If oxalate formations are detected in the kidneys, then it is imperative to adhere to a special diet. Products containing oxalic acid are especially prohibited. You should not switch to diet food on your own; you should consult a doctor.
Preliminary diagnosis is important, as well as correctly selected treatment tactics.
If you do not sound the alarm in time, the oxalate stones will begin to harden and turn into coral formations that practically do not dissolve.
Diagnosis of oxalaturia
In the urology department, to diagnose oxalaturia the following can be carried out:
- general urinalysis (in which the most characteristic changes are visible).
- X-ray and ultrasound of the urinary system;
- survey and intravenous urography;
- computed tomography
- cystoscopy or chromocystoscopy.
- bacterial culture of urine;
Kumachev K.V.
Ph.D. urologist
Most patients are simply dumbfounded when they hear that they have kidney or bladder stones. It is very important not to panic after making a diagnosis! The level of modern urology allows you to effectively and non-traumaticly treat urolithiasis. The main thing is to go through all stages of treatment and monitor the result.
Diagnosis of the disease
The simplest method for detecting urolithiasis is a general urine test.
The study will confirm or deny the presence of stones and provide information about their chemical composition. The following effective diagnostic methods are currently used:
- X-ray examination of the kidneys;
- urography;
- ultrasonography;
- collection of daily urine.
The formation of stones is indicated by an increased level of red blood cells, leukocytes, and casts.
In any case, you should contact a specialist who will refer you for appropriate research.
Based on the data presented, he will receive a general symptomatic picture, which is necessary to prescribe effective treatment.
Oxalate kidney stone
Oxalates in the kidneys are the most common cause of urolithiasis. A person who has been diagnosed with oxalate stones in his kidneys must gather himself as much as possible and prepare for long-term treatment, because oxalate stones are very difficult to cure.
You should know that oxalate stones are special kidney formations that arise due to the uric acid reaction. Therefore, the composition of oxalates necessarily includes salts of oxalic acid. The most common oxalates in the kidneys are calcium.
This article will give a general assessment of oxalates, provide information about oxalates and what measures a urologist will take if they detect oxalates in the urine.
Oxalate can confidently be called the king of stones. In case of urolithiasis, doctors most often encounter oxalates. When treating nephrolithiasis, any urologist encounters oxalate stones in approximately 60% of cases.
Oxalate stones are difficult to chemically attack due to their high hardness. They are very difficult to dissolve or crush during kidney lithotripsy.
Oxalates are practically insoluble in the kidneys. These are dangerous stones. While dormant, oxalates grow in size over time and can become the basis for the formation of large coral stones.
Fruits and vegetables with a high content of oxalic acid or with an excessive amount of vitamin C are very favorable for the concentration of oxalates in the urine: rose hips, citrus fruits, currants, sorrel.
Coffee, cocoa and chocolate also lead to the accumulation of calcium in urine. These pleasant and tasty foods, unfortunately, seriously increase the risk of developing sand or kidney stones.
Studies of the causes of ICD have repeatedly confirmed that oxalates in the urine are detected mainly in residents of areas with a natural deficiency of vitamin B6 and a lack of magnesium in drinking water and foods.
- Salts oxalates in the urine of a child
Sometimes various chronic diseases or impaired metabolism in the body lead to the development of oxalaturia. Oxalaturia can occur together with granulomatous enteritis, diabetes mellitus, and pyelonephritis.
If a repeat urine test confirms the presence of oxalates, this definitely indicates the imminent appearance of kidney stones. At the first signs of oxalaturia, you need to consult a good urologist.
Factors leading to the formation of oxalates
The causes of kidney pathology, in which the main factor is oxalate kidney stones, are important to know not only for doctors, but also for patients. This information is important for preventive measures aimed at preventing the disease and preventing the development of nephrolithiasis. Another important point: knowing the causes of the occurrence, you can overcome the relapse of a serious pathology with terrible complications.
