Reasons for the development of the disease
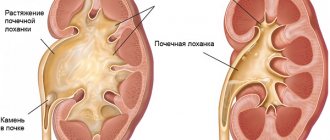
In a normal state, the kidney consists of a large number of nephrons, in which urine is formed after the process of filtering it is completed. The renal pelvis is a so-called muscular organ and a kind of cavity that sucks urine into itself due to natural negative pressure indicators. In this case, urine initially enters from the renal papillae into the renal calyx, and only subsequently into the renal pelvis.
When a decrease in tone occurs, the processes of urine discharge are disrupted, congestion is formed in the renal pelvis, as a result of which various complications arise, such as pyelectasia, pyelonephritis, etc.
The main reasons when hypotension of the pelvis of the right kidney or left kidney develops may be the following:
- Changes in the ratio of hormones in the body that occur during hormonal disruptions are the period of puberty, pregnancy, menopause, that is, the period of extinction of sexual functions.
- Taking certain medications can cause hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Damage to the body by acute and chronic infectious pathologies, causing a state of general intoxication.
- Prolonged stay of a person in a lying position due to illness.
- Congenital anomalies of the renal pelvis
- Hypotension of the stomach, provoking the formation of hypotension in the kidney.
- Prolonged emotional tension and stress.
- Disruption of the central nervous system.
- Mechanical damage to the upper urinary canals.
- Anatomical and physiological characteristics of the human body.
Arterial hypertension in renal failure
Danger of pressure
The kidney is a universal paired organ that filters the body, cleansing it of harmful substances, but also performs many other functions, directly participating in them. It would seem, what relationship can kidneys and unstable blood pressure have?! In fact, the most direct one.
But, the kidneys themselves do not cause low blood pressure, and the reasons for the decrease in pressure lie in other factors. In turn, low pressure has a negative effect on the kidneys, as a result of which the kidneys cease to function normally. Unstable pressure readings have led to diseases such as hypotension and hypertension.
Hypotension
This disease involves low blood pressure, which is more common among women. The structural features of a woman’s body predispose her to have low blood pressure, as a result of which women tend to experience dizziness, headaches and unreasonable fatigue more often. Hypotension is not considered a separate disease, but rather a condition where a person's blood pressure levels decrease.
Hypotension has an extremely negative effect on the kidneys. When a person has low blood pressure, the stability of kidney function is disrupted. And if the indicator falls below 75 mm, this becomes a real threat to life.
When the pressure level is below 75 mm, the kidneys stop functioning completely.
The blood that the kidneys are supposed to filter remains uncleaned from excess impurities. During pregnancy, even if a woman can avoid a miscarriage, children are born with complications, since harmful toxins from the mother’s body are not eliminated, but accumulate in the amniotic fluid.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Low blood pressure and rapid pulse
Treatment of an ailment such as low blood pressure involves treating its cause. To prevent low blood pressure from becoming a regular occurrence, you need to see a doctor and get examined. Unfortunately, most people accept low blood pressure as normal and prefer to increase their blood pressure to improve their well-being. However, the effect will be short-lived.
Hypertension
Hypertension refers to high blood pressure. About 25% of 100 people with hypertension have kidney disease and may not even know it. If a person has high blood pressure, then it cannot be said for sure that he has kidney disease, however, there are still impaired kidney function. High blood pressure can be caused by many kidney diseases, including pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, and others.
Consequently, any impairment of kidney function contributes to fluid retention in the body, as a result of which circulating blood increases in volume and high blood pressure occurs.
First, you need to see a therapist and talk about your symptoms. But, it is worth understanding in advance that the doctor will not be able to make a final diagnosis based solely on the patient’s symptoms, since the symptoms of renal hypertension and ordinary hypertension are very similar to each other. However, with renal hypertension, unlike arterial hypertension, there is no risk of heart attack or stroke. Also, with renal hypertension, cases of hypertensive crises are exceptions.
It is worth noting that if a person is aware of his illness, it is necessary to regularly monitor and, if possible, prevent high blood pressure. Particular vigilance must be exercised on days of inclement weather, when exacerbations often occur in hypertensive patients.
Treatment of renal hypertension consists of conservative therapy, drugs are prescribed to reduce high blood pressure. Also, the treatment of hypertension includes procedures for relieving swelling. To relieve swelling, the patient is prescribed diuretics (diuretics). In addition, it is especially important to treat kidney disease, which is the cause of renal hypertension.
