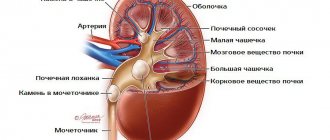
Coral kidney stones are a fairly common disease in modern urology. Inappropriate treatment can cause dangerous complications. Prompt diagnosis and proper treatment guarantee a positive outcome for patients. Directly for this reason, it is so important to notice the signs of the disease in a timely manner and immediately consult a doctor.
First, you need to understand what exactly this pathology is and what to do with it. Coral stone is a mineral with a special appearance and structure. This type of neoplasm looks like a piece of coral or a deer antler.
Features and symptoms
The course of the disease occurs latently when coral stones in the kidneys just begin to form. Patients' complaints are predominantly of a general nature, including severe fatigue, malaise, frequent migraines, a feeling of dry mouth, and less often chills. At a later stage, during which the stones grow rapidly, severe pain in the lumbar region and impaired thermoregulation of the body are noted. Manifestations characteristic of pyelonephritis and renal failure are observed.
Initial symptoms signaling the formation of coral kidney stones:
- Pain in the lower back;
- Difficulty urinating;
- Urine mixed with blood;
- Anuria;
- Discomfort during active movement;
- Fever and chills.
Prognosis, consequences and prevention
The prognosis for the presence of stones of this type is favorable, but if the stone reaches a significant size, the risk of dangerous consequences increases, including loss of the kidney. The most common complications:
- addition of infection;
- exacerbation of cystitis and pyelonephritis;
- acute urinary retention;
- blockage of the urinary duct by a stone fragment.
To avoid complications, the following preventive rules should be followed:
- Once a year, undergo an ultrasound of the kidneys and donate urine for a general analysis.
- Eat right, avoiding overly salty and spicy foods.
- Drink enough clean water of low hardness.
- To live an active lifestyle.
If you have constant nagging back pain and urinary problems, it is recommended to consult a urologist.
Causes
There are many reasons for the formation of this pathology. There is no clear explanation for the appearance of coral stones in the kidneys, so there are some difficulties associated with treating the disease. Stones are formed due to disruption of physical and chemical processes in the human body. The patient cannot always recognize the disease and contact a medical facility in a timely manner. Risk factors include:
- Congenital and acquired renal diseases;
- The presence of vascular pathologies;
- Infectious diseases, especially damage to the urinary system;
- Bone fractures requiring prolonged bed rest;
- High content of salts and proteins in the urine, as they are the main component in the formation of stones;
- The climate is predominantly hot, as well as the general regional ecology.
If the patient spends little time in the fresh air and leads a sedentary lifestyle, then metabolic processes decrease and coral stones form.
Treatment with folk remedies
You can get rid of kidney stones at home, the main thing is to know what you need to drink. We offer several effective folk remedies that will help dissolve stones and remove them naturally.
Important! Treatment at home should begin only after undergoing an ultrasound and passing all the necessary tests. If the stones are very large, it is important to consult with a doctor and be observed by him during treatment, it is also important to understand that there are different compositions of stones. Under no circumstances should you resort to this method in the presence of calcium oxalates; this is fraught with dire consequences.
Onions and sugar
A good tool for crushing stones is onion. For treatment you will need only 1 kg of onion and 500 g of sugar. The course lasts a day, but the effect is incredible, you can even get rid of large stones (up to 2 cm) in the kidneys.
For treatment, you need to prepare a decoction of onions. You need to prepare it as follows: pass the onion through a meat grinder, add sugar to it and cook for two hours. You will get about 500 ml of decoction. You need to drink it 15 minutes before meals 4 times a day at regular intervals. Don't drink.
Also in the treatment of stones, herbs such as parsley, bearberry, sunflower roots, birch, cornflower flowers, horsetail and others give good results.
We will present recipes with some of these herbs below.
Before moving on to treatment for kidney stones, you need to cleanse the body of toxins. For this purpose, decoctions of dandelion roots or blackhead herb are used. Brew one teaspoon of herb in a glass of boiling water. After completing the cleansing course, they proceed directly to crushing the stones.
sunflower root
Sunflower root is suitable for crushing stones at home. A decoction of sunflower roots will help dissolve kidney and liver stones that were previously resistant to treatment, and all thanks to the healing properties of sunflower root.
Sunflower root is used to remove salts from the body and destroy insoluble compounds, which are stones.
Important! Sunflower root will not be effective in the presence of phosphate stones; a stone analysis must be done before treatment.
Let's look at some recipes with this plant.
To prepare a medicinal decoction of sunflower roots, you need to take one root of this plant, chop it and add three liters of water. Boil for about 10 minutes. You need to drink the entire decoction within three days. You can drink it instead of water. The course of treatment with a decoction of sunflower roots is one month.
There are many positive reviews about the healing effects of sunflower root. After a month of treatment, all patients’ tests return to normal.
Herbs that drive away stones
If, in addition to stones, the patient’s tests reveal a large number of leukocytes, which indicates an inflammatory process in the kidneys, then the following collection will help to recover. Take lingonberry, bearberry and horsetail leaves in equal proportions (you should get 1.5 teaspoons) and pour 300 g of boiling water. Infuse the decoction in a thermos for 2 hours. Drink 100 g half an hour before meals. The course of treatment is a month.
Important! These herbs have a diuretic effect, i.e. They simply drive out the stones, without crushing them. Therefore, this method is applicable only for small stones up to 0.8 cm.