The main reason for the onset of the disease is the consumption of large amounts of fermented milk products, sour fruits and the use of calcium-based medications, as well as the growth of kidney stones can provoke the disease.
The combination of factors includes:
- Calcium oxalate spikes that injure the kidney and urinary tract
chronic pyelonephritis; - cystitis;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- oncological diseases of the genitourinary system;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- injuries in the kidney area;
- metabolic disease;
- chemical poisoning.
Nutrition for oxalaturia
What should people with oxalate stones eat? The main task of nutrition for oxalaturia is to restore the calcium-magnesium balance, relieve the kidneys, and help them recover. To do this, the menu should be as balanced as possible.
Can:
- lean boiled meat;
- cereals;
- fruits;
- mineral waters without gas with an optimal pH composition;
- wheat and rye bread;
- high-quality butter and vegetable oil);
- low-fat dairy products.
boiled eggs;
Limit:
- leaf lettuce (primarily sorrel),
- lemons
- cranberries
Eliminate completely:
- pickles;
- canned food;
- smoked meat and fish;
- offal;
- sweets;
- strong broths;
- coffee;
- highly carbonated drinks;
- alcohol (including beer).
doctor and receive an answer by email
Types of kidney stones
And finally, about prevention
When faced with the problem of oxalate (as well as urate, phosphate, uric acid, struvite) stones, you need to make every effort to ensure that they do not increase (in case of observation) or re-form (if the problem has been solved). For this it is recommended:
- drink enough clean water;
- follow a diet (eat small meals, often, little by little, excluding foods from the list above);
- lead an active lifestyle;
- do not overcool;
Dissolution and removal methods
There are several methods you can use to get rid of oxalates. They will be discussed below.
Diet
All therapeutic measures must be combined with special nutrition.
In the first place is the restriction on the intake of products that contain oxalic acid.
This:
- Spinach.
- Sorrel leaves.
- Potato.
- Lettuce leaves.
- Citrus.
- Milk.
The following products must be included in the diet:
- Pears.
- Dried fruits.
- Apples.
- Grape.
- Products that contain magnesium, as it is able to bind oxalic acid.
In addition, there are general menu recommendations for all types of stones:
- The volume of daily fluid consumed should be within 2.5 liters, no less.
- If your doctor has prescribed it, you must take diuretic infusions.
- There is no need to eat more than you should, you should avoid eating fried, fatty, spicy and salty foods, and smoked foods.
Mineral waters with an alkaline reaction are beneficial for the patient.
Drugs
The drugs in this case are mainly used on a plant basis.
They perform the following functions:
- Slows down the growth of stones.
- Helps dissolve them.
- Remove formations from the kidneys.
The most commonly used medications are:
- Pyridoxine or thiamine, the first preparation contains vitamin B6, the second - vitamin B1.
- Preparations containing magnesium (Asparkam, Xidifon, etc.).
- Retinol, which contains vitamin A, alpha-tocopherol with vitamin E.
- Blemaren.
- Herbal preparations, for example, pol-paly, bearberry, etc.
Important ! It is necessary to check the condition of urine; normally it should be light and its volume per day should be at least two liters. In this case, the drinking regime is up to 2.5 liters of liquid per day according to the doctor’s indications, if there is no renal failure.
Types of operations
If the stones are large, then you will have to get rid of them surgically.
Problems Caused by Oxalates
Oxalate stone can partially block the urethra, being securely held in it by sharp tubercles. This will greatly disrupt the flow of urine, and the patient will begin to experience signs of renal colic. Often pain can be reduced only by changing the position of the body; the body itself will prompt it.
This is precisely what can explain the completely exotic poses that a patient with urolithiasis with a blocked urethra is forced to take.
The most dangerous case is anuria, an absolute blockage of the urethra by a calculus. With anuria, the pressure on the kidney increases significantly. Harmful metabolic products quickly accumulate in the kidney, which ends in uremia, that is, self-poisoning of the body.