If the patient has kidney failure, then high blood pressure is guaranteed. But you should not try hard to reduce its lower value if it is at around 90 mm. Even high blood pressure must be reduced gradually, since a sharp drop in levels has an even more detrimental effect on the organs.
The doctor prescribes treatment with drugs for each patient individually, taking into account his characteristics. As a rule, any drug is started in small doses to assess the patient's body's response to this drug, and then, if necessary, the dose is increased. In addition to medications, the patient is prescribed a special diet. Treatment with diet, in combination with conservative therapy, will have a more effective result.
According to recent studies, scientists have proven that stroke is closely related to the kidneys. This is due to the close interactions of processes in the body. The kidneys are no exception, because disrupted processes in the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system can increase the risk of stroke.
Stroke involves the process of bleeding in the brain and is one of the most common causes of death today. Since kidney diseases can provoke a stroke, for patients in the field of urology, not only the basic treatment of their ailments is carried out, but also preventive measures against the occurrence of strokes.
Reasons why kidney problems can trigger a stroke:
- Sudden changes in pressure that occur due to damage to the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
- Kidney diseases in which red blood cells increase in the blood. A large number of red blood cells in the blood makes the blood viscous.
- Kidney diseases in which excess amounts of calcium are formed in the human body.
- Kidney diseases, which lead to an imbalance of water balance, as a result of which fluid is retained in the body and blood pressure increases.
In case of kidney disease, and in the presence of the above-mentioned factors, processes occur in the body that affect the blood vessels of the brain. In addition, stress, emotional disorders, etc. increase the risk of stroke.
Thus, hypertensive patients should carefully monitor their kidney health. Also, and vice versa, people with kidney disorders should monitor their blood pressure and be treated promptly.
Kidney disease can cause secondary hypertension, which is called hypertension due to renal failure. The peculiarity of this condition is that, along with nephropathy, the patient experiences high values of systolic and diastolic pressure. Treatment of the disease is long-term.
Where is the connection?
The occurrence of arterial hypertension in chronic renal failure (chronic renal failure) is due to changes in the normal functioning of the urinary system, when the blood filtration mechanism is disrupted. In this case, excess fluid and toxic substances (sodium salts and protein breakdown products) cease to be removed from the body. Excess water accumulated in the extracellular space provokes the appearance of swelling of internal organs, arms, legs, and face.
Large amounts of fluid irritate the kidney receptors, increasing the production of the enzyme renin, which breaks down proteins. In this case, there is no increase in pressure, but by interacting with other blood proteins, renin promotes the formation of angiotensin, which promotes the formation of aldosterone, which retains sodium.
At the same time, the content of derivatives of polyunsaturated fatty acids and bradykinin, which reduce the elasticity of blood vessels, decreases in the kidneys. As a result, in hypertension of renovascular origin, high blood pressure is persistent. Hemodynamic disorder leads to cardiomyopathy (left ventricular hypertrophy) or other pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system.
The functioning of the renal arteries is impaired due to nephropathology. A common cause of nephrogenic arterial hypertension is arterial stenosis. A narrowing of the cross-section of the renal arteries due to thickening of the muscle walls is observed in young women. In older patients, narrowing appears due to atherosclerotic plaques that impede the free flow of blood.
Factors that provoke high blood pressure in nephropathies can be divided into 3 groups - negative changes in the parenchyma (kidney lining), damage to blood vessels and combined pathologies. The causes of diffuse pathologies of the parenchyma are:
- pyelonephritis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- lupus erythematosus;
- diabetes;
- urolithiasis pathologies;
- congenital and acquired kidney anomalies;
- tuberculosis.
Among the causes of renovascular hypertension associated with the condition of blood vessels are:
- atherosclerotic manifestations in the older age group;
- abnormalities in the formation of blood vessels;
- tumors;
- cysts;
- hematomas.
Nephrogenic hypertension is very resistant to medications that lower blood pressure.
A characteristic feature of nephrogenic hypertension is the ineffectiveness of drugs that lower blood pressure, even in the case of high values. Provoking factors can have a negative effect either individually or in any combination of damage to the parenchyma and blood vessels. In this situation, it is very important to identify existing problems in a timely manner.
