Urinary tract infection
Urinary tract infection is an infection of the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
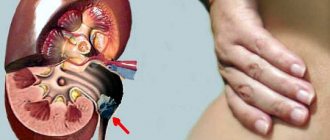
The kidneys form urine by removing excess fluid and waste substances unnecessary for the body from the blood. Urine from the kidneys passes through special tubes (ureters) into the bladder, where it accumulates and is periodically discharged through the urethra (urethra). The lower parts of the urinary system are most often affected: the bladder and urethra. A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria enter the urethra and multiply in the bladder. With further development of the inflammatory process and a decrease in the body's defenses, the infection can spread through the ureters and affect the kidneys, causing serious complications.
Urinary tract infections occur more often in women than in men. This is due to the structural features of the male and female genitourinary systems. Various antibacterial drugs are prescribed to treat these diseases.
Urinary tract infection, urinary system infection.
English synonyms
Urinary tract infection, urinary system infection.
- Frequent, strong urge to urinate
- Excretion of urine in small portions
- Pain, burning sensation when urinating
- Change in urine color
- Cloudy urine, flaky discharge in the urine
- Strong odor of urine
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Pain in the lumbar region
- Increased body temperature
- Nausea, vomiting
General information about the disease
The organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys are paired organs located in the lumbar region. Their function is to remove unnecessary and harmful substances that are formed during human life. The kidneys extract these substances from the blood and excrete them along with excess fluid (urine). They also play an important role in maintaining blood pressure, the formation of red blood cells and other vital functions. Through the ureters, urine from the kidneys enters the bladder, and then, when its walls contract, into the urethra (urethra) and is discharged out.
More often, urinary tract infections develop in women. This is due to the structural features of the male and female genitourinary systems. In women, the urethra is shorter, which reduces the path for bacteria to the bladder, where infection can develop more intensely. When the urethra becomes inflamed, urethritis occurs, when the bladder becomes inflamed, cystitis occurs, and when infection penetrates the kidneys, pyelonephritis occurs.
- Urethritis is inflammation of the urethra. One of the reasons may be the penetration of infection from the anus into the urethra. This route of transmission of infection is especially common in women, since their anus and urethral opening are located close to each other. Urethritis is caused by sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, gonorrhea, herpes and others.
- Cystitis is inflammation of the bladder. Occurs when infection spreads through the urethra into the bladder. The short urethra in women causes them to often develop cystitis.
- Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the renal pelvis (part of the kidney). One of the reasons for the development of pyelonephritis is the penetration of infection from the bladder through the ureters into the kidneys. At the same time, body temperature rises, intense pain occurs in the lumbar region. Pyelonephritis may be accompanied by kidney damage and impairment of their functions.
Who is at risk?
- Women, in particular: using certain forms of contraception - vaginal caps;
- in menopause (hormonal changes make the urinary tract more susceptible to infections)
Laboratory diagnostics plays a leading role in identifying urinary system infections.
- General urine analysis. Allows you to determine various properties of urine (color, density, transparency), identify inflammatory changes in the organs of the urinary system. An increase in the number of leukocytes in the urine, the presence of bacteria, and mucus is observed with infections of the urinary system.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko. May be prescribed if there are changes in the general urine test. This analysis shows the exact number of red blood cells, white blood cells, casts (protein particles that should not normally be present) in the urine. The level of leukocytes indicates the severity of the inflammatory process.
- Culture of flora with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics (morning urine). This study is of great importance for the treatment of infectious diseases of the urinary system. It allows you to identify the bacteria that caused the inflammation and antibiotics that act specifically on this type of bacteria.
- Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR). Allows you to determine the number of red blood cells, platelets, leukocytes, hemoglobin content in red blood cells. The number of leukocytes increases during various inflammatory processes.
- Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). One of the reasons for the increase in erythrocyte sedimentation rate is the inflammatory process. Changes in ESR are not specific for urinary tract infection, but this indicator can be useful in assessing the severity of inflammation.