Drug treatment
Preparations for dissolving and removing oxalates are selected according to the principle of an integrated approach:
- Possessing antimicrobial action;
- Having anti-inflammatory properties;
- Promoting the dissolution of oxalates and their removal from the body.
If, during examination, an infection is diagnosed in a patient, antibacterial agents and sulfonamides are prescribed. Antispasmodics help painlessly accompany the process of removing oxalates, without damaging the urinary tract.
An approximate scheme of drug therapy for detection of oxalate conglomerates:
- The drug Blemaren for maintaining urine pH within normal limits has a wide range of medicinal properties:
- Dissolution of oxalates;
- Prevention of their occurrence;
- Preparation for surgery to destroy oxalates;
- Increasing the efficiency of the operation.
- Medicines Canephron, Phytolysin, Cyston - help eliminate uric acid;
- Baralgin, No-shpa relieve pain;
- Vitamins E, A, B6 serve to prevent the formation of oxalate stones and normalize metabolism.
- Asparkam and preparations containing magnesium.
Self-medication with medications will lead to premature transport of oxalate stone through the urinary tract. Its sharp thorns injure the tissues of the genitourinary system, causing severe pain to the patient.
The surest tactic is to crush the stone into small fragments and remove these remains in the most gentle way.
Symptoms of the disease
In nephrolithiasis, when the disease occurs with symptoms, it is customary to distinguish between acute and interictal periods. In the acute period, kidney stone disease is indicated by an attack of renal colic, which is characterized by sudden and violent pain in the lower back (often after physical strain), radiating to the groin and abdomen.
Other typical symptoms are nausea, bloating, gas and stool retention, sometimes developing into intestinal obstruction, in which the nature of the pain becomes cramping. The attacks are repeated with a certain frequency.
During the interictal period, some signs characteristic of pyelonephritis may be observed (pain in the kidney area when tapping the upper part of the lower back), as well as slightly increased urine output.
- Kidney stones: methods of treating nephrolithiasis. Folk remedies and disease prevention (90 photos)
The diagnosis of kidney stones is finally confirmed only by ultrasound examination of the kidneys or X-ray examination (X-rays best identify urate stones and less clearly - phosphate stones). A urine test can detect a shift in the acid-base balance to the acidic or alkaline side, as well as the presence in the urine of certain substances that promote the growth of stones.
Elimination of nephrolithiasis depends primarily on the type of disease (dysfunction) that caused the deposition of stones - this includes metabolic disorders, vitamin A deficiency, etc. In the acute period, a painful attack is controlled by the following measures. The patient is supposed to immediately lie down in bed, and so that the upper part of the body takes an elevated position (pillows are placed under the back).
Heat (compress or heating pad) is applied to the kidney area. If a person is able to move, it is advisable to take a general or at least a local (to the waist) hot bath. Painful sensations are eliminated with the help of analgin, as well as antispasmodics such as baralgin (5 ml intravenously) and no-spa (2-3 tablets orally or intramuscularly 2 ml of a 2% solution).
When a person suffers from flatulence, which increases pain, you can use a gas tube or do an enema with chamomile infusion. A persistent absence of urine in the bladder or the presence of blood (pus) in the urine usually serves as a basis for surgical intervention.
Treatment options
Complex methods of therapy include conservative and surgical measures affecting the kidneys and stones.
- Conservative treatment.
Any medicinal methods are possible only for small formations in the absence of complications. The main treatment measures will be:
- pain relief, which is especially important for renal colic;
- impact on the inflammatory process;
- improved urine flow;
- the use of drugs for spontaneous passage of stones;
- use of drugs with litholytic effect.
Small oxalate stones can be eliminated with the help of drugs that enhance urodynamics. The treatment method involves the use of special medications that help the stones to pass out on their own.
Oxalate stones are hard and dense, so the litholytic method (method of dissolving stones) is practically ineffective.
