Detection of bacteria in urine can be observed in three cases: contamination of the material collected for analysis, infection of the urinary system, and the presence of asymptomatic bacteriuria in the patient. It is the latter that we will devote this material to.
According to the definition of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, asymptomatic bacteriuria is the isolation of more than 10x5 (for men more than 10x3) bacteria per 1 milliliter of urine in individuals without clinical symptoms of a urinary tract infection.
Let's try to explain it more simply. If bacteria are found in the patient’s urine in quantities exceeding the norm, but the person is not bothered by any symptoms from the urinary system (no cutting or burning when urinating, no pain in the bladder and kidneys, no leukocytes in the urine and no temperature), then this situation is called asymptomatic bacteriuria.
In different countries, the incidence of bacteriuria is 3-25% among the general population. In people who initially have a dysfunction of the urinary system, chronic diseases of the urological tract, as well as congenital anomalies of the structure of the urinary organs, the prevalence of bacteriuria is much higher and can reach 40-50%.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is most often observed in the following groups (see Table 1 below).
| Category of persons | Frequency of occurrence |
| Preschool girls | Less than 2% |
| Pregnant | 2-9,5% |
| Elderly women 65-80 years old | 18-43% |
| Elderly men 65-80 years old | 1,5-15,3% |
| Women over 80 years old | 18-43% |
| Men over 80 years old | 5,4-21% |
| Patients with spinal cord injury | 70-100% |
| Patients with diabetes mellitus | up to 17.7% |
| Patients after kidney transplantation | up to 41% in the first month, up to 21% in the second |
| Bladder catheterization | Increases by 2-7% for each additional day of catheterization |
Table 1 - Frequency of asymptomatic bacteriuria in different categories of the population (Source - Medscape)
What is asymptomatic bacteriuria
As mentioned above, asymptomatic bacteriuria is the presence of microorganisms in the urine in the absence of symptoms characteristic of a urinary tract infection. The frequency of asymptomatic bacteriuria in women of childbearing age ranges from 1–5%, in pregnant women - 2–9%. In men of reproductive age, it is very rare as an independent symptom and requires differential diagnosis with bacterial prostatitis.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is detected only by urine test results
In infants, asymptomatic bacteriuria is most often detected by bacterial culture of urine and can sometimes be the only sign of urinary tract damage. Due to the fact that newborns and small children cannot complain of pain in the lumbar region or pain during urination, the detected disorder requires additional studies - a general urine test and a clinical blood test, in which signs of inflammation may be observed. For premature infants, who often do not have a temperature reaction in response to an infectious process, asymptomatic bacteriuria may be the only evidence of developed pyelonephritis.
Table: comparative characteristics of the signs of true and asymptomatic bacteriuria
| State | Symptoms | General urine analysis | Clinical blood | Bacteriological culture of urine |
| Urinary tract infections |
|
|
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, Escherichia coli, Proteus, as well as a combination of microorganisms in an amount of at least 105 colony-forming units in 1 ml of urine. |
| Asymptomatic bacteriuria | no clinical symptoms | There may be an increased level of leukocytes in the urine | no pronounced changes | Escherichia coli, enterococci, Klebsiella, Proteus in an amount of at least 105 in 1 ml of urine with double sowing in women and once in men. |
What are the dangers of asymptomatic bacteriuria?
The described process is the colonization of the urinary tract by microflora without their reproduction. These microorganisms are called commensal bacteria, that is, those that pose neither harm nor benefit to the body. Most often, with asymptomatic bacteriuria, such bacteria are Escherichia coli and various types of enterococci, Proteus, and Klebsiella. On the one hand, these microorganisms do not allow pathological microflora to colonize, on the other hand, in certain situations they themselves can become a source of inflammation . Similar situations can be observed with decreased immunity, weakening of the body's defenses during hypothermia or stressful situations, irregular urination and stagnation of urine. The latter occurs most often in children due to reluctance to sit on the potty, as well as in pregnant women, in whom stagnation of urine is explained by a decrease in the tone of the ureters under the influence of the hormone progesterone and the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the bladder. Therefore, these two categories of patients are at risk for developing pyelonephritis, and asymptomatic bacteriuria in them should not be ignored.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria during pregnancy threatens the development of pyelonephritis
How to protect yourself from pathology
Such an illness is extremely difficult to detect, but it is even more difficult to ensure that the microbes leave the body. Since asymptomatic bacteriuria can cause harm to the mother and child, doctors believe that it will be much easier to prevent pathology than to deal with its consequences. For timely detection of the disease, it is necessary to undergo all examinations and consult with a gynecologist.
Rules for individual prevention:
- Try to lead an active lifestyle. In the absence of regular physical activity, blood stagnation may develop in the pelvic veins, which creates optimal conditions for the formation of infection. To avoid this, expectant mothers are advised to take more walks in the fresh air, do gymnastics with fitball or yoga. In some cases, you can attend water aerobics training in the pool.
Exercising with a fitball helps strengthen muscles - Take a responsible approach to planning your pregnancy. It is recommended to begin treatment of chronic and acute pathologies of the urinary system at least six months before the planned conception. After effective therapy, not a trace will remain of many diseases: this will help protect the woman’s body from reoccurrence of infection.
- Wear special bandages. Since the uterus enlarges during pregnancy, the internal organs are displaced relative to each other and are compressed in places. This causes asymptomatic bacteriuria. The bandage promotes more rational weight distribution and protects against such consequences.
