Pregnancy is not only pleasant moments of waiting to meet your baby, but also a complete transformation of the functionality of all internal systems and organs. A woman’s body experiences severe stress, especially in the last trimester. During this period, the immune system decreases, physiological changes in the urinary system occur and all the conditions are created for the formation of infection in the kidneys. In this article we will talk about kidney infection during pregnancy, its symptoms, causes of formation and treatment methods.
Features of the urinary tract in pregnant women
h2 1,0,0,0,0 —>
p, blockquote 3,0,0,0,0 —>
Urinary tract infections are a common concomitant complication of pregnancy. It can occur as an asymptomatic appearance of bacterial flora in urine tests or with clinical manifestations of cystitis. The incidence depends on the presence of pathology of the bladder or urethra before conception, as well as on existing kidney stones or other pathological conditions.
p, blockquote 4,0,0,0,0 —>
Progesterone not only reduces the tone of the myometrium, but also affects the rest of the smooth muscles. This shows up:
p, blockquote 5,0,0,0,0 —>
- expansion of the renal pelvis system;
- decreased tone of the ureters;
- slight relaxation of the bladder sphincter.
These changes lead to a slow passage of urine from the kidneys. The bladder does not empty completely. Decreased tone and the presence of residual urine promotes reflux back into the ureters. This causes pathogens to enter the kidneys through an ascending route.
p, blockquote 6,0,0,0,0 —>
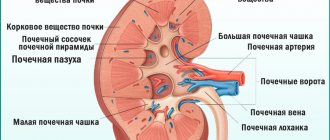
Dilated renal pelvis leads to the development of physiological hydronephrosis in pregnant women, as an additional factor in infectious pathology.
- Urinary tract infection in newborn boys. Urinary tract infections in infants
p, blockquote 7,0,0,0,0 —>
Changes also occur in the chemical properties of urine. Its pH increases, and the concentration of estrogen increases. The presence in women of a tendency to high blood sugar or gestational diabetes is a provoking factor for the proliferation of microbes.
p, blockquote 8,0,0,0,0 —>
Changes in the composition of the vaginal microflora and a decrease in local immunological defense lead to the activation of an opportunistic infection in the genital tract. Pathogens can easily penetrate the urethra and then spread upward to the bladder and kidneys.
p, blockquote 9,0,0,0,0 —>
How to treat
Treatment of genitourinary infections during pregnancy should only be prescribed by an experienced specialist. Many medications in this case are strictly contraindicated because they are toxic to the fetus.
Cystitis is usually treated without antibiotics; in extreme cases, they are used after three months. From 3 to 6 months, protected penicillins and second-generation cephalosporins are used. After 6 months, you can take cephalosporins of the latest generations - 3 and 4. The course of treatment is 14 days, it cannot be stopped earlier, even after the signs of the disease have completely disappeared.
After treatment, two weeks later, the urine is re-examined for the presence of bacterial flora.
After using antibiotics, it is recommended to drink phytouroseptics, which are sold in pharmacies, and cranberry juice.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria should be treated according to the same regimen. This disease should not be ignored, since, despite the absence of symptoms, it turns into pyelonephritis.
Pyelonephritis during pregnancy requires special attention and a careful approach to treatment. In case of severe inflammation, the pregnant woman is placed in a specialized hospital, where antibiotics are administered intravenously. After which they switch to taking them internally. Throughout the treatment, the doctor monitors the condition of the woman and the fetus in order to prevent premature birth.
It is very important for final recovery to complete the course of antibacterial therapy completely. This will avoid relapse of the disease.
It is a good idea to use Canephron in this situation, a herbal preparation that acts as an antibacterial, diuretic and anti-inflammatory agent. Its effectiveness in treating kidney inflammation during pregnancy has been proven by many scientific studies.
Severe exacerbation of the disease in the last trimester, symptoms of fever and intoxication are dangerous for the life of the mother and fetus, and are an indication for cesarean section.
