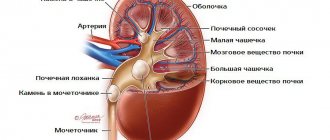
Kidney agenesis: why it is dangerous and how it manifests itself
Causes of the anomaly
The exact reasons why renal aplasia or agenesis develops have not been fully established. Among the possible provoking factors, scientists identify the following:
The action of any of them disrupts cell differentiation in the embryonic period. The fusion of the metanephric canal and the metanephrogenic blastema does not occur, and the organ does not develop normally. As a rule, renal aplasia is accompanied by normal formation of the ureter, but combined malformations of internal organs are often encountered.
There are several forms of anomaly:
- unilateral aplasia with ureter;
- unilateral aplasia without ureter;
- bilateral aplasia.
The bilateral form of the pathology has an extremely unfavorable prognosis. Such newborns are often stillborn or die during the first days of life from progressive renal failure.
Does a missing kidney “hurt”?
Clinical manifestations of unilateral agenesis can appear from the first days of a baby’s life. Noteworthy:
Parents should be alert to the following signs:
Such stigmas of disembryogenesis may indicate congenital anomalies in the development of internal organs.
Current methods of diagnosis and treatment of aplasia
Diagnosing aplasia is not difficult. Using modern instrumental methods, it is possible to identify the localization, nature and severity of the pathological process. Most often used:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- survey R-graphy of the abdominal cavity;
- excretory urography;
- renal angiography;
- CT scan;
- laboratory tests: OAM, tests according to Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky, Reberg.
Disability is assigned to patients with such a developmental defect only in the event of a decrease in the functional activity of a healthy organ and the appearance of clear signs of renal failure.
https://pochkizdrav.ru/drugie-zabolevaniya/aplaziya-pochki.html
Diagnostics
The appearance of any sign requires a careful study of the cause of the deviation. Doctors often observe a combination of two or three symptoms. Based on the examination results, doctors understand whether there are deviations in the size, shape, structure, and location of organs.
It is important to make an appointment with a urologist before negative signs become pronounced. For an accurate diagnosis, the help of an endocrinologist or gynecologist is required; if tumors are suspected of being malignant, a visit to an oncologist is required.
Required research:
Kidney agenesis: why it is dangerous and how it manifests itself
Causes of the anomaly
The exact reasons why renal aplasia or agenesis develops have not been fully established. Among the possible provoking factors, scientists identify the following:
The action of any of them disrupts cell differentiation in the embryonic period. The fusion of the metanephric canal and the metanephrogenic blastema does not occur, and the organ does not develop normally. As a rule, renal aplasia is accompanied by normal formation of the ureter, but combined malformations of internal organs are often encountered.
There are several forms of anomaly:
- unilateral aplasia with ureter;
- unilateral aplasia without ureter;
- bilateral aplasia.
The bilateral form of the pathology has an extremely unfavorable prognosis. Such newborns are often stillborn or die during the first days of life from progressive renal failure.
Does a missing kidney “hurt”?
Clinical manifestations of unilateral agenesis can appear from the first days of a baby’s life. Noteworthy:
Parents should be alert to the following signs:
Such stigmas of disembryogenesis may indicate congenital anomalies in the development of internal organs.
Current methods of diagnosis and treatment of aplasia
Diagnosing aplasia is not difficult. Using modern instrumental methods, it is possible to identify the localization, nature and severity of the pathological process. Most often used:
- ultrasound examination (ultrasound);
- survey R-graphy of the abdominal cavity;
- excretory urography;
- renal angiography;
- CT scan;
- laboratory tests: OAM, tests according to Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky, Reberg.
Disability is assigned to patients with such a developmental defect only in the event of a decrease in the functional activity of a healthy organ and the appearance of clear signs of renal failure.
https://pochkizdrav.ru/drugie-zabolevaniya/aplaziya-pochki.html
Horseshoe kidney in the fetus
Perinatal diagnosis of the defect is difficult due to the frequent combination of fusion of areas of natural filters with anomalies of other organs. Often, fetal malformations are more severe, problems with the genital area, cardiovascular system, and skeletal formation appear.
To prevent severe deviations when planning pregnancy, a woman must undergo an in-depth examination and treat chronic pathologies. Kidney problems in the expectant mother often affect the health of the fetus.
To timely detect developmental anomalies in a child, a pregnant woman should attend all scheduled ultrasound scans and undergo regular tests. When urine becomes cloudy and hematuria appears. development of pain syndrome, increased discomfort in the lower back during exercise, it is important to report negative signs to your gynecologist. The doctor prescribes an examination by a nephrologist to prevent dangerous complications. Pyelonephritis. Urolithiasis kidney prolapse. nephrolithiasis. the penetration of infectious agents into the urinary tract negatively affects the health of the expectant mother and interferes with the proper development of the fetus.
If a horseshoe kidney is detected, doctors decide on surgical treatment after the birth of the child. Each case is individual: doctors determine the optimal age for surgery, taking into account the presence or absence of other defects in parts of the body. Sometimes the child’s condition is so severe that surgical treatment is performed at an early age.
Negative signs with a horseshoe kidney appear in a third of young patients; approximately the same number of children have additional abnormalities in the genitourinary, nervous and cardiovascular systems.
Kidney fusion is a pathology that negatively affects the functioning of the entire body. After an anomaly is detected, the child or adult should be under the supervision of specialists. After treatment, it is important to regularly visit a nephrologist, take tests, and undergo instrumental studies. To reduce the load on the kidneys, you need to give up alcohol, smoking, and limit weight lifting. It is useful to do therapeutic exercises, maintain a drinking regime, and maintain mental balance. Violation of the rules can lead to serious consequences for the kidneys and the entire body.
