A human organ, a kidney, a vital filter of the human body. It is responsible for cleansing the body of harmful and toxic substances and breakdown products.
When examining this organ using various diagnostic measures, the main indicator of their health is the size of the kidneys.
This indicator of organ health is influenced by many factors, including: the person’s gender; his age; even the mass of the human body.
Therefore, measurements of this organ were taken, which became the norm in determining pathologies and deviations from normal development.
The data obtained are the standard for carrying out diagnostic measures.
Kidneys - anatomical features of the organ
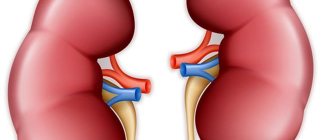
The structure of the kidneys has the structure and elements:
- Nephrons. The smallest part of the structure of the renal organ, consisting of the epithelial canals, the renal body and a huge number of blood vessels. Their numerical composition is approximately equal to one million nephrons.
- The connective tissue of the kidney is parenchyma. Consists of epithelial channels and renal rings. The composition of this part of the organ is the cortex and medulla.
- The cortical mass completely surrounds the kidney and is located under the renal capsule. As professional researchers say and confirm, in one day the kidney parenchyma cleanses the human bloodstream and his blood about 45-55 times.
- As for the medulla, these are 11-20 conical pyramids, which are located at the base of the medullary rays, included in the cortex.
- According to external data, the kidney organ is covered with connective tissue, and in front of the organ there is a serous membrane.
- The cavity in the organ is funnel-shaped and is located inside the human filter (kidney). This funnel receives organic urine from the nephron and redirects it to the ureter. The ureter itself transmits the bladder and is discharged out through the channels. This part of the organ is designated the pelvis.
- The kidney contains the renal artery. This is a blood vessel through which processed substances are delivered to the kidneys, polluting the body with its waste. All this is removed over time through the artery.
- Renal vein of the organ. With the help of this vein, through the bloodstream, this purified state of blood is transferred by the body to the vena cava of the human organ.
These listed types, which make up the kidney structure and anatomical abilities, are beneficial for the affected wards.
Decoding
First, let’s determine what exactly the doctor finds out during an ultrasound examination of the urinary system of an adult.
Appendix 1. Sample kidney ultrasound protocol (form)
What are they watching (video)?
The video below talks about what an ultrasound diagnostic specialist pays attention to when examining the kidneys.
Looking at the monitor of the diagnostic device, the doctor pays special attention to:
- Number of organs.
It is well known that a person has two kidneys. But it happens that one is removed during surgery or it is missing due to a congenital anomaly. And, on the contrary, a person may have an additional organ or its doubling (which can also be complete or partial). - Dimensions.
Ultrasound will help determine all parameters of the kidney, which physiologically depend on the patient’s age, height and weight category. - Location.
Normally, the kidneys are located behind the peritoneum, the right one slightly lower than the left. Physiologically, the kidneys take their place on both sides of the spinal column and have some mobility. - Shape and contour.
Healthy organs are bean-shaped, their structure is uniform, and their contours are smooth. - Parenchyma.
This is the tissue that “fills” the kidney; it serves as a “biological filter”. Normally, its thickness varies from 14 to 26 mm, but with age the parenchyma loses thickness. For older people, a tissue thickness of 10-11 mm is considered normal. If this indicator exceeds the norm, then the organ is inflamed or there is edema, but if the parenchyma is below normal, then we are talking about dystrophic changes, for example, against the background of diabetes or chronic inflammation. - If the study is supplemented with Doppler measurements, the patient will also learn about the characteristics of the blood supply to the kidneys.
Table 1. Normal parenchyma sizes in an adult
Structural changes
The medical report will necessarily contain words such as “hypoechogenicity” and “hyperechogenicity”.
Reference!
These concepts mean different degrees of reflection of the ultrasonic wave from the obstacle, which is the kidney tissue.
The indicators depend on the density of a particular area. Kidney tissue should normally have a homogeneous structure:
- Liquids and air are not echogenic because these substances do not reflect sound.
- Hypoechogenicity is manifested by loose tissues with low density; they appear on the monitor of an ultrasound machine as areas of a darker color
. - Hyperechogenicity is characteristic of dense tissues, whose structure is impermeable to sound. They will appear as light spots on the screen.
A change in tissue density indicates some disease process that has affected the “throughput” of the organ.
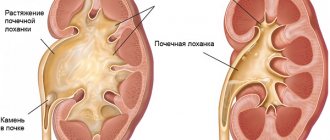
Changes in the renal pelvis
Pelvis are the cavities inside the organ in which urine accumulates, forming in the renal calyces. From the pelvis through the ureters it enters the bladder. Neither the pelvis nor the calyces of the kidneys are normally visible, however:
- Visualization of the cups or pelvis means that fluid has accumulated in them. This may indicate a blockage of the ureter or stenosis.
