The procedure is not a routine examination and is prescribed to the patient based on certain indications. As a rule, the reason for histological analysis is cancer or suspicion of it, tuberculosis, cystitis of long-term and unknown etiology.
The main idea is to take a tissue sample and then analyze it in the laboratory. There are two methods of bladder biopsy used in practice.
Most often, a bladder biopsy is performed when cancer is suspected.
Indications for use
A referral for testing is given by a doctor (urologist, nephrologist, oncologist, surgeon or other specialists).
The basis is the patient’s complaints or the presence of characteristic symptoms:
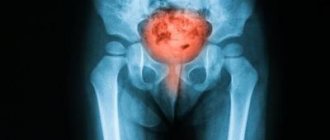
- tumor in the bladder;
- pretumor condition, precancer (malakoplakia and leukoplakia);
- interstitial cystitis;
- the presence of a tuberculosis process;
- frequent pain in the lower part of the peritoneum;
- discomfort when urinating;
- the presence of blood in the urine (which may be noticeable to the eye or an increased number of red blood cells in a general analysis);
- pathologies of urination, for example, retention, incontinence, feeling of incomplete emptying and others;
- ineffectiveness of the therapy provided;
- development and aggravation of chronic bladder diseases.
Note. In practice and in the medical literature, there are other names that can denote the same procedure, for example: endovesical biopsy, cystoscopy with biopsy, multifocal biopsy of the bladder mucosa.
Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen is a reason to examine the bladder
Results of histological and cytological examination of the material
The results of the biopsy submitted to the laboratory are received by the attending physician in about a week. After deciphering the received data, the urologist makes a preliminary diagnosis and discusses the existing problem with the patient.
During such diagnostics the following may be revealed:
- Norm. No abnormal cell changes were detected, and the alarming symptoms were most likely caused by the influence of external or internal (infectious lesions, nutritional disorders, etc.) factors. In this case, a repeat study is necessary to accurately confirm the absence of a possible false negative result.
- The presence of cellular elements degenerated into a malignant type. The patient is given a presumptive diagnosis of bladder cancer, and additional diagnostic tests are prescribed to confirm or refute the onset of a malignant tumor, to clarify its nature and the degree of invasion of the walls of the urinary storage organ.
Important! The results of cytological and histological examination of modified tissues taken from the walls of the urinary storage organ play a decisive role in choosing a treatment regimen.
Contraindications
The analysis is not carried out in case of acute pathologies of the bladder, urethritis, cystitis, as well as in the presence of inflammatory foci in the genitourinary tract. However, if the damage is assessed as less than the expected benefit, then doctors decide in favor of endoscopic manipulation to collect a histological sample.
Important. A complete ban on this procedure applies to people who have problems with blood clotting. In this case, there may be extremely serious complications, so a different technique is chosen for analysis.
Due to the long urethra for men, cytoscopy is a rather painful procedure, both physically and mentally.
Cystoscopy with biopsy
A cystoscope is a tubular device with a light that is inserted into the urethra to examine the bladder. Typically, the procedure is performed using local anesthesia. Sometimes general anesthesia is used, and in this case it is not recommended to eat food 8 hours before the cystoscopy.
With careful insertion of the cystoscope, the procedure is not accompanied by inflammatory processes, pain, or subsequent deterioration of urine outflow
When carrying out this procedure to examine the bladder and take a biopsy in men, it is recommended:
- Do not empty your bladder for 1 hour before the procedure.
- If you have a history of adenoma and prostatitis, do a cleansing enema.
- During the procedure, take a horizontal position.
Taking into account the physiological structure, insertion of the device in women is much easier than in men. To facilitate the task, the cystoscope used should be as thin as possible, and the doctor should have a high level of qualifications. An examination cystoscopy takes a few minutes, and if it is accompanied by a biopsy, the procedure can take 1 hour.
Preparation and execution
Some sources indicate a whole range of measures from complete cleansing of the intestines to fasting on the eve of the study and others. It is important to understand that in this case there is no special preparation, since the manipulations are performed on an outpatient basis (during hospitalization in a hospital). Before the procedure, you do not need to eat in the morning, it is advisable not to drink, therefore, the patient comes to the clinicians on an empty stomach. One hour before the procedure, you should not urinate.
Regardless of the type of urinary biopsy (table), in most cases the analysis is done under local anesthesia. Performing under general anesthesia is possible if there are appropriate indications or the patient’s persistent desire.