Source: https://vseopochkah.com/anatomiya/patologii/podkovoobraznaya-pochka.html
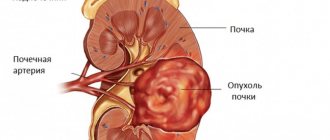
Angiomyolipoma of the kidney, ICD code 10
Prevalence
International classification
ICD-10 divides all diseases into groups. Each pathology, including tumors, is designated by a Latin letter and a digital code. This formulation will be understood anywhere in the world.
Regarding kidney cancer, the following groups and their ICD codes can be distinguished:
- C64 #8212; malignant neoplasm localized within the kidney,
- C65 #8212; malignant tumors of the renal pelvis.
Both ICD-10 diagnoses belong to the “neoplasms” class, the “malignant tumors” section. At the same time, the C64 code completely excludes the disease localized in the pelvis and calyces.
According to the worldwide TNM classification, the following stages of kidney cancer (C64) are distinguished:
Using this classification of kidney cancer according to the ICD greatly simplifies the diagnosis for doctors and gives direction regarding treatment.
Symptoms of malignant neoplasm
In 100% of cases, patients at the third stage of the disease had severe weakness. 30% of men were diagnosed with varicocele, 20% of patients suffered from high blood pressure. At this stage there was pain in the lumbar region (59%).
As the disease progresses, symptoms worsen. As the kidney tumor increases in size, it can be felt during a physical examination.
Even advanced kidney stones can be quickly eliminated. Just remember to drink once a day.
The following changes are detected in the laboratory:
- anemia,
- decrease in the amount of protein in the blood,
- acceleration of ESR,
- the appearance of red blood cells in the urine,
- increased activity of certain enzymes (LDH, ALT, PME-1).
Most cases of detection of kidney tumors occur by chance during examination for other pathologies. At the same time, subjectively, patients do not note any changes in their well-being.
Diagnostics
The basis for diagnosing a kidney tumor is instrumental examination methods. The simplest and most accessible is ultrasound scanning of the retroperitoneal space. During an ultrasound, it is possible to detect a volumetric formation of the kidneys and evaluate parameters such as:
- size and structure of the tumor,
- deformation of the contour of the renal capsule,
- the presence of foci of hemorrhage and necrosis,
- the state of blood flow in the formation and the organ itself,
- accompanying changes in the urinary tract.
Other methods of examining oncological patients include CT, MRI, excretory urography, and renal angiography. They allow you to assess the functional ability of an organ and identify even small tumors.
The last stage of the examination is a biopsy. As a rule, the diagnosis is made based on minimally invasive methods, and histology is performed after the neoplastic lesion has been removed.
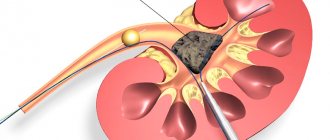
Treatment of malignant kidney tumors
The main treatment method is radical nephrectomy (removal of the organ). It can be performed using various accesses. This method of treatment allows you to completely remove the cancer and prevent its further spread.
Sometimes tumor resection is performed. Such cases include:
- bilateral kidney cancer (ICD-10 code also C64),
- the only spare kidney
- carefully selected patients,
- dysfunction of the contralateral organ,
- refusal of the patient or his guardians from radical treatment.
If the tumor has affected distant lymph nodes (ICD stage #8212; 4, M1), immunotherapy with interferons is performed. To ensure that the patient receives palliative treatment, a nephrectomy is performed.
The role of chemotherapy and radiation therapy in the treatment of malignant kidney tumors (C64) is minimal. Therefore, they are practically not used. There are no specific methods for preventing the disease.
Signs and symptoms
In most patients, a horseshoe kidney is detected by chance, during an ultrasound examination during a routine examination or a deterioration in urine tests. The most common concern is not the fusion of natural filters, but the pressure of the isthmus on the vessels, ureter, and neighboring organs.
Often the anomaly is combined with other types of birth defects. The patient's condition worsens when fused kidneys, hydrocephalus, and polycystic disease are detected. improper formation of parts of the skeleton, splitting of the spinal column.
Clinical picture of a horseshoe kidney:
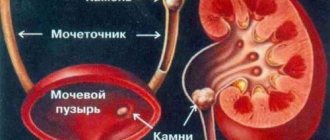
Simple kidney cyst: Causes
Etiology
Congenital - develops from germinal tubules that have lost connection with the urinary tract (5% of cases) • Acquired - develops with obstruction of the tubules due to other diseases (95% of cases).
Pathogenesis
Violation of the drainage function of the tubules • Development of the retention process • Ischemia of the renal tissue.
Risk factors
Benign prostatic hyperplasia • Pyelonephritis • Urolithiasis • Anomalies of the kidneys and urinary tract • Kidney tumor • Glomerulonephritis • Renal tuberculosis.
Simple kidney cyst: Brief description
A simple kidney cyst is a rounded formation with a fibrous capsule and an epithelial lining filled with serous or hemorrhagic contents.
Code according to the international classification of diseases ICD-10:
- N28. 1 - Kidney cyst, acquired
- Q61. 0 - Congenital single renal cyst
- Q61. 9 - Cystic kidney disease, unspecified
Frequency
Found in 3–5% of all autopsies. In the presence of urological diseases - 50%. The predominant age is 40–60 years.
Classification
Intraparenchymal • Cortical • Peripelvic • Multilocular • Subcapsular.