Knotweed has a diuretic effect. This herb will help remove small stones and sand. After completing the course of treatment, your urine test will be normal. To prepare a decoction, you need to take two teaspoons of this herb and pour half a liter of boiling water. Leave for 4 hours. Drink 100 g with meals.
Pumpkin seeds and cranberries are also good for removing stones. Pumpkin seeds should be eaten raw, then they will produce the desired effect. But you can drink cranberries in the form of compote, jelly or fruit drink with the addition of honey.
Oats have not only a choleretic, but also a diuretic effect. To prepare the decoction, just take a glass of oats and 4 glasses of water. Steam and consume 100 g of decoction before meals.
Classification of coral stones
Depending on how many years or months the disease resides and develops in the human body, it is customary to distinguish the following stages of coral nephrolithiasis:
- First. There are no characteristic signs of nephrolithiasis; the patient complains of general symptoms: weakness, chills, and the oral mucosa often dry out. At the first stage, the coral-shaped formation is located in the pelvis and calyx;
- Second. The pathology develops, the stones increase in size, the color of the urine changes, and the lumbar pain intensifies. Coral-shaped stones occupy the extrarenal pelvis; during diagnosis, doctors identify processes of this type;
- Third. Symptoms of the disease are very pronounced, high temperature, urine mixed with blood, pain worsens, and insomnia develops. Many patients notice small stones that are in the urine. Doctors note that the lack of treatment leads to disruption of the bean-shaped organs;
- Fourth. Urine excretion is complicated, signs of the disease intensify, a coral-shaped formation occupies most of the kidney, and deformation of the pelvicaliceal system occurs. If the patient is weak, has low immunity, or has chronic diseases, the load on problem organs increases, and end-stage kidney disease may develop.
Doctors distinguish advanced forms of the disease, that is, complete disruption of the kidneys, where chronic renal failure has passed into the final, thermal stage.
General characteristics of stones
Coral kidney stones are hard formations in a paired organ, which are characterized by large sizes.
Treatment of the complication is amenable to various treatment methods, but conservative methods rarely produce positive results.
Their removal is carried out using crushing methods, and if the sizes are quite large, then surgical removal methods must be used.
Coral stones in the kidney do not develop immediately; doctors identify several main stages in the development of the problem.
The localization of solid particles, the patient’s symptoms, as well as the growth rate depend on a certain stage:
- At the beginning of development, at stage 1, the solid part in the paired organ will be small in size, localized in the pelvis, as well as one of the calyces of the kidney.
- As the disease progresses to stage 2, the stone moves to the extrarenal pelvis. The shoots of the calculus may be in several cups.
- Stage 3 is characterized by localization of the stone on the intrarenal pelvis, and parts of the formation spread to all calyces.
- The last stage is considered the most difficult for humans, since the solid particle becomes very large and can fill the entire volume of the kidney, which causes gradual deformation of the organ, significantly impaired functions, and mechanical damage to the walls. This phase of the disease is treated surgically, and the stone is removed along with the organ.
The main danger of complications of urolithiasis is that people may not be aware of the development of coral stones, since during the first 2 stages there are no symptoms or they are almost invisible.
The risk group includes patients aged 30-50 years, since it is they who are most often diagnosed with staghorn stone.
Comparing men and women, the latter develop education 3 times more often. In medicine, this disease is called coral nephrolithiasis. Without proper treatment, the problem causes failure of the paired organ, constant inflammation and kidney failure.
Diagnostics
With this pathology, it is very important to detect a coral stone in the kidney in time, so that you know what to do in the early stages. According to statistics, most often stones in the initial stages of development are diagnosed by chance. Among the most informative methods for diagnosing the disease are: ultrasound examination and x-ray - a specialist can confirm the presence of mineral formations, determine their location and size.
Patients undergo blood tests and urine tests. Laboratory tests will show an increased ESR, an increased number of white blood cells, the presence of purulent discharge and blood in the urine.
Therapy of coral nephrolithiasis is a complex process. The earlier it is started, the greater the chances of recovery and preventing the development of renal failure and chronic pyelonephritis.
Coral stones can be removed from the kidney in several ways: therapeutic treatment, surgery, lithotripsy.
In the presence of stones consisting of uric acid salts, treatment is carried out with medications that can dissolve corals in the kidneys. This therapy is effective only for these tumors; with a different composition, surgery is performed to remove them.
It is impossible to cure coral stone with folk remedies, but you can stabilize kidney function and improve immunity. Medicines must be natural, based on herbal ingredients.
Only a doctor can select a specific regimen for the treatment and removal of coral stones, especially since conservative therapy is not indicated for all patients. The main method of therapy will depend on the structure of the stones, size and stage of the process.
Several years ago, the removal of staghorn stones was carried out only by dissecting the abdominal cavity. Directly through such large incisions, renal coral stones were removed, which were previously crushed into pieces. Sometimes there were cases of removal of the entire kidney.
The operation to remove a coral stone from the right or left kidney is performed through laparoscopic access. At this stage, the surgeon removes the stone and cleans the pelvis of its particles. It is possible to perform another type of intervention - removing stones with a fiberscope through a small puncture. Excellent results are obtained by crushing stones with a phosphate or mixed composition.
Symptomatic treatment is also important. At high temperatures, patients are prescribed antipyretic drugs, and taking painkillers helps the patient get rid of pain.