Main pathogens
h2 2,0,0,0,0 —>
Cystitis and pyelonephritis of a non-infectious nature rarely develop in pregnant women. Infectious diseases develop against the background of activation of opportunistic microflora. The most common causes are the following pathogens:
- Urinary tract infection in children: causes and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
p, blockquote 10,0,0,0,0 —>
- coli;
- Klebsiella;
- staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- enterococci;
- Proteus.
The cause of damage to the urinary tract can be sexually transmitted infections:
p, blockquote 11,0,0,0,0 —>
- chlamydia;
- ureaplasma;
- mycoplasma;
- gonococci.
In rare cases, the causative agents are Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Treponema pallidum.
p, blockquote 12,0,0,0,0 —>
How to identify an infection
Diagnosing a urinary tract infection in pregnant women usually does not cause difficulties. The diagnosis is made on the basis of complaints and symptoms, as well as urine examination - general and according to Nechiporenko. A blood test can confirm the presence of inflammation, and bacteria can be found in the urine.
These types of tests are prescribed to almost every pregnant woman, since this is the only way to detect infections that occur without any symptoms.
If the results of mandatory studies indicate a pathological process, then additional ones must be done after that. For kidney disease you need to undergo an ultrasound. Other methods (radioisotope or x-ray examination) are not recommended due to their negative effect on the fetus. They are performed only in cases of emergency.
Characteristic symptoms
An infectious disease may have pronounced symptoms or not appear at all. Acute cystitis manifests itself:
- pain when urinating;
- false urge to go to the toilet;
- splashes of blood and increased levels of leukocytes in the urine;
- aching pain in the lower abdomen;
- increase in body temperature.
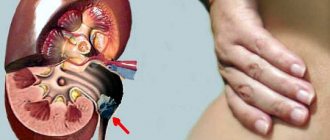
If the infection reaches the kidneys and causes pyelonephritis, then girdling pain in the back occurs, nausea and vomiting also appear, and body temperature may rise. This is the most serious infectious disease of the urinary system. In turn, bacteriuria does not cause inconvenience, but is detected through laboratory testing.
Return to contents
Symptoms of the disease
All infectious diseases of the urinary tract have almost the same symptoms, which manifest themselves in:
- constant desire to go to the toilet, provided the bladder is almost half empty;
- attacks of pain in the lower abdomen and lumbar region;
- feeling of discomfort or burning during urination or sexual intercourse;
- the urine becomes cloudy, may have an unpleasant odor or may contain blood clots.
For information! During the infectious period, low-grade fever can rise to 37.5C degrees, but most often the temperature remains normal.
Symptoms of a kidney infection can occur either unnoticed by a woman or appear suddenly, they are expressed:
- increased sweating, chills;
- fever or sudden increase in temperature;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen, side, and hypochondrium.
For information! Asymptomatic bacteriuria leads to the premature birth of a child with low birth weight. If the disease is left untreated, the risk of developing a kidney infection increases to 40%.
Most often, a woman does not immediately notice an infection, for example, cystitis, because... Due to fetal growth, the number of urinations increases. However, if you notice any changes, contact a specialist immediately.
Mechanism of development of pathology and complications of gestation
h2 3,0,0,0,0 —>
- What is kidney hydronephrosis during pregnancy and why is the pathology dangerous for mother and child?
The spread of infection occurs in several ways:
p, blockquote 13,0,0,0,0 —>
- ascending;
- downward;
- hematogenous;
- lymphogenous;
- contact
Most often, pregnant women experience ascending infection. Pathogens enter the urethra from the vagina. This is due to their close location, as well as the anatomical features of the urethra itself, which in women is short and wide.
p, blockquote 14,0,0,0,0 —>
Ascending infection
The mucous membrane of the bladder effectively resists the development of inflammation, but during pregnancy the influence of additional risk factors increases:
p, blockquote 15,0,0,0,0 —>
- immunosuppression;
- hypovitaminosis;
- overwork;
- hormonal changes;
- hypothermia;
- promiscuity;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- anatomical abnormalities;
- surgical interventions and manipulations.
