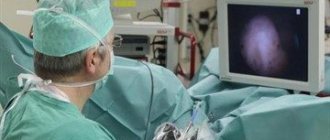
Signs of urolithiasis
Considering the location of the stone, the signs of the disease may vary. But the main symptoms include:
- Painful attacks in the back or side, under the ribs. They can shift if the stone moves;
- Blood in the urine . Before their appearance, renal colic occurs. Cloudy urine that has sediment or an unpleasant odor can be another confirming factor that the stone has begun to move;
- Poor health , expressed by nausea or vomiting. Such signs are most characteristic of pyelonephritis - an inflammatory process;
- Output of sand or stones. At this time, chills may appear and the temperature may rise.
Diagnosis of stones in the bladder
As soon as the first signs of stones appear, you should visit a doctor who will perform diagnostics and determine the correct diagnosis.
The diagnostic methods are as follows:
- Visual examination, palpation , if necessary, rectal examination to determine prostate adenoma;
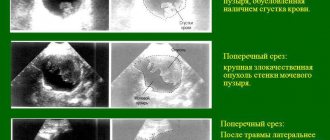
- Ultrasound examination . With its help, the presence, location, size and shape of stones are determined;
- Submitting urine for analysis to detect the presence of salts, bacteria, and leukocytes. These signs determine the likelihood of genitourinary infection;
- Cystoscopy . A visual examination of the internal structure of the bladder is performed;
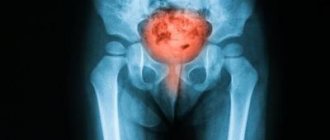
- Spiral computed tomography . It is considered the most accurate method, capable of identifying even the smallest stones;
- Intravenous pyelography. X-rays will help identify pathological changes.
Procedure Details
In men, surgery to remove stones from the bladder can be performed in two ways - open or removal through the urethra. The advantage of the second option is a short rehabilitation period and a low likelihood of injuries or infections. But such intervention is only possible if the size of the stone is not large enough.
The open method is suitable for four-millimeter stones, or there are obstacles that prevent the introduction of a cystoscope. The method is very traumatic and is accompanied by dissection of the skin.
Indications for surgery may include lack of results after therapeutic treatment, numerous infections in the ureteral canals, signs of severe fluid retention, and pain that is not relieved by therapy.
Preparation and progress of the operation
Urine and blood samples are taken for analysis in advance. It is imperative to visit an anesthesiologist in order to correctly assess the risks and choose the appropriate anesthesia. The surgical field is prepared for shaving the groin area.
Before the operation begins, the bladder should be emptied.
With the open method, access to the organ in the area above the pubis is performed in stages. Each urethral membrane is cut in layers, the stone is removed from the cavity, then everything is sutured in the reverse order.
In the second case, the urea is first flushed through the catheter to remove the remaining liquid. Then a cystolithotripter is inserted, the labial ends of which are brought together.
Having filled the bladder and inspected the walls, it is necessary to evaluate the location of the instruments in relation to the stone.
After this, the teeth open, the stone is captured, crumbled into small stones, and the fragments are removed. The main advantage of the method is that all actions can be observed visually.
Quick removal of stones at home
To remove stones, it is best to go to a medical facility. If this is not possible, you should try to remove the formations using home methods. The simplest and most effective way is to drink plenty of liquid.
Small stones under pressure will gradually come out on their own.
After removal, the stone must be submitted for analysis.
Some patients benefit from warm medicinal baths. This procedure is effective in the presence of acute persistent pain and a burning sensation. Warm water helps relax muscles, dilate blood vessels, and normalize blood circulation. The walls of the ureter also expand under the influence of temperature. To obtain the greatest effect, you can add a couple of drops of essential oil or decoctions of medicinal herbs to the water. The time spent in hot water should not exceed 20 minutes.
Home treatment can be combined with diuretic infusions and decoctions. According to some data, such drugs work much better than synthetic diuretics. Among other things, herbal medicines are safe and have virtually no contraindications.
