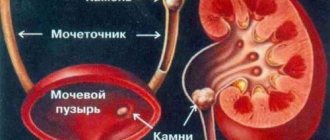
Types of stones
Stones appear gradually. When metabolism in the body is disrupted, sand and microliths—small stones—appear in the collecting ducts. Usually they do not bother a person in any way and are excreted in urine. But with a serious failure, small particles are retained in the kidneys. There is a layering of bacteria, salts, amorphous sediments of urine and fibrin threads. This is how a microlith becomes a kidney stone.
According to ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases), kidney stones or stones are designated N20.0. Sediments are divided into several types based on their chemical composition, size and shape:
- oxalates;
- cholesterol;
- urates;
- cystines;
- phosphates;
- protein;
- carbonates.
Oxalates appear when urine is acidic or alkaline; they arise from oxalic acid salts. They look like dense gray or black crystals, the edges are sharp, and the shape can be spiky. Cholesterol stones are considered a rare phenomenon - they are dark and fragile, difficult to see even with an x-ray.
Urates arise from uric acid salts during an acidic urinary reaction. They are smooth red-orange crystals with a hard consistency. Cystines are found in people suffering from hereditary disorders associated with the absorption of diaminomonocarboxylic acids and cystine. Such stones are round, soft and smooth, light yellow or whitish in color.
Phosphates are formed during an alkaline reaction from calcium salts of phosphoric acid - this often occurs against the background of exacerbation of pyelonephritis. Their structure is soft, the stones are light gray and smooth. Albuminous, soft white stones are a mixture of salts, fibrin and bacteria. Carbons are soft, smooth and light-colored stones made from calcium carbonate.
How to treat kidney stones?
Medical technologies allow surgical endoscopic removal of stones in the left and right kidneys. There are also several methods of lithotripsy - percutaneous shock-acoustic techniques for crushing stones without the use of a scalpel.
To relieve pain and improve the passage of stones through the urinary tract, take:
- Antispasmodics: papazole, papaverine, no-spa.
- Painkillers: baralgin, ketanov, etc.
- Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic urological drugs: urolesan, canephron, trinephron.
The disease must be treated comprehensively, and diet plays a major role in therapy. But there is no need to rush to limit food on your own, because different types of stones require the exclusion of foods specific to them.
Symptoms
Even if stones begin to appear in a person’s kidneys, he may not know about it for a long time. The smallest stones do not cause discomfort and do not manifest themselves in any way.
With large and hard deposits, one of the first symptoms is renal colic - sharp and acute pain in the lumbar region. It occurs when the ureter or pelvis is blocked by a calculus. The cramping attack lasts from several minutes to two hours and begins to gradually subside. After it, sand and minor traces of blood may be found in the urine if the mucous membrane has been damaged.
The patient may also experience the following symptoms;
- problems with urination;
- change in urine color;
- periodic aching pain in the lower back;
- temperature rise to 38 degrees;
- nausea;
- severe swelling of the limbs.
As a rule, during illness, urine becomes significantly less. The urge to defecate can be false and are accompanied by pain and burning.
Specific symptoms also appear depending on which side the deposits appeared on. Left kidney stones are accompanied by acute pain in the pit of the stomach, discomfort behind the sternum, severe weakness and rapid heartbeat.
Stones in the right kidney are found less frequently. They experience nausea, loss of appetite and constant dry mouth. Soreness usually occurs in the abdominal area on the right side. Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor.
Possible reasons
The formation of stones in the kidney is facilitated by an increase in the pH of the urine - hydrolysis, which provokes alkalization. This factor stimulates the formation of crystals, which after some time will turn into stones. Risk factors include:
- poor nutrition;
- infectious diseases;
- bad habits;
- harmful environment;
- renal pathologies;
- long-term use of medications;
- endocrine disorders;
- genetics.
Various diseases can negatively affect the composition of urine, from problems with the gastrointestinal tract to inflammatory processes in the urinary system. Often the cause of urolithiasis is insufficient fluid intake or hard water that has not undergone the necessary purification.
The area in which a person lives has a certain influence on the kidneys. External factors that can lead to the formation of stones include soil composition, weather conditions, humidity, local fauna and flora.
Diagnostics
Due to the fact that symptoms may be absent for a long time, the disorder is rarely detected in the initial stages of deposit formation. But if there are signs hinting that these are kidney stones, you should contact a urologist or nephrologist.
The specialist needs to be told about the nature of the pain, the presence or absence of sandy sediment in the urine and existing problems with urination. Some symptoms may resemble other diseases. Thus, pain in the right kidney is often confused with cholecystitis or appendicitis. These pathologies must be excluded.
The patient is prescribed the following laboratory tests:
- general blood analysis;
- urine tests;
- blood biochemistry;
- urine biochemistry;
- general urine analysis.