Infectious diseases of the urinary system may impair kidney function. To assess its function, various tests are carried out, which include:
- Serum creatinine. Creatinine is formed in muscles during various energy processes and is then released into the blood. It is excreted from the body by the kidneys, and if their function is impaired, its level may increase.
- Urea in serum. Urea is the end product of protein metabolism in the body. Excreted by the kidneys. When they become ill, its level increases.
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder (ultrasound). Allows you to obtain images of internal organs, identify developmental disorders of the urinary system, kidney stones and other changes.
- Computed tomography of the urinary system. Obtaining accurate layer-by-layer images of internal organs is of great importance in determining the possible causes of infectious diseases of the urinary system.
- Intravenous urography. X-ray method for examining the urinary system. A special contrast agent is injected into a vein, then after a certain time a series of X-rays are taken, which show the passage of this substance through the urinary system. At the same time, kidney function is assessed, disorders in the structure of the urinary tract, kidney stones and other diseases of the urinary system are identified.
- Cystoscopy. The method allows you to see the inner wall of the bladder and perform various manipulations (for example, removing stones, some tumors). A tube of the device with an optical lens system is inserted into the urethra, then into the bladder, thus obtaining images. It is also used for chronic, frequently occurring inflammatory diseases of the bladder.
Kidney structure and functions
The anatomy of the urinary system begins with a paired organ located near the posterior wall of the peritoneum below the pancreas - the kidneys. This is the most complex organ that performs the main functions of filtering blood and producing urine. The average weight of one kidney of an adult is 200 grams. They are located near the spine and are connected to the central arterial and venous channels. During normal operation, the kidneys pass through all the blood in the human body in 3 minutes. 2 liters of urine are produced.
The kidney is a large gland. It has a protective layer on top. The bulk of the organ is parenchyma - loose tissue consisting of epithelial cells of nephrons. Capillaries from venous and arterial vessels approach each cell, forming a glomerulus, a node for blood synthesis and urine formation. Plasma, together with harmful substances and waste products collected throughout the body, enters the parenchyma cell, everything is removed from it, including plasma and all substances contained in it.
When the resulting primary urine passes through the nephrons again, useful substances are released from it and, together with hormones and enzymes produced by the kidney, saturate the purified blood.
Liquid - urine, flows through the collecting ducts into the pelvis and through them enters the ureter.
How to cure urinary tract inflammation in adults
Urinary tract infections occur due to the action of various pathogenic microorganisms. Such diseases are common among adults and children and have their own symptoms and differences. In many people, inflammation of the urinary tract occurs repeatedly even with proper treatment, so the problem requires special attention and prevention. If urinary tract diseases are left untreated, they will become chronic and lead to serious complications.
Most often, the inflammatory process worries people during the cold season, when the body's defenses weaken. More than half of the disease cases are acute cystitis. Women and children are predominantly affected, while cystitis and other similar diseases occur much less frequently in men.
Possible reasons
The cause of the inflammatory process is E. coli, which causes the disease against the background of predisposing factors. If a person has reduced immunity, the outflow of urine is impaired, then the possibility of microbes entering the bladder is quite high. In women, symptoms of cystitis occur up to 5 times more often than in men due to anatomical features. Through the short urethra, pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate the bladder and cause the first signs of the disease.
The risk group includes children under 3 years of age. While the child’s immune system has not yet formed, his body is susceptible to attacks by various bacteria.
Due to the inflammatory process, boys experience a high temperature. Elderly people, patients after surgery, as well as people with chronic inflammatory processes are often exposed to urinary tract diseases. Women who use the diaphragm ring and spermicides as contraception also have a high risk of disease.
The inflammatory process can develop in three directions:
- urethritis that occurs after inflammation of the urethra;
- cystitis, during which the bladder becomes inflamed;
- pyelonephritis or inflammatory process in the kidneys.