Possible complications
Such surgical intervention does not entail problematic issues. However, there is a possibility of bleeding and infection in the lower parts of the ureteral canals.
Currently, urolithiasis is one of the most common pathologies. According to statistics, 50% of patients who seek help from a specialist suffer from this disease. In cases where conservative treatment methods are powerless, the doctor decides to perform surgery to remove stones from the bladder. In medical language, this surgical intervention is called cystolithotomy.
After stone removal
It must be remembered that any procedures for crushing or removing stones are not a method of treating urolithiasis. These are only options for eliminating the consequences of the disease. After the patient leaves the hospital, it will be important for him to continue to follow all medical recommendations. It is important to prevent the recurrence of stones in the ureter. To do this, you will need to follow a special diet, drinking regime is important (at least two liters of clean drinking water during the day). Herbal medicine is also prescribed. Every three months it is necessary to visit the treating specialist in order to undergo repeated examinations. After a year, examinations are carried out every 6 months.
Urolithiasis: causes, symptoms
This pathology can occur in people of any age. The disease is characterized by the formation of stones in the bladder, kidneys or ureters.
At present, there is no single picture of the mechanism of development of the disease, and the reasons for its occurrence are also not fully understood.
However, it has been proven that the triggering factors for the development of the disease are:
- inflammatory processes in the organs of the urinary system;
- taking certain medications;
- unbalanced diet;
- irregular physical activity or lack thereof;
- low quality of consumed water;
- deficiency of vitamins A and group B;
- unfavorable working conditions;
- metabolic disorders;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- dehydration;
- congenital anomalies of the kidneys and bladder.
Types of stones
The stones that form in the bladder may differ in chemical composition, size, density, shape and other properties. Based on their composition, the following types of bladder stones are distinguished:
- oxalate. These are brown neoplasms based on oxalic acid salts, which cause severe pain, causing microdamage to the mucous membranes, resulting in red specks appearing in the urine;
- urate. Such stones appear with gout and lack of water in the body, they do not injure the mucous membrane and have a smooth surface;
- cystoneaceae. They are distinguished by their hexagonal shape and are formed in the body due to congenital metabolic pathologies that cause an increase in cystine levels;
- phosphate. Such stones can be detected if the patient has hormonal imbalance or weakened immunity; they are elements of a light gray hue, have a fragile structure and are easily crushed;
- struvite. They are formed when bacteria appear that cause an alkaline reaction and lead to the formation of precipitates of magnesium, phosphate, carbonate or ammonium.
- combined. They usually have increased hardness and several types of salts are involved in their creation.
Indications and contraindications for cystolithotomy
Surgical removal of stones from the bladder is prescribed mainly when drug therapy is ineffective.
In addition, indications for surgery are:
- Acute urinary retention. This is a condition in which there is a strong urge, but a person cannot empty the bladder on his own.
- Increased number of red blood cells in urine.
Surgical intervention is not performed if there are obstructions in the urethra (in men) or infectious diseases of the bladder. Also contraindications are pregnancy and the presence of tumors on the organ.
Preparation
Before surgery to remove stones from the bladder, you need to have your urine and blood tested.
In addition, you must undergo the following types of research:
- Ultrasound of the vesical triangle. This is an area located in the bottom of the organ. It is of great diagnostic importance, since it is in this area that inflammatory processes often develop.
- Spiral CT. One of the most informative research methods. With its help, the doctor receives a complete picture of the structure of the bladder and all existing diseases of the organ. The essence of the method is layer-by-layer scanning, the result of which is a two- or three-dimensional image.
- Intravenous pyelography. Allows you to assess the degree of kidney function. To do this, a special substance is injected into the person, after which an image is taken using X-ray equipment.
If, based on the results of all studies, no contraindications are identified, the patient is sent for surgery.
