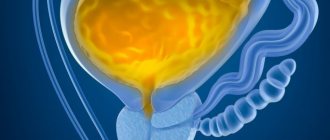
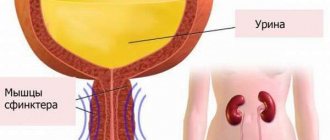
Urinary retention or ischuria is not a disease. This is a symptom complex caused by the inability to urinate. The accumulation of urine in the bladder reaches a liter or more. The person experiences strong urges and pain, but cannot urinate on his own.
The situation occurs more often in men, in women - much less often. It is impossible to cope with it on your own. The administration of antispasmodic drugs is ineffective. The greatest difficulties in diagnosis are caused by paradoxical ischuria. It is manifested by bladder overflow and spontaneous urine leakage. Residual urine creates a feeling of incomplete emptying.
What causes the emergence of ishuria?
Paradoxical ischuria is a common symptom of urological diseases, that is, it is not considered a separate disease. According to statistics, 85% of all cases of urinary retention affect men over 55 years of age, which is caused by inflammation of the prostate.
Among other reasons leading to the pathological condition:
- Mechanical obstruction of the urethra . It may contain stones, tumors, and blood clots. Also, mechanical obstruction can be caused by edema - for example, with prostate adenoma, the surrounding structures, including the urethra, swell.
- The patient remains in a state of severe stress for a long time . Nervous experiences can provoke inhibition of reflexes responsible for full urination. The reason is more typical for individuals who have been diagnosed with mental disorders.
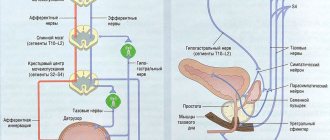
- Dysfunctional disorders . This refers to nerve conduction disorders in neurological diagnoses, dystrophy of the muscular layer of the bladder and other conditions in which normal contraction of the organ becomes impossible.
Some medications can cause problems. Thus, a number of sleeping pills and narcotic drugs cause urinary retention and have a depressing effect on bladder contractility.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid the occurrence of such a disease, you must:
- completely stop drinking alcoholic beverages;
- avoid injuries to the genitourinary system;
- prevent hypothermia of the body;
- take medications only after being prescribed by a clinician - it is very important to follow the daily dosage and duration of use;
- engage in early diagnosis and timely treatment of diseases that can lead to ischuria;
- before undergoing a planned surgical operation, it will be useful to learn how to urinate in a horizontal position, especially for men;
- undergo a full examination at a medical facility several times a year.
Since the symptoms of ischuria cannot be ignored, this disease has a favorable prognosis. However, we should not forget about the possible development of complications from those pathologies that caused such a violation of the urination process.
ISHURIA
(urinary retention) - the inability to empty the bladder, despite its overflowing with urine. If it occurs suddenly, it is called acute; if it develops gradually due to an increasing, long-term obstruction to the outflow of urine, it is called chronic.
Urinary retention may occur as a result of the following factors:
1) mechanical causes (adenoma, or prostate gland, acute, urethral trauma, bladder or urethral stone, tumor of the urethra or bladder neck, phimosis);
2) diseases of the central nervous system (tumor and injuries of the brain or spinal cord, tabes dorsalis, myelitis);
3) reflex functional causes (after surgery on the perineum, rectum, female genital organs, after childbirth, during stress, alcohol intoxication, hysteria, forced long-term stay of the patient in bed, etc.);
4) drug intoxication (hypnotics, narcotic analgesics).
The most common cause of acute urinary retention is the prostate gland, which often occurs in men over 60 years of age. Naturally, acute is predominantly a pathology of older men. Urinary retention in the presence of an adenoma is facilitated by reasons that cause a rush of blood to it (prolonged stay in a sitting position, constipation, diarrhea, cooling, drinking alcohol). The history reveals frequent urination (especially at night), difficulty starting urination, and a sluggish stream of urine. In acute prostatitis, acute prostatitis develops against the background of fever, pain, and terminal hematuria.
Less commonly, acute occurs with injuries to the urethra, fractures of the pelvic bones; it is also observed predominantly in men.
A peculiar form of urinary retention is the sudden “interruption” of the urine stream, which is usually a symptom of bladder stones. When urination begins, the moving stone “closes” the internal opening of the urethra, and urination is interrupted. The patient has to change position for it to resume. Some patients with bladder stones can only urinate in a certain position (squatting, side lying, sitting). Urinary retention is associated with pain and hematuria.
Acute may be one of the manifestations of diseases or injuries of the brain or spinal cord with a disorder of the nervous regulation of the detrusor and sphincters of the bladder (tabes dorsalis, myelitis, spinal cord with compression of the spinal cord or hemorrhage into it); in diseases of the central nervous system there is no pain with ischuria.
Acute can be of a reflex nature: in the first days after surgical interventions on the abdominal organs, operations for abdominal hernias, hemorrhoids, etc. Sometimes it occurs in completely healthy subjects after taking large amounts of alcohol: its cause is atony of the bladder muscle. In elderly people, bladder atony with the development of urinary retention may be a consequence of treatment with atropine-type drugs.
Urinary retention can be complete or incomplete. With complete retention, the patient, despite a strong urge to urinate and strong straining, cannot release a single drop of urine; Such patients sometimes have their urine released through a catheter for years. With incomplete, partial retention, urination occurs, but after it part of the urine remains in the bladder (residual urine), its amount sometimes reaches 1 liter. If the amount of residual urine exceeds 100 ml, it can be determined by percussion. Chronic incomplete ischuria can occur unnoticed by the patient and is detected only when complications develop; it leads to stagnation of urine in the urinary tract and impaired renal function.
With prolonged urinary retention, not only extreme stretching of the muscular wall of the bladder occurs, but its atony with stretching of the sphincters, and urine from an overfilled bladder is involuntarily released in drops. This condition is called paradoxical ischuria. Often accompanying indications from patients that they constantly urinate in small portions lead to the fact that acute ischuria in the presence of paradoxical ischuria is not recognized in a timely manner.
Diagnosis
based on anamnesis and objective examination. Severe pain syndrome causes extremely restless behavior of the patient. Upon examination, a bulge is revealed in the suprapubic region due to a full bladder. Percussion determines the upper border of the bladder, which in case of acute urinary retention may be located in the middle of the distance between the navel and the pubic symphysis; The bottom of a full bladder can often be palpated.
Complete urinary retention should not be confused with anuria, in which urine production stops. With it, urination is also impossible, but there is no urge, the bladder is empty.
Treatment
. Acute causes severe pain and requires emergency care. Catheterization of the bladder in the presence of prostate adenoma should be performed only with a rubber catheter. After treating the external opening of the urethra with an antiseptic solution, a catheter, generously moistened with glycerin or petroleum jelly, is inserted into the urethra with tweezers. The forward movement is made in “short steps” of 2 cm. You should not try to forcibly insert the catheter into the urethra, since in case of urolithiasis and acute prostatitis, catheterization of the bladder can lead to complications. If necessary, the catheter can be left in the bladder for several days (permanent catheter), but in this case, in order to avoid infection, the bladder is washed with an antiseptic solution, antibiotics are prescribed, etc. If it is impossible to insert a rubber catheter, the patient should be immediately referred to a urologist.
In the case of reflex urinary retention (for example, with postpartum, postoperative ischuria), you can try to induce urination by irrigating the external genitalia with warm water, by pouring water from one vessel to another (the sound of a falling stream of water can reflexively cause urination), introducing 5 -10 ml of 1-2% novocaine solution; if these methods are ineffective and there are no contraindications, administration of 1 ml of a 1% solution of pilocarpine or 1 ml of a 0.05% solution of prozerin subcutaneously is indicated; if there is no result, bladder catheterization is indicated.
In some cases, acute disease often recurs. The main danger of repeated catheterization is the inevitable urinary tract infection, including the development of urosepsis. After emergency care, patients with acute urinary retention must be referred to a urologist for examination, after which the question of the possibility and advisability of surgical treatment aimed at eliminating the obstacle to emptying the bladder can be decided.
Paradoxical ischuria is a condition in which the bladder cannot empty completely. As a result, a large amount of urine accumulates in it, which is why periodic involuntary leakage is observed. When the urinary tract is full, the patient experiences discomfort and severe pain in the lower abdomen.
Men are more likely to experience this pathology. It is diagnosed less frequently in women.
Types of disease
Paradoxical ischuria is classified into types based on the following criteria:
- Retained ability to urinate.
- Duration of delay.
If the patient, by strongly straining the muscles, can empty the bladder even a little, they speak of incomplete retention. If it is possible to remove stagnant urine exclusively with the help of a catheter, a diagnosis of complete paradoxical ischuria is made.
As for the duration of urinary retention, there are two forms:
- Spicy . Develops like an attack. Severe pain appears in the pubic bone area, the urge to urinate becomes pronounced. Visually, the doctor sees a protrusion in the lower abdomen.
- Chronic . The patient's condition worsens gradually. For several weeks/months he complains of a feeling of incomplete emptying, and then there comes a point when he cannot empty his bladder on his own.
Possible consequences and complications
The prognosis is favorable. The main thing is to quickly establish the cause of paradoxical ischuria and carry out its competent treatment. In advanced cases, the disease can lead to acute renal failure and bilateral hydronephrosis.
Chronic ischuria paradox is fraught with inflammation and infection of the urinary tract.
Ischuria is urinary retention, characterized by the inability to empty the bladder. This is a symptomatic manifestation of various pathologies: urolithiasis, urethral trauma, cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis. Problems with urination appear due to a primary disease.