Additional instrumental studies are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Plain X-ray urography allows you to detect stones, cysts or tumors. The procedure is performed in a lying position, and the patient will have to temporarily hold his breath.
A little preparation is required: the last meal is allowed 12-18 hours before the visit to the radiologist's office. The method has disadvantages: it can be carried out no more often than once every six months, and only large and dense formations are displayed.
Thanks to ultrasound, doctors determine the shape of the kidneys, their location and size, as well as the presence or absence of stones. The examination is carried out on an empty stomach, but if the bladder is full, the patient will have to drink at least half a liter of water. A conductive gel will be applied to the skin to facilitate the passage of ultrasound waves.
The most effective diagnostic method is MRI of the kidneys. A special magnetic tunnel is used for this. Using high radiofrequency pulses, images of organs are taken in all planes. The method is absolutely safe; before visiting the office, you must remove all metal objects from your body. If there are metal prostheses in the body, other than dental ones, MRI is prohibited.
Stones in the kidneys - what are they?
Stone-like or crystalline dense formations in the right and left intrarenal space are called calculi. But it is not the particles that are treated, but diseases called nephrolithiasis and urolithiasis. Nephrolithiasis is a pathological condition in which multiple stones are found directly in the right or left renal cavities, and urolithiasis is a condition in which salt crystals descend into the bladder or urinary tract.
Treatment options
Optimal treatment methods are selected depending on the size of the stones. If the grains of sand do not reach one millimeter, no specific treatment is required - it is enough to simply adjust the drinking regime to ensure that the deposits are washed out. For small stones (up to five millimeters), specialists can ensure their removal from the kidneys naturally.
Stones larger than five millimeters cannot enter the ureter on their own and require drug therapy. Large crystals (from ten millimeters) pose a serious threat to health. They can be eliminated through surgery.
Surgery
There are several methods for getting rid of large kidney stones; doctors determine which one is suitable for a particular patient. Can be used:
- laparoscopy;
- remote crushing;
- abdominal surgery;
- nephroscopy;
- contact crushing.
During laparoscopy, kidney stones are removed through three small incisions, each no more than five millimeters in size. The likelihood of tissue scarring is minimal, and recovery will only take a few days.
Remote crushing is considered the most gentle option, but the method is used only when necessary to remove stones that are less than two centimeters in size. Dense neoplasms are broken up by laser or ultrasonic waves. They turn sediment into sand, which is then excreted from the body through urine.
Abdominal intervention is performed only in complex cases, if other procedures seem to doctors to be insufficiently effective. The disadvantages include a long and difficult rehabilitation period. With contact crushing, the impact on the stone occurs using special equipment that is inserted through the urinary canal. The stones become smaller and leave the body on their own.
During nephroscopy, a small puncture is made in the lumbar region on the right or left. Through it, a metal tube is inserted into the kidney and removes or destroys the stone. The method is used for single formations and the absence of diseases of the urinary system.
Drug therapy
Conservative treatment is possible for small stones, and only if they do not interfere with the flow of urine. Conventionally, medications can be divided into two types. Some of them are effective against all types of stones, while others are only suitable for getting rid of specific types.
Allopurinol, potassium citrate and Purinol contribute to the destruction of urates. They reduce the acidity of urine, after which the stones gradually dissolve. You must first make sure that the patient is not diagnosed with excess calcium in the urine.
To remove phosphates, the acidity in the urine must be increased. This can be achieved through diet (the diet includes acidic foods) and madder extract. Thanks to the antispasmodic effect of the drug, the process of removing stones through the urinary tract is facilitated.
A universal medicine is Blemaren. Due to its use, the composition of urine changes - it becomes alkalized, the content of potassium and sodium ions increases. The product helps remove existing stones from the kidneys and prevents the formation of new ones. This occurs due to the normalization of acidity levels.
Education mechanism
There is no exact answer to what exactly triggers the formation of stones. According to research, they can be formed due to complex chemical and physical processes that are caused by changes in the equilibrium of colloids and renal parenchyma. The basis for the formation of stones can be salts, bacteria, and foreign bodies.
The main component of stones are urine salts. Urine is a kind of saline solution. Chemical compounds do not dissolve in water, in order to be evenly distributed in the urine; they combine with different proteins, forming complexes. This balance may not always be constant. Any change in the concentration of compounds in urine, its acidity level, or the presence of impurities lead to the destruction of complexes and create the preconditions for the formation of stones.
Salts precipitate and their crystallization begins. The core of the stone is formed. Gradually new crystalloids and colloids join it. According to this theory, all types of stones are formed this way, except cystines. It is believed that they are formed due to precipitation when the concentration in the urine is exceeded. This pathology occurs in people with congenital cystinuria.
What is cystocele in women and how to prevent the development of pathology? We have the answer!
Effective treatment methods for angiomyolipoma of the left kidney are described in this article.