What to do after crushing kidney stones. Ultrasonic crushing
The procedure is prescribed if the size of the stones exceeds ten to twenty millimeters. It is carried out in laboratory conditions. There is a possibility of complications, so specialists should have a rehabilitation kit on hand. Today, there are three types of stone removal using ultrasound:
- extracorporeal crushing. Can be used in case of detection of stones with a diameter of up to thirty-five millimeters. The shock wave is directed to a specific point on the stone. At the peak of energy tension, the stone is divided into several smaller formations. The procedure takes up to forty minutes. If the result is successful, the patient can be discharged the next day;
- remote. The acoustic wave is focused at a certain point, thereby not damaging soft tissue. The complexity of the method lies in the need to accurately target the wave, since the effect of its action is felt in the small area to which it is aimed.
- contact. The impact of ultrasound occurs at the site of contact of the stone with the genitourinary tract. After crushing, the fragments are removed using a nephroscope or urethroscope.
Many people are interested in: how are kidney stones crushed? The whole operation consists of the following steps:
- determining the exact location of the stone;
- placement of an ultrasonic sensor over the location of the stone;
- exposure of the stone to high-intensity rays (ten to fifteen minutes);
- removal of small fragments using a nephroscope or urethroscope (optional).
Depending on how exactly the kidney stones were crushed with ultrasound, the patient may leave the hospital one to four days after the operation. After two weeks, intravenous urography is performed. It can be used to determine whether there is still a stone in the kidney and whether there is a possibility of blocking urine flow.
Transurethral method of cystolithotomy
This method of removing stones from the bladder is one of the endoscopic methods of intervention. It is considered the most gentle and is used in practice most often. Its essence is as follows: the operating channel of the cystoscope (it can be looped or basket-shaped) is inserted into the bladder, captures small stones and brings them out.
Large stones must first be crushed. This process is called cystolithotripsy.
It can be of 2 types:
In the first case, not only a cystoscope, but also a lithotripter is inserted transurethrally. It acts on the stone with an energy flow, crushing it into small parts, which are then easily removed from the organ.
Remote cystolithotripsy is used less frequently in practice due to its low efficiency rate. It is carried out as follows: the device is placed outside the human body, after which the process of generating a shock wave is started, which affects only the stones, without having a negative effect on soft tissues.
Removal of stones from the bladder in both men and women is done through the urethra.
How is bladder stones removed?
Urolithiasis is a pathology caused by a metabolic disorder that results in the formation of stones in the urinary tract.
Most often, stones appear in the kidneys, ureters, and bladder. Most often, urolithiasis is accompanied by pain in the groin and lower back, however, asymptomatic disease can also occur
Urolithiasis: a brief description
Bladder stones mainly affect men over 50 years of age and boys under 7 years of age. This statistics is explained by various diseases of the urinary system in adult men and the narrowness of the urethra in children.
There are single and multiple stones. By their nature, stones are :
- primary (formed directly in the cavity of the bladder);
- secondary (entered the bladder with a stream of urine from the kidneys or renal pelvis.).
The causes of stone formation in the bladder in men include:
- violations of organ emptying of various etiologies (prostatic hypertrophy, prostate sclerosis, stenosis of the bladder neck, neurogenic pathologies, narrowing at various levels of the ureters);
- urolithiasis of the kidneys or ureters;
- the presence of a foreign body in the organ;
- cystoptosis or protrusion of the organ wall;
- any anomalies in the anatomy of the urinary system;
- urinary system infections;
- prolonged presence of drainage in the urinary tract
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms and clinical course of the disease depend on the degree of movement of stones in the organ and their location. Cystolithiasis is characterized by the so-called triad of symptoms: pain, hematuria (the appearance of traces of blood in the urine), and the passage of stones in the urine. Sometimes patients have only one or two symptoms.
Small stones block the urethra and cause severe pain. Pain may increase during movement. A reliable sign indicating the presence of stones in the bladder is interruption of the stream during urination. In this case, urination occurs normally in a horizontal position of the patient, so in some cases patients with cystolithiasis can only urinate while lying down. If the stone wedges into the neck of the organ or gets into the urethra, then acute urinary retention will occur.
Treatment methods
Treatment of cystolithiasis includes:
- pain relief;
- normalization of urine excretion;
- stone-expelling therapy, or destruction and removal of stones;
- prevention of various complications;
- preventive measures to prevent the formation of new stones.
Stone expulsion therapy is suitable for stones not exceeding 4 mm in diameter. Only with this size of the stone is its spontaneous passage possible. In cases where the stones in the bladder are larger, their removal is indicated.
bladder stones are currently practiced
- remote cystolithotripsy;
- contact cystolitripsy;
- cystolithotomy.
Cislithotripsy is the crushing of stones, cislithotomy is stone cutting.
External lithotripsy
A method based on the impact of a focused and directed shock wave on a stone, causing its destruction. The lithotripter is represented by a shock wave generator, a focusing and targeting system for a foreign body. Localization and focusing occurs through beam guidance (X-ray and/or ultrasound). This method of breaking stones is suitable if they do not exceed 1.5 cm in diameter.
In addition to limiting the use of the method by the size of the stones, there are a number of contraindications to extracorporeal lithotripsy.
External lithotripsy is a method of treating urolithiasis based on hardware crushing of stones with a shock wave
Technical contraindications:
- the patient's body weight is more than 200 kg;
- height more than 2 m;
- disorders of the musculoskeletal system that do not allow accurate focusing.
General somatic contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- poor blood clotting;
- serious disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
Urological indications:
- acute inflammatory processes of the urinary system;
- severe renal failure;
- obstruction of the urinary tract below the stone.
Contact cystolithotripsy
Second in frequency after remote. This operation is carried out by inserting a special endoscope through the urethra, which destroys the stones to a small size and washes out its remains. The method is considered non-invasive, since it does not violate the integrity of the skin. The procedure is performed under local or spinal anesthesia. Cystolithotripsy can be of the following types (depending on the method of destruction of stones):
The most effective type of contact lithotripsy is laser. Ultrasound lithotripsy only works on low-density stones. When performing pneumatic (compressed air acts on the stones) cystolithotripsy, damage to soft tissues is possible. There is a possibility of remnants of stones being thrown into the kidneys.
There are also several contraindications to contact cystolithotripsy.
Method of contact cystolithotripsy: 1 - endoscope; 2 - prostate; 3 - bladder stones.
General somatic contraindications:
- presence of a heart pacemaker;
- acute respiratory failure;
- pregnancy;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract during exacerbation.
Urological contraindications:
- inflammatory processes in the urethra;
- small bladder volume;
- prostatitis.
Cystolithotomy
But, in some cases, open surgery may still be prescribed. Indications for such interventions are:
- anatomical features of the bladder;
- acute inflammation of the urethra;
- large size of the stone.
Cystolithotomy is performed under general anesthesia. After the intervention, catheterization of the bladder is performed for some time. Unpleasant side effects of this procedure are: large incision, surgical risks, long rehabilitation period. But there are also advantages of cystolithotomy: quick results, no trauma to the urethra (which is especially important for children).
Possible complications and preventive measures
As a rule, there are no complications after stone removal. In rare cases, a secondary infection may occur and postoperative bleeding may develop. Removing stones from the bladder does not affect men's health. The prognosis for operations is favorable. When the underlying disease is eliminated, recurrent stone formation does not occur.
As measures to prevent the development of urolithiasis, men are recommended to drink at least 2.5-3 liters of water per day, consume less salt and animal protein. It is necessary to follow a diet, limit stress and monitor balanced fluid loss. A specialist may prescribe a special diet.
Open method of cystolithotomy
Abdominal surgery is a surgical intervention that is prescribed in cases where there are large stones and they cannot be crushed and removed using a cystoscope.
After general anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision with a scalpel in the area above the pubis. Once access to the bladder is gained, the doctor opens it. This is also done through an incision. After examining the cavity of the bladder, the surgeon removes the stones, after which he sutures both it and the wound.
The open method is considered the most aggressive. After surgery to remove stones from the bladder, both women and men may experience complications. To reduce the likelihood of their occurrence, it is necessary to contact only trusted medical institutions and highly qualified specialists.
MINIMALLY INVASIVE METHODS
Contact ureterolithotripsy
Transurethral manipulation, which is performed through the natural urinary tract. During the procedure, the ureteral stone is crushed into small pieces using ultrasound, pneumatic or laser lithotripter and the fragments are removed using a Dormia basket.
Efficiency – 95%.
Cystolithotripsy
Transurethral fragmentation of bladder stones is performed through the urethra using modern optical and surgical techniques.
Efficiency – 100%.
Possible complications
After any surgical intervention there is a small chance of negative consequences. Bladder function may be impaired after stone removal. As a rule, this manifests itself in the form of difficulty urinating. It bothers you for a short time, but in some cases it can become protracted.
Other possible complications:
- bleeding (it can appear either immediately after surgery or after a few days);
- infectious diseases;
- hernia;
- fistulas;
- urosepsis.
If any of these conditions occur, drug therapy is indicated. If it does not bring visible results, urgent surgery is indicated.
It is worth noting that complications most often appear after open surgery.
Price
The operation is performed both in public hospitals and in private clinics. Regarding how much it costs to remove stones from the bladder, you need to check with the selected institution. In some public hospitals, abdominal surgery is performed free of charge (if you have an insurance policy) or for a minimal cost (about 1 thousand rubles). The average price for removing bladder stones in Russia is 15 thousand rubles. In most cases, the operation is performed transurethral method.
Removing stones at home
If getting rid of stones from the ureters using medical methods is not suitable or there is a desire to use exclusively traditional medicine at home, then the following methods can be used.
One of the most important ways is to drink large amounts of liquid; using this method you can get rid of small stones.
You can also use medicinal baths. They are effective in case of acute pain and burning. Herbal decoctions and essential oils are added to medicinal baths. A warm bath helps to relax, dilate blood vessels, improve blood circulation, and most importantly, dilate the walls of the ureter. You should not stay in such a bath for more than 20 minutes, since a long stay in hot water may not help, but rather aggravate the existing problem.
Herbal decoctions are also very helpful. You should take diuretic infusions.
Some doctors claim that diuretic decoctions prepared at home are more effective than synthetic diuretics because they have fewer components and contraindications.
Who needs surgery
Who needs surgery:
- patients whose urolithiasis cannot be treated with drug therapy;
- if non-contact methods of crushing stones do not achieve the desired effect;
- if a male patient develops a life-threatening symptom.
Dangerous symptoms are:
- severe renal colic;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the groin;
- severe discomfort when urinating;
- blood-stained urine;
- constantly elevated body temperature.
Symptoms
The effectiveness of treatment for cystolithiasis depends on how quickly the patient seeks medical help. It is recommended to immediately consult a urologist as soon as symptoms occur:
- pain in the lumbar region and lower abdomen, intensifying when urinating;
- increased frequency of urination;
- change in urine color (presence of blood, cloudiness);
- false urge to urinate;
- increased body temperature;
- A symptom of urine blockage is a sudden interruption of the urine stream during urination.
Preparing for surgery
Preparing for surgery to remove bladder stones involves performing the following procedures:
- Laboratory tests: general urine and blood tests. Possibly also blood biochemistry and clotting tests.
- Hardware diagnostics: ultrasound, computed tomography, survey and contrast urography, pyelography.
At the stage of preparation for surgery, the doctor determines the type of anesthesia that is suitable for a particular patient and the method of removing stones. Thus, it can be local and general anesthesia.