Table. Comparison of the main methods for diagnosing the bladder:
| Type of biopsy | Peculiarities | Advantages | Flaws |
| Used for small neoplasia or mild erosion. During a cytoscopy, the doctor uses special forceps to pinch off a small sample of tissue. | Low invasiveness | There is no way to determine the stage, because it is impossible to assess the level of tumor growth in depth. |
| Transurethral biopsy is performed using an elastic cytoscope and an electrocoagulator. Using the latter, a sample is taken. | Allows you to select a sample of any size, determine the depth of infiltration, and determine the stages. Low probability of bleeding (tissue coagulation). | Electrical damage. |
Important. TUR for a small tumor up to 1 cm (at the initial stages of pathogenesis) allows for its complete resection, which is equivalent to a low-traumatic endoscopic surgery to remove the tumor.
Types of bladder biopsy
There are two ways to biopsy a bladder:
- Cold. A biopsy is performed during cystoscopy by pinching off a piece of tissue from a suspicious area. The advantage of a cold biopsy is that the resulting material remains intact. The disadvantage is the impossibility of assessing the depth of tumor ingrowth into the tissue.
- TUR biopsy . At its core, this is an operation called transurethral removal. That is, first the doctor removes the formation with an electric knife, and then the removed pieces of tissue are sent for histological examination. The advantage of the method is the ability to assess the depth of tumor invasion. Disadvantage - part of the biopsy material is damaged due to exposure to electric current.
Small tumors (less than 10 mm) are removed monolithically, partially capturing the bladder membrane surrounding the tumor. If the tumor is large, then it is removed in parts. In addition, both the membrane located around the formation and the muscles of the MP are subjected to resection.
Cystoscopy with biopsy - how to do it in men and women
Before undergoing the procedure, consult with your physician and follow their instructions, including prohibiting smoking before and after the procedure. Smokers heal more slowly after surgery. They are also more likely to have trouble breathing during surgery.
For these reasons, if you smoke, you should quit at least 2 weeks before your procedure. It is best to quit 6 to 8 weeks before surgery.
If you need minor pain relief in the week before surgery, choose acetaminophen rather than aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen. This helps avoid additional bleeding during surgery. If you take aspirin daily for a medical condition, ask your doctor if you need to stop taking it before surgery.
The procedure is carried out using a cystoscope - a tubular device equipped with a lamp, which is inserted into the urethra to examine the bladder cavity.
Usually the manipulation is carried out using local anesthesia. But in some cases, general anesthesia is used, and then the patient should not eat food for at least 8 hours before the procedure.
If the cystoscope is inserted carefully, the patient will not feel pain, and subsequently everything goes away without inflammation or worsening the outflow of urine.
If a bladder biopsy is performed in men, the following recommendations should be followed::
- Do not empty your bladder for 1 hour before taking a biopsy.
- Perform a cleansing enema if there is a history of prostatitis or adenoma.
Many women are concerned about the question of whether it is painful or not to do a bladder biopsy. Taking into account the peculiarities of the physiological structure of the genitourinary system, the insertion of a cystoscope in women is much easier and painless than in men.
In order to alleviate the discomfort of patients and the task of the doctor, the device used for the procedure must be thin. A lot depends on the skill level of the doctor.
A survey cystoscopy usually takes only a few minutes, and if it is performed in conjunction with a biopsy, the time increases to 1 hour.
TUR-biopsy - preparation and implementation
To perform surgery, the patient is hospitalized in a urology department specializing in oncological diseases for several days.
Before hospitalization, the patient undergoes an examination, which involves conducting thorough laboratory and instrumental studies.
Both men and women need to pass:
- blood test for RW or test for syphilis;
- clinical blood and urine analysis;
- blood to determine the group and Rh factor;
- electrocardiogram and fluorography.
Patients must be consulted with a therapist and anesthesiologist. In addition, men undergo a rectal examination, women - a vaginal examination.
The day before the intervention, the patient should not eat or drink (even water) in the morning.
The algorithm for performing a TUR biopsy is as follows::
- The patient lies on the operating table with his legs spread and knees bent.
- Through the urethra, the doctor inserts an endoscopic device into the bladder cavity, intended for transurethral electroresection of the urethral neck.
- The organ cavity is filled with a sterile solution.
- Every action performed by the doctor is visualized on the screen of the endoscopic device.
- First of all, a thorough examination of the entire organ is carried out, and then the tumor is resected and a biopsy is taken.
- In order to prevent the risk of extensive bleeding, the vessels of the bed of the removed pathological focus are coagulated with electric current.
- Surgical procedures are completed with catheterization to flush (irrigate) the bladder cavity and administer chemotherapy drugs to prevent relapse of the disease.
In cases of widespread multiple tumors, a repeat biopsy can be taken at the request of the cytologist. However, its implementation is possible only 2-6 weeks after the first intervention. The main guideline in this case is the patient’s condition.