Tags: hypotension, disease, kidney
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry
Signs of the disease
A decrease in tone and a deterioration in the process of movement of urine to the ureter from the kidneys may not manifest itself with any clinical symptoms. Hypotension of the renal pelvis does not in any way affect the process of urine discharge and does not provoke difficulties in passing this process.
As a rule, this pathology is diagnosed during an ultrasound examination, which reveals pyelectasia or pyelonephritis.
Often, complications develop when the nervous regulation of the functioning of the bladder is disrupted. Complications may be congenital. In this case, the newborn has inadequate development of the muscular layer of the renal pelvis and a decrease in tone. These patients require an ultrasound examination after a few months.
Symptoms
Hypotony of the kidney can manifest itself on one side or on both sides. Unfortunately, it does not have pronounced clinical signs, and the patient, for a long time, can live with this pathology without knowing about its presence. In most cases, hypotension is detected during an ultrasound examination of the patient.
In addition, often, along with hypotension, the patient is diagnosed with complications such as renal failure or pyelectasis. The manifestation of pathology occurs due to the innervation of the urinary tract. With congenital hypotonia of the kidney, the child experiences underdevelopment of muscle tissue and decreased tone of the pelvis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Methods for diagnosing the presence of this pathology include:
- Taking a general urine test.
- Urine culture to identify pathological microflora.
- Clinical blood tests.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
- Cystography.
- Cystoscopy.
- Excretory urography.
- Cystometry.
- Contrast radiographic examination of the kidneys.
When a decrease in tone occurs, the processes of urine discharge are disrupted, congestion is formed in the renal pelvis, as a result of which various complications arise, such as pyelectasia, pyelonephritis, etc.
The main reasons when hypotension of the pelvis of the right kidney or left kidney develops may be the following:
- Changes in the ratio of hormones in the body that occur during hormonal disruptions are the period of puberty, pregnancy, menopause, that is, the period of extinction of sexual functions.
- Taking certain medications can cause hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Damage to the body by acute and chronic infectious pathologies, causing a state of general intoxication.
- Prolonged stay of a person in a lying position due to illness.
- Congenital anomalies of the renal pelvis
- Hypotension of the stomach, provoking the formation of hypotension in the kidney.
- Prolonged emotional tension and stress.
- Disruption of the central nervous system.
- Mechanical damage to the upper urinary canals.
- Anatomical and physiological characteristics of the human body.
Signs of the disease
A decrease in tone and a deterioration in the process of movement of urine to the ureter from the kidneys may not manifest itself with any clinical symptoms. Hypotension of the renal pelvis does not in any way affect the process of urine discharge and does not provoke difficulties in passing this process.
As a rule, this pathology is diagnosed during an ultrasound examination, which reveals pyelectasia or pyelonephritis.
Often, complications develop when the nervous regulation of the functioning of the bladder is disrupted. Complications may be congenital. In this case, the newborn has inadequate development of the muscular layer of the renal pelvis and a decrease in tone. These patients require an ultrasound examination after a few months.
Hypertension
Hypertension refers to high blood pressure. About 25% of 100 people with hypertension have kidney disease and may not even know it. If a person has high blood pressure, then it cannot be said for sure that he has kidney disease, however, there are still impaired kidney function. High blood pressure can be caused by many kidney diseases, including pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, and others. In addition, high blood pressure may occur in patients who have had nephrolithiasis, urolithiasis, ureteral problems, or prostatic hypertrophy (in men). Simply put, any disturbances in urinary outflow in the past can be the real reason why a person will have high blood pressure.
Consequently, any impairment of kidney function contributes to fluid retention in the body, as a result of which circulating blood increases in volume and high blood pressure occurs.
Diagnosis of the disease
Methods for diagnosing the presence of this pathology include:
- Taking a general urine test.
- Urine culture to identify pathological microflora.
- Clinical blood tests.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
- Cystography.
- Cystoscopy.
- Excretory urography.
- Cystometry.
- Contrast radiographic examination of the kidneys.
In normal condition, the size of the renal pelvis does not exceed 10 mm and on the monitor screen during ultrasound it looks flat.
If the pelvis is enlarged or a change in its shape has occurred, then pyelectasia can be diagnosed - unilateral or bilateral expansion of the renal pelvis. When performing a general urine test, many leukocytes are detected in the blood, which indicates the development of inflammation in the kidneys. In this case, it is necessary to exclude the presence of gynecological diseases in female representatives.