Removing staghorn kidney stones is not everything. The patient needs to carefully monitor his diet if he has coral stones, and follow a diet because the functioning of the excretory system largely depends on this. The patient is recommended to completely remove semi-finished products from the diet, as well as fermented milk products. During the diet for coral kidney stones, patients should avoid eating salt. It is best to create a menu for each week.
In addition, to prevent the formation of coral stones, it is recommended to drink at least two liters of fluid per day, if there is no tendency to develop edema.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Coral conglomerates can be identified using ultrasound and radiography. They make it possible to describe with a high degree of accuracy the size and contours of the kidney, determine the size of the stone, and assess the degree of deformation of the organ’s pyelocaliceal system.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qzbuJIsCc9o
Invasive methods for examining the urinary system include cystoscopy. Using an optical instrument inserted through the urethra, the doctor assesses the condition of the bladder.
To obtain additional data on kidney function, the patient undergoes tests:
- Blood analysis. With exacerbation of pyelonephritis or renal colic caused by coral stones, an increase in leukocytes and ESR, the presence of large granules of neutrophils, or “toxic granularity,” are observed.
- Analysis of urine. During inflammation, an increase in red blood cells and salts is observed, and admixtures of pus (pyuria), blood (hematuria), proteins (albumin, glycoprotein, transferrin, IgG, and in rare cases - IgA and 2 - macroglobulin) are detected. This indicates the development of tubular (tubular) proteinuria, damage to the glomerular apparatus, or glomerulopathy.
To exclude the development of a bacterial infection, urine culture is performed. It is used to determine the presence of bacteria and study the effect of antibiotics on the infectious focus.
- The first phase of the disease occurs with virtually no renal symptoms. Common patient complaints at this time: chronic fatigue syndrome, dry oral mucosa. Sometimes a headache comes along.
- At the second stage of the disease, these same symptoms become more pronounced, but also do not signal a pathological process in the kidneys. Associated pain in the lumbar region of an aching nature is often mistaken by patients for neurological manifestations of incipient radiculitis.
- The third stage is characterized by pronounced symptoms. Thus, pain in the kidney area becomes quite severe and incessant. Body temperature becomes elevated. Colic in the kidneys may occur, as well as signs of developing renal failure.
- The last stage of the disease is accompanied by dysuria, severe intoxication of the body, and symptoms of renal failure against the background of pyelonephritis.
To identify a coral stone in the kidneys, the doctor prescribes an examination, including general urine and blood tests, radioisotope and ultrasound examinations.
Most often, patients seek help from a doctor at the very last, fourth, stage of the pathology, when only removal of the kidney can radically help. Early consultation with a doctor will help avoid surgical intervention.
Frequent reasons for the discovery of coral stones in the kidneys in patients are random ultrasound examinations prescribed to detect extraneous diseases.
Diagnosis includes: collecting the patient’s medical history, examining the clinical picture, and ordering laboratory tests.
Changes in kidney function are necessarily accompanied by impaired carbohydrate metabolism and cause an increase in insulin in the bloodstream.
Various kidney diseases may have similar symptoms with the appearance of staghorn stones. It is necessary to differentiate them from the following violations:
- chronic pyelonephritis
- urolithiasis
- polycystic kidney disease
- kidney tumors
In a laboratory test, a blood test is prescribed to help identify an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, an increase in the level of white blood cells, and the appearance of white blood cells in the urine.
As well as bacterioscopic examination, general urine analysis, blood test for the presence of ionized calcium.
The most effective diagnostic method is ultrasound. In 100% of cases, the study will help confirm or refute the clinical diagnosis. Using ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible not only to detect the formation of stones, but also to examine in detail their size and location. In addition, this will allow us to study the degree of change in the parenchyma of the organ.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y0JKjv7EQzc
In addition to ultrasound diagnostics, radiography is used to determine the shape and size of the formation.
One of the methods used in modern diagnostics is renal angiography. Using this method, the location of the artery in the kidney and its origin from the aorta, as well as the diameter and number of branches, are determined.
Coral kidney stones are detected through ultrasound and radiography. These methods show the size and configuration of the organ with extreme accuracy and allow one to estimate the size of the stone and the degree of deformation of the kidney calyces.
An invasive diagnostic method is cystoscopy. Using an endoscope, which is inserted through the urethra, a specialist can assess the condition of the bladder.
Additional information about the functioning of the kidneys is obtained through laboratory tests - blood and urine tests. To exclude the development of a microbial infection, a urine culture is performed, which helps determine the presence of bacteria, as well as the effect of antimicrobial drugs on the site of infection.
Prevention
An important factor in preventing the development of the disease is preventive measures. First of all, they should be aimed at properly balancing metabolic processes in the patient’s body. For this use:
- Phototherapy;
- Herbal Treatment;
- Water therapy;
- Proper nutrition;
- Physical activity, special exercises.
The following foods should be avoided: fresh milk, alcoholic beverages, coffee, nuts, black currants.
source: moi-pochki.ru
Nephrolithiasis is a chronic disease caused by pathological metabolic processes, prone to relapses and the formation of stones in the human urinary system.
Urolithiasis, like many others, has various forms of severity, the most complicated of which is such a neoplasm as coral kidney stones.
Diet
Proper nutrition and following the doctor’s recommendations are a necessary condition for successful therapy for coral stones. The diet includes restrictions on the following foods:
- fermented milk products, including all their derivatives,
- fruits and vegetables,
- carbonated drinks,
- spices and seasonings,
- alcohol,
- coffee.