- Lithotripsy.
The method of remote destruction of stones followed by spontaneous passage of fragments is called lithotripsy. This procedure is good because it does not require abdominal surgery. Among the disadvantages, it should be noted: the need to go through several stages and the possible risk of an attack of renal colic.
- Surgery.
Most often, the following surgical methods are used to eliminate nephrolithiasis:
- pyelolithotomy;
- nephrolithotomy;
- kidney resection;
- nephrectomy.
In each specific case, the doctor selects the treatment option individually, depending on the location and size of the stones, necessarily taking into account the preservation of the healthy part of the kidney. The most difficult options would be staghorn stones or multiple large stones.
The nuances of stone formation
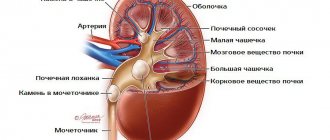
Calcium oxalate salts in urine
Oxalate formations begin to develop in an environment rich in oxalic acid, which is saturated due to the increased concentration of calcium. Due to stagnation of urine due to an inflammatory factor or obstruction of the lumen of the ureters, the amount of oxalate in the urine increases (oxalaturia). Calcium has the ability to form a sediment; layers with spike-like growths build up around this slowly rotating substance.
Stones of other origin can be washed out, and oxalate stones are attached to the walls of the cups and pelvis due to sharp spines.
As they grow, other substances can become layered, so laboratory tests of kidney stones often show these layers.
Diagnostics
Information on how to remove oxalate stones from the kidneys is provided by a nephrologist. It is he who should be contacted at the first alarming symptoms. During the initial appointment, the doctor will collect anamnesis and examine the patient, after which he will issue referrals for laboratory and instrumental studies.
Clinically significant for the disease is a general urine test. The specialist is interested in the following changes that confirm the diagnosis:
- Hyperoxalaturia. This is a condition characterized by excessive accumulation of oxalic acid in the body, which then enters the blood and is excreted through the kidneys in the urine.
- Microhematuria. Characterized by the presence of blood impurities in urine. In this case, liquid connective tissue in the urine cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Mild proteinuria. In this condition, protein is released from the body along with urine, the amount of which exceeds normal values.
- The presence of glycolate and glyoxylic acid in the urine.
- Increased degree of crystal formation in urine.
- Moderate tubular dysfunction.
- The presence of markers indicating instability of cell membranes.
Urinalysis is the most accessible type of research, allowing not only to confirm the diagnosis, but also to determine the chemical composition of the stones.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing pathology include the following:
- radiography of the kidneys;
- bacterial culture of urine;
- Ultrasound;
- scanning of the urinary system;
- contrast techniques;
- chromocystoscopy;
- urography.
The advisability of prescribing certain studies is determined by the doctor. They are necessary in order to identify the exact location of the stones, their number, size and shape. Based on the diagnostic results, the most effective treatment regimen is drawn up. In addition, the question of the advisability of surgical intervention is being resolved.
Dietary nutrition for oxalates
An important place in therapy is occupied by diet for oxalate kidney stones. Since oxalaturia can be caused by eating excessive amounts of fruits and vegetables that are high in oxalic acid, you should avoid eating such foods. It is necessary to exclude dough products, ice cream, sweets, chocolate, cookies, jam, fatty meat, vinegar, mustard and tomatoes.
- Kidney stones: symptoms in women, causes during pregnancy, treatment
If we talk about broths, they should not be rich. Liver, gelatin, jellies, aspic, jellies, brains, kidneys, and other offal should also be excluded from the diet. In addition, you should refrain from canned food, sauces, pates, sausages, smoked meats, fried and spicy, sour and salty foods.
Mushrooms, peas and other legumes, spinach, sorrel, salads, parsley, beets and asparagus, Brussels sprouts and red cabbage, and broccoli are also prohibited. Horseradish, figs, nettles, celery, and bell peppers should also be excluded.