When carrying out bacterial culture of urine, it is necessary to pay attention that when organizing the first culture, in 20% of cases, incorrect results may be obtained, and therefore, a three-fold culture is performed. The disadvantage of this method is the duration of the procedure, and treatment must be started urgently. Despite this, this method is actively used because it helps to identify the causative agent of the pathology, determine the level of its sensitivity to antibiotic drugs, and this will definitely be required in the implementation of subsequent treatment.
General blood tests establish indicators that correspond to the presence of infection in the human body, namely a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an increased concentration of leukocytes.
Hypotension of the renal pelvis in a child
Renal hypotension - causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Content
Kidneys play a very important role in the human body, like any other organ; there is nothing superfluous in our body. Diseases of the genitourinary system develop for many reasons, and disruption of the basic (excretory) function of the kidneys can lead to a number of complications.
Thus, renal hypotension can be caused by functional or organic disorders of the structure of the kidneys or urinary tract. Hypotonia of the kidney should be understood as hypotension of the renal pelvis. The definition speaks for itself - decreased tone of the renal pelvis.
What are the causes and mechanism of development of renal hypotension?
Normally, in a healthy person, urine enters the pelvis, without any effort, into an area of negative pressure, from where, after a sufficient amount has collected, the valve is activated and the urine is directed through the ureters into the bladder and then through the urethra is excreted from the body. The valve operates only in one direction, i.e. from the pelvis to the ureters. But with certain obstacles in its path, the outflow of urine becomes difficult and the tension in the pelvis increases, it stretches, expands, its walls become thinner, and pathology occurs - pyelectasia.
In turn, hypotension of the renal pelvis can also provoke the development of pyelonephritis or other infectious kidney disease of the ascending type. That is, if there is an inflammatory process in the lower parts of the urinary tract or in the bladder, then in an ascending manner, due to the reduced tone of the pelvis and its dilated state, the infection rises directly to the kidney. As complications of such a process, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hydronephrosis, renal failure and even necrosis of renal tissue can develop.
Causes of difficulty in urine flow:
- abnormal development of the ureters
- kink of the ureter
- ureteral compression
- narrowing of the ureter
- temporary or permanent overfullness of the bladder
- presence of obstructions in the passage of urine from the ureters to the bladder
- blockage of the ureter by a tumor, stones, or pus
- location of the pelvis outside the kidney
- reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureter or pelvis
- urinary tract infections (pyelonephritis)
- muscle weakness in premature babies
- hormonal imbalances during adolescence
- hormonal imbalance during pregnancy
- hormonal changes in the body during menopause
- taking hormonal medications, resulting in changes in hormonal levels
- congenital anomaly of the structure of the renal pelvis
- prolonged stay in a horizontal position for bedridden patients
- hypotension of the stomach, causing hypotension of the kidneys
- nervous stress or prolonged depression
- mechanical damage to the urinary tract
- neurological problems.
- heat
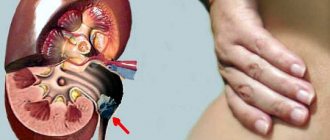
- pain in the lumbar region
- pain in the lower abdomen
- regional “psoasis symptom”
- frequent urination
- burning after urination
- unpleasant smell of urine
- pus or blood in the urine.
- general urine analysis
- urine test according to Nechiporenko
- urine culture for detection and differentiation of pathological microflora
- clinical blood test
- Kidney ultrasound
- cystography
- excretory urography
- cystoscopy
- cystometry
- contrast radiograph of the kidneys.
- Changes in the ratio of hormones in the body that occur during hormonal disruptions are the period of puberty, pregnancy, menopause, that is, the period of extinction of sexual functions.
- Taking certain medications can cause hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Damage to the body by acute and chronic infectious pathologies, causing a state of general intoxication.
- Prolonged stay of a person in a lying position due to illness.
- Congenital anomalies of the renal pelvis
- Stomach hypotension. provoking the formation of hypotension in the kidney.
- Prolonged emotional tension and stress.
- Disruption of the central nervous system.
- Mechanical damage to the upper urinary canals.
- Anatomical and physiological characteristics of the human body.
- Taking a general urine test.
- Urine culture to identify pathological microflora.