You should also minimize your salt intake.
List of permitted products:
- bread,
- pasta,
- meat and fish,
- oil, both vegetable and butter,
- all types of soups,
- sour juices, compotes and fruit drinks.
What it is?
Coraloid (coral) calculus is a pathological formation that can reach the size of the renal pelvis and occupy almost all of its space.
In medical practice, such cases are quite rare and account for about 5% of the total number of patients with urolithiasis , but they almost always require surgical intervention rather than conservative treatment.
These formations in the kidneys are usually classified as struvite or infectious types of stones, which are characterized by rapid development compared to other types of formations and fill most of the patient’s kidney.
The process of development of coral nephrolithiasis in some cases can take only a few weeks and is characterized in medical practice by several stages :
- At the first stage of the disease, the calculus reaches a small size and may be located in the pelvis and one calyx;
- The second stage involves an increase in the size of the stone and its further spread into the area of the extrarenal pelvis with the presence of processes in several cups at once;
- As the formation increases, the calculus occupies the entire space of the renal pelvis, and its processes are located in all calyces;
- The final stage causes deformation of the entire pelvicaliceal system due to its filling with calculus.
What is a coral kidney stone and how to treat such a phenomenon?
Coral kidney stone is one of the serious urological diseases. This disease is an independent pathological process, the development and course of which differs from other forms of urolithiasis. Coral kidney stones (or coral nephrolithiasis) are characterized by the appearance of specific neoplasms in the organs of the human urinary system, which in their structure resemble coral.
Basically, the development of such a pathological process as coral nephrolithiasis is observed in those people whose age is 20-50 years. In addition, the disease most often affects women.
Coral kidney stones are the largest stones (clusters of stones of a dense structure that can form in the excretory ducts of the glands and cavitary organs of a person) of all such neoplasms observed in people with urolithiasis. Stones that appear during the development of carpal nephrolithiasis can reach quite large sizes, which are comparable to the kidney affected by the pathological process, that is, about 8 cm. In most cases, such neoplasms are localized in the renal pelvis.
The appearance of coral stones in the internal organs of the human urinary system indicates the occurrence of serious pathological processes in the kidneys, which in turn leads to disruption of the normal excretion of urine from the body. The occurrence of such deviations is mainly associated with the presence of a bacterial infectious disease in a person that affects the kidneys.
How is the presence of stones manifested?
This disease is more common in women between 30 and 50 years of age and is more than three times greater than the number of men with this problem.
The greatest danger of this disease is that patients often do not experience any discomfort in the first two stages of the development of coral nephrolithiasis, which subsequently determines the treatment of the disease already at serious stages of its development and sometimes requires complete removal of the affected kidney.
In most cases, the development of such a pathology always begins under the influence of an infection on the body , as a result of which the outflow of urine is disrupted and, as a result, a chronic inflammatory process develops, leading to inhibition of the renal parenchyma, and then the kidney itself.
Read our article about what kidney parenchyma is.
Experts recommend taking a responsible attitude towards any signs of discomfort in the lumbar region, especially if they come with fever and chills, fatigue and chronic fatigue, dry mouth and headaches, as well as some changes in urination.
Depending on the stage of development of the disease and the position of the stone in the patient, the following characteristic symptoms :
- At the first stage, the patient may only feel general malaise and fatigue, which may be accompanied by headache, thirst and chills;
- Later, as the disease develops, cramping pain appears in the back or on the side under the ribs, spreading as the disease progresses to the groin area and inner thigh;
- The third stage is accompanied by an even more intense pain syndrome, with an increase in temperature to 38 degrees, the presence of blood in the patient’s urine and a general disturbance of the outflow of urine;
- The final stage retains the current symptoms, which are accompanied by a general disturbance of the outflow of urine, vomiting and nausea, which indicate the manifestation of pyelonephritis.
Advanced forms of the disease are characterized by complete disruption of the kidneys, where chronic renal failure has progressed to the final, thermal stage.
Symptoms
Until the size of the stones reaches a critical size, the patient does not feel discomfort. Most patients are admitted to the hospital with renal colic, which indicates urolithiasis. In addition, a considerable number of people simply prefer not to pay attention to what they consider to be minor symptoms:
- frequent urge to urinate, while the process of urination itself causes difficulty;
- blood appears in the urine;
- pain in the lumbar region, spreading to the genitals, groin and side.
Formation of coral stones due to calcium metabolism disorders
Coral formations appear nonspecifically in patients. The vast majority of patients consult a doctor with complaints of discomfort (dull pain) in the lower back, increased body temperature and impaired urine flow. In this case, you feel dry mouth, weakness, the skin acquires a yellowish tint, and itching appears.
Based on the information received from the patient and the clinical picture studied, the doctor diagnoses one of four stages of the pathology:
- latent current;
- First stage;
- clinical symptoms;
- hyperazotemic stage, when nitrogenous products of protein metabolism are found in the patient’s blood.
The first stage is characterized by the absence of symptoms of urolithiasis. There is only a general malaise, which is manifested by fatigue, headaches, dry mouth and chills.
Localization of pain when renal colic occurs
At the second stage, the active development of the disease begins, accompanied by pain in the lumbar region and a slight change in the color of urine.
At the third stage, the symptoms become clearer, lower back pain intensifies, the temperature rises within 37-38 degrees, and the patient’s general condition worsens. Blood appears in the urine and small stones are passed out. Renal colic may occur, and symptoms of renal failure may appear.