If a woman had chronic cystitis before pregnancy, then in most cases it will worsen during gestation. As gestational age increases, the risk also increases. Mechanical compression of the bladder and ureters by the uterus interferes with the normal outflow of urine. Therefore, cystitis can acquire a recurrent course.
p, blockquote 16,0,1,0,0 —>
Any infection in the body increases the risk of developing gestational complications. After infection of the lower urinary tract, pathogens easily penetrate higher. This is due to the natural lack of resistance of the kidney medulla to microbial agents. This environment is characterized by a hypertensive state, which prevents the penetration of leukocytes and phagocytes, the action of the complement system is limited, which causes a lack of resistance to infection.
p, blockquote 17,0,0,0,0 —>
Against the background of inflammation of the urinary tract, the likelihood of spontaneous abortion and the birth of a premature baby increases. The risk of premature birth increases due to the local synthesis of prostaglandins, which are mediators of inflammation and increase uterine contractions.
p, blockquote 18,0,0,0,0 —>
Inflammation of the urinary tract can develop as a complication of the postpartum period. During childbirth, compression of the bladder occurs, its innervation and blood supply are disrupted. This is an additional factor in urinary retention. If there is an infection of the vaginal vestibule, vaginitis, then pathogens can be introduced into the bladder during mandatory catheterization.
p, blockquote 19,0,0,0,0 —>
What happens if there is no treatment
Most often, the development of genitourinary infections during pregnancy can be stopped, and they pass without any special complications. But the lack of timely treatment and delayed treatment can lead to big problems for both the expectant mother and the fetus, as a result of which the following develops:
- hypertension;
- anemia;
- inflammation in the amniotic space and membrane.
The most dangerous thing is that this leads to miscarriage, since the fetus experiences severe hypoxia. After birth, a baby may develop an infection if the mother had an untreated genitourinary infection. Such babies are often registered at the clinic as being predisposed to colds.
Why is it dangerous?
In most cases, infections of the genitourinary system during pregnancy are curable if the woman regularly attends consultations and passes the necessary tests. If the disease is detected late, we can talk about the risk of pathological changes in the fetus. The placenta thickens and ages faster, this impairs the conductivity of oxygen and nutrients, causing premature birth, which is especially dangerous before 25 weeks. In addition, you may develop:
Such a pathology for expectant mothers can result in hypertension.
- anemia;
- hypertension;
- inflammation of amniotic fluid;
- early miscarriage;
- fetal hypoxia;
- complications during pregnancy and after delivery;
- pressure changes;
- preeclampsia.
Return to contents
Disease prevention
The main danger of developing an infection during pregnancy lies in its irreversible processes and negative impact on the health and development of the fetus. Complications of a kidney infection may include:
- anemia;
- formation of gestosis;
- formation of toxic shock;
- surges in blood pressure;
- insufficiency and inflammation of the placenta;
- lack of oxygen for the fetus;
- premature labor;
- death of the fetus.
To prevent and preserve the health and life of the mother and fetus, experts recommend taking the following measures:
- pregnancy planning, timely examination and treatment of all chronic diseases;
- normalize hormonal levels with the help of medications;
- in the absence of severe swelling, drink a sufficient amount of fluid;
- do not restrain yourself at every urge to urinate;
- during pregnancy, avoid douching;
- observe personal hygiene rules, wear loose underwear and do not take a bath;
- take tests in a timely manner and report the presence of suspicious symptoms;
- If you have a chronic disease, take herbal medicines.
Remember, any infection of the genitourinary system during pregnancy has a number of its own characteristics and indications. Register with the antenatal clinic in a timely manner, take the necessary tests, and most importantly, always report any symptoms or phenomena that cause discomfort. Remember, timely treatment is the key to the health of not only the pregnant woman, but also the unborn baby.
