- approximately 2800 kcal are consumed per day,
- carbohydrate consumption up to 400 g/day,
- protein consumption up to 80 g/day,
- fat norm up to 90 g/day,
- It is forbidden to eat very chilled food,
- five meals a day are recommended,
- Weekly fasting days should be organized with the consumption of exclusively fruits or milk, cottage cheese.
Prescribing a healthy diet will eliminate the incorrect salt balance in the urine and prevent the formation of stones and sand as a result of acid reactions. By changing your food intake and diet, you can achieve significant improvements and be completely cured, and vice versa, continuing to maintain your usual lifestyle with foods that increase acidity, there is a possibility of getting more severe diseases.
Urate treatment diet. Diet for urate kidney stones (uraturia)
An indicator of purine metabolism in the body is the concentration of uric acid in the blood.
Purines are synthesized in the body and also come from food. The consequence of disturbances in this metabolism is an increase in uric acid levels. Salts of uric acid found in urine are called urates. The main reasons for its occurrence are:
- abuse of foods rich in purines;
- an abundance of high-calorie foods and fatty foods in the diet;
- malignant neoplasms;
- starvation;
- tissue destruction.
If increased synthesis of uric acid occurs, its level in the blood increases, and at the same time crystals of its salts appear in the urine. Urate nephrolithiasis develops in young children; symptoms of hyperuricemia are manifested by muscle pain, arthralgia, tics, nocturnal enuresis, excessive sweating, intoxication and asthenic syndrome.
With uraturia, the patient's nutrition should be aimed at reducing the level of uric acid. The diet is characterized by limiting foods containing purines (meat, offal), oxalic acid (sorrel, radishes, spinach, raspberries, cauliflower, asparagus, cranberries) and salt. At the same time, increase the proportion of alkalizing foods (vegetables, milk, fruits) and the amount of liquid in the diet.
If there is urate in the urine, it is necessary to exclude:
- Canned fish.
- Meat and poultry of young animals, offal, due to the high content of purines. It is allowed to eat meat from older animals to a limited extent - these dishes are included in the diet no more than 2 times a week. Meat portions are up to 150 g, and fish - 170 g.
- Meat broths, smoked meat dishes.
- Cereal sprouts.
- Cheeses, strong tea, chocolate, alcohol.
- Eggs, mushrooms, tomatoes, legumes.
- Limit flour and various confectionery products.
The basis of the diet is milk, fermented milk products and vegetables, berries, fruits (seaweed, pumpkin, cabbage, grapes, apples, all citrus fruits, figs, bananas, raisins, currants, gooseberries, lingonberries, strawberries, cherries). Patients should periodically take courses of diuretic herbs: clover, cornflower, burdock and dandelion roots, infusions of dried apricots, blueberries, boneberries, apples, rowan, barberry, carrots, pumpkin, parsley root, beets. Decoctions of grape and black currant leaves help remove stones. During the season, you need to consume these berries as much as possible.
The culinary processing of meat and fish products has its own peculiarities - they must be boiled, and only then used to prepare various dishes. When cooked, 50% of the purines are lost and should never be consumed. Meat, poultry or fish, devoid of some purines, can be stewed, baked, ground for minced meat or fried.
Cereals are an integral part of the diet
The duration of this diet ranges from several months to permanent. The patient should drink 2.5 liters of liquid per day (alkaline mineral water of Essentuki, Borjomi, natural juices) and have fasting days once a week - kefir, curd, fruit, milk.
The main method of treatment and prevention of this type of stones is alkalinization of urine, since urates are poorly soluble in an acidic environment and easily turn into solid form. It is enough to maintain the pH at 6-6.5. Citrate preparations are effective because they prevent crystallization and create conditions for the dissolution of already formed stones.
