaliceal pathology is formed. Hydronephrosis can be infected or aseptic.
In this article we will tell you why urine stagnation occurs in the kidneys, we will analyze the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of the pathology.
Reasons for the formation of stagnant urine
Hydronephrosis is stagnation of urine in the kidneys, enlargement of the renal system and its calyxes
Impaired functioning of the renal system and the formation of stagnation of urine can occur due to the following reasons:
- the presence of pathological processes in the urethra and bladder; such a disorder can be provoked by tumor processes, previous infectious diseases, phimosis;
- external compression of the ureter, which is formed due to a violation of the lymphatic system, cysts, after surgery;
- changes in the lumen of the ureter caused by urolithiasis, torsion or kinking of the ureter caused by injury or congenital disorder;
- congenital anomaly or the presence of VUR, which can impair the functioning of the renal system and pelvis.
For information! There are congenital hydronephrosis, which forms in fetal development, and acquired hydronephrosis, which occurs as a result of damage to a previously healthy kidney.
Stagnation of urine in the kidneys during pregnancy is considered a fairly common phenomenon. The disorder occurs due to changes in hormonal levels, which affect the rhythmic contractions of the ureter.
The last trimester is dangerous because due to the increase in the size of the uterus, mechanical compression of the ureter occurs.
To monitor the situation and the health of a pregnant woman, a urine test is taken on a regular basis for culture, and if obvious deviations from the norm are confirmed, therapy is carried out.
Symptoms of hydronephrosis
With chronic stagnation of urine in the kidneys, the patient feels attacks of severe pain in the lumbar region
At the initial stage of hydronephrosis, a person does not feel any symptoms or changes in his health. There may be a feeling of general malaise, tiredness or increased fatigue. It is precisely because of the absence of symptoms that it is quite difficult to identify the problem, however, it is possible with a random examination. The main symptoms of congestion include:
- the organ increases in size and weight;
- the organ acquires a blue-red color;
- the appearance of yellow spots;
- tense state of the renal capsule;
- pronounced venous pattern;
- connective tissue shrinks as a result of which the organ acquires an uneven surface;
- with enlargement of the glomeruli, red spots are observed;
- during a period of prolonged stagnation, atrophy of the renal substance occurs and its replacement with connective tissue;
- the kidney substance changes to fat.
With chronic stagnation of urine in the kidneys, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- attacks of severe pain in the lumbar region;
- intense pain attacks radiating to the genitals appear after eating food;
- irregular attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- temperature rise to 39C degrees;
- presence of blood clots in urine.
For information! In urological practice there is such a thing as a congestive kidney. This condition is accompanied by poor circulation, resulting in heart failure.
Most often, the chronic form passes without permanent symptoms; attacks are increasing and intermittent. If you feel discomfort and notice changes, contact a specialist for advice.
Diagnosis of the disease
The purpose of diagnostic measures is determined based on the patient’s complaints
The purpose of diagnostic measures is determined based on the patient’s complaints and includes:
- general urine analysis;
- biochemical and general blood test;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder and renal system;
- examination of the urinary system using magnetic resonance imaging;
- intravenous urography;
- CT scan;
- retrograde pyelogram;
- radionuclide research.
For information! Diagnostics allows you to determine the pathological disorder of the internal structure of the organ, and also reflects the general condition of the vessels and ureter.
Microscopic examination reveals how dilated the vessels are, as well as the presence of protein in the collapsed capillaries and tubules.
Treatment of hydronephrosis
To reduce and prevent pain, the patient is prescribed painkillers and antibacterial medications.
Long-term morphology of the disease significantly impairs the functionality of the renal system and causes renal failure. Stagnation of urine in the kidneys causes the following complications:
- pyelonephritis of all forms;
- stone formation;
- progression of inflammatory processes throughout the body, which can result in death;
- secondary reduction in kidney size;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure.
If the disease is confirmed, treatment should be started immediately. To reduce and prevent pain, the patient is prescribed painkillers and antibacterial medications. Normalization and restoration of urine outflow is carried out using surgical intervention. The choice of surgery depends entirely on the cause of congestion in the kidneys.