Kidney infections during pregnancy include a group of inflammatory diseases affecting the pyelocaliceal system of the kidney, its glomeruli and vessels.
Among kidney diseases that occur during pregnancy, gestational pyelonephritis is the most common. It can be both acute and chronic. Most often, gestational pyelonephritis occurs in pregnant women for the first time and appears after 20-22 weeks.
It should be taken into account that the likelihood of developing this pathology practically does not depend on the woman’s health status before pregnancy. The changes that occur in the kidneys are directly related to the anatomical, physiological and hormonal characteristics of the body of a pregnant woman. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, urolithiasis, and genital tract infections.
Infectious pyelonephritis during pregnancy requires mandatory treatment, as it can pose a danger to both the health of the woman and the health of the child.
Causes and risk factors
The main number of pathogenic microorganisms enters from the anus, or through sexual contact. The length of the urinary canal (urethra) is short, so the infectious pathogen quickly ascends through the bladder to the kidneys. In pregnant women, the body produces an excess amount of progesterone, and the smooth muscles are relaxed. The outflow of urine is disrupted, urine stagnates and favorable conditions are created for their reproduction. In addition, if a pregnant woman does not observe the rules of personal hygiene, does not eat properly and is promiscuous, then infectious diseases rapidly progress and make themselves felt already at the end of the first trimester.
Risk factors for developing genitourinary infections during pregnancy:
- unprotected sex with different partners;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- side diseases of the reproductive system;
- chronic pathologies.
Return to contents
Diagnostics
If you suspect a kidney infection in a pregnant woman, you should pay attention to the presence of chronic diseases of the genitourinary system and diabetes mellitus.
Diagnosis of kidney infection during pregnancy is carried out on the basis of complaints, clinical presentation, physical and additional research methods.
During the examination, attention is drawn to pain upon palpation and tapping with the edge of the palm on the lumbar region on the side of the affected kidney, and tension in the abdominal muscles.
A general blood test and a general urinalysis, a Nechiporenko test, a biochemical blood test, and a microscopic urine test are prescribed.
Diagnostically significant in combination with the clinic are:
- Pyuria with a predominance of leukocyte casts of more than 10 per 1 μl of urine.
- Detection of 1 or more bacterial cells in the field of view during microscopic analysis of urine.
The diagnosis is indirectly confirmed by an alkaline reaction of urine, an increase in mucoproteins and a positive reaction to C-reactive protein in a biochemical blood test, dysproteinemia with an increase in γ-globulin and ά2-globulin.
Important! Impaired filtration capacity of the kidneys is determined only in severe cases of the disease and cannot serve as a diagnostic criterion.
It is necessary to differentiate gestational pyelonephritis with appendicitis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, renal colic due to urolithiasis, ARVI (with the prevalence of general symptoms of the infectious-inflammatory process), ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption.
Treatment
You will take antibiotics for 3-7 days or as recommended by your doctor. If your infection is causing you discomfort, your doctor will likely begin treatment before you receive your urine test results.
Symptoms should disappear after 3 days. In any case, take all medications as scheduled. Do not stop treatment even if your symptoms disappear.
Many common antibiotics—such as amoxicillin, erythromycin, and penicillin—are considered relatively safe for pregnant women. Your doctor will not prescribe other drugs such as sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, which may affect your baby's development.3
Diagnosis of kidney infection
The diagnosis and treatment are determined only after laboratory testing. A pregnant woman is prescribed:
- bacteriological examination of urine;
- urine analysis using the Nechiporenko method;
- general urine analysis;
- general blood analysis.
All tests are taken once a month by every pregnant woman; if necessary, the attending physician may ask for additional tests. If a preliminary laboratory report confirms the presence of the disease, instrumental diagnosis is prescribed using:
- ultrasound examination of the urinary system, kidneys and adjacent organs;
- radioisotope research;
- X-ray examination;
- computed tomography.