Possible complications
No matter how safe the procedure may seem, it should be remembered that it is a surgical intervention in which the development of side effects cannot be ruled out. The main negative point may be the formation of bleeding, however, TUR analysis significantly reduces this probability due to coagulation (an open wound does not form).
If the patient suffers from chronic pathologies of the genitourinary system, for example, cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis and others, then there is a possibility of their exacerbation.
Where can I undergo the procedure, what is its cost and patient reviews?
A bladder biopsy is a fairly serious intervention in the structure of the main organ of the urinary system, therefore, when prescribing this procedure, it is necessary to decide on the medical institution where it will be performed. It is best if it is a specialized urological center, private or public, staffed by urologists with appropriate qualifications and extensive experience.
The price for a histological examination of the bladder (biopsy and subsequent laboratory analysis of the resulting biopsy) can reach 3,000-5,000 rubles, depending on the cost of the reagents used by the clinic for laboratory testing. Carrying out manipulations alone to collect biopsy material costs 1.5-2 thousand rubles, and is performed in some laboratories without a doctor’s referral. But it is not recommended to carry out such an analysis on your own, since only a qualified specialist can give a competent interpretation.
Reviews of the biopsy from most patients boil down to the fact that this procedure, although it causes a number of unpleasant sensations after the anesthesia wears off, is not as scary as it seems at first glance. In addition, people who have undergone this procedure note its benefits in identifying a dubious diagnosis. According to unambiguous reviews from urologists, the most informative is a tour biopsy, since this procedure allows the doctor to identify dangerous diseases of the urinary system that are not confirmed by other types of diagnostics and prescribe the correct treatment.
Result
As the doctor examines the bladder wall, he sees some changes, such as erosions or tumors, but an accurate diagnosis can only be obtained after a few days because the sample taken must be examined by clinicians.
In order to prepare a specimen for microscopic examination, the tissue undergoes quite labor-intensive processing:
- coloring;
- dehydration;
- waxing;
- cutting on a microtome;
- fixation on a glass slide.
After these procedures, the doctor examines the drug and describes the result. This will be a view of the tumor with a detailed description of its qualities. Thus, the preparation for the analysis is quite long, and the examination of the tissue and the conclusion itself are completed within a few minutes.
After receiving the results, consultations are held with doctors and appropriate treatment is determined, if necessary.
The note. Women tolerate the procedure much easier because their urethra is much shorter than men. For the latter, cytoscopy is a rather unpleasant medical procedure.
After collecting and processing the selected tissue, it is examined under a microscope
Consequences of bladder biopsy and rehabilitation period
Feedback from patients indicates that MP biopsy is usually well tolerated.
However, in some cases, people face consequences in the form of:
- burning and cutting in the urethra;
- frequent urination, but in small portions due to catheter removal;
- bleeding;
- addition of a secondary infection;
- complete inability to empty the MP on your own;
- damage to the walls of the bladder or intestines;
- relapse of pathology.
Postoperative period:
- At the conclusion of the intervention, chemotherapy drugs are introduced into the organ cavity to prevent recurrence of cancer. They also install a urinary catheter for irrigation and control of discharge from the bladder, for example, small blood clots.
- If 2 hours have passed since the end of the operation, and the patient feels relatively normal, then he can drink still water with lemon and eat bland food.
- If spinal anesthesia is used during the procedure, the patient should remain in bed for 24 hours.
- Depending on the extent of the operation and focusing on discharge from the bladder during irrigation, the catheter can be removed on the same day after 2-3 hours. In some cases, the urinary catheter is left in place for several days.
- A course of antibiotics begins 5-7 days after surgery.
- During the rehabilitation period, the patient must adhere to the recommended diet and avoid increased physical activity.
- You should not have sex for two weeks after the biopsy.
What diseases can it detect?
Examination of the tissues of the affected organ at the cellular level is the most informative and reliable method for diagnosing the disease. A bladder biopsy helps identify the following pathologies:
- tumors (benign, malignant);
- bladder tuberculosis;
- interstitial cystitis;
- precancerous diseases.
The results of the biopsy give the doctor the opportunity not only to make an accurate diagnosis, but also to choose the right treatment regimen. This depends on the size of the lesion, the degree and speed of its development. Morphological characteristics are data obtained during the study of a biopsy (material, tissue taken from an organ), which fully describe its condition.
Progress of the intervention
Since transurethral access is the most commonly practiced approach, it makes sense to consider it. The patient is placed on the operating table or placed in a special chair.
After this, the penis and pubic area are treated with a special antiseptic solution. Then endoscopic equipment (a flexible endoscope with a light bulb and a video camera for access control) is inserted into the urethral canal.
The next stage is control over the introduction of the flexible probe. Once the area of interest is reached, a sample is required for subsequent histological and morphological evaluation.
The entire procedure lasts no more than 10-20 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia.