The article talks about the causes and symptoms of kidney stones. The principles of treatment are described.
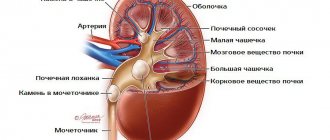
All the blood in the human body passes through the kidneys. With an increased content of various salts in it, they settle in the kidney tissue. This is how kidney stones form in women - the symptoms of this disease are varied and depend on the volume and number of stones.
The disease is diagnosed in women of any age
Causes of pathology in women
Kidney stone disease is a disease that affects an average of 3% of the world's population. Most often, urolithiasis in women develops for the following reasons:
- A metabolic disorder in the body that changes the chemical composition of the blood. In this case, metabolic disorders can be caused by inflammatory diseases, decreased immunity, hormonal imbalance, uncontrolled and long-term use of medications of a certain group.
- Hereditary predisposition of the female body.
- Poor quality drinking water. It is worth noting that in underdeveloped countries, where the quality of drinking water is low, urolithiasis occurs in almost 30% of regional residents. At the same time, when drinking soft drinking water (melt, lake), the disease practically does not occur.
Important: special attention should be paid to water rich in limestone inclusions. It is this fluid that can cause the formation of stones in the kidneys and urinary tract.
Causes and risk factors
The formation of stones can occur for many reasons. These include:
- developmental abnormalities of the urinary system organs;
- infectious and inflammatory kidney diseases (pyelonephritis);
- genetic predisposition;
- unfavorable climatic conditions;
- sudden climate change;
- living in hot, arid climates or mountainous areas;
- drinking disorders;
- changes in diet;
- dehydration;
- infectious diseases (intestinal infections);
- thyroid diseases;
- lack of vitamins;
- oncological diseases;
- tumor disintegration;
- disorders of mineral metabolism;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathological changes in the liver;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- stagnation of urine due to injury or developmental abnormalities.
There are some factors that may cause a high risk of stone formation. These include the following factors:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- overweight;
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- children under 5 years of age;
- old age over 65 years;
- pregnancy.
Causes of kidney stones in women
The process of formation of kidney stones has been known for a long time, but the causes of formation have not been established. Factors that explain the development of pathology have been identified. The main point is heredity or congenital changes in metabolism. The following metabolic disorders can provoke the process of stone formation:
- uric acid in urine and blood;
- phosphate salts in urine;
- calcium salt or oxolates.
Violation does not happen just like that; changes are provoked by certain factors. The causes of metabolic changes are divided into 2 types:
- External:
- climate;
- chemical composition of water and products;
- minerals in the soil;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- features of the labor process.
- Internal:
- enzyme deficiency;
- genitourinary tract infection;
- digestive disorders.
Return to contents
Features of stone formation in children
The formation of kidney stones in children is a fairly common pathology. Most often it is diagnosed in children under 5 years of age and in adolescence.
Unlike older patients, the course of this pathology is asymptomatic. For example, in children under the age of 1 year, stones can only be determined by ultrasound of the kidneys; symptoms cannot be detected.
If an acute attack is observed, provoked by the movement of a stone, then the symptoms may be similar to the development of an infectious disease.
Accompanied by the following symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting;
- breast refusal;
- increased body temperature;
- frequent regurgitation;
- strong crying.
In older children, an acute attack can proceed in the same way as in adult patients and have the same symptoms.
The most common types of kidney stones are phosphate, oxalate and calcium stones. This is due to the innate developmental characteristics of the body. The formation of stones in childhood directly correlates with hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms of kidney stones in women
If the stone is larger in size and has an irregular geometric shape (the presence of thorns, corals, sharp corners), then when it moves, severe renal colic occurs.
Kidney stones are formed when there is excess salt in the body. In this case, the salts first precipitate, and then acquire various inclusions such as mucus, epithelium, protein, etc. The diameter of the stones can vary from several millimeters to several tens of centimeters. Most often, there are no symptoms of kidney stones at all. However, stones can manifest themselves in the following ways:
Recommended reading:
Causes of tingling in the kidneys: diagnosis and treatment
- If the stones are small in diameter (up to 5 mm), it is considered sand. When their kidneys exit and enter the bladder, and then into the urine, a woman may experience a slight burning sensation when urinating. Most often, a woman does not even pay attention to such a symptom.
- If the stone is larger in size and has an irregular geometric shape (the presence of thorns, corals, sharp corners), then when it moves, severe renal colic occurs. In this state, a woman may not find a place for herself, trying to relieve the pain. Often, renal colic is accompanied by an increase in temperature to 38-39 degrees, fever, cold sweat, a feeling of panic, and possible vomiting. The pain in this case can be girdling, sharp, and radiate to the side and/or labia.
Important: Renal colic can be so severe that it can cause shock. You cannot take analgesics if you have renal colic. You need to save yourself with antispasmodics until the ambulance arrives.
- After renal colic, a woman may experience cloudy urine, mucus, pus and blood in it. If such symptoms periodically bother the patient, then you should immediately contact a urologist and gynecologist.
Why do stones appear?
The reasons for the formation of stones are different. Everything happens against the background of metabolic disorders in the body and nutritional problems. Main reasons:
- Violation of water balance in the body.
- Frequent use of diuretics, dehydration.
- Poor nutrition.
- Chronic diseases.
- Bad heredity.
If the body does not receive enough water, this can cause urine to become more acidic. This is what causes the risk of kidney stones. If dehydration is frequent or constant, this can make the situation worse.
Poor nutrition, excessive love for salty, spicy, meat or even dairy foods can cause urolithiasis. Stones have different compositions and classifications.
A chronic infectious process is what causes pathology to develop. In patients diagnosed with pyelonephritis, ICD is diagnosed more often. In this case, the signs of the disease can be confused. That is, a person simultaneously experiences symptoms of an inflammatory disease and urolithiasis. ICD occurs with impaired renal function and more. The pathological process may also be associated with the adrenal glands.
ICD is not inherited, but a predisposition to urolithiasis is transmitted. That is, in the presence of unfavorable factors, the risk of kidney stones increases.
- How to cure kidney stones using traditional medicine methods
In most cases, a woman does not even suspect that stones are forming in her kidneys. The pathology occurs without pronounced symptoms. Signs appear when the stone changes its location or, more simply put, moves.
Areas of pain
Stones during pregnancy
Often, a renal tumor is detected in women during pregnancy and many wonder what to do about it. In pregnant women, stones can form due to poor diet and lack of physical activity. If a pregnant woman experiences nagging pain in the lumbar region and lower back, she should urgently consult a doctor; the patient should be given first aid without the use of potent analgesics.
All kinds of signs of movement of stones, a feeling of discomfort in the genitourinary organs require monitoring by the attending physician. Treatment of pathology in pregnant women is reduced to relieving pain, dissolving and removing soft deposits.
Kidney stones in pregnant women
If a pregnant woman is carrying a fetus, she must be especially attentive to her health.
If a pregnant woman is carrying a fetus, she must be especially attentive to her health. Thus, the chronic course of urolithiasis does not in any way affect the bearing of the baby. However, if the pathology enters the acute phase, termination of pregnancy is possible. This is due to the fact that when a stone moves through the urinary tract, the entire body goes into spasm. Thus, the organs try to push the foreign body out. Unfortunately, the smooth muscle spasm will also extend to the uterus, which is a large muscular organ. In this case, with a strong spasm, the embryo may simply be rejected.
Important: therefore, in order to avoid the occurrence of an acute form of pathology, it is better to consult your urologist about the optimal diet. It is worth remembering that it is more difficult to treat a pregnant woman due to the fact that most drugs are contraindicated for the expectant mother. Surgical intervention for severe renal colic is carried out only in case of vital indications, when the life of the mother is put above the life of the unborn baby.
Therapy
A woman with urolithiasis should be treated by a urologist. A specialist will suggest the best solution to the problem and help get rid of the pathology.