Catheterization
This operation is performed in the presence of a malignant or benign tumor in the prostate gland, as well as in the presence of sclerosis of the bladder neck
This operation is performed in the presence of a malignant or benign tumor in the prostate gland, as well as in the presence of sclerosis of the bladder neck. The site of narrowing of the ureter is widened using a ureteral stent and an endoscope is inserted to perform retrograde pyelography.
Percutaneous nephrostomy
Using ultrasound, an external drainage is installed into the cavity system of the organ; the drainage helps urine flow into the external collection system.
Carrying out open surgery
Open surgery is performed if there are indications:
- the presence of a tumor in the retroperitoneal region;
- the presence of stones that cannot be eliminated endoscopically or with shock wave therapy;
- presence of retroperitoneal fibrosis;
- with pathological dilatation of a blood vessel.
Endoscopic method
Used in the presence of stones that prevent normal urine flow. Any surgical intervention can partially or completely remove the cause of the formation of compression of the kidney, however, the result of the operation completely depends on the stage and form of the disease.
Disease prevention
Timely and high-quality implementation of preventive measures to eliminate the causes of hydronephrosis contributes to the complete and rapid restoration of the functioning of the renal system.
With a long-term and bilateral course of the pathology, the prognosis of the pathology ends with the appointment of hemodialysis or a kidney transplant.
The main preventive measures for the formation of stagnation in the kidneys include:
- daily observance of personal hygiene rules;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- prevention of pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- timely treatment and prevention of infectious diseases, including sexually transmitted diseases;
- following a diet with a reduced amount of table salt, as well as a complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages.
Remember, the development of the disease and its complications can be prevented only by strictly following all recommendations, timely examination and treatment.
Source:
Kidney urostasis - what it is, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
A person suffering from kidney urostasis has difficulty passing urine. With this disease, quite unpleasant consequences can occur. That is why, with its acute development, you should immediately seek help from a specialist.
Urostasis (from the Greek “urinary cessation”) is a pathology in which urinary stagnation . Complications begin during its outflow, and sometimes there is a complete absence of its release. This disease can be triggered by various factors and develop in either one or two kidneys.
Classification of urostasis
The disease is divided into two groups, taking into account the complexity of its course:
- Chronic urostasis.
- Acute urostasis.
- Mechanical.
- Dynamic.
In the first case, the disease actively develops over many months or years. During the course of the disease, favorable conditions appear for the emergence of any infectious or atrophic processes.
The acute form is characterized by a high rate of development and requires immediate attention to the clinic.
Causes of pathology
The most common manifestation of this disease is chronic. At the same time, urine is released from the body very slowly.
After a long period of time, contraction of the ureteric muscles begins to deteriorate . Then, on top of everything else, processes of an inflammatory and obstructive nature are added.
Based on this, the reasons that provoke the appearance of this pathology are divided into two categories:
Mechanical action creates an obstruction to the passage of urine. It is worth noting that it appears in any organ of the urinary system.
There are quite a few reasons for the mechanical development of urostasis. However, it is worth highlighting the most popular of them:
Dynamic causes include those that contribute to the incorrect direction of urine in the urinary system:
- Weak ureteral peristalsis (acquired or congenital),
- Backflow of urine, as well as reflux.
It is dynamic factors, due to long-term effects on the body, that become provocateurs of the chronic form of the disease.
Consequences
To avoid undesirable consequences of urostasis, do not hesitate to visit a doctor and promptly get rid of all the causes that can provoke it.
Refusal of a specialist’s instructions entails such consequences as: kidney deformation, reflux nephropathy, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, arterial hypertension and cystitis. However, the most unpleasant thing, in addition to the above, is kidney failure .
Only strict adherence to the specialist’s instructions makes it possible to protect yourself from the negative consequences of urostasis.