There are two types of spread of the infectious process, when the infection is descending and ascending. Microorganisms immediately attack the organs of the genitourinary system located below, and then rise higher. Treatment for an adult or child depends on the type of infection and the obvious symptoms of the disease. Drugs are prescribed according to age and type of infection.
Features of the process in childhood
The diagnosis of “cystitis” in a child is made only after 10 years of age due to the anatomical structure of the genitourinary system; in other cases, the doctor, based on the symptoms, makes a diagnosis of “urinary tract infection”. Since the disease is not detected immediately, the infection penetrates from the urinary tract to the kidneys, and children develop chronic pathology and then kidney failure. The problem is that the symptoms of the disease in a child are similar to other ailments.
In most cases, children experience low fever, nausea, abdominal pain, and abnormal bowel movements. Children are also prescribed antibiotics, nitrofuran drugs, plenty of fluids, diet and other methods to eliminate the infection. Medicines have a positive effect only if complex treatment of the disease is carried out.
The incidence of diseases depends entirely on the age and gender of children. For girls, the risk of infection entering the genitourinary system is slightly higher than for boys. A high incidence is observed in newborns up to one year old, when intimate hygiene of children is not observed. Antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. The best way to prevent diseases in children is daily proper hygiene of the genital organs, the use of diapers and breastfeeding the child to protect the immune system of infants.
Successful treatment of urinary tract inflammation depends on age, gender and approach to the problem. Only a comprehensive method, the right medicine and diet can defeat regular attacks by microorganisms. Antibiotics and other drugs may not be needed if you follow basic infection prevention rules.
Main symptoms
The main signs of urinary tract inflammation are the following symptoms:
- the appearance of pain in the abdomen and back;
- uncharacteristic color of urine;
- frequent painful urination;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- unpleasant odor of urine;
- possible increase in temperature.
If men and women have infections in their bodies that are transmitted during sexual intercourse, they experience symptoms in the form of sharp pain during urination, caused by chlamydia and other microorganisms.
Women often suffer from adnexitis simultaneously with inflammation of the genitourinary system, which subsequently leads to complications during pregnancy and childbirth. Symptoms of diseases will disappear only with properly selected treatment. When making a diagnosis in women and men, the following points are taken into account:
- hereditary factor;
- repeated cases of infection;
- the appearance of thirst;
- total volume of urine excreted;
- urinary incontinence.
Although in women, as well as in children, the inflammatory process develops faster, men also often develop symptoms of cystitis or pyelonephritis due to hypothermia, respiratory diseases and other factors. Timely treatment, which contains antibiotics, nitrofurans, and herbal decoctions, will help eliminate infections of the genitourinary system in adults and children.
Urinary system
The human urinary system ends with the urethra, which enters from the bladder. Its function is to remove urine outside. It consists of a mucous membrane and a muscular layer. There is connective tissue around the canal. The canal begins immediately behind the urethral sphincter. In men, it is surrounded at the junction by the prostate gland. It has a length of 16–22 cm with a lumen width of 8 mm, passes inside the penis. In the upper part it is connected to the testis and sperm comes out through it.
In women, the canal is short, 3–4 cm, and goes directly into the vagina. Its width is 1.5 cm. If there is a disease of the urinary system in women, there is a high probability of damage to the reproductive organs.
Diseases of the urinary system most often occur as cystitis in women and prostatitis in men. The pathology occurs mainly as a viral disease due to hypothermia, colds, or bacterial infection. The cause may be a violation of personal hygiene rules or sexual transmission of pathogens. Through the channels, the lesion can reach the kidneys.
The urinary system, which has its own unique characteristics and functions, plays an important role for humans, removing toxins and waste products produced by cells during metabolism.
The human urinary system rids the body of excess waste after drinking and eating. It regulates the volume and composition of blood, stabilizes blood pressure, and all due to controlling the amount of fluid, salt and water balance.