Treatment main methods:
- surgery;
- laser crushing;
- ultrasound lithotripsy;
- crushing stones using shock waves;
- ureteroscopy.
Surgery is used in emergency cases. The specialist recommends surgical intervention if:
- The stone is too large to pass through the ureter on its own.
- If the kidneys are clogged with large stones.
- If the patient has concomitant diseases of the genitourinary system.
If a large stone comes out, it can cause serious harm to the patient’s body. In this case, a medical council meets and doctors decide whether to perform surgery.
The laser beam is a source of heat and energy; it is capable of crushing large stones. A specialist uses a beam to crush stones into sand, thereby solving the patient’s problems.
Ultrasonic crushing is a very effective method. It helps get rid of the problem. The specialist makes an incision in the back area and inserts a special device there, with the help of which the procedure is carried out.
Crushing stones using shock waves helps reduce the formation in size. That is, a large stone turns into several small ones. The specialist closely monitors the process. Once the stones reach the desired size, the procedure is considered successful. Such stones pass out of the kidney on their own.
- Is it possible to get rid of kidney stones with pills that break them up?
Urethroscopy involves a specialist inserting a device into the bladder and through the urethra into the kidney. Thus, the stone is removed or crushed. A small stone easily passes out of the kidney without causing much discomfort.
Treatment of urolithiasis takes place in several stages and after removing the stone, the specialist must prescribe a diet to the patient.
Treatment
Treatment of kidney stones includes the following methods:
- conservative therapy;
- surgery.
When prescribing treatment, the doctor relies on data about the patient’s condition, the size and shape of the stones, as well as their location.
Any of these treatment methods has the following goals:
- relieving an acute attack of renal colic;
- elimination of stones from the urinary tract;
- prevention of infectious complications;
- elimination of accompanying pathological changes;
- improvement of urinary function;
- prevention of emergency conditions (acute renal failure, blockage of the urinary tract with stones, bleeding).
Conservative treatment
This type of kidney stone treatment includes:
- drug treatment;
- phytotherapy;
- physiotherapy;
- diet.
Conservative treatment is prescribed if the stone has not reached a large size and there is no tendency to develop dangerous complications.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy includes the use of antibacterial drugs, synthetic antimicrobial drugs, diuretics, antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
| Group of drugs and their action | Examples |
| Antibacterial drugs (prevention of infectious processes in the kidneys) | Ceftriaxone (intramuscular) 7-10 days. |
| Synthetic antimicrobials | Furazolidone (tablets) 10-14 days. |
| Antispasmodics (to relieve an attack of renal colic) | No-spa (2 tablets 3 times a day). For pain syndrome. |
| Diuretics (to remove kidney stones) | Furosemide (intravenous drip as prescribed by a doctor). |
| Anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs (to reduce body temperature) | Ibuprofen or Paracetamol (use according to instructions). |
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed to prevent kidney infection, because Stone formation is often accompanied by acute pyelonephritis (inflammation of the renal pelvis system).
Phytotherapy
Herbal medicine is the treatment of kidney stones using herbal preparations. These include collections of various herbs, preparations which include plant components. These medications include oral tablets, solutions, or pastes that help remove kidney stones.
Phytotherapy treatment is carried out in conjunction with the main therapy, because Many herbs have a cumulative effect in the body and the results from taking them are observed after some time.
Herbal medicine in the treatment of kidney stones is aimed at the following effects:
- anti-inflammatory effect;
- destruction of stones;
- removal of stone residues through the urinary tract;
- antispasmodic effect;
- antimicrobial effect;
- healing of damaged mucous membrane;
- analgesic effect;
- diuretic effect.
Herbal medicine will complement basic therapy and help remove kidney stones.
Treatment of kidney stones involves taking the following medications:
- Phytolysin (oral paste). Use 3 times a day, 1 teaspoon, which is dissolved in half a glass of warm sweet liquid. The course of treatment is 1 month.
- Canephron (tablets or drops for oral administration). Take 2 tablets 3 times a day for 1-2 months.