Source: https://uroscope.ru/diagnostika/urostaz-pochki-chto-eto-takoe-simptomy-zastoya-mochi-v-pochkah-i-mochevom-puzyre.html
Symptoms of pathology
It must be remembered that back pain in the kidney area is relatively high - at the level of the lower ribs and upper lumbar region, the pain can be long-term aching (with chronic inflammatory processes) or acute, intense (with urolithiasis, acute inflammation and prolapse of the kidney) - true renal colic.
Renal colic is accompanied by nausea, vomiting (due to severe pain), profuse sweat, chills and fever. During an attack of renal colic, it is necessary to seek medical help to relieve spasm, pain and determine the cause of the attack using instrumental examination methods.
The following diseases can also cause pain:
- benign and malignant neoplasms (cancer, fibroma, adenoma);
- hydronephrosis (expansion of the kidney cavity due to atrophy of the kidney tissue);
- chronic renal failure.
Pain in the lower back on the right or left, in the kidney area, is a characteristic sign of the development of many diseases. It is important to pay attention to additional manifestations that accompany pain in the lumbar region and kidneys:
- weakness, loss of strength, lethargy;
- increased blood pressure (head pain);
- morning swelling, it goes away in the evening (face, legs);
- abnormal urination (signs of cystitis);
- increase in temperature (chills, weakness).
The severity of symptoms does not change with changes in body position. Self-medication is prohibited. If the symptoms described above occur, you should immediately seek medical help.
The most important sign of the development of the disease is a decrease in the amount of urine excreted, or oliguria. A person may notice both a general decrease in urine and its appearance in small portions in some cases. In acute urostasis, anuria, or complete cessation of urine flow, is often observed.
Stagnation of secreted fluid and stretching of the renal tubules cause the development of all other components of the clinical picture:
- Pain syndrome localized in the back, lower back (in the projection of the kidneys). In chronic urostasis it is dull in nature, in acute urostasis against the background of urolithiasis it is cutting, as in renal colic
- Pain during urination, as well as burning and itching in the urethra
- The appearance of swelling on the face and legs (swelling occurs in chronic urostasis and indicates the development of chronic renal failure)
Stagnation of urine creates conditions for the active proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which causes infectious complications of kidney urostasis.
Nephroptosis in children
Nephroptosis in children is associated with weak ligaments that secure the kidneys. Quite often, pathology develops in children with spinal curvature. Girls develop nephroptosis much more than boys.
The disease in children leads to the following complications:
- Hemodynamics are impaired;
- Urodynamics;
- Pyelonephritis develops;
- Blood pressure rises.
Clinical manifestations occur in 3 ways:
- The first stage occurs without symptoms;
- The second manifests itself with minor symptoms;
- And the last stage is characterized by complicated nephroptosis.
Characteristics of all options:
- Pathology is detected by chance and is observed in 14% of children during examination of other diseases;
- Occurs in half of all cases of nephroptosis. During this process, the following symptoms develop:
- Lower abdominal pain;
- Urinary syndrome develops;
- The process of urination is disrupted;
- Blood pressure indicators increase;
- Neurological abnormalities begin;
- The child is lagging behind in physical development;
- The child experiences nausea and diarrhea;
- The urine contains protein, red blood cells, white blood cells, and bacteria;
- urinary incontinence is noted;
Preventive methods for children are:
- proper physical education;
- exclusion of heavy loads and emotional stress;
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- balanced diet.
Diagnostics
If your left kidney hurts, then you should not postpone a visit to a specialist. Before seeing a doctor, you can ease the pain with antispasmodics, for example, No-shpa, Dibazol, Papazol, Drotaverine, Spazmalgon, Iberogast, Papaverine or Baralgin.
The medical institution will conduct a comprehensive examination of the body, which will accurately identify the cause of the ailment. Diagnostics will begin with a general examination and collection of information about the history and course of the disease, after which the following procedures will be prescribed: general and biochemical blood tests, urine tests, collection of daily urine, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and kidneys, x-rays, angiography, urography and kidney biopsy.
First of all, attention is paid to the nature of the pain syndrome. A correctly collected anamnesis, as well as additional research, will help with this:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract;
- General urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity.