- Increased density of the mucous membrane of the pelvis is a sign of pyelonephritis.
- Also, during the examination, small stones may be detected - they will be designated by the term “hyperechoic inclusions”; if we are talking about sand, then the conclusion will indicate: “kidney microcalculosis.”
What factors influence the size?
As described above, the size of a person’s kidneys is influenced by certain factors. First of all, the gender of the person.
As research data show, the thickness and size, as well as the length and width of the cortical connective layer, significantly exceed those of the female sex.
This is simply explained by the difference in body structure, because a man’s body is also more massive than a weaker female’s.
In addition, studies have shown that there is a difference in the size of a person’s kidney from each other, depending on whether it is left or right. An explanation was also found for this fact - the liver interfering with the development of the right kidney.
Age also produces significant differences in kidney size. This organ grows until the age of 27, after which its development stops and it remains at the same level. With advancing age, the kidneys begin to decrease in size.
Organ development and size
Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) is used to detect kidney pathology. This device is able to detect abnormalities and the size of this organ.
In addition, an ultrasound will show the functions and structure of the kidneys. True, when receiving the results of the study, some additional data can be calculated according to the table.
As experts say, body weight and organ size are closely intertwined. The greater the weight of a person, the larger the kidney and its height and width. What is the norm for adults and their normal size?
Adult organ size
The normal size of the kidneys in an adult is from 75 to 135 mm. Taking the anatomical dimensions, you can determine the length using the vertebrae.
Indeed, according to confirmed data, the size corresponds to the height of 3 lumbar vertebrae, while the width reaches 75 mm.
As for the thickness of the organ, it will be up to 55 mm. Some begin to measure the size by a person’s fist.
The data was verified experimentally, which confirms this statement.
In young men, the thickness of the kidney and its tissues ranges from 12 to 27 mm. With old age, the connective tissue of the organ significantly reduces its size. In people over 60 years old, the thickness becomes 12 mm, and in some cases even less.
Kidney organ size in children
As stated above, the kidney organ and its size depend on body weight and gender. Taking into account that children develop according to individual characteristics, clear criteria for determining sizes have not been established.
Doctors are beginning to navigate statistical data in the context of age development groups.
The kidney pelvis in a newborn has a normal kidney size of 5 mm; up to 4 years, this figure increases by 1 mm. According to statistics, the average size of a person’s kidneys at birth is 48 mm.
- As for ages from 3 to 12 months, the size reaches 60 mm.
- From one to five years, the size of the organ corresponds to 72 mm.
- From five years to 10 years, the size is already 86 mm.
- Age ranges from 10 to 14 years, size up to 100 mm.
- From 14 to 20 years old – 107 mm.
For a more accurate determination, the doctor calculates the height and weight of the patient, a small person.
Characteristics of pathologies
But before analyzing the data obtained, you need to know what a kidney ultrasound shows, since not all types of pathologies are visualized using this diagnostic method. Ultrasonography “sees” the following pathology:
- Anomalies of development and location.
- Echopositive stones.
- Neoplasms of various nature.
- Acute obstructive or chronic pyelonephritis.
- Chronic forms of glomerulonephritis.
- Hydronephrosis and abscesses.
- Amyloidosis.
- Nephroptosis, etc.
Developmental anomalies
Quantitative and qualitative changes in the urinary system, namely: hypo- or aplasia of the kidney, its complete or incomplete doubling. Such anomalies of location as lumbar or pelvic dystopia, horseshoe-shaped, L and S-shaped kidneys.
Urolithiasis disease
It is possible to detect various kidney stones using ultrasound, which are visualized as hyperechoic (that is, brighter than the kidney tissue itself) round or oval formations with an anechoic track. Being in the pyelocaliceal system, they can move relative to each other. In addition, the diagnostician must determine their number, size and location.
Unfortunately, not all stones are visualized using ultrasound, but obstruction of the lumen of the pelvis or ureter by a stone can be suspected by the pronounced hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney above the obstacle.
Cysts and tumors
Volumetric neoplasms. Cysts of various etiologies are defined as round volumetric formations with smooth and clear contours, having an anechoic internal structure and distal ultrasound enhancement. Benign tumors have a homogeneous hyperechoic echostructure, an even contour and a rounded shape. Malignant ones are distinguished by uneven contours, even blurring, and heterogeneity of structure. The appearance of echo-negative areas in the tumor indicates the presence of hemorrhages or foci of necrosis.
Pyelonephritis
Ultrasound of the kidneys for pyelonephritis has the following indicators:
- Due to tissue infiltration, an uneven contour of the kidneys appears.