- Urolesan (tablets). 1 tablet 2 times a day for 2-3 weeks.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used as an additional treatment for kidney stones. The following methods are used:
- medicinal electrophoresis (with an antispasmodic drug);
- electrical stimulation with currents;
- inductothermy;
- amplipulse therapy.
Physiotherapeutic methods are used both during the acute stage (with severe pain) and during the recovery period. The course of physiotherapy treatment is from 10 to 14 days.
Diet
The basis of therapeutic nutrition is a complete abstinence from salty foods, as excessive salt consumption can lead to the formation of salt crystals in the urine and, as a result, the formation of stones.
In addition, the patient must follow the following principles of diet when stones form:
- refusal of foods that cause irritation of the mucous membranes of the urinary tract (smoked, fried, sour);
- drinking plenty of fluids (fruit drinks, juices, tea);
- avoidance of carbonated drinks;
- reducing protein intake per day (this is necessary for normal kidney function);
- reducing the amount of sweet foods in the diet;
- inclusion of dairy products in the diet;
- consumption of vegetables and fruits.
The patient should pay maximum attention to the drinking regime, since abundant fluid intake helps cleanse the urinary tract of stones and sand. Low fluid intake promotes the formation of salt crystals.
Traditional treatment
Treatment with traditional medicine is used as an integral part of conservative therapy and is aimed at improving the removal of kidney stones, antibacterial and antispasmodic effects.
To do this, the patient is prescribed various herbal infusions, which can be prepared independently or purchased at a pharmacy.
| Folk remedy | Mode of application |
| Decoction of onions and sugar | For this you need to take 1 kg of onions and 500 g. Sahara. Mix the ingredients and boil for 2 hours, then strain the resulting broth through cheesecloth several times. After this, the broth should be divided into four equal parts. The first portion of the decoction is drunk on an empty stomach in the morning. The remaining portions are taken every 4 hours. This decoction can be drunk for up to 5 days. Contraindications for use are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and diabetes mellitus. |
| Rosehip root decoction | To prepare this remedy, you need to take 2 tablespoons of rose hip root (you can buy it at the pharmacy) and boil for 15 minutes. Then strain, cool and let it brew. Take this remedy 1/3 cup 3 times a day for 2-3 weeks. |
| Fresh lemon juice | You need to take 1 teaspoon of lemon juice 3 times a day. Contraindicated for patients with diseases of the digestive system. |
| Decoction of lingonberry leaves | To do this you need to take some lingonberry leaves. Boil them over medium heat for 15 minutes. After this, strain and cool. You need to take this decoction ½ cup 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 1-2 months. |
| "Watermelon Cleaning" | This “cleaning” can be done several times a month. To do this, you can eat watermelon in unlimited quantities, but at a strictly allotted time. For example, 3 o'clock in the evening. After this, the patient will experience forced diuresis (copious urination). This way the kidneys and urinary tract will be cleared of stones and their particles. |
Diagnosis of kidney stones in women
Diagnosis of kidney stones in women is carried out using ultrasound of the pelvic organs, kidneys and urinary tract.
Kidney stones and their symptoms in women require accurate diagnosis in order to accurately determine the type of formation by its chemical composition. Accurate identification of the type of stone makes it possible to select the correct therapy aimed at dissolving the stone and removing it from the body. So, the following methods are used for diagnosis:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs, kidneys and urinary tract.
- An X-ray examination, which, together with a general urine test, makes it possible to determine the type of stone by its chemical composition.
- In some cases, the doctor may order a CT or MRI.
In urology, the following types of stones in women are distinguished:
Recommended reading:
What to do if your kidneys are not working well: symptoms and diagnosis
- Oxalates (calcium stones). They are formed most often. The main reasons are high concentration of vitamin D in the body, drinking hard water, liver dysfunction and poor diet.
- Struvites (infectious and inflammatory stones). They tend to grow rapidly and manifest themselves already at critical sizes.