Treatment of renal colic is aimed at relieving pain. If the symptoms of pain suggest this pathology, then help can be provided even before the ambulance arrives in the form of a hot bath, which will reduce spasm and severe suffering.
But, this procedure is contraindicated in other pathologies associated with pain in the kidney on the left. What to do if there is pain in the left kidney if it is associated with urolithiasis? Before the specialist arrives, the patient can be given antispasmodics and analgesics (spasmalgon, baralgin, etc.).
But it is worth remembering that pain relief can significantly complicate diagnosis, since the symptoms will be erased. Medical care for renal colic should be provided in a specialized hospital by urologists.
If you feel pain in the kidney area on the right, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist who will prescribe the necessary tests. Diagnostics is carried out in 4 stages:
- A survey of the patient, during which the doctor asks the patient about the symptoms of pain in the right kidney and how long ago they began. This is followed by inspection and palpation. This is done to confirm or refute symptoms that do not relate to the reasons why problems in the functioning of the organ appeared.
- General blood and urine analysis. It is used to study the presence of inflammation in the organ and the condition of urine.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidney, which shows the appearance of the organ, the condition of its tissues and possible problems in its functioning.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is used in situations where there are doubts about the diagnosis. MRI makes it possible to obtain more accurate readings of kidney function.
If your back hurts in the kidney area, and the causes are unknown, a person should first of all pay attention to the temperature indicator (the presence of an inflammatory process), additional symptoms (nausea, vomiting, which side of the kidneys hurt) and immediately contact a specialist.
The doctor first questions the patient in detail and examines for the presence of edema. You can differentiate the presence of a kidney problem from a spinal one by tapping from behind in the lumbar region. Renal pathologies are accompanied by a dull pain when tapped. To confirm or refute the presumptive diagnosis, laboratory diagnostics are performed:
- general urine test (determines the presence of salts, density);
- general blood test (with kidney pathologies, changes are observed in the blood);
- blood chemistry;
- X-ray of the lumbar region (will show the presence of vertebral changes);
- Ultrasound (shows the size of the kidney and the presence of stones in it).
Stages of nephroptosis
There are three main degrees of development of nephroptosis:
You can feel the third part of the kidney under the ribs, but when you exhale it falls into place. Basically there are no visible symptoms at this stage. If the kidney is lowered by 6 cm, then the fascia stretches, and dull pain develops in the lumbar region. This mainly happens when a person sits down after lying down. Urine remains normal;
The first stage - this stage is characterized by displacement of the kidney during inspiration up to 9 cm.- The second degree is characterized by a vertical position, lowering of the kidney by two thirds in relation to the rib. When the patient takes a horizontal position, the kidney returns to its usual place. This is due to a violation of the venous outflow of blood. The patient develops symptoms. With increased loads and movement, the pain intensifies and resembles the development of renal colic. When a person takes a horizontal position, the pain subsides;
- The third stage is characterized by the descent of the kidney below the rib line to the small pelvis. The patient's pain is constant and intense below and radiates to the groin area. Relief does not come from lying down. This is associated with the development of pyelonephritis and hydronephrosis.
Treatment methods
Doctors strongly recommend avoiding self-medication for pain in the kidneys. Medicines or procedures performed incorrectly for pain relief can worsen the condition and complicate the work of doctors.
Acute, sudden, sharp pain is a reason to immediately contact a specialist. Prolonged aching pain should not be left to chance.
In a hospital or at an appointment, the doctor will conduct all the necessary diagnostics, which includes:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the kidneys and urinary system;
- abdominal x-ray;
- urine test for infections;
- biochemical, general blood test;
Contact doctors - urologist and nephrologist. If the pain in the left lower back is unbearable, it is better to call an ambulance. You should not strictly follow the prescribed treatment; you should not treat your kidneys with home remedies or folk remedies.
For sick kidneys, after consultation with specialized doctors, a complete cessation of alcohol and smoking is recommended to relieve and prevent pain symptoms. Restrictions on the consumption of salty, spicy, smoked foods are shown. Doctors include milk and dairy products, fish, coffee, tomatoes and mushrooms as other “heavy” foods.