Medical nutrition: delicious recipes
Borscht with vegetable broth
For one serving: 50 g tomatoes, 60 g beets, 130 g potatoes, 70 g carrots, 100 g cabbage, 10 g parsley, 30 g butter. Preparation: tomatoes (pre-peeled from seeds and skins), potatoes and carrots cut into cubes. Shred the cabbage. Boil all vegetables in a saucepan in boiling water. 15 minutes before the end of cooking, add grated beets, salt and season. Cook until done. Before serving, sprinkle with chopped parsley and add butter. Return to contents Per serving: 1 pc. potatoes, 90 g zucchini, 1 tbsp. l. flour, ¼ chicken egg, vegetable oil for frying, 30 g sour cream, 15 g dill, 10 g garlic, salt and pepper to taste. Preparation: grate the zucchini and potatoes on a fine grater, squeeze. Add egg, flour, salt and pepper, mix thoroughly. Form pancakes in a heated frying pan greased with vegetable oil. Fry on both sides until golden brown. Serve with aromatic sour cream sauce: add finely chopped garlic and dill to the sour cream and stir. Return to contents For one serving: 90 g cottage cheese, 100 g pumpkin, 2 tsp. semolina, 2 tbsp. l. sugar, ½ egg, 10 g butter, a pinch of soda, salt, lemon juice, 1 tbsp. l. sour cream. Preparation: Peel the pumpkin and grate it on a coarse grater. Mash the cottage cheese with butter. Add half a beaten egg, semolina, salt and sugar to the cottage cheese. Quench the baking soda with lemon juice and stir into the resulting mixture. Add pumpkin pulp to the dough. Place the casserole base in a greased baking dish and cook for 50 minutes at 200° C. Serve with sour cream.
Return to contents
Tweet
Garlic with urates. Diet for urolithiasis with urates
Urates are detected in patients of all ages (formed due to excess uric acid). They precipitate in a very acidic environment, have a red-orange hue, are smooth, and round in shape. If they are present, the diet should be such that the urine does not become alkaline. The stones grow quickly, and following a diet leads to their reduction.
The diet for urolithiasis with urates should be based on compliance with the following rules:
- Refusal or reduction in consumption of meat and fish dishes. Fish can only be eaten boiled and no more than twice a week. The ban includes liver, kidneys, meat and fish broths, meat of young animals, as well as canned food, sausages, marinades and animal fats.
- It is forbidden to eat cauliflower, legumes and mushrooms, sorrel, spinach, and figs. It is necessary to avoid alcoholic beverages, strong tea, coffee, cranberry juice, cocoa and chocolate.
- The diet should include fermented milk products, mild cheeses, cottage cheese, and eggs. Particular attention should be paid to various cereals, vegetable soups and herbs.
- You can eat pasta, bread, various dried fruits, honey, jam, berries and spices in moderation. Potatoes, eggplants, cucumbers, sweet peppers, tomatoes, beets, and radishes are allowed as vegetables.
Stones are formed due to a product of purine metabolism. Therapeutic nutrition involves reducing the amount of permitted foods that contain purine bases and cause alkalinization of urine. The diet is dairy-vegetable in nature.
During treatment, it is strictly contraindicated to fast, as this leads to acidification of the internal environment of the body and increased formation of uric acid, which settles in the kidneys. In this case, you can do fasting days on vegetables or dairy products, 1-2 times a week, drinking up to two liters of liquid.
Uric acid salts in a child
Urate salts in a child’s urine increase directly due to diet. Excess fish and meat dishes contribute to the deposition of salts due to the imperfection of the urinary system in children; it takes several years to form. Urate salts in the urine are accompanied by gout, dysbacteriosis, and the appearance of worms. If urates appear in a baby when he is breastfed, the mother is prescribed a certain diet, in which red meat is replaced with fish or poultry, and a large number of fruits and vegetables are included.
Below are some symptoms, based on which a general urine test is prescribed, which in the future can help remove urates:
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- heat;
- taking antibiotics;
- lack of appetite;
- abuse of chocolate, cheese, tomato juice, meat and fish products.
Urate salts in a child’s urine increase directly due to diet. Excess fish and meat dishes contribute to the deposition of salts due to the imperfection of the urinary system in children; it takes several years to form.
Urates in a child’s urine are sometimes normal, but you need to make sure of this. The child’s body is structured differently, the metabolic processes in it are significantly different from adults, therefore crystallization processes in the child appear due to the immaturity of the urinary system. Uric acid urate salts do not have time to break down in full, so the appearance of urates in the urine is a natural phenomenon.
List of products for urate stones. What are urate stones and why are they formed?
Urate kidney stones are a special type of urolithiasis. Sometimes urate stones cause complications in the human body, so we should be careful and follow a special diet to dissolve urate stones.
With uraturia, uric acid accumulates in the body. It begins its decomposition in the urinary organs, forming sand or small stones. Such stones can be found not only in the kidneys, but also in the bladder and ureters.
Reasons for the formation of urate stone
- Improper metabolism.