- Clinical blood tests.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
- Cystography.
- Cystoscopy.
- Excretory urography.
- Cystometry.
- Contrast radiographic examination of the kidneys.
- stress, neuroses
- urinary system injuries
- hormonal imbalance
- medications
- infections (acute, chronic)
- congenital hypotension
- physiological characteristics
- long horizontal position.
- Concussion in school-aged children
- Cold in a 1 5 month old child
Clinical picture
Typically, hypotension of the renal pelvis does not cause disturbances in the process of urination and, as an independent disease, does not manifest itself clinically. But, being a consequence of other renal pathologies, it can be identified by the corresponding symptoms (for example, pyelonephritis).
Classic symptoms of pyelonephritis:
It is usually discovered accidentally on an ultrasound due to pyelonephritis or other pathology of the genitourinary system.
Diagnostic methods:
Normally, the size of the renal pelvis is no more than 10 mm and it is flat on the monitor screen during ultrasound. If the size is increased or the shape of the pelvis is changed, we can talk about pyeloectasia (unilateral or bilateral expansion of the renal pelvis).
A general urine test reveals a large number of leukocytes, indicating an inflammatory process in the kidneys. But in this case, it is necessary to exclude gynecological pathology in women.
When doing bacterial culture of urine, it is necessary to pay attention that during the first culture, in 20% of cases there may be false tests. Therefore, three times urine culture is prescribed. The disadvantage of this method is that analysis takes a lot of time, and treatment must be started urgently. But still they do not refuse it, because... This analysis makes it possible to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to various antibiotics, which is very important for further treatment.
In a general blood test, indicators corresponding to the presence of infection in the body. This is an increased ESR, an increased number of leukocytes.
Treatment of hypotension of the renal pelvis
Since renal hypotension, as an independent disease, can only be a congenital anomaly of kidney development, treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause. Namely, for congenital anomalies of the development of the pelvis, a surgical method is used; sometimes it is enough to use endoscopic surgery through the urethra.
If pelvic hypotension is caused by another kidney disease, then appropriate treatment for this pathology is prescribed. If the indications for surgical intervention remain relevant even after conservative treatment, then surgery cannot be ruled out. This is necessary to avoid complications such as hydronephrosis or necrosis of the kidney.
After antibiotic therapy for the underlying renal pathology, it is recommended to conduct a course of herbal medicine. For this purpose, herbal kidney preparations are used.
Currently, technology such as phytoniring is widely and quite successfully used in the treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system.
What it is?
This is an independent branch of medicine, based on a combination of herbal medicine and nanotechnology. A special feature of the drug CANEPHRON® N, used in the treatment and prevention of diseases of the genitourinary system, is the exact amount of biologically active substance, which is guaranteed to have a therapeutic effect. At the same time, side effects are minimized.
In classical medicine, for infections of the kidneys and urinary tract, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. But with long-term treatment, a number of complications appear on the part of other organs and systems. And besides, bacteria develop resistance to the drug, and you have to change it to another, stronger one, and therefore more aggressive for the body as a whole. Therefore, it is recommended to use CANEPHRON® N together with antibiotic therapy. In this combination, the use of drugs at the onset of the disease significantly alleviates the condition of patients and accelerates the recovery process.
The drug is well tolerated by patients and even children, which makes it possible for its long-term use if necessary. Especially when it is necessary to consolidate the achieved treatment result. The drug contains plant components containing biologically active substances that have antibacterial, antispasmodic and diuretic effects.
Among specialists, CANEPHRON® N has proven itself well and is widely used in the treatment and prevention of diseases of the genitourinary organs. Based on the results of studies of the drug CANEPHRON® N, the effectiveness of antibiotic therapy in combination with phytoniring has been proven.
Traditional recipes to keep your kidneys healthy
Recipe No. 1 - onion peels with rose hips
Pour three tablespoons of dry onion peel into three glasses of hot water. Place on open fire, bring to a boil, turn off and leave overnight. The next morning, bring the broth to a boil again, add 20g of chopped rose hips. Let the broth brew and cool for one hour. Strain the broth and take 3 sips 6 times a day. It helps very well in the treatment of pyelonephritis.