For information! Ultrasound allows you to determine the size, damaged structure and changes occurring in the kidneys.
Most often, diagnosis consists solely of ultrasound, this is due to the possible mutagenic effect of the equipment on the fetus.
What are the dangers of UTI during pregnancy without treatment?
Although the incidence of UTIs among pregnant women is only slightly higher than among non-pregnant women, the consequences for both the mother and the unborn child are more serious.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
The only serious consequence of untreated asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women is a significant risk of developing acute pyelonephritis in late pregnancy (30–40% versus 3–4% with its treatment). Although some studies have also demonstrated an association between this condition in pregnant women and the risk of preterm birth and/or low birth weight, some other studies have failed to prove this association. 1
Symptomatic urinary tract infection
Pyelonephritis, which in 15-20% of cases is accompanied by the presence of bacteria in the urine, can cause various complications, such as acute kidney injury, anemia, hypertension, preeclampsia, sepsis and septic shock, hemolysis, thrombocytopenia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, especially if treatment is started too late. Although such a cause-and-effect relationship has not always been proven.
A number of observational studies have demonstrated an association between maternal UTI symptoms and the risk of preterm birth and low birth weight. Moreover, the frequency of premature births in women with acute pyelonephritis is significantly higher than in women without this complication. However, it is difficult to assess the overall contribution of UTIs specifically to preterm birth.
A rare but serious complication is transmission of the infection to the newborn. Very often, transmission occurs due to the birth canal being heavily colonized by bacteria, usually group B streptococci (GBS). 1
Causes
The classification of the causes of gestational pyelonephritis includes:
- Changes in the hormonal levels of a pregnant woman. As a result of the influence of progesterone, the muscles of the bladder relax, the ureters and renal pelvis expand, and as a result, the outflow of urine slows down and blood flow in the kidney tissue is impaired.
- Changes in the anatomy of the bladder in late pregnancy due to its compression by the enlarged uterus.
The resulting stagnation of urine in the bladder provides favorable conditions for the growth of bacteria. Rising up the ureter, bacteria penetrate the renal pelvis and cause inflammation. Inflammation further slows down the flow of urine from the kidney, thus provoking itself.
- Physiological decrease in the immunity of a pregnant woman. More often, inflammation is caused by the flora already present in the body of a pregnant woman, in particular, intestinal flora - E. coli and other enterobacteria. Under normal conditions, these microorganisms exist in the body without causing disease. Decreased immunity favors their reproduction.
Why are UTIs more common during pregnancy?
Hormones are one of the reasons. During pregnancy, they cause changes in the urinary tract, which increases the likelihood of infection.
Additionally, your growing uterus puts pressure on your bladder. This makes it difficult for all urine to leave the bladder. And urinary retention creates favorable conditions for bacterial growth and ascending infection.3
Additional predisposing factors include pregnancy-specific changes in urine composition—increases in glucose, amino acids, and hormone breakdown products that increase urine pH. 1
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
Bacteriuria can trigger premature birth.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is most often fraught with premature birth and excessively low baby weight. In situations where bacteriuria is not treated, there is a high risk of kidney failure. If bacteriuria is treated, the risk of development is reduced several times. To detect bacteriuria, the patient will need to undergo a general blood test, and often resort to ultrasound examination, which shows abnormalities in the renal pelvis.
In cases where bacteria are detected, the specialist prescribes the use of antibiotics that are harmless to pregnant women.
The duration of therapy is a week, after which the patient needs to undergo a control blood test to ensure that the bacteria are cured. In cases where the infection is not eliminated, doctors prescribe an additional course of treatment, prescribing a different antibiotic.
Return to contents
Treatment of infections
For infectious diseases, treatment is prescribed exclusively by a doctor, since most medications are prohibited for pregnant women. Therapy is carried out especially carefully for up to 12 weeks, during which time organs are formed and the use of antibacterial agents is contraindicated. Urinary tract infections in pregnant women that lead to the development of cystitis are treated with medication. If “light” medications do not have the desired effect, then after 3 months of pregnancy, protected penicillins and cephalosporins are prescribed; after 6 months, the latest generation cephalosporins are prescribed. After completing the course, the urine test is taken again. To restore beneficial microflora, cranberry juice and phytouroseptics are effective.