- Urates (acid stones). They are formed from insufficient drinking regime or due to serious violations of the water-salt balance.
- Cystine stones are formed when metabolic processes are disrupted, but are the rarest. They occupy only 2% in the segment of all possible renal calculi.
Important: residents of hot southern regions and patients diagnosed with gout are a special risk group for urolithiasis. Also, lovers of spicy and fatty foods may encounter urolithiasis.
Diagnostics
A nephrologist makes a diagnosis based on anamnesis, clinical picture of renal colic and data from laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Clinical examination. During renal colic, there are complaints of sharp pain on the side of the affected kidney. A positive symptom of concussion in the lumbar region is detected (pain when tapping the kidney). Deep palpation of the kidneys is performed with the patient in the lateral position, revealing an enlarged kidney. An examination of the woman's vagina is mandatory.
- Ultrasound . Ultrasound examination detects stones and their location, as well as the influence of pathology on the condition of the pyelocaliceal system.
- X-ray examination . With the help of urography, most of the stones, the condition of the kidneys and any existing changes are determined. To identify protein and urate stones, excretory urography (pictured) and pyelography (strictly according to indications) are performed.
- Morning and daily urine analysis . The main indicator of the disease is an increased level of red blood cells in urine. There is an increased content of protein, salt crystals, and the presence of bacteria.
- General blood analysis . May be normal. But with exacerbation of the disease, the level of leukocytes increases and the ESR increases.
Additional studies - CT, angiography are carried out to differentiate renal colic from an attack of appendicitis, peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis.
Kidney stones on excretory urogram
Insufficient physical activity in daily life
Modern man is accustomed to consuming several cups of coffee and tea a day. Due to the abundance of sugary carbonated drinks and juices on store shelves, the amount of clean water consumed is extremely small. Because of this, the urine becomes concentrated. The salts contained in urine crystallize and turn into stones.
By drinking enough water per day, harmful substances will be washed out of the body. This simple preventive measure will prevent the formation of stones and crystals. It is necessary to increase the daily volume of water consumed so that the person does not experience discomfort and does not harm other internal organs, for example, the heart.
A sedentary lifestyle is dangerous due to blood stagnation, which increases the risk of developing kidney stones. Poor blood circulation impairs the nutrition of tissues and internal organs. The musculoskeletal system also fails, causing calcium to begin to be washed out of the bones.
Because of this, its concentration in the blood and then in urine increases. Engaging in any active sports will significantly reduce the risk of developing the disease.
Treatment of kidney stones in women
Treatment of kidney stones in women is, in principle, no different from “male” therapy
- Treatment of kidney stones in women is, in principle, no different from “male” therapy. The doctor determines the tactics to combat the disease based on the type of stone, its size, the patient’s age, additional chronic diseases, etc. Most often, therapy is based on a balanced diet and plenty of fluids, which contribute to the dissolution of stones and their subsequent excretion along with urine. In addition, drug therapy can be used if a bacterial infection is mixed with the stones.
- For large stones, wave lithotripsy is prescribed (breaking/crushing/treating the stone using the effect of waves on formations in the kidneys). Works great if the diameter of the stone is no more than 2 cm.
- Laparoscopy and endoscopy are performed if crushing the stones does not bring results. Here the stones are removed through a small puncture in the lower back or by entering the urinary tract using a laser.
- Open surgery is indicated if the patient is at risk of a serious complication. This is the blockage of the urinary tract by a stone and, as a consequence, necrosis of the kidney. Or the ureter is blocked by a coral-shaped calculus.
Diet
Sticking to a diet for kidney stones is the main point of comprehensive treatment. The diet depends on the type of stone:
- If you have urates, eat dietary meat, boiled fish, and exclude sour berries and fruits, chocolate, salt, coffee, and legumes from the diet. The emphasis is on dairy and plant products.
- When dealing with oxalates, you should limit your consumption of foods containing ascorbic acid. The emphasis is on vegetable and butter, fatty cottage cheese, lard, apples
- If there is a risk of phosphate formation, dairy-containing and plant-based products and spices are excluded. The diet necessarily consists of lean meat and flour products.
The main requirement is to drink at least three liters of water every day. A healthy diet ensures the natural passage of stones through the urinary tract.
Types of kidney stones
The following types of stones are found, differing in their chemical composition:
- Oxalates are salts of oxalic acid. The stones are dark brown in color and have sharp edges and spines.
- Phosphates. They are formed by the crystallization of phosphoric acid salts, have a smooth or slightly rough surface, soft structure, and various shapes. Such crystals can quickly expand, filling the renal pelvis.
- Struvite - stones are gray in color, can be smooth, shapeless or form branches and sharp spines. They are the most dangerous because they grow very quickly, injuring the mucous membranes. Such formations are a combination of calcium and magnesium carbonates with ammonium phosphate.
- Urates are salts of uric acid. Smooth, hard, orange-colored stones may be present in any part of the urinary system.
- Carbonates. The composition of these loose, shapeless stones of grayish-white color includes carbonate salts of calcium and magnesium.
In addition to salt stones, there are also protein, cholesterol, amino acid (cystine) and xanthine stones (xanthine is one of the substances present in all tissues of the body).
- Bladder stones in men (causes of formation, symptoms, classification and treatment)
Video: Causes and signs of kidney stones
Dietary nutrition and prevention of urolithiasis
In order to soften the stones, the doctor may prescribe a special diet that will reduce the content of a certain type of salts that led to the formation of the stone.
In order to soften the stones, the doctor may prescribe a special diet that will reduce the content of the certain type of salts that led to the formation of the stone. And to prevent pathology, a woman must adhere to the following rules:
- Lead an active lifestyle (sports, movement, walking, etc.);
- Eat properly and balanced;
- Drink exclusively clean water (preferably filtered or bottled);
- Beware of hypothermia, especially in the autumn-winter period.
Therapy and surgery
The goal of conservative treatment is to remove pathological structures through the urinary canals and prevent the inflammatory process.
When diagnosing small stones, drinking plenty of fluids (up to three liters per day) and special medications that dissolve dense mineral formations are prescribed. The doctor creates a diet to prevent the secondary formation of stones.
Antibiotics are prescribed when concomitant infections of the genitourinary tract or kidneys are detected.
Surgical methods are advisable when standard therapy is ineffective or emergency measures are required to restore the outflow of urine and prevent necrosis of renal tissue.
Open surgery is performed only for health reasons (for example, when the ureter is blocked by a large coral stone). Endoscopy and laparoscopy are the most common medical techniques used in extraction.
Stones can be removed through a puncture in the lower back or through the urinary tract , depending on the structure and location of the formations.
Wave lithotripsy is a minimally invasive technique based on wave action on stones. It is used when the diameter of formations does not exceed 20 mm in diameter.
Drug therapy is suitable for patients whose stones are no more than 4 mm in diameter.
The treatment regimen used for urolithiasis is purely individual.
Methods are selected taking into account age, kidney condition , presence (absence) of chronic diseases and contraindications, size and structure of stones.
Do you know what the treatment for high progesterone in women is? We'll tell you!
Signs of chronic appendicitis in women are discussed in this article.
You can learn about the primary symptoms and signs of ovarian cancer in women from our publication.
Prevention
Even with proper treatment, the prognosis for women with urolithiasis can be unfavorable.
In general, if the stones increase in size and the removal surgery is carried out quickly, the results are positive, although there is a risk of relapse.
To prevent the re-development of stones, you need to follow the doctor’s recommendations and use preventive measures:
- Monitor your own weight and adjust it if necessary.
- Use proper nutrition as prescribed by the doctor.
- Carry out physical therapy and simply engage in activity.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Use folk remedies for prevention.
Knowing the characteristics of stones, treatment and prevention measures, each woman can exclude some of the causes of development.
When stones appear, you can quickly determine the pathology by symptoms, which will allow you to quickly begin treatment, eliminating complications.