Treatment tactics
To eliminate the inflammatory process of the urinary tract, timely and competent treatment, antibacterial drugs, as well as drinking regimen and nutrition correction are necessary. Treatment, in which antibiotics play an important role, is carried out in a hospital setting in severe cases of pathologies of the genitourinary system. If the infection has not caused serious harm to the body, the patient is sent home with the necessary medications prescribed.
The inflammatory process of the urinary tract involves the exclusion of spicy, smoked and salty foods. Treatment is impossible without drinking plenty of fluids, which cleanses the bladder. Plain water, along with other methods, is a real assistant in the fight against diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women. Cranberry juice is also beneficial. When taking antibiotics and other drugs, it is recommended to additionally brew various herbs. The herbs of immortelle, knotweed and corn silk have an anti-inflammatory effect. Herbal decoctions should be used with caution in children. Adults should give up bad habits, including alcohol and cigarettes.
A special regime during illness includes daily rest in a lying position for at least 40 minutes during the working day, absence of drafts and hypothermia, as well as frequent emptying of the bladder. If the disease has become chronic, then antibacterial drugs save only for a while. In such cases, regular doctor supervision and a detailed examination of the genitourinary system will be required.
How to prepare for a CT scan
For the procedure to be successful, you need to prepare for it. First of all, this applies to meals. The last meal should be 4-6 hours before the start of the diagnosis.
2-3 days before diagnosis, you need to exclude fatty, fried, salty, and peppery foods from your diet. It is worth giving up baked goods and carbonated waters, dairy and fermented milk products, i.e. limit the consumption of foods that contribute to increased intestinal gas formation.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to remove all metal accessories, it is advisable to wear loose clothing that is easy to take off and put on.
To play it safe, you should do an allergy test for iodine intolerance. If the result is positive (no negative reaction was detected), a computed tomography can be performed.
Use of antibiotics
In most cases, due to untimely identification of the disease in children and adults, there is a need to prescribe antibacterial agents. Penicillin antibiotics are predominantly prescribed. Penicillin is used to treat pyelonephritis during pregnancy. In adolescence, macrolides are used, and in adults, in addition to penicillins, cephalosporin antibiotics are prescribed. Cephalosporins make it possible to treat a person for two weeks, which promotes effectiveness and rapid recovery.
For various complications, gentamicin is used, but only in men and women under 60 years of age, since treatment with the drug causes deafness in older people. For children, drugs of the aminoglycoside group are prohibited. Antibiotics are prescribed by injection for severe forms of inflammatory processes of the genitourinary system. Drugs of the nitrofuran series are considered more gentle on the body and are used in children of all ages.
Treatment methods for ureters
Urinary tract disease
Urinary tract diseases are a fairly common disease today. Often, urinary tract diseases occur against the background of an inflammatory process. As a rule, when one of the organs becomes inflamed, the disease does not go away on its own, and in the absence of treatment, it only begins to develop. The process of inflammation, for example, if it began from the urethral canal, then, moving through the vessels of the urinary tract, it will reach the bladder, and then cover the ureters (unilateral and bilateral inflammation). Afterwards, the inflammatory process can also affect the kidneys. The ureters are vessels through which urinary fluid from the kidneys enters the bladder. For the ureters, the most well-known disease is urethritis (inflammation of the ureters).
Ureters and bladder - their position and structure of function
The ureters depart from the kidneys, the structure and functions of which are to distill urine from the kidneys to the bladder and prevent the reverse movement of fluid. The organ is paired, located in the upper part near the posterior wall of the peritoneum, then turns to the anterior cavity and connects to the bladder.
The structure of the ureter is a hollow muscular tube, up to 3 cm in diameter with a lumen of 12 mm, and an average length of 30 cm. In women, the ureters are 2–2.5 cm shorter. Pulse muscle contraction ensures the movement of urine in one direction, from the kidneys to the bladder regardless of body position. Along its length, the ureter has 4 narrowings.