Pyelonephritis requires special attention during pregnancy; in most cases, treatment takes place in a hospital setting, where antibiotics are administered intravenously and then replaced by oral administration. It is very important to monitor the condition of the fetus during therapy to avoid complications and premature birth. To avoid recurrent inflammation, the course must be completed to the end. The drug “Kanaferon” has proven itself well; it is quite safe during pregnancy, as it has a natural composition.
If the acute form of the disease manifests itself after 30 weeks, then this is fraught with consequences for the mother and child. To avoid risks, a caesarean section is performed.
Return to contents
Complications
The disease is prone to recurrence.
Without treatment, premature birth is possible.
Infectious kidney diseases are complicated by the formation of stones and the transition from acute to chronic. Gestational pyelonephritis significantly increases the risk of developing late gestosis.
Acute purulent pyelonephritis causes a complication in the form of urosepsis, leading to the development of acute renal failure. This complication is threatening for both the mother and the fetus, and requires emergency hospitalization and hospital treatment.
If the infection penetrates the fetoplacental barrier, intrauterine infection of the fetus is possible.
UTI classification
As in non-pregnant women, there are two types of urinary tract infections:
- asymptomatic bacteriuria , when the infection is limited only to bacterial growth in the urine;
- symptomatic infection (acute cystitis, acute pyelonephritis), when bacteria penetrate the tissues of the urinary tract, causing inflammation.
Although the incidence of bacteriuria in pregnant women is only slightly higher than in non-pregnant women, its consequences for both the mother and the unborn child are more serious. There is a much higher risk (up to 40%) of progression to pyelonephritis and possibly an increased risk of preeclampsia, preterm birth and low birth weight. 1
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease depend on its clinical form.
Acute pyelonephritis begins abruptly. General symptoms indicating the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process in the body (fever, poor health, joint and muscle pain, profuse sweating) accompany specific symptoms of kidney damage. The woman notes pain in the lower back, which often radiates to the groin, thigh and spreads to the upper abdomen. When urinating, pain is possible, urination disorder may occur, and it becomes more frequent. Sometimes general symptoms are more pronounced than specific ones.
In the chronic form, the disease develops gradually.
Important! Chronic kidney infections are often asymptomatic. In this case, bacteria are found in the urine, but the disease does not manifest itself clinically, and the woman feels well.
Methods for diagnosing urinary tract infections in pregnant women
To identify the problem, the expectant mother needs to undergo a urine test.
Diagnosis of genitourinary tract infections in pregnant women is standard. To do this, the patient’s medical history is studied, if time permits, a gynecological examination is performed and a smear is taken for bacteriological culture. General urine and blood tests are prescribed. They show the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and can identify the source of the disease. If the doctor has doubts, the tests are ordered again. If the kidneys are damaged, the woman undergoes an ultrasound; this is the only approved method with minimal impact on the fetus. If urgently necessary, radioisotope and x-ray examinations are carried out.
Return to contents
Sources used:
- https://ginekolog-i-ya.ru/infekcii-mochevyvodyashhih-putej-u-beremennyh.html
- https://budumama.club/zdorove-beremennoj/imp
- https://prourinu.ru/nedugi/eshe/infektsiya-mochevyvodyashhih-putej-u-beremennyh.html
Causes of infection
The formation of infections of the genitourinary system during pregnancy is considered the most common. According to statistics, 10% of pregnant women suffer from such infections:
- pyelonephritis;
- acute cystitis;
- bacteriuria is asymptomatic.
The reason for the formation of bacteria in the genitourinary system is the anatomical feature of the structure of the female genital organs. The genitourinary organs are located close to the anus, which is quite short, which in turn facilitates the movement of bacteria through the canal to the kidneys and bladder. During pregnancy, the urinary system:
- reduces the ability of muscles to contract in different parts;
- the renal pelvis expands and increases in size;
- the ureters acquire an elongated shape;
- the kidneys are displaced;
- the movement of urine slows down.
For information! Progesterone is able to relax the muscles in the body of a pregnant woman, resulting in stagnation of urine and the proliferation of bacteria and microorganisms.
As a rule, the main changes in the female body occur at the 12th week of pregnancy, which contributes to a greater risk of infection in the kidneys. Another reason for the formation of the disease can be simple non-compliance with personal hygiene rules, chronic forms of diseases and endocrine system disorders.
Urinary tract infections: management of pregnant women with acute pyelonephritis
Unlike cystitis, treatment of pyelonephritis is carried out exclusively in a hospital setting, since there is a high probability of serious and dangerous complications for mother and baby. Thus, 2% of patients with gestational pyelonephritis may develop septic shock, a severe life-threatening condition. All this confirms the need for special monitoring of the condition of mother and baby.
In the urology department, the patient undergoes monitoring of vital functions (respiration, blood circulation, etc.), bacteriological examination of blood and urine. One of the following antibiotics is also administered intravenously:
- amoxicillin/clavulanate;
- cefuroxime sodium;
- ceftriaxone;
- cefotaxime.
The duration of antibacterial therapy for pyelonephritis should be at least 14 days: intravenous administration is carried out for 5 days, then switch to tablet drugs.
The lack of improvement within 48-72 hours can be explained either by obstruction of the urinary tract (urolithiasis or narrowing of the ureter), or by resistance (resistance) of microorganisms to the treatment.
In the first case, the following are necessary: catheterization of the ureter in case of narrowing, surgical treatment for urolithiasis; in the second - changing the antibacterial drug under bacteriological control.
Also, if treatment is ineffective, it is necessary to prescribe “suppressive” therapy or conduct a urine culture every 2 weeks before delivery.
Prevention
For women who are planning a pregnancy or are already pregnant, it is important to adhere to rules that will help avoid the occurrence of urinary tract infections. To begin with, for women who are just planning a pregnancy, it is important to treat chronic diseases and eliminate possible sources of infection and inflammatory processes. In situations where women have endocrine pathologies, you need to consult a doctor who will prescribe a set of medications with the help of which the hormonal levels will return to normal.
During pregnancy, you should drink plenty of fluids. Not only water is taken into account, but also all liquids that enter the body, for example, teas, compotes, herbal decoctions and soups. However, it is important to note that only those pregnant women who do not have severe edema should follow a heavy drinking regime. It is important to empty your bladder on time when you feel the urge, even when it is not full. This rule plays a key role, since accumulated urine in the bladder puts pressure on the uterus, which can lead to miscarriage.
In addition, during pregnancy the patient is prohibited from douching. Instead, you should consult your doctor and choose a different path to treat your illnesses. The patient also needs to take care of personal hygiene. During pregnancy, it is forbidden to take a bath, and it is better to change underwear every day. We should not forget that pregnancy should proceed under the constant and careful supervision of the attending physician. If the patient experiences changes in her condition and new symptoms appear, she should immediately consult a doctor and find out the cause.
etopochki.ru
Kidney infections during pregnancy
Pregnancy is not only pleasant moments of waiting to meet your baby, but also a complete transformation of the functionality of all internal systems and organs. A woman’s body experiences severe stress, especially in the last trimester. During this period, the immune system decreases, physiological changes in the urinary system occur and all the conditions are created for the formation of infection in the kidneys. In this article we will talk about kidney infection during pregnancy, its symptoms, causes of formation and treatment methods.
Urinary tract infections: acute and chronic pyelonephritis
In 20-40% of pregnant women with lower urinary tract infections (cystitis, urethritis, asymptomatic bacteriuria), acute pyelonephritis develops - an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, which is characterized by damage to the cups and pelvis with impaired organ function.