In general, you need to ensure that the daily dose of protein in the diet does not exceed 30-35 g. Frequent consumption of liquids during the day has a beneficial effect on the condition of the kidneys. Better than regular water, not juices or soda.
Diet and diet
The first thing you need to pay attention to is your diet. Uncontrolled intake of liquid and salt are the first enemies in case of functional abnormalities in the functioning of the kidneys. Failure to comply with this rule leads to constant swelling and increased blood pressure. Depending on the severity of the disease, restrictions on salt intake are introduced. The norm is from 3 to 7 grams per day.
Having the health problems described above, it is necessary to control the intake of potassium and phosphorus. All dried fruits, fresh fruits (except apples and pears), fried vegetables, and lactic acid products must be limited in consumption, since they contain a large number of microelements.
The diet plan must be approved by your doctor. Only he can individually determine products that are unsuitable for consumption and those that are necessary for the diet.
Nephroptosis in men
A healthy man's kidney is located in its own special renal compartment. The renal artery and vein enter here and the ureter departs. With nephroptosis in men, the kidney may descend into the abdominal cavity and pelvis.
In the process, the following complications develop:
- When the ureter is bent, the blood supply to the renal tissue is disrupted;
- Urine is retained;
- Inflammation develops;
- The kidney has a high compensatory property and may not show symptoms for a long time;
- During this period, severe and irreversible phenomena in the kidney may develop;
- Men are much less likely to suffer from this pathology.
ethnoscience
Using traditional recipes in the treatment of renal pathologies can achieve effective results, but this will require a longer period of time. To use any herb or berry, you must obtain the approval of a specialist. The most effective recipes are:
- Corn silk. They cope well with swelling. Using them, it is very important to adhere to dietary nutrition. For 1 tbsp. l. You will need 200 ml of hot water and boil for 20 minutes. Then leave for about 30 minutes. Take 2 tbsp decoction. l. every 3 hours.
- Bearberry. The herb copes well with the inflammatory process and removes fluid from the body. For 1 tbsp. l. The plants will need 200 ml of boiling water, let it steam for about 30 minutes. Then it is filtered and taken 3 times a day, a quarter of a glass.
- Blue cornflower. Has a strong diuretic effect. To prepare the infusion you will need 1 tbsp. l. plants 400 ml boiling water. Take 3 times a day, 2 tbsp. l.
- Radish. Radish juice effectively relieves inflammation and has a diuretic effect. You will need about 100-150 ml per day. To improve the taste, you can add honey to the juice.
- Field horsetail. Suitable for those diseases where heat therapy is permitted. An infusion of the herb is added when taking thermal baths (foot, sitz, full).
How is the disease treated?
For mechanical urostasis, surgical intervention is often performed. When abnormal congenital abnormalities are detected, adhesions are dissected and the areas of stenosis of the renal canals and ureteric passages are expanded.
Pregnant women undergo stenting before giving birth. In such cases, a specialist can recommend a set of therapeutic exercises that can have a beneficial effect on the rehabilitation of the functions of the excretory system.
In cases of urolithiasis, laser equipment is used to crush the stones or eliminate them through surgery.
Possible consequences
Disturbances in the normal secretion of urine can provoke the development of processes that destroy the tissue of the paired organ and other areas of the ureteric passage. As a result, the functioning of organs is disrupted, which entails negative consequences. These include:
- entry of bacteria into the paired organ, development of inflammatory diseases;
- the formation of nephropathy, which causes shrinkage of the organ;
- the appearance of protein in biological fluid;
- arterial hypertension;
- swelling;
- toxicosis by products obtained during the breakdown of stagnant urine;
- chronic failure of a paired organ.
Modern equipment for diagnosing the disease helps to identify the formation of urostasis and determine its causes. Based on this, the specialist prescribes a course of treatment aimed at eliminating the problem and normalizing the excretion of urine from the body.