The vessel wall has several layers:
- outer;
- muscular;
- urothelium;
- submucosa;
- mucous membrane.
The mucous membrane has many blood and lymphatic vessels and connective tissues. It protects muscle tissue from the acid-base effects of urine.
The outer layer is formed by two axillary layers penetrating each other:
The muscle layer ensures the operation and functioning of the ureter. It consists of bundles of muscle cells directed:
They have different thicknesses and provide peristalsis of the vessel to move urine in one direction.
The ureter emerges from the kidney to form the ureteropelvic junction. It ends with a ureterovesical anastomosis in the bladder and a one-way valve that prevents the reverse flow of urine. In women, the vessel intersects with the mesentery of the uterus and the uterine artery at the entrance to the bladder.
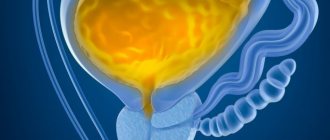
The bladder is a hollow organ in which urine that passes through the ureters accumulates. He has:
- shell;
- 2 holes – entrance of the ureters;
- urethral triangle;
- bladder neck;
- urethral sphincter;
- urethral opening.
The inside walls are covered with mucous membrane and have folds. On the outside there is a muscular layer of smooth multidirectional muscles. The folds allow the bladder to stretch when it becomes full.
The internal sphincter holds urine in the bladder and is opened by a signal sent by the person through the brain to the nerve endings in the sphincter muscles. The valve opens spontaneously when the bladder is overfilled and stretches to its maximum size. The cause of spontaneous activation of the sphincter may be inflammation and other diseases.
In the upper part there is an ejector muscle. When the bladder fills, it sends signals - the urge to urinate and contracts, facilitating complete emptying, pushing out the remaining urine.
Causes of the disease
The development of this process is preceded by a number of reasons, namely diseases of the urinary system and urinary tract. Most clinical cases prove that with urethritis, the patient is diagnosed with urolithiasis. Most often these are kidney stones, which the patient himself may not have previously suspected. Stones tend to form in the renal pelvis, and then they can move down through the vessels of the urinary tract and stop in the ureter. Thus, the presence of a stone in the ureter is accompanied by an inflammatory process. This process can cause the symptom of kidney colic.
Purpose of the elements
Separately, it is very difficult to provide each organ with the urinary system, so they are interconnected and serve a single purpose.
Therefore, the urinary system has functions such as:
- maintaining a constant internal environment (homeostasis);
- excretory;
- hormonal.
Each of them is located in the lumbar region and consists of 2 layers - the medulla and the cortex. On the outside it is covered with connective tissue and fat capsules. Weight can range from 120 to 200 grams. The kidney acini (that is, the structural and functional unit) is a nephron, which consists of many tubules and glomeruli. Bean-shaped buds have the following dimensions (in centimeters): length – 12-13, width – 5-6, thickness – 3-4. The small calyces of the kidneys fuse together to form the pelvis, the place where urine is directly formed and directly descends into the ureter.
- neutralization and destruction of toxic substances;
- conversion of arterial blood into venous;
- intrasecretory;
- metabolic;
- osmoregulatory (provides stability to osmotic pressure);
- excretory;
- endocrine;
- ion-regulating (monitors the concentration of ions in the blood plasma);
- volume-regulating (monitors the preservation, excretion, and volume of extracellular and intravascular fluid).
Ureter
Its anatomy consists of 2 paired tubes (about 30-35 centimeters in length), consisting of epithelium, muscle and connective tissue. Its walls are formed of 3 layers - mucous (internal), muscular (middle) and adventitial (external). The main purpose is the transport of urine due to the contraction of muscle fibers. After the bag is filled, the passage of the ureters is mechanically blocked to prevent fluid from flowing back into the kidneys.