In addition to all of the above food products with a high content of oxalic acid, the occurrence of oxalates in the kidneys can be affected by the consumption of large amounts of vitamin C. That is why the consumption of berries and fruits high in this vitamin is also not recommended. Strong tea, kvass, cocoa, chicory and tomato juice should be excluded from drinks.
Some people try to treat themselves - alternative traditional medicine methods can offer various methods for removing kidney stones. However, do not forget that not all stones can be dissolved and not all of them can come out on their own.
Self-medication is often thoughtless and ineffective; moreover, it often leads to aggravation of the disease, when emergency hospitalization is necessary, as well as to severe and irreversible consequences.
Diet for illness
Patients are advised to pay attention to the following products that should be present in the daily diet:
- potato;
- beans;
- eggplant;
- cauliflower;
- apples;
- grape;
- prunes;
- bananas;
- apricots;
- cereals;
- dairy products;
- lean fish.
It is strictly forbidden to use:
- leafy greens;
- chocolate or cocoa;
- beets, celery, sorrel;
- spices;
- jellies and marinades;
- fatty broths;
- smoked meats
In limited quantities you can:
- salt;
- citrus;
- berries;
- tomatoes;
- Tea coffee.
Features of oxalate stones
Oxalates in the kidneys are stones ranging in size from 1 mm to 4 cm. They have a hard layered structure, a black or gray tint and are distinguished by the presence of sharp convex parts, which often injure the kidney tissue and lead to the development of bleeding.
The composition of oxalate stones is determined by the mechanisms of stone formation. Oxalates arise from the binding of oxalic acid to calcium. Therefore, they are often called calcium oxalate.
When thinking about how to dissolve such stones, it is important to remember that this type of stone is the hardest of all types of such formations and is the most difficult to crush and remove.
Features of oxalate stones
Structure of stones
The “building material” for the formation of nephrolithiasis of oxalate etiology is oxalic acid. The chemical structure of oxalic acid contains calcium, which is directly involved in the formation of oxalate conglomerates. There are sufficiently acceptable conditions for the development of the disease, that is, urinary stasis and the inflammatory process, and from a small microscopic grain of sand a pebble grows 2-3 cm in size, less often 5 cm or more. Colic and pain syndrome begin due to roughness and spike formations on the surface of kidney stones when their migration. Sharp protrusions easily scratch the parenchyma and mucous membrane of the ureters, they get stuck inside the ureteral canals.
Removing large oxalate stones is impossible without surgery, so it is recommended to remove such kidney stones in the early stages, preventing further complications.
Main stages of treatment
- Control of fluid intake - drinking enough fluid helps remove oxalate plaques and wash out salts. For this purpose, it is recommended to drink at least 1.5-2 liters of water per day.
- Physical activity - in the process of removing sand and microliths from the kidneys, regular physical activity occupies a special place. Body movement (jumping, running) promotes the movement of oxalates down the ureter.
- Drug therapy. If necessary, a specialist can prescribe medications that help remove kidney stones and also normalize metabolism.
If the diagnosis shows the presence of oxalates in the urine, further treatment occurs according to a strict plan.
1.Operation
If large oxalates are detected in the kidneys, the urologist prescribes surgery for the patient. Removal of kidney stones is performed by various methods, surgical, with kidney lithotripsy, etc., which option to prefer will be advised by a urologist, based on the picture of the disease, well-being and capabilities of the patient’s body. You can read about this in our publications on the treatment of urolithiasis.
2. Diet
The patient will need to remove foods high in oxalic acid from his daily diet, such as sorrel, lettuce, spinach, beets, cocoa, coffee, chocolate. You can read more about the proper diet for kidney oxalate in the publications section.
3. Therapeutic treatment of oxalate stones
The urologist prescribes sodium citrate and potassium citrate to the patient, which will reduce the formation of complexes of poorly soluble calcium salts, reduce the concentration of its ions and form complexes with citrate.