Recipe No. 2 – birch leaves
Take 100g of green birch leaves, pour 2 glasses of cold spring or purified water over them for 6 hours. After this, strain the greenish infusion and squeeze the leaves well. Take half a glass of infusion 3 times a day. It has a positive effect both in the treatment of many kidney diseases and for their prevention.
(No ratings yet)
How hypotension of the renal pelvis develops, its main manifestations and treatment
Hypotension of the renal pelvis is a process of decreased tone in the renal pelvis. This pathology can be caused by various organic and functional disorders in the structure of the kidneys.
Reasons for the development of the disease
In a normal state, the kidney consists of a large number of nephrons, in which urine is formed after the process of filtering it is completed. The renal pelvis is a so-called muscular organ and a kind of cavity that sucks urine into itself due to natural negative pressure indicators. In this case, urine initially enters from the renal papillae into the renal calyx, and only subsequently into the renal pelvis.
When a decrease in tone occurs, the processes of urine discharge are disrupted, congestion is formed in the renal pelvis, as a result of which various complications arise, such as pyelectasia, pyelonephritis, etc.
The main reasons when hypotension of the pelvis of the right kidney or left kidney develops may be the following:
Signs of the disease
A decrease in tone and a deterioration in the process of movement of urine to the ureter from the kidneys may not manifest itself with any clinical symptoms. Hypotension of the renal pelvis does not in any way affect the process of urine discharge and does not provoke difficulties in passing this process.
As a rule, this pathology is diagnosed during an ultrasound examination, which reveals pyelectasia or pyelonephritis.
Often, complications develop when the nervous regulation of the functioning of the bladder is disrupted. Complications may be congenital. In this case, the newborn has inadequate development of the muscular layer of the renal pelvis and a decrease in tone. These patients require an ultrasound examination after a few months.
Diagnosis of the disease
Methods for diagnosing the presence of this pathology include:
In normal condition, the size of the renal pelvis does not exceed 10 mm and on the monitor screen during ultrasound it looks flat. If the pelvis is enlarged or a change in its shape has occurred, then pyelectasia can be diagnosed - unilateral or bilateral expansion of the renal pelvis.
When performing a general urine test, many leukocytes are detected in the blood, which indicates the development of inflammation in the kidneys. In this case, it is necessary to exclude the presence of gynecological diseases in female representatives.
When carrying out bacterial culture of urine, it is necessary to pay attention that when organizing the first culture, in 20% of cases, incorrect results may be obtained, and therefore, a three-fold culture is performed. The disadvantage of this method is the duration of the procedure, and treatment must be started urgently. Despite this, this method is actively used because it helps to identify the causative agent of the pathology, determine the level of its sensitivity to antibiotic drugs, and this will definitely be required in the implementation of subsequent treatment.
General blood tests establish indicators that correspond to the presence of infection in the human body, namely a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate and an increased concentration of leukocytes.
Disease treatment process
To carry out correct and effective treatment, it is necessary first of all to establish the causes of the development of the abnormalities that provoked this condition. For example, if the cause of hypotension is stress, then during the treatment process it will be enough to get rid of all negative factors so that the condition of the renal pelvis normalizes within a few weeks.
Much attention is paid to the treatment of complications, for example, pyelectasis caused by hypotension of the renal pelvis. An increase in its size is formed due to the difficulty of pushing urine into the ureters. In some situations, surgery may be required because an enlarged pelvis can cause hydronephrosis due to strong pressure on the kidney.
When hypotension of the renal pelvis develops during pregnancy, the doctor must constantly monitor the patient, and also organize a repeat examination after the birth of the child for several months.
Please rate this article:
(No votes yet)
What to do if the renal pelvis is enlarged in a newborn?
As you know, all human internal organs are formed in the womb. Some of them do not perform their direct functions during intrauterine development. An example of such organs is the kidneys.
While inside its mother, the placenta works instead of the baby's kidneys. It performs an excretory function. Even after birth, in the first six months of life, the kidneys are immature, and only after this time do they return to normal.
But sometimes pathologies of intrauterine development occur, for example, an enlarged renal pelvis in a newborn. Or an enlarged renal pelvis can be detected in the fetus through an ultrasound examination.
What is the renal pelvis, and what are its functions in a newborn?
This is a kind of small cavity inside the kidney that serves to collect urine from the kidney tubules. As portions of urine collect in the pelvis, its walls begin to contract and direct urine into the bladder through the ureters.