The main signs of ischuria: pain in the lower abdomen, persistent urge to urinate, absence or weak urine output. Ishuria occurs in both women and men.
Pathology is diagnosed at the time of contacting the clinic: after a medical examination and hardware examination (ultrasound examination of the bladder, kidneys, ureters), laboratory procedures (blood and urine tests).
Therapeutic measures will be aimed at relieving inflammation, relieving the patient of pain and restoring the functioning of the bladder, kidneys and urinary canals.
Timely treatment of urinary disorder has a 100% positive prognosis. If the underlying disease is not treated on time, the risk of complications is high.
Symptoms
In the acute form, the patient experiences an irresistible desire to go to the toilet . However, urine does not come out even when he tenses his abs hard. Cutting pains appear in the lower abdomen.
As biological fluid accumulates above the pubis, a characteristic protrusion in the form of a roller appears. At the same time, the patient may complain of insomnia, increased fatigue, loss of appetite and constipation.
With chronic paradoxical ischuria, the symptoms are not so bright. A person feels that his urinary tract is not completely emptied. He goes to the toilet frequently, but the amount of urine he produces gradually decreases, even if he drinks a lot of fluids.
During urination, the patient strains greatly. The stream of urine is constantly interrupted. To feel relief, the patient can spend 5-10 minutes in the toilet.
How it manifests itself
Signs of the disease are determined by the form and intensity. Often, chronic ischuria is practically asymptomatic, and urinary retention is discovered only during examination for some other disease. However, it is also necessary to treat this “inconspicuous” form, since constant incomplete emptying of the bladder leads to atrophy of the muscle walls and the degeneration of muscle fibers into fibrous tissue.
General symptoms characteristic of the acute form and partly of the chronic form are as follows:
- severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- protrusion in the bladder area, painful to the touch – trabecular bladder;
- sharp, frequent, painful urge to urinate;
- irritation, anxiety and other psychological disorders associated with this condition.
The acute form may be accompanied by additional symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- signs of intoxication: vomiting, nausea, dizziness.
Diagnosis of the disease
When palpating/examining the patient's abdomen, the doctor feels/sees a protrusion. To alleviate the patient's condition, he is given an antispasmodic and urine is removed using a catheter.
Afterwards, studies are carried out aimed at establishing the cause of ischuria:
- General blood and urine tests.
- Cystoscopy.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Endoscopy and X-ray with contrast.
To assess the size of the prostate gland, a man may be asked to undergo TRUS. If there is a suspicion that paradoxical ischuria is provoked by nervous experiences, the patient is referred for consultation to a neurologist or psychiatrist.
First aid
If the patient exhibits the main symptoms, but there is no opportunity to consult a doctor or the wait for an ambulance is too long, you need to know how to provide first aid for acute ischuria.
The first step is to relieve the pain and temporarily restore the ability to empty the bladder on your own. You can give the victim 1 tbsp. cool water, and put a warm heating pad on the bladder area, on the lower abdomen. A cleansing enema and a belladonna suppository inserted into the rectum may help. If you don’t have candles, you can try taking a bath with chamomile infusion and drinking tea with mint, linden and chamomile.
At the first manifestation of pain, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Only a doctor can correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Treatment methods
Treatment for the described condition can be divided into:
- Emergency – designed to alleviate the patient’s condition.
- Comprehensive - eliminates the causes that provoked the symptom, relieves inflammation.
In the first case, bladder catheterization . If it turns out that it is impossible to install a catheter (for example, with a tumor, stricture, phimosis), an epicystostomy is performed: with the help of surgery, access to the bladder is gained and a tube is inserted into it, draining biological fluid towards the anterior surface of the abdomen.
As for complex treatment, it depends on the cause that caused urinary retention. If a stone or tumor is to blame, surgery is performed. For dysfunctional lesions, urologists work together with neurologists and surgeons.
They prescribe medications taking into account the patient’s age, the presence of chronic ailments, the severity of ischuria and some other factors. In each case, drug treatment is selected individually.
When urinary retention occurs as a result of stress, sedative pills and herbs help well.
Prevention of ischuria consists of timely detection and quality treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system, as well as pathologies that lead to damage to the prostate (in men).
Possible complications
Diagnosing the disease in incomplete or chronic ischuria in a timely manner is quite problematic, which often leads to a number of serious complications. And this condition itself is not considered an independent disease, but is a consequence of more serious problems in the body. Urinary retention can lead to serious consequences:
- diseases of the kidneys (pyelonephritis) and bladder (cystitis);
- dilation of the renal pelvis (hydronephrosis);
- formation of stones in the urinary system;
- chronic kidney failure.
It is worth remembering that identifying a symptom such as ischuria at the initial stage increases the chances of coping with the problem before complications arise. Therefore, you should not neglect your health. You should undergo routine examinations with a specialist annually.