At the last stage, all symptoms become more intense, the process of urination becomes difficult, and pyelonephritis worsens. Also, chronic renal failure enters the terminal stage when kidney function is completely impaired.
To prevent staghorn stones from growing to large sizes, nephrologists recommend undergoing an ultrasound examination of the kidneys even with a slight deterioration in health.
Causes of pathology
It is impossible to identify a clear cause of coral nephrolithiasis, since this pathology is largely due to a combination of several factors :
- Violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism due to physical inactivity (sedentary lifestyle);
- A sharp increase in salts and protein in the patient’s urine, which are the basis for the formation of coral stones;
- Predisposition of the body to the occurrence of urolithiasis;
- Infections of the urinary system, kidneys and vascular disorders;
- Nutritional factors - poor nutrition, lack of vitamins A and D in the diet, poor water;
- Living in a climate that is too hot.
Causes
This serious disease, for the most part, occurs with progressive disorders of urodynamics and blood circulation in the kidney area, as well as with various types of metabolic pathologies. Often, coral stones form in people with congenital kidney diseases and abnormalities of their structure, with tubulopathies (impaired movement of electrolytes and other substances through the renal tubules). Hereditary transmission of this type of nephrolithiasis is observed in 20% of cases.
There are a number of risk factors that contribute to the development of the disease:
- Dramatic climate change;
- Consumption of poor quality water and food;
- Bad ecology;
- Liver and gastrointestinal diseases;
- Hyperthyroidism, parahyperthyroidism;
- Prolonged bed rest;
- Increased amount of salts in urine;
- Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
Sometimes staghorn stones appear in pregnant women, which is believed to be due to hormonal shifts. Many cases of coral nephrolithiasis remain unclear as to the causes of their occurrence.
Coral stones appear on a “matrix,” or framework of protein deposits. Then mineral salts are layered onto the frame, the calculus grows in size and occupies the entire renal pelvis system (without treatment).
Diagnostic and treatment methods
Diagnosis of the presence of coral stones in a patient does not differ in structure from examinations to identify other forms of stones.
The initial stage of diagnosis involves an appointment and consultation with a urologist, whose main task is to assess the patient’s condition during anamnesis, an initial examination and prescribe a basic examination, which consists of:
- A general analysis of the patient’s blood and urine, which allows us to identify any changes and the presence of an inflammatory process within the body;
- Ultrasound examination of the urinary system, which will be relevant at the entire stage of the patient’s treatment, as it allows you to monitor any changes in the course of the disease (see photo of stones on ultrasound);
- Survey and excretory urography, which allows you to establish the presence of stones in the kidneys.
- Computed tomography, which allows you to most fully assess the position of the stones, their size, analyze their density and the condition of the surrounding tissues;
- Carrying out nephroscintigraphy to determine the degree of kidney damage;
- Urine culture, which will reveal the presence of infection in the urinary tract and the general level of inflammation.
Further examination may include:
Based on such examinations, an individual treatment plan for each patient, which is based on one of several methods, namely:
- Drug treatment aimed at gradually dissolving the stone and its subsequent passage through the urinary tract. It is most effective in the early stages of the disease, when the stones have a loose structure and small shape.
- External shock wave lithotripsy.
It involves crushing the formation of any localization with shock waves, without injuring adjacent tissues of the body and destroying the calculus into small fragments, which are then independently excreted along with urine. The success rate of this method is up to 90%.
Its essence lies in the fact that the attending physician makes a puncture in the lumbar region, after which he inserts a nephroscope into the patient’s kidney and destroys the stone using a laser or ultrasound lithotripter into small fragments. Their extraction occurs thanks to the use of plastic fiberscopes even from the most inaccessible areas.
The use of traditional medicine is permissible and advisable only during remission of the disease, but in no case as the main treatment.
It has been proven that a variety of herbs can reduce pain and promote accelerated removal of sand or stone fragments.
However, it is necessary to use folk remedies only after consultation with your doctor - such remedies can dissolve stones, they can begin to move, which threatens the presence of some complications in the form of blockage of the ureter and hydronephrosis of the kidney.
Treatment
In modern medicine, three methods are used to treat coral kidney stones:
- therapeutic treatment;
- surgery;
- lithotripsy (crushing stones).
Conservative (therapeutic) treatment
The only stones that can be dissolved with medications are those formed from uric acid salts. A course of therapy for two or three months will allow you to forget about the problem of coral stones forever. If the chemical composition of the stones is different, different treatment is necessary.
Comparative characteristics of drugs to reduce the formation of uric acid and enhance its excretion
Conservative treatment involves taking the following medications:
- which prevent the formation of new stones;
- which reduce the amount of uric acid in the body;
- B vitamins to normalize urine acidity;
- which reduce the level of calcium in the urine.
The course of therapy is prescribed individually for each patient. Self-administration of medications, as a rule, is not effective, and can also provoke the development of irreversible processes in the kidney.
Surgery
In a situation where staghorn stones are diagnosed, surgery is considered the most effective and successful treatment method. During the operation, the doctor completely clears the upper urinary tract and renal pelvis of formations. Thus, the source of infection is removed from the body, which guarantees the patient’s recovery.
Removing kidney stones with laser
Previously, such operations were carried out as follows: coral stones were first crushed, then small parts of the stones were removed through the abdominal cavity. In some cases, the entire kidney needed to be removed.