- In the acute form of the disease, the uniformity of the renal tissue and its density may be unevenly reduced due to diffuse or focal inflammation. In the chronic form, on the contrary, echogenicity is increased.
- With unilateral pyelonephritis, due to swelling of inflammatory origin, asymmetry in size is observed (that is, the affected kidney is larger than the healthy one). If the process is bilateral, then both kidneys exceed normal sizes.
- Also, ultrasound with pyelonephritis notes a decrease in the mobility of the organ with its simultaneous increase.
- The diagnostic criterion for acute obstructive pyelonephritis is expansion or deformation of the collecting system.
- However, primary pyelonephritis (non-obstructive) on ultrasound may give an ultrasonographic picture that is normal. Only as inflammation and edema increase does the echogenicity of the kidney tissue increase.
Glomerulonephritis
In acute glomerulonephritis, ultrasound diagnosis is practically uninformative; the diagnosis is made on the basis of complaints, clinical manifestations and results of laboratory examination methods. Only occasionally can an experienced diagnostician detect protruding pyramids of the medulla and tissue hyperinfiltration.
Chronic glomerulonephritis is characterized by hyperechogenicity of the tissue, reduction of the kidneys in size, blurring of the boundaries between the medulla and cortex, the appearance of scars, abscesses and areas of necrosis.
Hydronephrosis and abscesses
With hydronephrotic transformation, the ultrasound conclusion of the organ structure looks like this (depending on the stage):
- I degree – slight flattening of the arches of the cups.
- II degree – flattening is accompanied by expansion of the arches of the calyxes, while the papillae are clearly visualized.
- Ⅲ degree - the calyxes become rounded and the papillae become obliterated.
- Ⅳ degree - the cups are sharply expanded.
Abscesses (enclosed collections of pus) look like this - round, hypoechoic formations with smooth but uneven contours.
Organ size on ultrasound
Data when the size of the kidneys is normal can be confirmed by diagnostics using ultrasound. This event is important when determining the disease or examining the ward.
This method will show not only the size, but also the location of organs and their structure. The doctor will not always explain what the epicrisis of examination data says.
Often, he will pass this conclusion on to the attending physician and absolve himself of responsibility. But curiosity overcomes society, and he begins to inquire about his diagnosis.
To do this, we will try to explain the size of the kidneys according to diagnosis. What does it mean? In an adult, the length of the kidneys should be from 11 to 12 centimeters, and the width should be at least 5.5 centimeters, and the thickness should be from 4 to 5.5 cm.
As for the organ, the normal sizes of the kidneys and pelvis should have an acceptable value of 1 to 1.6 centimeters.
Woman's organ
When diagnosed, there are no big differences between women and men. Possible changes can only occur during pregnancy at the time of carrying the fetus.
At this time, the organ lengthens to 2.5 cm. These are acceptable values during pregnancy, which does not pose a risk to the woman’s health.
Kidneys in males
For males, it is necessary to build on generally accepted ultrasound readings. If there is a discrepancy between the results obtained, the doctor will prescribe a more thorough diagnosis to identify the pathology of the disease.
Preparation
To obtain the most reliable information, you need to pay attention to preparatory activities. Before the procedure, it is important not to eat for 6 hours. For 3 days you should avoid eating foods that cause increased gas formation. It is also not recommended to smoke, suck candy, or chew gum immediately before an ultrasound.
In addition, in order to properly prepare, you should drink at least 1 liter of clean water an hour before the procedure. Filling the bladder will help improve the ultrasound and improve the quality of the examination. During pregnancy, women can have their kidneys diagnosed by ultrasound; this procedure does not have a detrimental effect on the fragile fetus.
For your information, if the transcript indicates increased pneumatosis, then this is considered a sign of increased gas formation. This circumstance is evidence that the preparation for the procedure was poorly carried out. Ultrasound is a fairly informative method for diagnosing the condition of the renal apparatus. It allows you to identify many diseases at their initial stage of manifestation.
Leave a comment 63,558
At the moment, one of the frequently prescribed diagnostic methods that determine the condition of the kidneys is ultrasound examination. The results of a kidney ultrasound will help identify possible organ diseases or pathological manifestations. Using ultrasound, the following parameters are determined: quantity, location, contours, shape and size, structure of parenchymal tissue. It is determined whether there are neoplasms, stones, inflammation and swelling. Renal blood flow is visualized.
Functional features of the organ
During the biological life of this organ, it passes through itself up to 250 liters of blood per day.
At the same time, the bloodstream is cleansed of pathogenic bacteria and microbes, cleanses the blood of toxins and harmful substances.