Causes
Concretions (kidney stones) are solid formations that are located in different areas of the urinary organs; they differ in composition and size. Urolithiasis in women is associated with metabolic disorders. In a healthy body, salts are completely excreted in the urine. If the process goes wrong, substances stick together and accumulate. Stones during movement lead to severe pain and other unpleasant symptoms.
The causes of pathology in women include:
- lack of vitamins, ultraviolet radiation, hormonal imbalance;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- too hard water, dehydration;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the genitourinary system;
- course of gynecological diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- lack of physical activity.
Learn about the typical symptoms and treatments for urethritis in women.
How and how to reduce kidney pressure at home? Read the answer at this address.
Complications
Solid formations in a paired organ in women can cause global changes that cannot be restored. The disease can cause complications, including:
- Pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the kidney tissues, which can be complicated by purulent formation and significantly complicates a woman’s life.
- Hydronephrosis - due to solid particles, it is possible to block the ducts and disrupt the outflow of urine.
- Urosepsis is a pathology that, without treatment, causes fatal consequences.
- Failure of a paired organ.
- Pathologies of the cardiovascular system, which can subsequently lead to stroke.
In addition to the described consequences, women experience many unpleasant sensations that prevent them from living normally.
The formation of stones will be most dangerous for patients who already have a kidney transplant or serious disruptions in the immune system.
Kidney stones - symptoms in women
The severity of symptoms depends on the size, configuration and number of stones that are present in the kidneys. But there are common signs that can be observed with kidney stones.
Pain in the lumbar region
They can appear in individual areas or involve the entire lumbar region. They are dull in nature: the larger the stone, the more strongly the woman feels them.
A characteristic feature of pain in urolithiasis is that it intensifies with physical activity or a change in body position in space.
Pain in neighboring organs
Such pain occurs when a kidney stone passes into the ureter. Pain then appears in the lower abdomen. It occurs due to the fact that the stone damages the walls of the urinary tract along its path.
Renal colic
These are severe cramping pains that most often occur in the lumbar region. During the day they can intensify, and then subside and return again with great force.
The duration of such attacks is usually several hours. And after they are over, sand or small stones may appear in the urine.
Frequent urination
This is one of the most common symptoms of kidney stones in women. Most often the urge is causeless and very strong.
Painful sensations when urinating
This symptom also indicates that the stone has left the kidney and is located in the bladder or ureter. In addition to pain, you may experience a burning sensation or even severe itching.
Cloudy urine
This is due to the fact that the urine contains a large number of excess elements: red blood cells, mucous secretions, epithelial cells, mineral salts, leukocytes. In the presence of kidney stones, such urine usually appears at the beginning of urination.
Fever, high blood pressure and rapid heartbeat
Body temperature ranges from 38 to 39 degrees. Many of the previously described symptoms are accompanied by an increase in body temperature. And an increase in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate are associated with a disruption in the production of hormones in the kidneys, which are responsible for these indicators.
Urinary retention
This is a very serious symptom that indicates that a stone has blocked the urinary tract; this condition is called uremia.
Prolonged urinary retention can be fatal due to severe intoxication of the body.
Uremia may be accompanied by headache, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, skin rashes, cramps, and severe pain in the lower abdomen. It can also lead to the development of coma.
Radical procedures to get rid of stones
Surgical treatment is indicated when the size of the stones is too large and they are unable to leave the woman’s body on their own. This is also practiced after unsuccessful conservative therapy or when any complications develop. In this case, use one of the methods:
- shock wave lithotripsy. It involves the use of ultrasound, with the help of which stones break up into small fragments. They are able to freely leave the urinary system, which leads to complete recovery. This procedure is used if the size of the stones does not exceed 2 cm. To obtain the desired effect, you need to conduct 1-2 ultrasound sessions;
- normal open surgery. The stones are removed surgically, which is very traumatic, but effective;
- endoscopic surgery. Special equipment is inserted into small incisions in the skin to remove the stone from the kidney. This method is less traumatic than conventional surgery, so it is used more often.