Today, medicine has a large amount of modern equipment that allows you to remove coral stones without open surgery. The least traumatic method is a minimally invasive technique, due to which one puncture with a diameter of no more than one centimeter is required to remove the stone. First, the stones are crushed. Then a puncture is made in the lumbar region, special medical equipment is inserted into it - a fiberscope - and small parts of the stones are removed.
Stone removal using a lithotripter
The method of crushing coral stones in each clinical case is individual, it can be:
- laser exposure;
- exposure to ultrasound;
- using a special device - a lithotripter.
The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the qualifications of the specialist and the equipment used for manipulation. After the stones are removed, the patient is under medical supervision for five years.
Diet recommendations
When treating coral stones, the attending physician always prescribes a diet to patients in combination with other therapeutic methods of treatment.
Dietary nutrition for pathologies of the urinary system is not only a powerful tool in the fight against the disease, but also an effective method of prevention , which allows you to prevent further relapses and complications.
The main goal of such a diet is to reduce calcium levels in the patient's body. The diet should include such products as:
An important aspect is also compliance with water load . It is advisable for patients to drink at least two liters of water per day.
It is necessary to exclude all foods that contribute to the formation of gastric juice, for example, all spicy, salty and spicy foods, coffee and carbonated drinks, as well as foods high in calcium - all fermented milk products, most vegetables and fruits.
Meals should be fractional, up to 4-5 times a day , in small portions, where the patient himself creates a nutrition menu based on acceptable foods.
It will also be important to combine such a diet with procedures aimed at the general restoration of metabolic processes, for example, special physical exercises and water treatments.
As for folk remedies, for such a disease it is necessary to take decoctions of bean inflorescences and juice from pumpkin pulp .
Methods of drug therapy
In order to reduce the formation of uric acid in the kidneys, patients are prescribed medications that speed up the cleansing of uric acid from the body. Among other drugs, medications are prescribed to maintain the acid-base balance in urine.
When calcium oxalate crystals are excreted in the urine, I prescribe Pyrodoxin. To maintain normal calcium in the blood, the diet is enriched with dried fruits: raisins and dried apricots, as well as baked potatoes.
Sample menu for the day
Breakfast: carrot or pumpkin juice, unsweetened oatmeal with raisins, dried apricots and butter.
Lunch: full-fat cottage cheese, juices and fruit drinks.
Lunch: soups of any kind, whole grain bread, dried fruit compote.
Afternoon snack: vegetable salad with vegetable oil.
Dinner: boiled fish and meat, cabbage salad, berry juice or jelly.
If you seek help in a timely manner and strictly follow all treatment instructions and recommendations, the prognosis and further recovery of patients with coral stones are quite positive.
Find out what new methods are now used to get rid of stones from the video:
source: opochke.com
Coral kidney stones are one of the most severe manifestations of urolithiasis. According to statistics, pathology occurs in 5% of all cases. Women aged 20–50 years are mainly affected.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of coral stones involves an integrated approach. In the presence of small stones, conservative therapy is used. It is important to adhere to a special diet. Traditional medicine recipes are used as an additional treatment method. If the stones reach a significant size, then mandatory surgical intervention is indicated.
Surgical removal
Currently, open operations are practically not performed. They have been replaced by more modern techniques that allow you to quickly and safely get rid of stones. Depending on the size of the stone, laser or ultrasound techniques are used. First of all, access to the kidney is made through the urethra using a special flexible device that resembles a thin tube. The concrement is crushed into small pieces. A urethroscope allows you to do this quite quickly. In this case, laser or ultrasonic waves are applied. It all depends on the technique the doctor chooses.
A urethroscope is a flexible optical device with which you can examine the condition of the urinary tract and perform a number of manipulations
After this, a small puncture is made in the lumbar area, through which a fiberscope is inserted into the kidney, thanks to which the stones crushed into fragments are removed. Recovery occurs in a short time, however, provided that the stone does not lead to severe stretching of the pelvis.
After surgery, the patient may feel pain when urinating. This is due to the release of smaller fragments of stones through the urethra.
Conservative methods
Groups of drugs that are used in the presence of coral stones:
- Medicines that help dissolve stones: Allopurinol, Blemaren. These medications reduce the amount of uric acid and promote the destruction of already formed stones.
- Anti-inflammatory: Canephron, Phytolysin, Cyston, etc. They relieve painful symptoms and also improve kidney function, increasing daily diuresis. Relieves inflammation and prevents the formation of stones.
- Drugs that normalize the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus: Xidifon, etc. The products in this line are necessary to prevent the progression of the disease and eliminate its main cause.
Drug treatment is carried out for 3 months. The amount of the drug and the exact course are determined by the doctor depending on the diagnostic results and clinical picture.
Drugs that are used to get rid of staghorn stones - photo gallery
Canephron has an anti-inflammatory effect
Phytolysin improves the functional state of the kidneys
Cyston helps reduce inflammation and relieve pain
Allopurinol is a drug that interferes with the synthesis of uric acid.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of treatment can stop the growth of coral formations and improve the functioning of the kidneys, but they cannot get rid of large stones. The most effective recipes:
- Anti-inflammatory decoction. You will need oregano in combination with sage. Both ingredients need to be mixed. 1 tbsp. l. raw materials should be poured with 400 ml of boiling water and cooked for 10 minutes. Then cool, filter and take 150 ml 3 times a day half an hour before meals for 14 days.