- Genetic predisposition, in other words, heredity.
- Eating sour, spicy foods.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Diseases of the esophagus or genitourinary organs.
- Poor blood supply to the kidney.
- Violation of fluid volume in the body.
The volume of fluid is impaired in case of excessive loss: with high fever, vomiting or excessive physical activity.
It should be noted the peculiarity of the formation of urates in the kidneys with excessive and unbalanced food consumption:
- fried meat, meat broths
- canned fish
- legumes
- tomatoes
- alcohol
- chocolate
Forced fasting can also cause the formation of urates.
When urate is formed in the kidneys or urinary tract, the body accumulates excess uric acid, the formation of which is facilitated by purine substances in foods. The diet limits the consumption of foods rich in purines, such as meat, meat by-products, fish, as well as mushrooms and legumes.
Urates, kidney urate stones, can appear at any age in both male and female bodies. For prevention, you should adhere to a balanced diet and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Possible treatments
Patients are advised to reduce uric acid concentrations through dietary measures. Intake of purines, which are metabolized into urates, should be reduced. Alcoholic drinks should be consumed only in small quantities, since ethanol increases the production of uric acid in the liver and suppresses its excretion (depending on how much food is taken) through the kidneys. Some alcoholic drinks contain purines (such as beer). Normalizing body weight can have a beneficial effect on blood uric acid levels.
In cases of very high uric acid levels (>8.5 mg/dL), frequent attacks of gout, or other complications of hyperuricemia, medical treatment is appropriate or necessary in addition to dietary recommendations. Step-by-step therapy for amorphous kidney stones is important.
For severe hyperuricemia, it is recommended to take Allopurinol or uricosuric drugs (Benzbromarone, Probenecid). Once urate levels have normalized, discontinuation of the drug may be considered. Reducing the level of uric acid is intended to prevent complications (gout, kidney stones, nephropathy).
For acute attacks of gout, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are prescribed - Indomethacin, Ibuprofen or Diclofenac. An alternative is Colchicine. In case of insufficient effect, intolerance or contraindications, short-term administration of glucocorticoids (Prednisolone) may be required. It is not recommended to give corticosteroids to a child or during pregnancy.
Recipes for dishes with urate stones. What are the dangers of urate kidney stones?
If we consider the types of urolithiasis, then the detection of urate stones (uraturia) in the kidneys is the second most common form of pathology after oxalates. Such stones are found mainly in men; for women they are typical only in the last stages of the disease.
The presence of urate stones can be diagnosed using ultrasound, since X-rays are ineffective. In appearance, these formations have a yellow color, sometimes with a brick tint, and a smooth texture. The size of stones can vary from 1 mm to several centimeters. Urate stones can be seen not only in the kidneys, but also in the bladder and ureters.
Urates are salts of uric acid. A certain amount of these compounds is always present in the body, and this is a normal variant. Under certain circumstances, the concentration of urates in the urine increases, resulting in their precipitation and the gradual formation of formations of increased density - stones.
Reasons contributing to the appearance of urate stones:
- sedentary lifestyle, physical inactivity,
- lack of food, hunger,
- exceeding the recommended dosages of some analgesic drugs,
- lack of vitamins, especially group B,
- incorrect approach to nutrition, consumption of large amounts of animal protein,
- impaired urine formation and low acidity.
Improper nutrition gives rise to an increase in the concentration of urates in the urine. Consumption of certain food groups (for example, rich in purines: meat, legumes) increases the amount of uric acid salts as a result of their processing by the body. In addition, those dishes that help reduce the acidity of urine are also dangerous. These conditions are ideal for the development of urolithiasis.
A person may not even be aware of the presence of urate stones in the urinary system; usually symptoms develop at lightning speed and at an unexpected moment:
- Renal colic appears - severe pain in the lumbar region. They can be either on one side or encircling, extending to the abdomen, bladder and genitals. The pain is not easy to stop,
- changing a person’s posture does not relieve severe pain,
- sometimes chills, nausea and vomiting appear.
If, along with other symptoms, the temperature rises, this signals the development of acute inflammation in the kidneys.
When a person is diagnosed with urolithiasis, and the stones are identified as urate, then this option is the best possible. The thing is that this type of stones can be dissolved and removed from the body naturally. This is accompanied by a decrease and complete disappearance of the above symptoms of the disease, and therefore a cure. Therefore, it is so important to understand that following a diet for urate stones is not just a recommendation, but a direct path to recovery. Only in severe cases, changing the diet does not lead to the desired results, and the doctor prescribes medication or surgical treatment.
Diet for urolithiasis urates and oxalates. Diet for urolithiasis with oxalates
Oxalates are formed in the urinary system due to increased intake of oxalic and ascorbic acid into the body. Oxalate deposits are crystals of the calcium salt of oxalic acid. Also, oxalic acid accumulates in greater volumes against the background of a lack of foods rich in calcium and vitamin B6 in the diet.
If there are oxalates in the organs of the urinary system, the following should be excluded from the diet:
- Leafy vegetables, sorrel, celery, parsley
- Beetroot
- Chocolate and cocoa
- Jelly, jellied meat, jelly
- Figs
- Smoked products, pickles and marinated dishes
- Broths
- Spices
- By-products
- Vitamins with ascorbic acid, as well as dishes for which vitamin C is used for preservation
The diet for urolithiasis (oxalates) implies a serious restriction:
- Salty foods. This is especially true for children, since oxalate deposits most often form in childhood
- Carrots and tomatoes
- Green beans
- Beef and chicken meat
- Oranges, tangerines, lemons, pomelo and other citrus fruits
- Berries: black and red currants, rose hips, gooseberries and blueberries
- Sour apples
- Sweets
- Tea and coffee, if possible they should be diluted with milk
Patients with oscalates should include in their diet:
- Potatoes, carrots, pumpkin, peas, eggplants
- Beans (red)
- Bran, buckwheat, oatmeal
- Bran bread
- Various nuts
- Milk and dairy products
- Infusions of madder, birch leaves
- Lean fish
In mild forms of urolithiasis with oscalates, there is no need to follow a diet, but long-term treatment can lead to pyelonephritis (secondary inflammation), which threatens alkalinization of urine and the formation of phosphate stones. Nutrition rules for this disease become more strict, because you need to combine two diets at once.
Drinking regimen
Normalizing the drinking regime is important for treating uraturia with diet. In the vast majority of cases, patients are recommended:
- mineral water with a healing effect half an hour before meals and in a volume not exceeding half a liter per day;
- table mineral water in a volume not exceeding one and a half liters per day;
- milk and fermented milk drinks;
- fruit drinks;
- drinking water without restrictions;
- compotes;
- weak tea;
- herbal decoctions and teas.
Attention! Recommendations on the choice and mode of drinking mineral water and herbal infusions are given exclusively by a doctor.
Proper nutrition for urate kidney stones. Diet for kidney stones
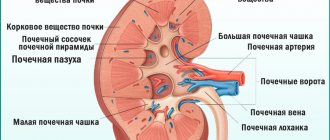
The patient’s nutrition does not depend on the location of the stones, but is completely determined by their composition and the reaction of the urine. The position of the stone determines only the clinical picture of the disease. With kidney stones (located in the pelvis), the outflow of urine is most often not impaired and there may be no pain symptom. When a stone is in the ureter and while passing through it, a blockage of the lumen occurs and the outflow of urine is disrupted. This is accompanied by an attack of renal colic. Acute, paroxysmal pain occurs in the lumbar region. It can radiate to the testicle or labia, accompanied by vomiting and nausea. If the stone is located in the lower third of the ureter, there is a frequent urge to urinate.
Bladder stones are most common in older men. These are single round-shaped stones, and their composition is urate. Their formation is promoted by stagnation of urine in prostate adenoma. In other age categories, the causes are dietary habits, bladder inflammation, alcohol consumption, bladder diverticula, or passing of a kidney stone. An effective and least traumatic method of treatment is endoscopic crushing (cystolitholapaxy) through the urethra.
What diet will be prescribed depends entirely on the composition of the stones. In a nutshell, with urate you need to limit meat and eggs, soups with meat broths and sweet wines. With phosphates, the consumption of milk, eggs and all types of cabbage is reduced; with oxalates, you cannot eat radishes, onions, sorrel, spinach, legumes and tomatoes. This will be discussed in more detail below.
Norm of uric acid salts in urine
In a general urine test, some presence of salts is allowed. The reasons may be nutritional errors or water imbalance. The amount of salts is calculated using a special comparative scale. The norm should not be higher than two pluses (), this indicator is considered acceptable. If there is an increase to 3-4 pluses, both in children and adults, it is necessary to undergo the study again, and then look for the cause of the pathological condition.
There is a maximum permissible norm - a one-time increase in these salts to two pluses in a urine test. With urates in the urine, if there are more pluses (three or four), it is necessary to follow a diet and undergo treatment, because neglect leads to serious consequences, such as gout or kidney stones.
Diet for urate nephrolithiasis. Diet No. 6 (for uraturia)
Uraturia is a type of urolithiasis in which excess uric acid is formed in the body. Uric acid in the form of insoluble salts is deposited in various organs, forming sand or stones (urates). Urate stones can form in joints and all parts of the urinary tract. They can be found in the bladder, ureters and kidneys. Urates are formed due to a violation of the water-salt balance in the body and problems with metabolism. The appearance of urates can be influenced by many internal and external factors. For example, hereditary predisposition, regular consumption of too spicy and sour foods, drinking water that is too hard, the presence of chronic diseases of the genitourinary and digestive system, leading a sedentary (inactive) lifestyle, and much more. Urolithiasis is dangerous due to its unpredictable course and complications. In addition to discomfort and unbearable pain, during the movement of the stone, the disease causes exacerbation of chronic diseases such as cystitis, pyelonephritis and others. Urate stones can form in the body in both men and women, regardless of age. You can prevent the occurrence of urolithiasis with the help of a balanced diet and properly organized physical activity. That is why, when urate stones are detected, the doctor, along with drug therapy, necessarily prescribes a therapeutic diet, the main goal of which is to make the work of the urinary system as easy as possible, normalize metabolic processes and prevent further formation of salt deposits. Treatment of urolithiasis depends on the nature of the deposits, the size of the stone, its location in the urinary organs, the age and condition of the patient. For small stones, treatment consists of strict adherence to diet and drug therapy. The doctor may also additionally recommend diuretics, physical therapy and physiotherapy. In more complex cases (for example, when the stone is large, if the stone has sharp surfaces, etc.), surgical treatment is performed. Diet therapy for uraturia will be useful at any stage of the disease, as well as in the postoperative period. It will help maintain optimal water-salt balance and prevent the formation of urate stones in the future. Diet No. 6 involves a maximum reduction in the intake of uric and oxalic acid into the body, as well as alkalization of urine (since urates are formed precisely when urine is highly acidic). To do this, it is necessary to limit as much as possible the intake of the main source of uric acid into the body - purine bases, which are found in excess in meat (especially young animals) and offal. The list of prohibited products for uraturia includes all offal (kidneys, liver, brains, heart, ventricles, etc.), as well as young meat (veal, lamb, chickens, piglets, etc.) and fish; - meat, mushroom and fish rich broths (since part of the purine bases goes into the broth during cooking); - fried, smoked and salted foods (sausages, sausages, salted cheeses); - animal fats (lard); - vegetables and fruits with a high content of organic acids: sorrel, lettuce, spinach, parsley, green onions, currants, sour apples, etc.; - sweets, chocolate, as well as coffee and cocoa; — alcoholic and low-alcohol drinks; - legumes; — baked goods (pies, buns, etc.). The list of permitted products for uraturia is milk and products based on it (cottage cheese, unsalted cheese, sour cream, etc.); - sweet fruits (raspberries, strawberries, strawberries, etc.); — vegetables: cauliflower, potatoes, zucchini, squash, pumpkin, peppers, carrots, cucumbers, etc.; - vegetarian soups with permitted vegetables; — dried black and white bread (yesterday’s baking); - the amount of salt is reduced to six to eight grams per day, and the amount of liquid drunk (in the absence of contraindications) is increased to two to three liters. Sample menu for one day with uraturia (urate stones) Breakfast: wheat pudding with apples and carrots (150 grams), one soft-boiled egg, weak tea (one mug, about 250 ml). Second breakfast: salad with vegetable oil from fresh vegetables (allowed during the diet), serving - 200 grams, rosehip decoction (one mug, about 250 ml). Lunch: mashed potato cutlets (150 grams), milk noodle soup (250 ml), fruit jelly (250 ml). Afternoon snack: fresh pears (two pieces). Dinner: bell peppers stuffed with boiled rice and vegetables (200 grams), mineral medicinal table water, still water (250 ml). At night: freshly prepared wheat bran decoction (250 ml). Such a diet should be formulated by the attending physician, based on the results of the tests obtained, taking into account the patient’s health condition and the presence of concomitant diseases.