Bladder
The physiological characteristics of any person determine the location and individual parameters of the hollow organ, which has the shape of a bag. This organ is muscular; it is located in the small pelvis. The structure of the walls, lined with epithelium, is very elastic (the smooth muscles of which allow it to stretch, holding 400-700 ml). The urge to urinate begins when about 200 ml of urine accumulates. The urinary pouch consists of a neck, apex, bottom and body. Its muscles expand when it is full and contract when it empties. Its role is the accumulation of urine in 3-3.5 hours and its release to the outside.
Urine, due to the work of muscles, enters the urethra. This is the final part of the urinary tract in the form of a narrow tube through which fluid descends. Its functions are not as wide as those of others. The urethra releases accumulated urine into the external environment.
2 sphincters help control the secretion of urine - internal and external. The first is a ring-shaped muscle that is located at the very beginning of the urethra; it relaxes and contracts on its own, without the desire or consciousness of a person. The second sphincter includes the muscles of the pelvic floor, which hold the internal abdominal cavity. A person is consciously able to control them and regulate the secretion of urine.
A number of diseases that can cause ureteral urethritis
1. Pyelonephritis. Kidney disease is accompanied by an inflammatory process. It occurs more often due to the entry of bacteria through the urethra, after which these bacteria move through the vessels of the urinary tract and enter the kidneys. Usually, with this disease, only one kidney suffers; in rare cases and with incompetent treatment, the second kidney can also become infected. To eliminate the bacterial infection and treat pyelonephritis, antibiotics are prescribed.
2. Pyelitis. Kidney disease, the process of which develops in the renal pelvis. Like pyelonephritis, pyelitis is also an infectious and inflammatory disease. The disease develops as a result of infection and bacteria and affects the mucous membrane of the kidneys. In this case, damage to the organs of the genitourinary system occurs, and the outflow of urinary fluid is disrupted. When treating pyelitis, antibiotics are used to eliminate the infection from the body.
3. Cystitis. A disease characterized by inflammation of the bladder. The disease often occurs due to infection entering the vessels of the tract leading to the bladder. Women are more susceptible to cystitis, which is explained by the peculiar structure of the genitourinary tract in women. Due to the wide urethra in women, bacteria and infections are much more likely to enter the body. Most often, the development of cystitis is promoted by E. coli, and rarely by other types of bacteria, for example, candida fungi (candidiasis or thrush). To eliminate the source of infection and pathogenic bacteria, in addition to the main treatment process, the doctor prescribes antibiotics. In the treatment of cystitis, decoctions containing medicinal herbs are often used.
In addition to the formations listed above, ureteral urethritis can also be caused by a sexually transmitted infection.
The organs of the genitourinary and urinary systems are located at a close distance from each other, as a result of which the infection penetrates through the openings of the genital tract and enters the ureter and other organs. With any infectious disease, it will invariably be accompanied by an inflammatory process. And the inflammatory process, as we know, does not disappear on its own, but only expands the area of its influence in the absence of proper treatment. During any infectious disease, the doctor prescribes antibiotics to relieve inflammation and destroy the infection.
Symptoms of the disease
As you know, urethritis does not occur on its own, but only as a result of any of the diseases. Symptoms of urethritis caused by stone disease: - pain in the lumbar region, accompanied by contractions; - pain “scoots” from the lumbar region to the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity (can radiate to the groin and genitals); - increased body temperature, increased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting (these symptoms are usually variable); - discomfort and pain when urinating; - cloudy urine and blood impurities; — stone loss (apparently visually)
Symptoms of inflammation of the ureter caused by cystitis: - cutting pain and burning sensation during urination; - dull pain in the lumbar region; - cloudy urine (blood stains and purulent discharge are possible); With inflammation of the ureter, often the earlier symptoms of the previous disease become less noticeable. In addition to the signs listed above, there is also a deterioration in the person’s general condition (weakness, headaches, fatigue, fever, etc.)