- Infusion to improve kidney function. You will need lemon balm, knotweed and St. John's wort in equal quantities. 2 tbsp. l. the mixture of raw materials must be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and left for 40 minutes. Then filter and take 200 ml 3 times a day 20 minutes before meals for 10 days for two weeks.
- Diuretic decoction. You will need 2 tbsp. l. dry rose hips, which need to be poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water and put on fire. Cook for 10 minutes. Then let it brew for two hours, filter and take a glass 3 times a day for a week, half an hour before meals.
A new decoction or infusion must be prepared every day. You should not take yesterday's remedy, as herbs tend to quickly become moldy.
Ingredients for preparing decoctions and infusions - photo gallery
Oregano has a mild diuretic effect
Sage reduces the severity of the inflammatory process
Melissa improves immunity. Knotweed improves kidney condition and has a diuretic effect.
St. John's wort has a general strengthening effect
Rosehip accelerates urine output, increasing diuresis
Diet for coral stones
With staghorn kidney stones, diet plays an important role. It is important to exclude from the menu:
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- semi-finished products;
- fast food;
- hot spices;
- soy;
- beans;
- salty dishes;
- black currant;
- milk.
Preference should be given to:
- grapes;
- kefir and yogurt;
- cottage cheese and sour cream;
- sauerkraut;
- fish;
- watermelons;
- lean meat;
- pumpkin
It is important to maintain a drinking regime. If you have coral stones, it is recommended to drink up to 2 liters of clean water per day. You can also drink juices, green tea, rosehip decoction.
Food should be cooked mainly by steaming with a minimum amount of salt. Frying and baking with oil should be avoided. It is not recommended to eat foods that are too cold or hot. Food should be warm. You should eat at least 5 times a day in small portions.
What to eat if you have coral stones - photo gallery
Kefir and yogurt should be consumed with an average fat content of 3%
Cottage cheese and sour cream can be consumed with dried fruits
Sauerkraut has a beneficial effect on the kidneys
Steamed fish is best combined with vegetables
Watermelon has a strong diuretic effect
Boiled chicken is best for urolithiasis
You can bake pumpkin or make soup from it.
It is better to replace chocolate with dried fruits
Vegetable oil should be used instead of butter
Grapes can be consumed of any variety
Pasta should be consumed without spicy sauces
Reasons for formation
Various factors can trigger the development of staghorn stones. In modern medicine, it is customary to identify several main reasons:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Increased content of protein and salts in the urine.
- Violation of phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the body.
- Infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Cardiovascular diseases.
Coral stone is formed according to the matrix theory. First, a “framework” of protein compounds (bacteria, blood cells) appears. Further, mineral salts are gradually deposited on this basis.
Coral kidney stones may have a layered, heterogeneous chemical composition. In most cases, there are no more than 3–4 stone-forming minerals, but monomineral stones are also found. According to the chemical composition, coral stones are:
- dense and strong oxalates, which consist of calcium compounds of oxalic acid;
- solid urates formed from uric acid salts;
- soft phosphates arising from calcium salts of phosphoric acid;
- stones of mixed composition.
Carbonate, cystine, cholesterol and protein stones are much less common.
Types of coral stones and stages of the disease
Coral nephrolithiasis got its name solely due to the similarity of the stones to the skeleton of coral polyps. Based on their chemical composition, the following types of coral stones are distinguished:
- urates – crystals of uric acid;
- struvites – crystals of magnesium and phosphorus salts;
- oxalates – minerals of ethanedioic (oxalic) acid;
- phosphates – crystals of orthophosphoric acid;
- carbonates – esters and salts of carbonic acid.
Protein and amino acid stones occur in only 0.6% of patients. In 80% of cases, coral-shaped stones made of inorganic compounds - carbonate, oxalate, urate - are found in the CLS.
Coral kidney stones are a cast of the pelvis. Therefore, independent release of deposits is practically impossible.
In its course, coral nephrolithiasis goes through several stages:
- The first (latent). At the initial stage, deposits form in individual calyxes of the kidneys. Their dimensions are 1-3 mm, so the functions of the organs are not impaired.
- Second (beginning of the disease). Changes in the color and density of urine are key features of the second stage of kidney stones. Coral-shaped deposits gradually increase and fill the CLS. Patients are bothered by dull back pain and weakness. Due to the scanty symptoms, the pathology is detected by chance during laboratory testing of urine or blood.
- Third (stage of clinical manifestations). The proliferation of coral stones leads to damage to the renal parenchyma. As a result, the blood mixes with the urine, so it takes on a pinkish tint. The liquid becomes cloudy and small acid crystals are found in it.
- Fourth (hyperazotemic). Coral stones almost completely block the kidneys, which makes it difficult to drain urine. There are complaints of severe pain in the lower back, difficulty urinating, increased temperature, thirst, and decreased amount of urine.
Depending on the location of coral stones, unilateral and bilateral nephrolithiasis are distinguished. At stages 3 and 4, it almost does not respond to conservative therapy and leads to kidney failure.
Clinical signs
Unlike small stones, which can move towards the ureters and cause an attack of renal colic, coral stones in the kidneys are inactive. There are practically no acute pain sensations.
The following symptoms will appear:
- dull or aching pain in the side or lower back;
- increased discomfort due to active movement (sports, riding a horse or in a car on a rough road);
- difficulty urinating (decreased amount of urine and frequent unreasonable urge);
- external changes in urine associated with the entry of blood and inflammatory exudate into the secreted fluid (hematuria, pyuria);
- temperature reaction (inflammation in the kidney).