A bandage during pregnancy reduces pressure on internal organs
Causes and development factors
Urine, which is formed in the kidneys and enters the bladder through the ureters, is normally sterile, that is, it does not contain any microorganisms. There are several mechanisms for the development of bacteriuria:
- descending, when bacteria enter the urine from the kidneys, ureters or bladder affected by the infectious process;
- ascending, in which the microflora rises through the urethra, occurs when personal hygiene rules are not followed, poor quality care for infants, or swimming in dirty ponds. Similarly, infection can be introduced during medical procedures, for example, during bladder catheterization;
- hematogenous route (through the blood), in which the infectious process spreads from neighboring organs, for example, with proctitis (inflammation of the rectum), hemorrhoids, vulvovaginitis (inflammation of the vagina);
- the lymphogenous route of transmission (through lymphatic vessels) occurs when the walls of the large and small intestines are affected by the infectious process in certain diseases, for example, typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever.
The proliferation of bacteria and the development of clinical symptoms are prevented by:
- strong immunity and good resistance to infections;
- taking antibiotics due to the development of infectious diseases in other organs;
- the presence of certain diseases, for example, diabetes.
Age plays a certain role - the incidence of asymptomatic bacteriuria over the age of 60 years is 20%.
When installing a long-term bladder catheter, asymptomatic bacteriuria occurs in almost one hundred percent of cases.
An indwelling bladder catheter is almost always accompanied by asymptomatic bacteriuria.
Bacteria in urine in infants
Diagnosis of the disease in infants is quite difficult. The thing is that the symptoms of bacteriuria may coincide with some other diseases. It is difficult to determine the final diagnosis in this case, since lack of appetite, lethargy and fever accompany many childhood diseases. That is why infants are prescribed not only OAM, but also OAC. The number of microorganisms in a child’s urine is significantly less than in an adult’s. In children under 6 years of age, the appearance of bacteria in the urine may indicate the development of a serious pathological process. Bacteria can enter urine in two ways: through the blood and through the lymph.
It is very difficult to suspect problems with the urinary tract in a newborn and a child under one year old
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of asymptomatic bacteriuria is established on the basis of bacteriological examination data - urine culture for sterility. For men, urine is collected once, for women twice, with an interval of at least 24 hours. To prevent the entry of microorganisms from the outside, urine must be collected in a sterile container, while the rules of personal hygiene must be strictly observed, and the procedure must be carried out after thorough treatment of the genitals. An average urine sample should be used for analysis. The detection of more than 100,000 bacteria in 1 ml of urine is diagnostically significant.
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is diagnosed based on bacteriological culture of urine for sterility
Classification
Depending on the number of bacteria, some experts conditionally distinguish minor and severe bacteriuria. In clinical practice, only one classification is used to determine the patient’s treatment tactics:
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria.
It is characterized by the detection of bacteria in the urine in the absence of any complaints and other laboratory signs of urinary system infections (leukocyturia, etc.) in the patient. - Symptomatic bacteriuria.
A combination of clinical symptoms and identification of bacteria in a urine sample.
Principles of treatment
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is not always treated. It must be remembered that the antibacterial therapy carried out can neutralize the microflora that caused the disorder, but at the same time another, more pathogenic and aggressive microflora can take its place . Another possible complication of taking antibiotics may be the development of candidiasis due to the fact that such drugs also destroy normal microflora. Therefore, treatment is usually not prescribed:
- patients with diabetes mellitus;
- persons with an installed permanent urinary catheter;
- elderly people and schoolchildren.
Treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria is recommended in the following cases:
- during pregnancy, since this condition increases the risk of developing pyelonephritis;
- newborns and young children, since they are not yet able to complain about the discomfort that accompanies inflammatory processes;
- men under the age of 60 - in this situation, asymptomatic bacteriuria very often indicates the presence of chronic bacterial prostatitis.
Drugs for the treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria
To treat the above pathology, the following medications are usually prescribed:
- second generation fluoroquinolones, acting mainly on gram-negative flora - Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin. The first course of treatment is three days, after which it is necessary to repeat the bacterial culture of the urine; if the therapy is ineffective, the course is repeated for 5 or 7 days;
- nitrofuran derivatives - Nitrofurantoin, Furadonin; it must be remembered that both fluoroquinolones and nitrofuran derivatives are contraindicated during pregnancy;
- semisynthetic penicillins or cephalosporins - Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Cephalexin, Cefuroxime, which are the drugs of choice for pregnant women with asymptomatic bacteriuria. They are prescribed in a course of 3–5–7 days;
- Fosfomycin (Monural) 3 g, a single use of which is allowed instead of the listed antibacterial drugs. You can repeat the administration of this remedy after 10 days.
In addition to antibacterial therapy, increasing the passage of urine (preventing its stagnation), which is facilitated by taking herbal preparations Cyston or Canephron, and diuretics, is of great importance.
Cranberry juice is a very effective natural uroseptic; in case of asymptomatic bacteriuria, its use is recommended for all groups of patients.
Photo gallery: drugs for the treatment of pathology
Norfloxacin is a drug that has a bactericidal effect
Monural is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent
Amoxiclav is a combination drug of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
Cyston is a combined herbal preparation
Video: treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnant women
Symptoms
The symptoms of bacteriuria can be very diverse - from asymptomatic to acute pain. Bacteriuria is not an independent disease, but a clinical symptom of a number of pathological processes, often inflammatory, occurring in the body.
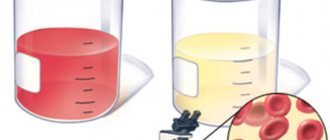
You can independently identify bacteriuria by observing the color of your own urine. If the urine is cloudy, has an unpleasant odor (from sour to the smell of rotten vegetables), has sediment in the form of flakes or mucus, then this is most likely how bacteriuria manifests itself.