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of the ureter includes a number of procedures: - general blood test; - general urine analysis; - blood chemistry; - urography (X-ray method that detects disturbances in the outflow of urinary fluid and the presence of stones); - cystoscopy (a procedure for checking the inflamed ureter for swelling); - ureteroscopy (detection of swelling and damage to the ureter); — catheterization of the ureter (detection of the presence of pus and cloudiness in the urinary fluid); — Ultrasound (examines the ureters and kidneys) Diagnostics is necessary for the doctor to accurately prescribe treatment procedures and for their high effectiveness. Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in special medical centers in the direction of the attending physician.
Treatment of the disease
There are two main methods of treating urethritis (inflammation of the bladder) - a conservative method and a surgical method. The conservative method of treating urethritis is selected individually. The choice of method directly depends on the cause that led to inflammation of the bladder. If the cause is the presence of urolithiasis, then the doctor prescribes antispasmodics and drugs that lead to the dissolution of stones . If these stones are not large or are sand, then in addition the doctor may recommend the use of medicinal herbs that relieve inflammation. If the cause of inflammation of the ureter is cystitis, pyelonephritis or pyelitis, then all efforts should be devoted to treating these diseases first. When treating urethritis, the doctor usually prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs and uroseptics. Also, saline solutions and glucose mixtures are indicated for intravenous use. But the main drugs in the fight against urethritis are antibiotics. In the treatment process, both diuretic drugs and diuretic herbs are often used. After reducing the exacerbation process, physiotherapy is used.
ethnoscience
Treatment of kidney inflammation, as well as bladder infections, is best started in the early stages. Folk remedies play an important role in treatment - these are decoctions and tinctures of medicinal plants. Folk remedies are used as an addition to medications. Medicines such as Cyston, Urolesan are made on a herbal basis.
For cystitis and nephritis, use a decoction of blue cornflower flowers or an infusion of horsetail. An infusion of bearberry leaves not only relieves inflammation in the kidneys, but also has an analgesic effect. Herbal preparations from plantain, birch leaves, cinquefoil, horsetail, and corn silk are widely used. The medicinal drink is usually taken before meals.
The course of herbal treatment usually lasts a month, then take a break for two weeks. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs should be taken only after the doctor’s recommendations, as they also have their contraindications.
Surgical intervention
Most often, surgical intervention is necessary if inflammation of the ureter is caused by urolithiasis.
When the stone reaches a huge size and lingers in the ureter for a long time, thereby causing inflammation, it must be removed surgically
Surgery is also performed if the ureteral cavity is damaged. If most of the ureter is damaged, a tube is usually installed to drain urinary fluid.
Treatment of urethritis with folk remedies
Traditional medicine is gaining more and more popularity every day. Sometimes, medicinal herbs become an indispensable assistant in everyday life. However, it is worth considering that diseases are different and can be of different nature, degree of danger, and form, when the use of medicinal herbs may not have an effect, and a person will only prolong the disease process. To take any type of herbal medicine, you must first consult a doctor. If the doctor approves and appreciates that the medicinal herb chosen by the patient is useful and can be used, only then should it be done. A well-known herb that can help in the treatment of many diseases (urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.) is yellow zelenchuk. Otherwise, people call it “yellow wrasse” or “earth incense”. Directions for use: 1 tsp. Brew the herbs in a glass of boiling water and let it brew, then consume before meals. This decoction should be taken 3 times a day, one glass. No less effective is the herb called “hernia naked”. Method of preparation: 1 tsp. pour 200 ml of boiling water and infuse. It is recommended to consume 0.5 cups 2 times a day, preferably in the morning and evening.
Principle of operation
The job of the urinary system is to maintain fluid balance, filter blood, and produce urine. The constant functioning of the kidneys controls the body’s acid and water-salt balances. They pass about 175 liters of blood through themselves per day (and the amount of accumulated urine is 1.5 liters).
This is a cyclical process:
- urine appears during filtering of toxic substances;
- the bubble gradually fills, irritating its walls to such an extent that the pressure rises;
- emptying occurs.
Impaired functions lead not only to the unconscious leakage of formed urine.