Recipes for treatment
Treatment of kidney stones is effective if you choose the right traditional medicine. Let's look at recipes for getting rid of kidney stones.
- Lemon mixture. You need to take a lemon with the peel, scald it and grate it. Add honey and olive oil to the juice in equal proportions. Drink a tablespoon 3 times a day.
- An infusion of apple peels ground into powder. To prepare it, you need to take a tablespoon of apple peel powder and a glass of boiled water. You need to drink the infusion 3 times a day. This recipe will help crush even large kidney stones (urate stones).
- A decoction of lingonberry leaves, cornflower flowers, horsetail, bearberry and birch leaves. All components must be taken in equal proportions.
- Beetroot juice will help dissolve kidney stones. You need to drink 100 g three times a day.
- To crush stones and remove sand, you need to drink a glass of water daily with the addition of one teaspoon of apple cider vinegar (necessarily natural and high-quality; this method is contraindicated for ulcers). You can add sugar to taste.
- You can crush stones with tangerines. For a week, you need to eat 1 kg of tangerines every day. After a week's break, repeat the course of treatment again.
- This method will help remove stones. Take 70 peppercorns and crush them in a coffee grinder. Mix the resulting mixture with flour and make small cakes (about 35 pieces). You need to eat one a day.
- A decoction of oats, rose hips, honey and aloe will have a diuretic effect and relieve stones. To prepare, you need to take 1 kg of oats and steam them in 5 liters of water. After the contents are reduced by half, add a glass of rose hips and after 10 minutes turn off the gas. After the broth has cooled, add 200 g of honey and 50 ml of aloe juice. Drink after meals.
Important! Any of the methods may have contraindications, depending on the presence of other diseases, such as gastritis, ulcers, hypertension, allergic reactions, etc. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor or naturopath.
Diagnostic methods
To accurately identify a coral stone in the kidney and choose treatment tactics, 2 diagnostic methods are sufficient:
- Ultrasound scanning (ultrasound).
- X-ray examination (general X-ray or urography with contrast).
In some cases, if the doctor has doubts or to choose treatment, a CT scan will be required. To determine the chemical composition of stones, laboratory tests of urine and blood are performed.
Classification
Coral kidney stones are usually classified as:
- When a stone in an organ cavity fills one renal pelvis or calyx
- The appearance of shoots in 2-3 cups
- The processes fill all the calyces of the organ
- The processes fill and deform the entire pelvic-renal system
Factors influencing the choice of treatment method are the degree of renal dysfunction. Using the classification, it is possible to assess the size and placement of stones, as well as assess the degree of disturbance and the stage of the inflammation process.
Main types of treatment
The main and most effective treatment for coral kidney stones is surgery. The most commonly used option is nephrolithotomy, when after dissection of the kidney the coral calculus is removed. Indications for surgical removal will be:
- A large shapeless formation that occupies the internal space of the kidney, for which it is impossible to carry out conservative treatment.
- Severe pathological condition of the urinary system due to impaired urine outflow.
- Identification of severe complications such as hydronephrosis, organ shrinkage, suppuration and renal failure.
- Frequent episodes of exacerbation of chronic pyelonephritis with severe disease and ineffective treatment.
- Severe hematuria with blood loss through the urinary tract.
The doctor may also suggest a non-surgical technique - remote or percutaneous nephrolithotripsy using shock wave therapy. Crushing coral stones is not always successful, especially if they are oxalate or urate stones. However, with mixed and phosphate stones, the technique is used quite successfully.
Formation mechanism
Coral stones are conventionally called “infectious”, since their formation begins with bacterial burden of the kidneys. Most often, the provocateurs are Klebsiella, Proteus or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. During their life, pathogens produce an enzymatic substance - urease, which breaks down the urea contained in urine to form magnesium, ammonium phosphate and calcium carbonate. These mineral salts themselves can be a sandy suspension and can be painlessly washed out of the kidneys. But if protein appears in the urine (due to severe kidney disease) and red blood cells (as a result of pathologies and trauma by grains of sand), in combination with urease they play the role of a “glue” that connects inorganic substances. This is how a pebble initially appears, which, under favorable conditions, quickly grows with the formation of branches.
A prerequisite for the formation of struvite is the alkaline reaction of urine. Highly acidic urine reduces bacterial activity. Many chemical reactions, as a result of which building material appears in the kidneys for the formation of coral stones, do not occur under the influence of acids.
An important role in the mechanism of struvite formation is played by disturbances in the outflow of urine. This factor may be fundamental, since stagnation of urine provokes the development of bacterial kidney diseases. At the same time, impaired outflow of urine develops when the stone is already partially formed and blocks part of the pelvis.
Peculiarities
Coral stone is a mineral with a special structure and appearance. In “appearance” it resembles a deer antler, a piece of coral (the latter comparison gave the name to the concretion). The sizes of the formation are varied - from a couple of millimeters to 7-9 cm and more.
The chemical composition of a calculus is often heterogeneous and may be different in different layers.
The composition contains one or a whole set of the following substances:
- Compounds of oxalic acid and calcium (oxalates).
- Uric acid salts (urates).
- Calcium salts of phosphoric acid (phosphates).
- Salts of carbonic acid (carbonates).
In rare cases, stones include protein, cholesterol, cystine (a sulfur-containing amino acid).
The photo shows a coral-shaped stone