4. Further treatment in sanatoriums
For subsequent treatment of urolithiasis, it is advisable to visit sanatorium-resort complexes in the Russian Federation and the CIS, such as Truskavets, Pyatigorsk, Zheleznovodsk, Essentuki, Kislovodsk, Arzni, Jermuk.
Symptoms and treatment
Characteristic symptoms for nephrolithiasis of oxalate etiology are:
- scanty and frequent urination;
- pain in the lumbar region and lumbar area, radiating to the groin;
- changes in general urine tests, that is, upon visual examination, the urine is dark with an admixture of blood, and laboratory testing reveals a high content of leukocytes, red blood cells, protein, pus and oxalates;
- nausea, vomiting and fainting;
- elevated temperature up to 39-40 degrees.
Treatment of oxalate kidney stones consists of a whole range of measures, which has a positive effect if only the stones are small. They can be removed or crushed. Dissolution of stones is possible at the initial stage, and at medium sizes they can be crushed with a laser or ultrasound, after which they can be easily removed from the body along with urine.
Stones in the form of sand or small formations are successfully treated conservatively, and their reappearance is stopped as follows:
- Daily consumption of 2-3 liters of drinking water (or mineral water without gases).
- Regular exercise.
- The use of medications (Blemaren, Panangin and Asparkam), through which lithiasis is dissolved.
- Consumption of B vitamins.
- Dietary food that excludes dishes containing high amounts of oxalic acid and calcium.
Attention! By strictly observing the above points, you can forget about oxalate stones forever.
Why is oxalaturia dangerous in children and adults?
Kidney stone formation leads to dysfunction of the entire urinary system. Nephrolithiasis in adults is often complicated by:
- chronic pyelonephritis;
- kidney failure;
- hypertrophic cystitis.
Chronic kidney failure is the most serious complication of kidney stones. When they are irreversibly damaged, toxic substances accumulate in the body. The result is uremia - autointoxication with nitrogenous substances and other metabolites. Against this background, children experience physical and mental retardation, heart failure, and osteoporosis (brittle bones).
Symptoms indicating a problem
In adult patients, the following symptoms of oxalate stones appear:
- nagging, dull pain in the abdomen and lumbar region radiating to the groin;
- hematuria – change in the color of urine, the predominance of a red tint in it;
- colic, pain when urinating;
- cold sweat;
- nausea, vomiting
- impaired urination.
In children under 6 years of age, “oxalum diathesis” practically does not manifest itself, and the disease can be detected only after tests or a preventive examination. Already at school age, children can feel:
- pain in the abdomen and lower lumbar region;
- periodic colic in the kidneys;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- lethargy, loss of strength, sudden mood changes.
Sources used:
- https://lithotripsy.ru/mkb/stones/oksalaty/
- https://opochk.ru/oksalatnyie-kamni-v-pochkah/
- https://boleznipochek.ru/pochki/mochekamennaya-bolezn/oksalatnye-kamni-v-pochkax-ix-rastvorenie.html
- https://pochkam.ru/bolezni-pochek/oksalatnye-kamni.html
- https://simptom.info/nefrologiya/oksalatnye-kamni-v-pochkah
- https://urohelp.guru/pochki/mkb/oksalatnye.html
Prohibited Products
Foods that should be excluded from the diet:
- legumes;
- spinach;
- beets;
- rhubarb;
- asparagus;
- radish;
- sour tomatoes;
- bell pepper
Meat broths and baked goods will also have to be completely excluded from the diet. Chocolate, sausage, offal, aspic, ice cream, candy - these are the foods that provoke the formation of oxalates, so their consumption should also be completely limited.
Protein chem. compound:
- fats – 70 grams;
- proteins – 100 grams;
- carbohydrates – 500 grams.
In total – up to 3500 calories.
In addition, a five-course diet with the exception of cold dishes and the introduction of plenty of fluids (at least 2 liters per day) is recommended.