If it is discovered that the renal pelvis of a newborn child is enlarged, then there is no need to panic in such a situation. This anomaly is not critical, and in most cases goes away on its own. The pelvis takes on the appropriate size, and the kidneys adequately perform their functions.
Enlargement of the renal pelvis occurs more often in boys than in girls. Boys experience this 4-5 times more often.
Hypotony of the renal pelvis: signs, diagnosis, treatment
Content
Diseases of the genitourinary system include hypotension of the renal pelvis. This pathology is caused by various reasons and requires appropriate treatment. Problems with the formation and removal of urine can lead to a variety of complications.
Kidney function
The kidneys are a paired organ that is located in the spine in the posterior abdominal wall. Each of them weighs approximately 200 g.
The main function of the kidneys is to cleanse the blood of harmful substances and metabolic products. Therefore, a large amount of blood in the body passes through them every day. Kidneys also help maintain acid-base balance.
Causes of hypotension
The kidney consists of a basic structural unit, the nephron, which in turn consists of a body and tubules. The nephrons are where urine is filtered and formed. The renal pelvis is a muscular organ that receives urine under pressure: first into the renal calyx, then into the pelvis.
Decreased tone causes disruption of urine output and leads to congestion in the renal pelvis. As a result, other complications appear in the form of pyelonephritis, renal failure, etc.
Today, there are several reasons leading to hypotension of the renal pelvis:
Signs
Hypotension of the renal pelvis can be unilateral or bilateral. In some cases, there may be no visible clinical signs. Therefore, the disease is often detected during an ultrasound examination or other preventive examination.
The disease manifests itself as a result of a violation of the nervous regulation of the bladder. With congenital pathology, children experience underdevelopment of the muscle layer and decreased tone of the renal pelvis.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a medical examination of the patient is performed. The most common diagnostic methods are laboratory tests, which include a blood test and a general urine test. In the presence of an infectious process, protein, salts and various microorganisms will be detected in the urine.
Instrumental methods include kidney urography, angiography, and X-ray examination. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to obtain layer-by-layer visualization of the kidneys.
Using radionuclide scintigraphy, the kidneys are examined with a radioisotope substance. X-ray of the kidneys also gives a complete picture of the condition of the organ and the presence of pathological processes.
Treatment of hypotension
To treat hypotension of the renal pelvis, it is necessary to find the underlying cause of the disease. In case of nervous stress or overstrain, it is only necessary to eliminate the negative factor and the condition of the kidneys will be restored.
For pyelectasis, surgical treatment is recommended in order to avoid such a serious complication as hydronephrosis. During pregnancy, it is necessary to monitor the woman until the moment of birth and after - for a certain period of time.
To prevent diseases of the genitourinary system, you need to monitor fluid control, especially during pregnancy. Bad habits are excluded for the entire duration of treatment.
The daily diet should consist of natural products and be balanced. The amount of salt consumed is limited. In addition, you need to avoid stress and hypothermia.
Sources: tvoyaybolit.ru, tvoelechenie.ru, medik-plus.ru, tvoipochki.ru
Next articles:
September 14, 2020
No comments yet!
Disease treatment process
To carry out correct and effective treatment, it is necessary first of all to establish the causes of the development of the abnormalities that provoked this condition. For example, if the cause of hypotension is stress, then during the treatment process it will be enough to get rid of all negative factors so that the condition of the renal pelvis normalizes within a few weeks.
Much attention is paid to the treatment of complications, for example, pyelectasis caused by hypotension of the renal pelvis. An increase in its size is formed due to the difficulty of pushing urine into the ureters. In some situations, surgery may be required because an enlarged pelvis can cause hydronephrosis due to strong pressure on the kidney.
When hypotension of the renal pelvis develops during pregnancy, the doctor must constantly monitor the patient, and also organize a repeat examination after the birth of the child for several months.
Congenital disorders of the renal pelvis and congenital anomalies of the ureter (Q62)
Congenital occlusion:
- ureter
- ureteropelvic junction
- ureterovesical orifice
Congenital dilatation of the ureter
Deviation of the ureter or ureteral orifice
Displacement of the ureter or ureteral orifice
Abnormal implantation of the ureter or ureteral orifice
Ureteral anomaly NOS
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997. No. 170
The release of a new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2017-2018.
Sources used: mkb-10.com