The main functions and responsibilities of this body:
- excretory function;
- homeostatic function;
- carry out metabolism;
- support the endocrine system;
- participate in the secretory activity of the body;
- carry out hematopoiesis, which significantly renews the contents of the blood.
Excretory function of the kidneys
The production of urine and its further removal from the body is the main task of the kidney organ.
This function involves the removal of toxins or harmful substances, regulates the presence of salts in the body, and is heavily involved in maintaining blood pressure.
Big problems are caused by the lack of necessary treatment for pathology, and a violation in the excretory systems causes a complete lack of control over the state of the body.
The excretory function itself passes through the nephrons, which control the proper functioning of the organ and the small internal mechanisms of the kidneys.
This function has its own individual stages, which include:
- secretion function;
- filtering human urine and bloodstream;
- reabsorption.
When this system malfunctions, the body begins to choke from toxic poisoning.
Homeostatic function of the body
This function controls the salt and acid-base balances of the human body.
- Water-salt functions – constant maintenance of a liquid substance in the body.
- Acid-base balance – maintaining blood in normal working condition. If there is a malfunction, an irreparable blow to health is caused.
Changes in the pelvis
Typically, the only changes that can occur to the pelvis are thickening of the lining or the presence of stones/sand in them. In the first case, the mucous membrane of the pelvis increases with acute pyelonephritis or hydronephrosis. That is, the mucous membrane is inflamed due to overflow of urine with the inclusion of pathogenic bacteria. If stones are localized in the pelvis, this also indicates inflammation of the mucous membrane. In this case, the pelvis will be expanded.
Important: stones smaller than 2 mm are not visible on ultrasound. Only stones of larger diameter are echogenic.
Kidney dysfunction - organ dysfunction
Kidneys, when the organ is damaged, cause dysfunction to the human body. This occurrence of pathology, in most cases, is asymptomatic, which creates difficulties in identifying the pathology in a timely manner.
After all, it is always simpler and easier to treat the initial stage of a disease than to deal with the consequences of a serious illness.
What symptoms may indicate kidney problems? There are individual symptoms:
- pale skin;
- black circles under the eyes;
- the pain threshold occurs when gallstone disease appears;
- blood pressure increases, which can cause exacerbations of chronic diseases;
- determining the color of urine;
- constant and frequent urination;
- in children, abnormalities are detected only during diagnosis and laboratory tests.
All these factors may be signs of pathological changes in the kidneys, which require urgent intervention by specialists.
How is the procedure carried out?
After going through the necessary preparatory stage, which consists of a three-day diet, the patient comes for an ultrasound scan. The urine container must be completely filled. The examination is carried out in a supine position (back or side), which makes it possible to obtain the maximum amount of information. The patient's skin is lubricated with a special gel to prevent air bubbles from appearing in the path of the ultrasound beam and not to interfere with the hair.
When performing ultrasound in children, young patients should remain calm, not cry, lie still and not move. All this allows you to perform the procedure to the maximum extent.
The duration of the session takes no more than half an hour, its time depends on the patient’s condition. During the session, the doctor examines various parameters of the organs and records certain moments in color or black and white. Upon completion of the study, a conclusion is drawn up, which does not contain a clinical diagnosis.
Diagnosis and methods
Kidney diseases have a different nature and causes of manifestation. Since the kidneys are responsible not only for purifying the blood.
The manifestations of disturbances and deviations in work may result in renal failure.
What are the symptoms of progression of kidney disease:
- pain in the lower back, at the location of the kidneys;
- severe swelling and redness of the skin in the area where the kidneys are located;
- dark skin appearance;
- frequent urination, sometimes accompanied by painful symptoms;
- strong and unpleasant odor of urine at the time of bowel movement;
- swelling of the facial part in the morning and of the limbs in the evening.
These symptoms of the disease, based on general signs, cannot always confirm kidney pathology, so it is necessary to contact a medical institution for diagnostic measures and laboratory tests.
Diagnostic methods for kidney disease
Diagnosis of kidneys and possible pathologies is carried out with the full consent of the treating doctor.
Also, during the initial examination, based on the patient’s complaints, an experienced doctor would already be able to draw up a clinical picture of the disease.
Based on the established diagnosis, the following diagnostic measures are prescribed:
- X-ray of the body and general condition of the body;
- performing an ultrasound (ultrasound analysis of the condition of internal organs);
- renal biopsy;
- excretory urography.
In addition, laboratory tests are also carried out;
- passing a general urine test;
- taking a general blood test;
- complete control over the human condition.
The most common form of the disease, with kidney pathologies, is heart disease.
Therefore, only complete control will be able to identify disturbances in kidney function and eliminate the consequences of this condition.
Self-medication for possible kidney diseases can lead to exacerbation and death for the patient.