Gestational pyelonephritis most often occurs in the second and third trimesters, and relapses occur in 10-30% of pregnant women. In the majority (75%) of women, only the right kidney is affected, in 10-15% - only the left, in 10-15% - both.
In addition to urination disorders, acute pyelonephritis, unlike cystitis, has pronounced general manifestations. Here are the main complaints of patients with this disease:
- sudden increase in body temperature, chills,
- nausea, vomiting,
- weakness, lethargy,
- pain in the lumbar region,
- muscle pain and headaches,
- decreased appetite.
In a general urine test, in addition to leukocyturia, protein and red blood cells can be detected. Laboratory markers of pyelonephritis in urine examination, including microscopy and bacteriological culture, are similar to those for acute cystitis:
- leukocyturia (more than 10 leukocytes in 1 μl of non-centrifuged urine);
- bacteriuria (number of microorganisms more than 104 CFU/ml).
Also, to assess the patient’s condition, a clinical and biochemical blood test is performed, which may reveal:
- increased level of leukocytes,
- decrease in hemoglobin,
- acceleration of ESR,
- increase in the concentration of urea and creatinine, etc.
The influence of the disease on the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus
Like any infectious disease, pyelonephritis has a negative impact on the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus. Bacteria, as well as their toxins, can penetrate the uteroplacental barrier and cause intrauterine infection.
- In the first trimester, infection can cause the death of the embryo.
- After the formation of the placenta, from the 14th week, feto-placental insufficiency may develop against the background of pyelonephritis. This chronic circulatory disorder causes a lack of oxygen in the fetus and intrauterine growth retardation.
The infection may not appear immediately, but will play a role during the first years of the baby’s life. Such children often get sick, especially during seasonal epidemics of respiratory diseases.
The main danger of pyelonephritis during pregnancy is the high probability of developing severe pathology, late toxicosis, or gestosis. This pregnancy complication combines a number of symptoms:
- increased blood pressure;
- loss of protein in urine;
- chronic intrauterine fetal suffering.
The most severe degree of gestosis is eclampsia, or convulsions. This emergency condition, which threatens the life of the woman and the fetus, can occur during pregnancy, before childbirth and directly during the process. In rare cases, eclampsia develops in the early postpartum period.
In addition, the presence of an infectious focus in the kidneys after childbirth can provoke inflammatory processes in the uterus - postpartum endometritis.
Urinary tract infections: treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria and acute cystitis
Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria and acute cystitis is carried out on an outpatient basis; these conditions do not require hospitalization. It is necessary to be especially careful when selecting an antibacterial drug, because it must be not only effective, but also safe.
The choice of medications is made by the doctor. For the treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria or acute cystitis, fosfomycin trometamol (monural) 3 g once or a 7-day course of one of the following antibiotics is prescribed:
- amoxicillin/clavulanate 375-625 mg 2-3 times a day;
- cefuroxime axetil 250-500 mg 2-3 times a day;
- ceftibuten 400 mg once daily;
- cefixime 400 mg once a day;
- nitrofurantoin 1000 mg 4 times a day.
After 7-14 days from the start of treatment, a urine culture test is performed. If the test results confirm a positive effect, then no further treatment is required and the patient remains under medical supervision. At the same time, she needs to undergo a control urine culture once a month.
If treatment is ineffective, the woman is prescribed so-called “suppressive” therapy until the end of pregnancy and for 2 weeks after birth with monthly bacteriological monitoring. Recommended regimens of “suppressive” therapy: fosfomycin trometamol (monural) 3 g every 10 days or nitrofurantoin 50-100 mg once a day.
Also, if the antibacterial treatment is ineffective, it is necessary to exclude urolithiasis and strictures (narrowing) of the ureter, which aggravate the infectious process. In this case, the issue of the need to catheterize the ureters is resolved - inserting a catheter into them.